| Oracle® Application Server Adapter for SAP R/3 User's Guide 10g Release 2 (10.1.2) B14061-03 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
| Oracle® Application Server Adapter for SAP R/3 User's Guide 10g Release 2 (10.1.2) B14061-03 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
This chapter describes how to use OracleAS Adapter Application Explorer (Application Explorer) to define a target to connect to an SAP system, view system objects, and create XML schemas and Web services. This chapter also explains how to configure an event adapter.
This chapter discusses the following topics:
To start Application Explorer:
Start the server where Application Explorer is deployed.
From the Windows Start menu, select Programs, OracleAS_home Adapters, and then Application Explorer.
On Windows, iaexplorer.bat is located under OracleAS_home\adapters\application\tools, where OracleAS_home is the directory where Oracle Application Server is installed.
On UNIX, load the script iwae.sh, located under OracleAS_home/adapters/application/tools, where OracleAS_home is the directory where Oracle Application Server is installed.
Application Explorer starts. You can now define new targets to your SAP system.
You need not configure BSE for a file-based repository because it is configured during the Oracle installation. You also need not configure the OracleAS Adapter J2CA because the ra.xml file is configured automatically during installation.
After BSE is deployed to Oracle Application Server, you can configure it through the BSE configuration page. This configuration is required only when using a database repository with BSE.
|
Note: Do not use a file repository for BSE in production environments. |
To configure BSE:
Display the following page in your browser:
http://hostname:port/ibse
Where hostname is the machine where BSE is installed and port is the HTTP port for Oracle Application Server.
For example,
http://localhost:7777/ibse
|
Note: If you are accessing this page for the first time, it may take longer to load. |
The BSE configuration page is displayed.
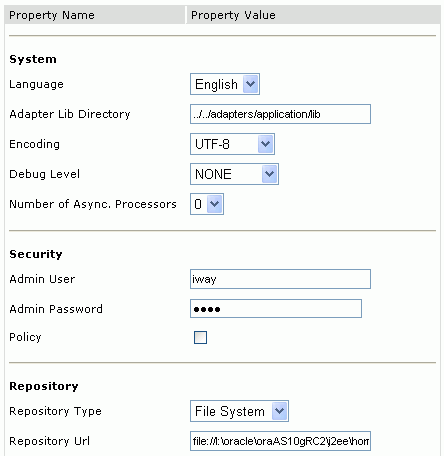
Ensure that the Adapter Lib Directory parameter specifies the path to the lib directory, for example:
OracleAS_home\adapters\application\lib
Where OracleAS_home is the directory where Oracle Application Server is installed.
After you specify the path, adapters in the lib directory are available to BSE.
|
Note: The Repository URL field specifies where the file system repository is located. To use a database repository, you must enter the repository connection information. For the initial verification, use a file system repository. See "Configuring an Oracle Repository" for information on switching to a database repository. |
To configure BSE system settings:
Display the BSE configuration page in a browser:
http://hostname:port/ibse/IBSEConfig
Where hostname is the machine where BSE is installed and port is the port number on which BSE is listening.
|
Note: The server to which BSE is deployed must be running. |
The BSE settings pane is displayed, as shown in the following figure.
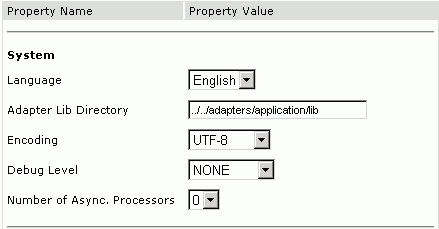
Configure the system settings.
The following table lists the parameters with descriptions of the information to provide.
The following image shows the Security pane.
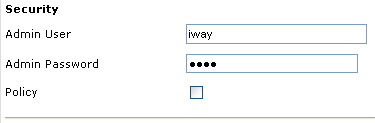
Configure the security settings.
The following table lists the parameters with descriptions of the information to provide.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Admin User | Provide a BSE administrator ID. |
| Admin Password | Enter the password associated with the BSE administrator ID. |
| Policy | Select the check box to enable policy security. |
The following image shows all fields and check boxes for the Repository pane.

Configure the repository settings.
BSE requires a repository to store transactions and metadata required for the delivery of Web services.
See "Configuring a File System Repository" and "Configuring an Oracle Repository" for more information.
The following table lists the parameters with descriptions of the information to provide.
Configuring a File System Repository
If you do not have access to a database for the repository, you can store repository information in an XML file on your local machine. However, a file system repository is less secure and efficient than a database repository. When BSE is first installed, it is automatically configured to use a file system repository.
|
Note: Do not use a file repository for BSE in production environments. |
The default location for the repository on Windows is:
OracleAS_home\j2ee\OC4J_CONTAINER\applications\ws-app-adapter \ibse\ibserepo.xml
On other platforms, use the corresponding location.
If you are using a file system repository, you are not required to configure any additional BSE components.
Configuring an Oracle Repository
To configure an Oracle repository:
Contact your database administrator to obtain an Oracle user ID and password to create the BSE repository.
This user ID should have rights to create and modify tables as well as the ability to create and run stored procedures.
Open a command prompt and navigate to the setup directory. The default directory location on Windows is:
OracleAS_home\adapters\application\etc
For other platforms, use the corresponding location.
This directory contains SQL to create the repository tables in the following file:
iwse.ora
|
Note: If Oracle is not on the same machine as the Oracle Application Server, copy the iwse.ora file to the Oracle machine. Then, from a command prompt on the Oracle machine, navigate to the directory containing the iwse.ora file. |
sqlplus userid/password @database @ iwse.ora
During the J2CA deployment of OracleAS Adapter for SAP, OC4J generates a deployment descriptor called oc4j-ra.xml. This descriptor provides OC4J-specific deployment information for resource adapters. See Chapter 3, "OC4J Deployment and Integration" for more information on J2CA deployment and configuration.
No configuration changes are necessary if you are using the default file based repository with J2CA deployment.
Configuring a Database Repository for J2CA
To configure a database repository for J2CA:
Execute the iwse.ora SQL statement on the machine where the database is installed.
Copy the jcatransport.properties file to the following directory:
OracleAS_home\adapters\application\config\jca_sample
Uncomment the following fields and enter details for them in the jcatransport.properties file. For example:
iwafjca.repo.url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@90.0.0.51:1521:orcl iwafjca.repo.user=scott iwafjca.repo.password=scott1
Alter the JDBC driver path in Application Explorer's lcp. For example:
lcp=..\lib\orabpel-adapters.jar;C:\jdev\jdbc\lib\classes12.jar;C:\jdev\jdbc\lib\nls_charset12.jar;%lcp% to lcp=..\lib\orabpel-adapters.jar;..\..\..\jdbc\lib\classes12.jar;..\..\..\jdbc\lib\nls_charset12.jar;%lcp%
Before you use Application Explorer with OracleAS Adapter for SAP, you must create a repository configuration. You can create two kinds of repository configurations, Web services and J2CA, depending on the container to which the adapter is deployed.
During design time, the repository is used to store metadata created when using Application Explorer to configure adapter connections, browse EIS objects, configure services, and configure listeners to listen for EIS events. The information in the repository is also referenced at runtime.
A default J2CA repository is created for the default ManagedConnectionFactory. The name of this configuration is jca_sample.
Web services and BSE refer to the same type of deployment. See "Adapter Features" for more information.
To create a configuration for BSE using Application Explorer, you must first define a new configuration.
Defining a New Configuration for BSE
To define a new configuration for BSE:
Enter a name for the new configuration, for example, SampleConfig, and click OK.
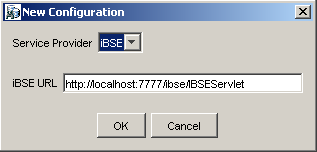
In the iBSE URL field, accept the default URL or replace it with a different URL with the following format:
http://hostname:port/ibse/IBSEServlet
Where hostname is the machine on which your application server resides and port is the port number where the application server is listening.
Click OK.
A node representing the new configuration appears beneath the root Configurations node.

The Web service repository configuration file is stored in OracleAS_home\j2ee\home\applications\ws-app-adapter\ibse.
To create a configuration for OracleAS Adapter J2CA using Application Explorer, you must first define a new configuration.
Defining a New Configuration for J2CA
To define a new configuration for J2CA:
Right-click Configurations and select New.
The New Configuration dialog box is displayed.
Enter a name for the new configuration, for example, SampleConfig, and click OK.
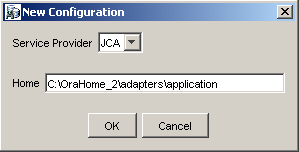
In the Home field, enter a path to your J2CA configuration directory where the repository, schemas, and other information is stored, for example:
OracleAS_home\adapters\application
Click OK.
A node representing the new configuration appears beneath the root Configurations node.

The OracleAS Adapter J2CA configuration file is stored in OracleAS_home\adapters\application\config\configuration_name
Where OracleAS_home is the directory where Oracle Application Server is installed and configuration_name is the name of the configuration you created; for example, SampleConfig.
To connect to a new configuration:
Right-click the configuration to which you want to connect, for example, SampleConfig.
Select Connect.
Nodes appear for Adapters, Events, and Business Services (also known as Web services). The Business Services node is only available for BSE configurations. If you are connected to a J2CA configuration, you will not see the Business Services node. The following is an example of a BSE configuration named SampleConfig:
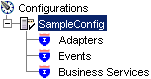
Use the Adapters folder to create inbound interaction with SAP. For example, you use the SAP node in the Adapters folder to configure a service that updates SAP.
Use the Events folder to configure listeners that listen for events in SAP.
Use the Business Services folder (available for BSE configurations only) to test Web services created in the Adapters folder. You can also control security settings for the Web services by using the security features of the Business Services folder.
You can now define new targets to SAP.
Defining the application includes adding a target for OracleAS Adapter for SAP. Setting up the target in Application Explorer requires information that is specific to the target.
To browse the available business functions, you must first define a target to SAP. After you define the target, it is automatically saved. You must connect to the SAP system every time you start Application Explorer or after you disconnect.
When you launch Application Explorer, the left pane displays (as nodes) the application systems supported by Application Explorer, based on the adapters that are installed.
To connect to SAP for the first time, you must define a new target. OracleAS Adapter for SAP supports SAP standard security and the additional protocol of SNC. Once connected to the SAP application server, application security is managed by user ID, roles and profiles. For more information on SAP application security, see the appropriate SAP documentation.
In the left pane, expand the Adapters node.
The application systems supported by Application Explorer appear as nodes based on the adapters that are installed.
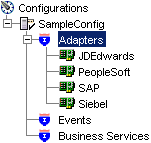
Right-click the SAP node and select Add Target.

The Add Target dialog box is displayed. Provide the following information:
In the Name field, enter a descriptive name, for example, SAPTarget.
In the Description field, enter a description for the target (optional).
From the Target Type list, select the type of target you are connecting to. The supported target types include Message Server or Application Server (default).
|
Note: For load balancing purposes, application servers from one SAP system are usually configured in logon groups, where each group serves a particular kind of user. The application servers in each group are assigned to users by a least-heavily-loaded strategy. This load balancing is done by message servers. Each SAP system has exactly one message server, which can be reached through TCP on a specific message server port. |
Click OK.
The Application Server dialog box is displayed.
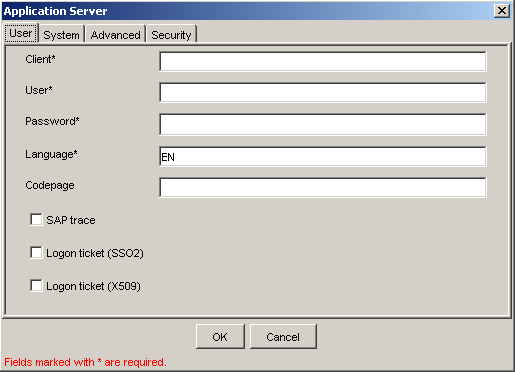
The following tabs are available:
User (Required)
System (Required)
Advanced
Security
For the User tab (required), enter the appropriate information for your SAP target based on the information in the following table.
Table 2-1 User Tab Parameters
| Target Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Client |
The client number defined for the SAP application for client communications. |
|
User |
A valid user ID for the SAP application. |
|
Password |
A valid password for the SAP application. |
|
Language |
A language key. EN (English) is the default. |
|
Code page |
A character code page value. |
|
SAP Trace |
Select this option to enable traces. |
|
Logon ticket (SSO2) |
If you are using a Secure Network Communications (SNC) adapter with SAP, select the Logon ticket (SSO2) check box. |
|
Logon ticket (X509) |
If you are using an SNC adapter with SAP, select the Logon ticket (X509) check box. |
Secure Network Communications (SNC) provides protection for the communication links between the distributed components of an R/3 System. Using SNC, SAP R/3 can support products that adhere to the GSS-API Version 2 standard. SNC supports application level (end-to-end security), Smartcard authentication, and Single Sign-On (SSO).
Depending on the SAP system release, logging on using SSO or X.509 certificates is supported.
For SSO, specify the user to be $MYSAPSSO2$ and pass the base64 encoded ticket as the passwd parameter.
For X509, specify the user to be $X509CERT$ and pass the base64 encoded certificate as the passwd parameter.
For more information, see your SAP system documentation.
For the System tab (required), enter the appropriate information for your SAP target based on the information in this section.
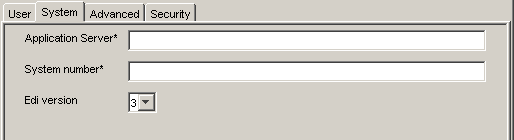
The System tab enables you to provide the application server name, system number, and EDI version for the SAP system to which you are connecting.
Table 2-2 System Tab Parameters
For the Advanced tab (optional), enter the appropriate information for your SAP target based on the information in this section.
The Advanced tab enables you to specify SAP connection pooling information for the SAP system to which you are connecting.
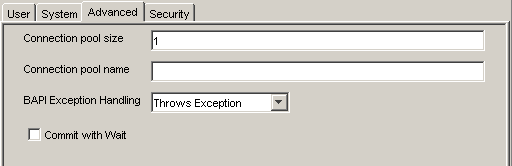
Connections to an R/3 server take up valuable resources on both the client and the remote server. You can create a pool of connections to minimize the resource and time constraints. In estimating the size of the pool, you may calculate pool size by the amount of server resources to be consumed, the number and size of the documents to be received, and the size of your Java Virtual Machine. The section of SAP documentation ÒMemory Management (BC-CST-MM)Ó explains in detail the resources required on the SAP system.
Table 2-3 Advanced Tab Parameters
| Target Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Connection pool size |
Connection pool size is used to specify the number of client connections in a pool you want to make available to SAP for Web service calls. Enter the number of connections you want to make available to SAP. To use a connection pool, enter a value that is greater than 1. Important: The default value of 1 does not create a connection pool. Instead, a single SAP connection with sequential processing is shared. A pooled connection invokes multiple connections to SAP with parallel processing. If you are using Application Explorer to create Web services, the connection pool size value is used by your Web service during runtime. As a result, ensure that the connection pool size is sufficient for your purposes. |
|
Connection pool name |
Enter the name of your SAP connection pool only if you specified a connection pool size greater than 1. |
|
BAPI Exception Handling |
From the list in the event of a BAPI exception, you can select Creates Error Document or Throws Exception. To receive more detailed error messages, select Creates Error Document. As a rule:
It is up to your application to read the XML document and obtain the error. |
|
Commit with wait |
If a high degree of accuracy is required in your application, select the Commit with Wait check box. The adapter waits until all records are physically written to the database before returning from the function call. The ÒCommit With WaitÓ has a performance impact on adapter performance, so consider carefully before selecting it. The commit behavior of BAPIs is described in the SAP documentation under ÒBAPI Programming Guide and Reference (CA-BFA).Ó All SAP Business Objects that change data must commit work to the database. Some BAPIs developed in version 3.1 of the R/3 system use an internal commit behavior, and their commit behavior cannot be changed by the adapter. As soon as they are called, they commit the work they did. BAPIs developed since release 3.1 use the external commit method. The adapter issues a commit command, and the commit is put in the database queue. If there is an application error in the first part of the commit, the error message ÒPosting could not be carried outÓ is returned, and the adapter rolls back the transaction. If in writing to the database, a database error occurs, a short dump is issued in the database records of SAP, but no message is returned to the adapter about the failure. This option is disabled by default. |
For the Security tab (optional), enter the appropriate information for your SAP target based on the information in this section.
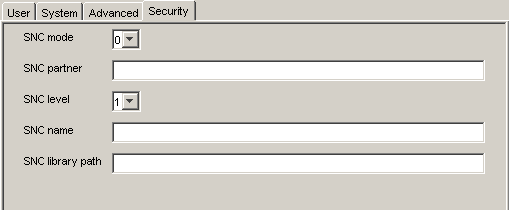
The Security tab enables you to specify Secure Network Communication (SNC) information for the SAP system to which you are connecting.
Table 2-4 Security Tab Parameters
| Target Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
SNC mode |
By default, SNC is disabled. To enable SNC, select 1 from the list. |
|
SNC partner |
Enter the name of the RFC server or message server (load balancing) that provides the SNC services. |
|
SNC level |
From the list select the version of the SNC library. |
|
SNC name |
Enter the name of the SNC library you are using. |
|
SNC library path |
SNC provides protection for the communication links between the distributed components of an R/3 System. Using SNC, SAP R/3 can support products that adhere to the GSS-API Version 2 standard. SNC supports application level (end-to-end security), Smartcard authentication, and single sign-on (SSO).
If you are using SAP Enterprise Portal, the J2EE engine generates the SAP logon ticket automatically. A possible SNC scenario would be from SAP Enterprise Portal to OracleAS Adapter for SAP.
If you want to use SAP logon tickets to enable SSO to non-SAP components, consult the SAP documentation regarding Pluggable Authentication Services. A possible SNC scenario in this case would be from a non-SAP Enterprise Portal to OracleAS Adapter for SAP.
When you have provided all the required information for your target, click OK.
After the extraction finishes, the new target, SAPTarget, appears under the SAP adapter node.

You can now connect to your SAP target.
See "Creating XML Schemas" for information on how to create schemas for the adapter.
To connect to an existing target:
In the left pane, expand the Adapters node.
Expand the SAP node.
Click the target name under the SAP node (for example, SAPTarget).
The Connection dialog box displays the values you entered for connection parameters.
Verify your connection parameters.
Provide the correct password.
Right-click the target name and select Connect.
The x icon disappears, indicating that the node is connected.
To manage SAP connections, you can:
Disconnect from a connection that is not currently in use.
Although you can maintain multiple open connections to different transaction processing systems, it is recommended to disconnect from connections not in use.
Edit a target.
You can modify the connection parameters when your system properties change. After you disconnect, you can modify an existing target.
Delete a connection that is no longer needed.
Disconnecting from a Connection to SAP
To disconnect a target:
Expand the Adapters node.
Expand the SAP node.
Right-click the target to which you are connected, for example, SAPTarget, and select Disconnect.
Disconnecting from the SAP target drops the connection with SAP, but the node remains.The x icon appears, indicating that the node is disconnected.

Modifying Connection Parameters
After you create a target for SAP using Application Explorer, you can edit any of the information that you provided previously.
Verify that the target you want to edit is disconnected.
Right-click the target and select Edit.
The Application Server dialog box displays the target connection information.
Change the properties in the dialog box as required and click OK.
Deleting a Connection to SAP
To delete a target:
Locate the target you want to delete.
Right-click the target (for example, SAPTarget), and select Delete.
The node disappears from the list of available connections.
As you connect to SAP, Application Explorer enables you to explore and browse SAP business objects that are used to support existing business processes.
|
Note: Depending on the release or service pack installed, certain RFCs, for example, RFC_CUSTOMER_GET, may not exist in your particular SAP system. Therefore, the examples included in this documentation may not be relevant to your system. If this is the case, you should use the examples as a general reference for adapter functionality and choose an RFC that exists within your SAP application environment.As described in SAP Release Note 109533, SAP Function Modules (RFCs) can be delivered with different release statuses. SAP supports only RFCs that are awarded the Released for Customer status. There is no claim to the release independencies of the interfaces and the continued existence/functionality of the modules. For more information on the status of a specific function module, consult your SAP Service Marketplace. |
See the SAP User's Guide for more information.
After you explore the SAP business function library and select an object, you can use Application Explorer to create the XML request schema and the XML response schema for that function.
To create request and response schemas for an SAP business function.
Connect to an SAP target as described in "Connecting to a Defined SAP Target".
Expand the Business Object Repository node.
Click the icon to the left of the Financial Accounting node.
Scroll down and click the icon to the left of the Company business object.
Scroll down and select the BAPI named BAPI_COMPANY_GETLIST.
The following screen appears on the right.

To view the XML for each schema type, click the appropriate tab.
The Web Service Definition Language (WSDL) description of a service enables you to make the service available to other services within a host server. You use Application Explorer to create both request-response (outbound) and event notification (inbound) J2CA services of the adapter.
|
Note: The Create Inbound JCA Service (Event) option is only available when the selected node supports events. |
To generate a WSDL file for request-response service:
After you create a schema, right-click the respective object.
The following menu is displayed:
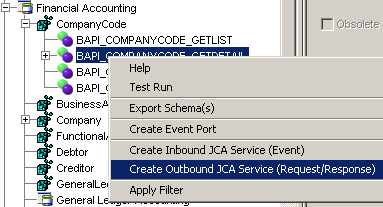
Select Create Outbound JCA Service (Request/Response).
The Export WSDL dialog box is displayed.
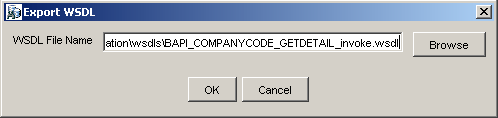
Accept the default name and location for the file.
The .wsdl file extension is added automatically. By default, the names of WSDL files generated for request-response services end with _invoke, while those generated for event notification end with _receive.
|
Note: You can organize your WSDL files in subfolders, creating your own WSDL hierarchy structure. Create the folders underOracleAS_home\adapters\application\wsdls\. The WSIL browser in JDeveloper will display the full tree structure of your WSDL hierarchy. |
Click OK.
The procedure for generating WSDL for event notification is similar to request-response. To generate WSDL for event notification, you must first create a channel for every event. See "Generating WSDL for Event Notification" for a detailed example.
Using Application Explorer, you can explore the business function repository and generate Web services (also known as a business service) for the SAP functions you want to use with the adapter. The following procedure uses the SAP BAPI method called BAPI_MATERIAL_GETLIST as an example and returns a list of materials from SAP.
|
Note: In a J2EE Connector Architecture (J2CA) implementation of the adapter, Web services are not available. When the adapter is deployed to use the OracleAS Adapter J2CA, the Common Client Interface provides integration services using the adapter. |
Creating a Web Service
To create a Web service for an SAP business function:
Connect to your SAP target and expand the Business Object Repository node.
Select the BAPI_MATERIAL_GETLIST method from the Business Object Repository.
Right-click the node from which you want to create a business service and select Create Web Service.
The Create Web Service dialog box is displayed. You can add the business function as a method for a new Web service or as a method for an existing one.
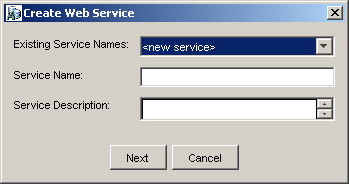
Perform the following steps:
Click Next.
The License and Method dialog box is displayed.
Provide the following information:
In the License Name field, select one or more license codes to assign to the Web service. To select more than one, hold down the Ctrl key and click the licenses.
In the Method Name field, enter a descriptive name for the method.
In the Method Description field, enter a brief description of the method.
Click OK.
Application Explorer switches the view to the Business Services node, and the new Web service appears in the left pane.
Testing a Web Service
After a Web service is created, you can test it to ensure it functions properly. A test tool is provided for testing the Web service.
To test a Web service:
Click the Business Services node to access your Web services.
Expand the Services node.
Select the name of the business service you want to test.
The business service name appears as a link in the right pane.
In the right pane, click the named business services link.
The test option appears in the right pane. If you are testing a Web service that requires XML input, an input field appears.
Enter the appropriate input.
Click Invoke.
Application Explorer displays the results.
Identity Propagation
If you test or run a Web service using a third party XML editor, the Username and Password values that you specify in the SOAP header must be valid and are used to connect to SAP. The user name and password values that you provided for SAP during target creation using Application Explorer are overwritten for this Web service request. The following is a sample SOAP header that is included in the WSDL file for a Web service:
<SOAP-ENV:Header>
<m:ibsinfo xmlns:m="urn:schemas-iwaysoftware-com:iwse">
<m:service>String</m:service>
<m:method>String</m:method>
<m:license>String</m:license>
<m:disposition>String</m:disposition>
<m:Username>String</m:Username>
<m:Password>String</m:Password>
<m:language>String</m:language>
</m:ibsinfo>
</SOAP-ENV:Header>
You can remove the <m:disposition> and <m:language> tags from the SOAP header, since they are not required.
Events are generated as a result of activity in a database or in an application system. You can use events to trigger an action in your application. For example, an update to a database can reflect an update to customer information. If your application must perform when this happens, your application is a consumer of this event.After you create a connection to your application system, you can add events using Application Explorer. To create an event, you must create a port and a channel.
|
Note: If you are using a J2CA configuration, you must create a new channel for every event and select this channel when you generate WSDL. Additionally, you are not required to create or configure ports for use with BPEL Process Manager. See "J2CA Filtering Port Option for Integration with BPEL Process Manager" for details on using ports under a J2CA configuration. |
A port associates a particular business object exposed by the adapter with a particular disposition. A disposition is a URL that defines the protocol and location of the event data. The port defines the end point of the event consumption. See "Creating and Editing an Event Port" for more information.
A channel represents configured connections to particular instances of back-end systems. A channel binds one or more event ports to a particular listener managed by the adapter. See "Creating a Channel" for more information.
|
Note: OC4J currently conforms to J2CA 1.0, which does not call for event capabilities. When conforming to J2CA 1.0, only service interactions are supported. |
Application Explorer enables you to create event ports from the Adapters node or from the Events node.
|
Note: You are not required to create event ports for J2CA configurations. You must create event ports for BSE configurations only. |
You cannot create an event port from the Services node; you must create it from the Adapters node.
To create an event port directly from the Adapters node:
Right-click a node under BAPI, RFC, or IDOC.
Select Create Event Port.
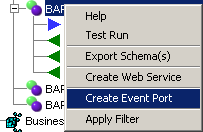
The Create Event Port dialog box is displayed. Perform the following steps:
Enter a name for the event port and provide a brief description.
From the Protocol drop-down list, select the required disposition, for example, RMI.
Enter the disposition URL.
Specify the location of your Web service.
Click OK.
See "Creating an Event Port from the Events Node" for information on configuring port dispositions.
The following procedures describe how to create an event port from the Events node for various dispositions using Application Explorer. You can switch between a BSE and a J2CA deployment by choosing one or the other from the menu in the upper right of Application Explorer.
See "Creating an Event Port from the Adapters Node" for information on creating an event port directly from the Adapters node.
Creating an Event Port for RMI
To create a specific event port for RMI:
Click the Events node.
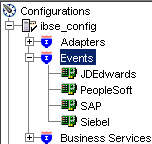
Expand the SAP node.
Right-click the Ports node and select Add Port.
The Add Port dialog box is displayed. Provide the following information:
Enter a name for the event port and provide a brief description.
From the Protocol list, select RMI.
In the URL field, specify a destination file to which the event data is written using the following format:
rmi://host:port;RemoteObject=APPNAME;errorTo=pre-defined port name or another disposition url
The following table defines the parameters for the disposition.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| host | The host name or IP address from which the RMI server accepts RMI requests. If you omit this attribute, the RMI server will accept RMI requests from any host. |
| port | The port number on which the RMI server listens for RMI requests. |
| RemoteObject | A home or Enterprise Java Bean (EJB) object. |
| errorTo | Predefined port name or another disposition URL to which error logs are sent. |
Click OK.
The port appears under the ports node in the left pane. In the right pane, a table appears that summarizes the information associated with the event port you created.
You can now associate the event port with a channel. See "Creating and Editing a Channel" for more information.
Editing an Event Port
In the left pane, select the event port you want to edit.
Right-click the port and select Edit.
The Edit Port pane is displayed.
Make the required changes and click OK.
Deleting an Event Port
In the left pane, select the event port you want to delete.
Right-click the port and select Delete.
A confirmation dialog box is displayed.
To delete the event port you selected, click OK.
The event port disappears from the list in the left pane.
J2CA Filtering Port Option for Integration with BPEL Process Manager
This feature provides the option to use event ports when using OracleAS Adapter for SAP with BPEL PM under a J2CA configuration. Without this feature, all messages from a particular channel are forwarded to the endpoint and then to the BPEL PM Server. In this case, no schema validation takes place. With the filtering feature, you have the option to associate an event schema to a port that you create and configure in Application Explorer. In this case, at runtime the message is validated against the event schema and only the validated event message is forwarded to the endpoint. If the event message does not match the event schema that is associated to the port, then an error message is written to the log and the event message is ignored.
The following procedure describes how to create a channel for your event. All defined event ports must be associated with a channel.
|
Note: If you are using a J2CA configuration, you must create a new channel for every event and select this channel when you generate WSDL. Creating a channel is required for both BSE and J2CA configurations. |
Creating a Channel
To create a channel:
Click the Events node.

Expand the SAP node.
Right-click Channels and select Add Channel.
The Add Channel dialog box is displayed.
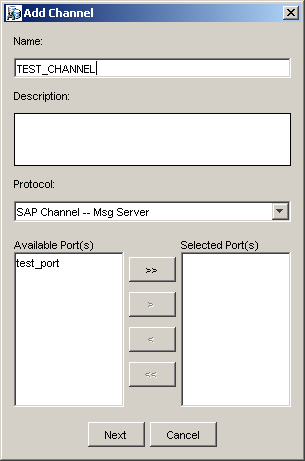
Provide the following information:
Enter a name for the channel, for example, TEST_CHANNEL.
Enter a brief description.
From the Protocol list, select SAP Channel -- Msg Server or SAP Channel -- App Server.
Important: If you are using BPEL Process Manager with a J2CA configuration without the optional port feature, skip the following two steps. See "J2CA Filtering Port Option for Integration with BPEL Process Manager".
Select an event port from the list of available ports. To select more than one, hold down the Ctrl key and click the ports.
Click >> to transfer the port(s) to the list of selected ports.
Click Next.
The Message Server dialog box is displayed. The following tabs are available:
System (Required)
User (Required)
Advanced
Preemitter
For the System tab, enter the appropriate information for your SAP channel based on the information in the following table.
Table 2-5 System Tab Parameters
| Target Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Gateway host |
A host name for the SAP Gateway. |
|
Gateway service |
A service for the SAP Gateway. |
|
Program ID of the server |
An SAP program ID you want to use for this channel. |
|
Message Server |
A host name for the message server. |
|
R/3 name |
An SAP R/3 name. |
|
Server group |
An SAP server group. |
For the User tab, enter the appropriate information for your SAP channel based on the information in the following table.
Table 2-6 User Tab Parameters
| Target Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Client |
The client number defined for the SAP application for client communications. |
|
User |
A valid user ID for the SAP application. |
|
Password |
A valid password for the SAP application. |
|
Language |
A language key. EN (English) is the default. |
|
Code page |
A character code page value. |
For the Advanced tab (optional), enter the appropriate information for your SAP channel based on the information in the following table.
Table 2-7 Advanced Tab Parameters
| Target Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
IDOC Format |
Select an IDoc type from the list. |
|
User Defined Function Modules |
Enter the path to the user-defined function module you created. |
|
SAP trace |
Select this check box if you want to enable SAP traces for troubleshooting purposes. |
|
Unicode |
Select this check box if you are expecting your response in Unicode format. |
|
Processing Mode |
Select the type of synchronous processing from the list. |
Click OK.
The channel appears under the channels node in the left pane.
An X over the icon indicates that the channel is currently disconnected. You must start the channel to activate your event configuration.
|
Note: If you are using OracleAS Adapter for SAP with BPEL Process Manager, do not start the channel, as it is managed by the BPEL PM Server. If you start the channel for testing and debugging purposes, stop it before runtime. |
Right-click the channels node and select Start.
The channel you created becomes active.
The X over the icon disappears.
To stop the channel, right-click the connected channel node and select Stop.
The channel becomes inactive and an X appears over the icon.
Editing a Channel
In the left pane, locate the channel you want to edit.
Right-click the channel and select Edit.
The Edit Channel pane is displayed.
Make the required changes to the channel configuration and click Finish.
Deleting a Channel