|
Oracle TopLink Developer's Guide
10g Release 3 (10.1.3) B13593-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
|
Oracle TopLink Developer's Guide
10g Release 3 (10.1.3) B13593-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
Direct mappings typically map simple, non-mutable values such as String or Integer. Transformation mappings can potentially map complex mutable object values, such as mapping several database field values to an instance of a Java class.
If a transformation mapping maps a mutable value, TopLink must clone and compare the value in a unit of work (see "Configuring Copy Policy").
By default, TopLink assumes that all transformation mappings are mutable. If the mapping maps a simple nonmutable value, you can improve unit of work performance by configuring the IsMutable option to false.
Table 35-18 summarizes which mappings support this option.
Use this table to complete the Object->Field Method fields:
Select the mapped attribute in the Navigator. Its properties appear in the Editor.
Figure 35-17 Transformation Mapping, Mutable Option
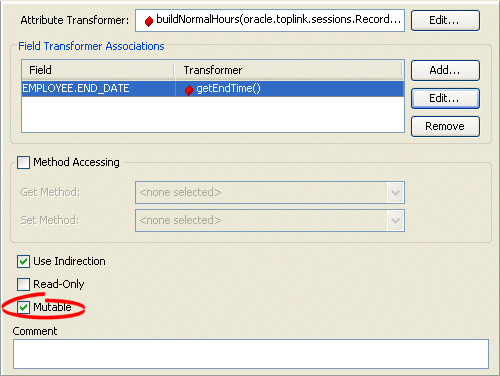
By default, the IsMutable option is selected in all transformation mappings. If the mapping maps to a simple atomic value, unselect this option.