|
Oracle TopLink Developer's Guide
10g Release 3 (10.1.3) B13593-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
|
Oracle TopLink Developer's Guide
10g Release 3 (10.1.3) B13593-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
Inheritance describes how a derived (child) class inherits the characteristics of its superclass (parent). When you designate a class as a child, you must also specify the descriptor that represents the child's parent in your inheritance hierarchy.
Table 28-38 summarizes which descriptors support child inheritance configuration.
Table 28-20 Descriptor Support for Child Inheritance Configuration
| Descriptor | Using TopLink Workbench
|
Using Java
|
|---|---|---|
|
Relational Descriptors |
|
|
|
Object-Relational Descriptors |

|
|
|
EIS Descriptors |
|
|
|
XML Descriptors |
|
|
For more information about inheritance, see "Descriptors and Inheritance".
For more information about configuring inheritance for a parent (root) class descriptor, see "Configuring Inheritance for a Parent (Root) Descriptor".
To create a child (branch or leaf class) for an inheritance, use this procedure.
In the Navigator, select the descriptor you wish to specify as a child.
Choose the Inheritance tab in the Property window.
If the Inheritance tab is not visible, right-click the descriptor and choose Select Advanced Properties > Inheritance.
Select the Is Child Descriptor option to specify this descriptor is a child class. The Parent Descriptor list is now enabled and the class indicator information is disabled.
Figure 28-32 Creating a Root Class, Inheritance Tab
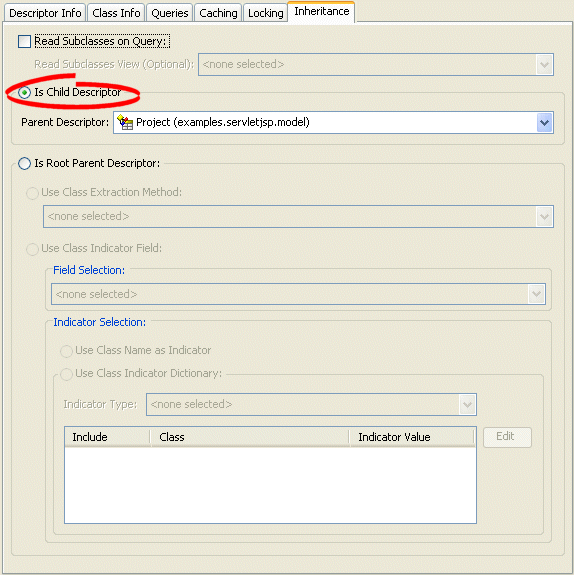
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Is Child Descriptor | Specify that this descriptor is a child class to be used in a branch or leaf. |
| Parent Descriptor | Use the list to select the parent of this descriptor. See "Descriptors and Inheritance" for more information. |
Using Java, you can configure an inheritance child descriptor using InheritancePolicy method setParentClass as Example Example 28-10 shows.