|
Oracle® Application Server Enterprise Deployment Guide
10g Release 3 (10.1.3) B25210-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
|
Oracle® Application Server Enterprise Deployment Guide
10g Release 3 (10.1.3) B25210-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
This chapter provides instructions for creating the Data, Application and Web Server tiers, distributing the software components into the DMZs shown in the Enterprise Deployment architecture for myJ2EECompany shown in Figure 2-1. Although Oracle Internet Directory is the LDAP server shown, you could use another server, such as iPlanet or Active Directory.
This chapter contains the following topics:
Section 5.1, "Installing and Configuring the Security Infrastructure"
Section 5.2, "Installing and Configuring the Application and Web Tiers"
Section 5.3, "Configuring the Oracle HTTP Server with the Load Balancing Router"
Section 5.4, "Configuring Application Authentication and Authorization"
The security infrastructure for myJ2EECompany contains the components depicted in Figure 4-16, "Data Tier Configuration". The Oracle Internet Directory administration utility oiddas is required for Oracle Internet Directory administration. oiddas is installed in the application server environment with the Oracle Internet Directory server.
To install and configure this security infrastructure:
Follow all instructions in Section 4.1, "Installing the Oracle Application Server Metadata Repository for the Security Infrastructure".
Follow all instructions in Section 4.2, "Installing the Oracle Internet Directory Instances in the Data Tier".
Follow all instructions in Section 4.3, "Configuring the Virtual Server to Use the Load Balancing Router".
Follow all instructions in Section 4.4, "Testing the Data Tier Components".
The application tier consists of multiple computers hosting middle tier Oracle Application Server instances. Each instance can contain multiple Oracle Containers for J2EE instances on which you deploy applications. In the complete configuration, requests are balanced among the OC4J instances on the application tier computers to create a performant and fault tolerant application environment.
The web tier consists of Oracle HTTP Servers. Figure 2-1, "Enterprise Deployment Architecture for myJ2EEcompany.com", shows the application tier (APPHOST1 and APPHOST2) and the web tier (WEBHOST1 and WEBHOST2).
You can install an Oracle Application Server instance consisting only of one OC4J instance, using the Advanced installation option of the Oracle Universal Installer. Follow these steps to install and create the instances on APPHOST1 and APPHOST2:
Ensure that the system, patch, kernel and other requirements are met as specified in the Oracle Application Server Installation Guide. You can find this guide in the Oracle Application Server platform documentation library for the platform and version you are using.
Start the Oracle Universal Installer as follows:
On UNIX, issue this command: runInstaller
On Windows, double-click setup.exe
The Oracle Application Server 10.1.3.0.0 Installation screen appears with the Basic Installation Mode and the Integrated Web Server, J2EE Web Server and Process Management installation type selected.
Specify an installation directory for the instance, or leave the default.
Select the Advanced Installation Mode and click Next.
A confirmation dialog appears.
Figure 5-1 Oracle Universal Installer Oracle Application Server 10.1.3.0.0 Installation Screen with Advanced Installation Mode Selected
Click Yes.
A progress dialog appears, then the Select Installation Type screen appears.
Figure 5-2 Oracle Universal Installer Select Installation Type Screen
Select the J2EE Server and Process Management option and click Next.
The Specify Port Configuration Options screen appears.
Figure 5-3 Oracle Universal Installer Specify Port Configuration Options Screen
Select Automatic and click Next.
The Administration Instance Settings screen appears.
Figure 5-4 Oracle Universal Installer Administration Instance Settings Screen
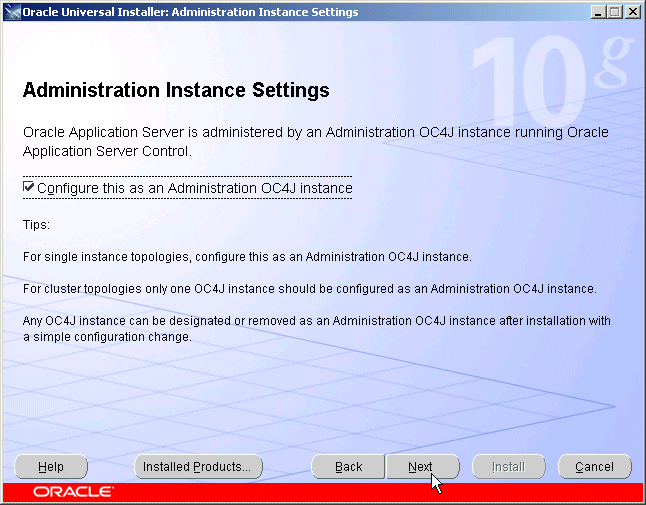
Check the box to designate the instance installed on APPHOST1 as an administration OC4J instance.
Click Next.
The Administration Settings screen appears.
Figure 5-5 Oracle Universal Installer Administration Settings Screen
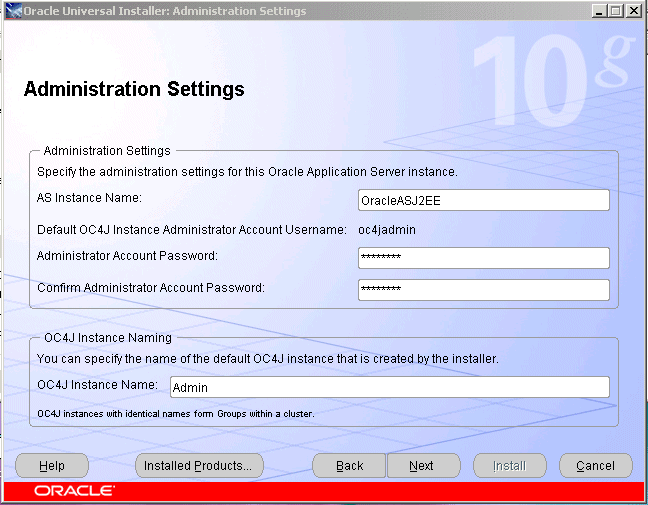
Specify an instance name for the application server instance.
|
Note: The instance name you specify will be prepended to the host name. For example, if you specifyJ2EE as the instance name and the host name is server1.mycompany.com, the instance name will be J2EE.server1.mycompany.com.
|
Specify and confirm the administrator password for the default OC4J instance.
Specify a name for the default OC4J instance created by the installer (the default is home), such as Admin, or a similar name that designates it as the instance dedicated to Application Server Control, and click Next.
|
Note: You will not deploy applications to this instance; it will not be clustered with the user-created OC4J instances on which applications are deployed. |
The Cluster Topology Configuration screen appears.
Figure 5-6 Oracle Universal Installer Cluster Topology Configuration Screen
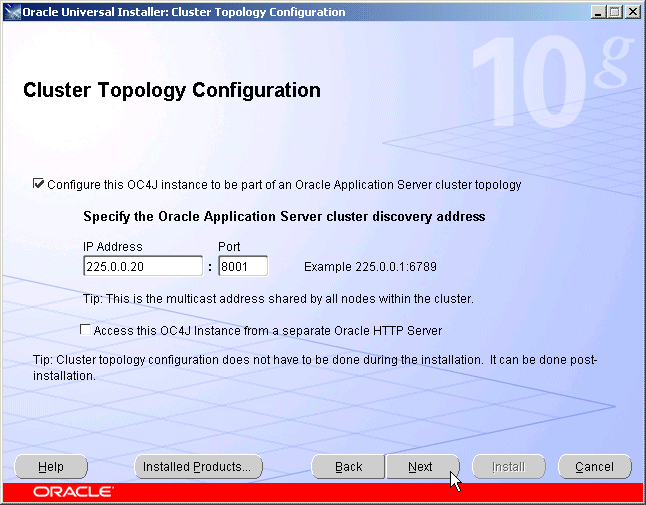
Specify the multicast address and port.
Leave the checkbox blank for the option Access this OC4J instance from a separate Oracle HTTP Server for the OC4J Admin instance installed on APPHOST1.
Click Next.
The Summary screen appears.
Click Install.
The Preparing to Install dialog appears, then the Install screen appears.
The Configuration Assistants screen appears. When the configuration process completes, the End of Installation screen appears.
Click Exit, and then confirm your choice to exit.
Use the netstat command to identify an unoccupied HTTP port:
netstat -an
Create one or more OC4J instances for application deployment by performing these steps:
Issue this command in APPHOST1_ORACLE_HOME/BIN:
createinstance -instancename Apps -port HTTP port
In the preceding command, Apps is the instance name and HTTP port is an unoccupied http port. Use the same instance name for all of the instances, so that the OC4J instances will be members of the same group.
The following message appears:
Creating OC4J instance "Apps"...
Set OC4J administrator's password for "Apps" (password text will not be displayed as it is entered:
Provide and confirm a password.
|
Note: The instances in a group of OC4J instances must have the same password, so that the user specified in a deployment command can deploy to the entire group. |
The following message appears:
The password for OC4J administrator "oc4jadmin" has been set.
New OC4J instance "Apps" is created.
|
Note: An OC4J instance that you create does not have its own OC4J binary libraries; it uses the libraries installed in the instance created by the installer. |
Start the newly created instance by issuing this command in APPHOST1_ORACLE_HOME/OPMN/BIN:
opmnctl startproc process-type=Apps
In the preceding command, Apps is the name you gave the OC4J instance when creating it.
Ensure that the AJP ports in the series 12501, 12502... are not in use by issuing the netstat command:
netstat -an
Specify the AJP port by issuing this command in APPHOST1_ORACLE_HOME/OPMN/BIN:
opmnctl config port update ias-component=OC4J process-type=Apps portid=default-web-site protocol=ajp range=12501
In the preceding command, Apps is the name you gave the OC4J instance when creating it.
Restart OPMN by issuing this command in APPHOST1_ORACLE_HOME/OPMN/BIN:
opmnctl reload
Verify that the installation was successful by viewing the instance in Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g. Start a browser and access the OC4J Admin instance at:
http://APPHOST1:8888/em
|
Note: TheORACLE_HOME/install/readme.txt file contains the URLs for the installation and a command to verify the status of processes.
|
Repeat Steps 1 through 24 to install the second Oracle Application Server instance on APPHOST2 and create OC4J instances, specifying the APPHOST2 host name.
Verify that the installation was successful by viewing the instance in Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g. Start a browser and access the OC4J Admin instance at:
http://APPHOST2:8888/em
|
Note: TheORACLE_HOME/install/readme.txt file contains the URLs for the installation and a command to verify the status of processes.
|
Follow these steps to install the Oracle HTTP Servers:
Use the Advanced option of the Oracle Universal Installer to install the Oracle HTTP Server instances. Follow these steps on WEBHOST1 and WEBHOST2 to install the Oracle HTTP Servers:
Ensure that the system, patch, kernel and other requirements are met as specified in the Oracle Application Server Installation Guide. You can find this guide in the Oracle Application Server platform documentation library for the platform and version you are using.
Copy the staticports.ini file from the Disk1/stage/Response directory to a local directory, such as TMP. You will provide the path to this file during installation.
Edit the staticport.ini file to assign the following custom ports:
Oracle HTTP Server port = 7777
|
Notes: Ensure that these ports are not already in use by any other service on the computer. Using the Static Ports feature to install the the Application Server Tier ensures that the port assignments will be consistent, if the ports are correctly specified in the file and the port is not already in use. If a port is incorrectly specified, the Oracle Universal Installer will assign the default port. If a port is already in use, the Oracle Universal Installer will select the next available port.See Section A.3, "Using the Static Ports Feature with Oracle Universal Installer" for more information. |
Start the Oracle Universal Installer as follows:
On UNIX, issue this command: runInstaller
On Windows, double-click setup.exe
The Oracle Application Server 10.1.3.0.0 Installation screen appears with the Basic Installation Mode and the Integrated Web Server, J2EE Web Server and Process Management installation type selected.
Specify an installation directory for the instance.
Select Advanced Installation Mode.
Figure 5-7 Oracle Universal Installer Oracle Application Server 10.1.3.0.0 Installation Screen with Advanced Installation Mode Selected

Click Install.
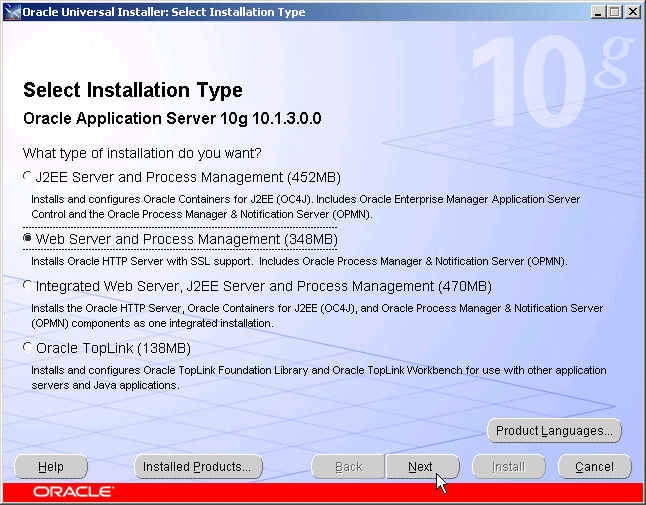
The Select Installation Type screen appears.
Select Web Server and Process Management and click Next.
Figure 5-8 Oracle Universal Installer Select Installation Type Screen
The Specify Port Configuration Options screen appears.
Figure 5-9 Oracle Universal Installer Specify Port Configuration Options Screen

Select Manual, specify the location of the staticports.ini file, and click Next.
The Specify Instance Name screen appears.
Figure 5-10 Oracle Universal Installer Administration and Management Settings Screen
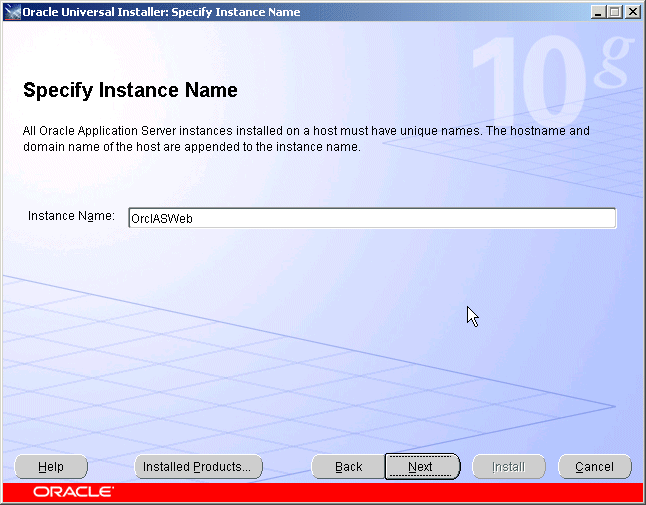
Specify the instance name and click Next.
The Cluster Topology Configuration screen appears.
Figure 5-11 Oracle Universal Installer Cluster Topology Configuration Screen
Check the box to configure the instance to be part of an Oracle Application Server cluster.
Specify the multicast address and port and click Next.
The Summary screen appears.
Click Install.
The Configuration Assistants screen appears. When the configuration process completes, the End of Installation screen appears.
Click Exit, and then confirm your choice to exit.
Verify that the installation was successful by viewing the Oracle HTTP Server instance. Start a browser and access:
http://hostname:7777
|
Note: TheORACLE_HOME/install/readme.txt file contains the URLs for the installation and a command to verify the status of processes.
|
Repeat the preceding steps to install and verify successful installation of the second instance on WEBHOST2.
Follow the steps in this section to deploy applications. You can perform this step before or after configuring clusters.
Deploying Applications with the Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Application Server Control Console
You can use Application Server Control Console to deploy applications. Follow these steps:
Access the Application Server Control Console at:
http://APPHOST1.us.oracle.com:8888/em
The Login page appears.
Provide the password that was set during installation and click Login.
The OC4J:home page appears.
Click the Cluster Topology link.
The Cluster Topology page appears.
Identify in the Members list the OC4J instance in which you will deploy applications. Ensure that a green upward arrow appears in its Status column, indicating that it is running.
|
Note: You can deploy an application into multiple instances that belong to the same group. Instances in a group have the same name and password. For instructions on creating a group, see the Oracle Application Server Administrator's Guide, Section 2.3.6, "Using Application Server Control to Create and Manage Groups".If a group exists, you can scroll down to the Groups section to see the list of instances in the group. To deploy to the group, click the Group name and continue with Step 8. |
If necessary, start the OC4J instance by clicking the Select checkbox at the beginning of the row and then clicking the Start button preceding the Members list.
The Processing: Starting screen appears with this message:
The selected topology members are being started.
The Cluster Topology screen appears with a message that the topology member was started.
Click the link for the OC4J instance for application deployment.
The OC4J screen for the instance appears.
Click the Applications link.
The Applications page for the instance appears.
Click Deploy.
The Deploy: Select Archive screen appears.
Provide the location of the archive and click Next.
The Deploy: Application Attributes screen appears.
Provide the application name and click Next.
The Deploy: Deployment Settings screen appears.
(Optional) Perform deployment tasks or deployment plan editing, or save the current settings as a deployment plan.
Click Deploy.
The Processing: Deploy screen appears with progress messages.
Deploying Applications on the Command Line
To deploy applications into OC4J instances using the command line, follow these steps:
Issue this command in APPHOST1_ORACLE_HOME\jdk\bin\java (the parameters are shown on separate lines for readability only):
java -jar admin_client.jar uri admin ID admin password
-deploy -file full path -deploymentName app name
[-bindAllWebApps [Web site name]]
[-targetPath full path] [-parent app name] [-deploymentDirectory full path]
[-iiopClientJar full path]
|
Note: Ideally, you should include the -bindAllWebApps subswitch to bind all Web modules within the EAR to the Web site through which they will be accessed. If no Web site is specified, modules will be bound to the default Web site.
|
The EAR file is deployed to the ORACLE_HOME/j2ee/instance name/applications/ directory by default. The deployed EAR file is also copied to this directory. Each successive deployment will cause this EAR file to be overwritten.
Because there is a firewall between the Web Server and Process management instances clustered on the Web tier and the J2EE Server and Process Management instances clustered on the Application tier, you must configure a cross-topology gateway to enable communication between the clusters. In the gateway configuration, one server on each side of the firewall is an entry point into the cluster. These instructions designate APPHOST1 and WEBHOST1 as the gateway servers, but any server may be designated the gateway server. The remote port is used for communication with the gateway server; it is designated in the <gateway> subelement in opmn.xml as shown in bold.
Follow these steps to specify gateway servers on the Application Tier and the Web Tier:
Open the APPHOST1_ORACLE_HOME/opmn/conf/opmn.xml file.
Create the <gateway> subelement as shown in the example:
<notification-server>
<port local="6101" remote="6201" request="6004"/>
<ssl enabled="true" wallet-file="$ORACLE_HOME\opmn\conf\ssl.wlt\default"/>
<topology>
<discover list="*225.0.0.20:8001"/>
<gateway list="apphost1.mycompany.com:6200&apphost2.mycompany.com:6200&webhost1.mycompany.com:6200&webhost2.mycompany.com:6200/"/>
</topology>
</notification-server>
...
|
Note: 6201 is the OPMN remote port onAPPHOST1, and 6202 is the OPMN remote port on WEBHOST1. You must view theopmn.xml file on each server to determine the port values needed for the configuration.
|
Issue this command in APPHOST1_ORACLE_HOME/opmn/bin:
opmnctl reload
Copy the <gateway> subelement to the WEBHOST1_ORACLE_HOME/opmn/conf/opmn.xml file.
Issue this command in WEBHOST1_ORACLE_HOME/opmn/bin:
opmnctl reload
|
Note: For more information, see "Configuring Cross-Topology Gateways" in Chapter 8 of the Oracle Containers for J2EE Configuration and Administration Guide. |
After you have installed all of the components on the Application Tier, you will be able to identify the port numbers that need to be opened on the firewall. This depends on the number of application server instances and types of components installed. In general, the process of configuring the firewall involves these steps:
For each installed instance, determine the component types and their designated port ranges (for example, the OC4J home instance and any instances you create) by examining the opmn.xml file. Example 5-1 shows components and default ports in the opmn.xml file. In the example, the OC4J Admin instance is listening on port 8888. Another instance, Apps, occupies port 12501.
Determine the ports in use with the netstat command:
netstat -an
Configure the firewall to open only the ports in use.
Example 5-1 Oracle Application Server components and port ranges in opmn.xml
<opmn xmlns="http://www.oracle.com/ias-instance"> <log path="$ORACLE_HOME\opmn\logs\opmn.log" comp="internal;ons;pm" rotation-size="1500000" /> <debug path="$ORACLE_HOME\opmn\logs\opmn.dbg" comp="internal" rotation-size="1500000" /> <notification-server> <port local="6100" remote="6200" request="6003" /> <ssl enabled="true" wallet-file="$ORACLE_HOME\opmn\conf\ssl.wlt\default" /> <topology> <discover list="*225.0.0.20:8001" /> </topology> </notification-server> ... <ias-component id="OC4J"> <process-type id="Admin" module-id="OC4J" status="enabled"> ... <port id="default-web-site" range="8888" protocol="http"/> ... </process-type> <process-type id="Apps" module-id="OC4J" status="enabled"> ... <port id="default-web-site" range="12501" protocol="ajp"/> ... </process-type> </ias-component> ...
Note that the AJP ports used by applications fall within the range 12501-12600. Ensure that all of the AJP ports used by OC4J applications are open on the firewall between the Web server and the application. If a port is not open, the following error occurs when access to the application from the Web tier is attempted (that is, when the URL web host:port/application is requested):
mod_oc4j: request to OC4J apphost1.us.oracle.com:12501 failed: Connect failed (errno=110)
This error creates an entry in a log file in the Apache/Apache/logs directory.
The Load Balancing Router (myapp.mycompany.com (shown in Figure 2-1, "Enterprise Deployment Architecture for myJ2EEcompany.com" must be configured to receive client requests and balance them to the two Oracle HTTP Server instances on the Web tier. See the load balancing router documentation for instructions on configuring the load balancer, and follow the instructions in this section configure the Oracle HTTP Server.
Incoming requests must be associated with the Load Balancing Router hostname and port in the myJ2EECompany configuration. To configure this, perform these steps on WEBHOST1 and WEBHOST2:
Open the Oracle HTTP Server configuration file:
ORACLE_HOME/Apache/Apache/conf/httpd.conf
Perform the following steps:
Add the LoadModule certheaders_module directive for the appropriate platform.
UNIX Apache 1.3:
LoadModule certheaders_module libexec/mod_certheaders.so
UNIX Apache 2.0; use this directive if you plan to use Apache 2.0 on UNIX:
LoadModule certheaders_module modules/mod_certheaders.so
Windows:
LoadModule certheaders_module modules/ApacheModuleCertHeaders.dll
Add the lines shown under the Apache version you are using to create a NameVirtualHost directive and a VirtualHost container for myapp.mycompany.com and port 443.
Apache 1.3:
NameVirtualHost *:7777<VirtualHost *:7777>ServerName myapp.mycompany.comPort 443ServerAdminyou@your.addressRewriteEngine OnRewriteOptions inheritSimulateHttps On</VirtualHost>
Apache 2.0 (UNIX):
NameVirtualHost *:7777<VirtualHost *:7777>ServerName myapp.mycompany.com:443ServerAdminyou@your.addressRewriteEngine OnRewriteOptions inheritSimulateHttps On</VirtualHost>
|
Notes: TheLoadModule LoadModule rewrite_module directive) must appear in the httpd.conf file at a location preceding the VirtualHost directives. The server must load all modules before it can execute the directives in the VirtualHost container.
It is a good idea to create the The |
Save the httpd.conf file.
Restart the components using these commands in ORACLE_HOME/opmn/bin:
opmnctl stopall
opmnctl startall
The Oracle Application Server Java Authentication and Authorization Service (JAAS) Provider (also referred to as JAZN) LDAP-based provider is used for authentication and authorization to the OC4J applications.
In the myJ2EECompany configuration, this provider is used without Oracle Application Server Single Sign-On. This section explains how to configure the Oracle Application Server instances on the application tier to use the JAZN LDAP provider. For instructions on how to use Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g to manage the data in this provider, see Chapter 8 in the Oracle Containers for J2EE Security Guide.
You will need to follow the steps in this section on both Oracle Application Server instances (APPHOST1 and APPHOST2) that will use the JAZN LDAP provider. Ensure that you specify the same Oracle Internet Directory computer for APPHOST1 and APPHOST2—that is, the load balancing router for OIDHOST1 and OIDHOST2.
Before you begin the steps in this section, ensure that the middle tier instance is stopped and the Oracle Internet Directory instance is running. Start the Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Application Server Control Console, if necessary, and perform these steps:
On the OC4J:home page, click the Administration link.
The Administration Tasks list appears.
In the Security section, click the Go To Task icon for Identity Management.
The Identity Management: page appears.
Click Configure if no host is configured, or click Change if you want to change the configured host.
The Configure Identity Management: Connect Information screen appears.
In the Oracle Internet Directory Host field, enter the host name of the Load Balancing Router (for example, oid.mycompany.com, in Figure 2-1).
In the Oracle Internet Directory User DN field, enter the Distinguished Name of the user that can log in to Oracle Internet Directory (the user must be in the IASAdmins group).
In the Password field, enter the Oracle Internet Directory user's password.
Select the checkbox to use the non-SSL connection to Oracle Internet Directory. In the Port field, enter 389.
Click Next.
The Configure Identity Management: Application Server Control page appears.
Select Use Oracle Identity Management Security Provider.
Click Next.
The Configure Identity Management: Deployed Applications page appears.
Select the applications deployed to the OC4J instance that you want to use the Oracle Identity Management Security Provider.
Click Configure.
A message appears notifying you that the configuration was successful, and notifies you that you must restart the OC4J instance.
Click Restart.
The instance is restarted, and the configuration is complete.
To use the OracleAS JAAS Provider, you must populate Oracle Internet Directory with certain user entries. In 10g Release 3 (10.1.3), the accounts and groups are managed by Mbeans. You may still need to map or create an anonymous user account. See "Summary of OC4J Accounts" in the Oracle Containers for J2EE Security Guide.