| Oracle® Database Express Edition 2 Day Plus Java Developer Guide 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B25320-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database Express Edition 2 Day Plus Java Developer Guide 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B25320-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
Oracle Database Express Edition (Oracle Database XE) is a relational database that you can use to store, use, and modify data. The Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) standard is used by Java applications to access and manipulate data in relational databases.
JDBC is an industry-standard application programming interface (API) developed by Sun Microsystems that lets you embed SQL statements in Java code. JDBC is based on the X/Open SQL Call Level Interface (CLI) and complies with the SQL92 Entry Level standard. Each vendor, such as Oracle, creates its JDBC implementation by implementing the interfaces of the standard java.sql package.
See Also:
The Sun Microsystems documentation site for JDBC atThis guide shows you how to use a simple Java application to connect to Oracle Database XE and access and modify data within the database.
This chapter introduces you to the Java application created in this guide, and to the tools you can use to develop this application in the following topics:
JDBC is a database access protocol that lets you connect to a database and run SQL statements and queries to the database. The core Java class libraries provide only one JDBC API, java.sql. However, JDBC is designed to allow vendors to supply drivers that offer the necessary specialization for a particular database.
Oracle Database XE provides support for the client-side application development through the JDBC Thin Driver and the Oracle Call Interface (OCI) driver and the oracle.sql and oracle.jdbc packages. These packages contain classes and interfaces that extend the JDBC standard, which help you to access and manipulate Oracle data types and use Oracle performance extensions with greater flexibility in a Java application.
This section describes Oracle JDBC support in the following subsections:
See Also:
You can use the Oracle JDBC Thin Driver to write Java applications and applets that access Oracle SQL data. The JDBC Thin Driver is especially well-suited for Web-based applications and applets, because you can dynamically download it from a Web page, like a Java applet.
The JDBC Thin Driver is a pure Java, Type IV driver. It supports the Java Development Kit (JDK) releases 1.4.x and 1.5.x. It is platform-independent and does not require any additional Oracle software for client-side application development. The JDBC Thin Driver communicates with the server using SQL*Net to access Oracle Database XE.
The JDBC Thin Driver allows a direct connection to the database by providing a pure Java implementation of Oracle network protocols (TTC, SQL*Net). The driver supports the TCP/IP protocol and requires a TNS listener on the TCP/IP sockets on the database server. The Thin driver will work on any machine that has a suitable Java virtual machine (JVM).
The JDBC Thin Driver is fully compatible with JDBC 3.0 specifications. You can access the Oracle-specific JDBC features and the standard features by using the oracle.jdbc package.
The JDBC OCI driver is a Type II driver used with Java applications. It requires an Oracle client installation. It supports all installed Oracle Net adapters, including IPC, named pipes, TCP/IP, and InternetworkPacket Exchange/Sequenced Packet Exchange (IPX/SPX).
OCI is an API that enables you to create applications that use the native procedures or function calls of a third-generation language to access Oracle Database and control all phases of the SQL statement processing.
The JDBC OCI driver, written in a combination of Java and C, converts JDBC calls to calls to OCI. It does this by using native methods to call C-entry points. These calls communicate with the database using SQL*Net.
Oracle support for the JDBC API is provided through the oracle.jdbc and oracle.sql packages. These packages support all Java Development Kit (JDK) releases from 1.4 through 1.5.
The oracle.sql package supports direct access to data in SQL format. This package consists primarily of classes that provide Java mappings to SQL data types and their support classes. Essentially, the classes act as Java wrappers for SQL data. The characters are converted to Java chars and, then, to bytes in the UCS2 character set.Each of the oracle.sql.* data type classes extends oracle.sql.Datum, a superclass that includes functions and features common to all the data types. Some of the classes are for JDBC 2.0-compliant data types. In addition to the data type classes, the oracle.sql package supports classes and interfaces for use with objects and collections.
The interfaces of the oracle.jdbc package define the Oracle extensions to the interfaces in the java.sql package. These extensions provide access to Oracle SQL-format data. They also provide access to other Oracle-specific features, including Oracle performance enhancements.
The key classes and interfaces of this package provide methods that support standard JDBC features and perform tasks such as:
Returning Oracle statement objects
Setting Oracle performance extensions for any statement
Binding oracle.sql.* types into prepared and callable statements
Retrieving data in oracle.sql format
Getting meta information about the database and result sets
Defining integer constants used to identify SQL types
See Also:
For more information on Oracle support for JDBC and other features provided by Oracle that extend the JDBC API, refer to Oracle Database JDBC Developer's Guide and Reference.The Java application tutorial in this guide uses Oracle JDeveloper 10g release 10.1.3 as the integrated development environment (IDE) for developing the Java application and creating Web pages for users to view and change the data.
Oracle JDeveloper is an IDE with support for modeling, developing, debugging, optimizing, and deploying Java applications and Web services.
JDeveloper provides features for you to write and run Java programs that access the database with SQL statements embedded in Java programs. For the database, JDeveloper provides functions and features to do the following:
Create a connection to a database
Browse database objects
Create, edit, or delete database objects
Create and edit PL/SQL functions, procedures, and packages
For creating a Java application, JDeveloper provides the following tools to simplify the process:
Structure Window, which provides a tree view of all of the elements in the application currently being edited be it Java, XML, or JSP/HTML.
Java Visual Editor, which you can use to assemble the elements of a user interface quickly and easily.
JSP/HTML Visual Editor, which you can use to visually edit HTML and JSP pages.
Java Source Editor, which provides extensive features for helping in writing the Java code, such as distinctive highlighting for syntax and semantic errors, assistance for adding and sorting import statements, the Java Code Insight feature, and code templates.
Note:
The Java Code Insight feature is a facility that provides context-specific, intelligent input when creating code in the Java Source Editor. In this guide, you will see many instances of how you can use Java Code Insight to insert code.Component Palette, from which you select the user interface components, such as buttons and text areas, that you want to display on your pages.
Property Inspector, which gives a simple way of setting properties of items such as user interface components.
Oracle JDeveloper is an IDE that uses windows for various application development tools. You can display or hide any of the windows, and you can dock them or undock them to create a desktop suited to your method of working.
In addition to these tools, JDeveloper provides a range of navigators to help you organize and view the contents of your projects. Application and System navigators show you the files in your projects, and a Structure window shows you the structure of individual items.
You can arrange the windows as you choose, and can close and open them from the View menu. Figure 1-1 shows the default layout of some of the available navigators, palettes, and work areas in the JDeveloper user interface (GUI).
See Also:
For details about working with windows in the JDeveloper IDE, refer to Working with Windows in the IDE, in the JDeveloper online Help.The sample Java application created in this guide will include functions and features to do the following:
Allow users to log in and validate the user name and password.
Establish a connection to the database.
Query the database for data and retrieve the data using a JavaBean.
Display the data using JavaServer Pages (JSP) technology.
Allow users to insert, update, or delete records.
Handle exceptions.
The application connects to the HR schema that ships with Oracle Database XE. Although the Oracle Database XE client installation comes with both the Thin and OCI drivers, the sample application will use only the JDBC Thin Driver.
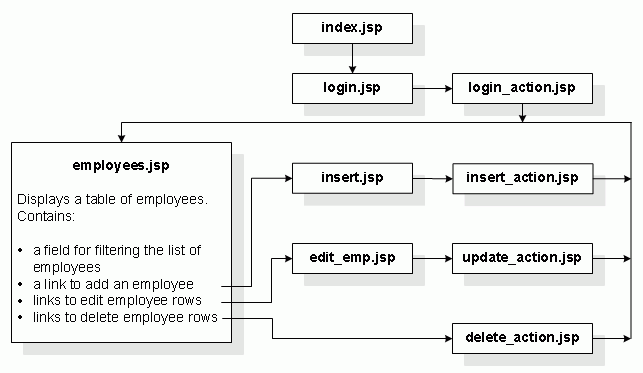
A brief description of the Web pages in the sample application follows:
This is the starting page of the application. It automatically forwards the user to the login page of the application, login.jsp.
This page allows users to log in to the application. The user name, password, and host information are validated and used to create the connection descriptor to log in to the database.
This is a nonvisual page that handles the authentication of the user-supplied login details from login.jsp. If authentication is successful, the page forwards the user to employees.jsp. Otherwise, it redisplays the login.jsp page including a message.
This is the main page of the application. It displays a list of all the employees in the HR schema for AnyCo Corporation and allows the user to filter the list of employees using any string. It also includes links to add, edit, and delete any user data. These actions, however, are handled by other JSP pages that are created specifically for each of these tasks.
The link to insert employee data on the employees.jsp page redirects the user to this page. This includes a form that accepts all the details for a new employee record. The details entered on this form are processed by the insert_action.jsp page.
This is a nonvisual page that handles the insertion of data for a new employee that is entered on the insert.jsp page.
The link to edit employee data on the employees.jsp page redirects the user to this page. This form displays current data of a single employee in text fields, and the user can edit this information.
The submit action on the edit_emp.jsp page directs the data to this nonvisual page, which inserts the edited data into the database.
The link to delete an employee record on the employees.jsp page is handled by this nonvisual page, which deletes the employee data and forwards the user back to the employees.jsp page.
Figure 1-2 shows the relationships among the pages developed for this application.
Figure 1-2 Web Pages in the Sample Application
The sample application includes the following classes:
This class contains all the methods that are used to implement the important functions of the sample application. It includes methods that validate user credentials, connect to the database, retrieve employee data with and without filters, insert data, update data, handle exceptions, and so on.
This class is a JavaBean that holds a single employee record. It contains accessor methods to get and set the values of each of the record fields. It also contains accessor methods to retrieve and modify employee records.
Note:
This application is developed throughout this book in the form of a tutorial. It is recommended, therefore, that you read these chapters in sequence.