| Oracle® SOA Suite Developer's Guide 10g (10.1.3.1.0) Part Number B28764-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® SOA Suite Developer's Guide 10g (10.1.3.1.0) Part Number B28764-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
Oracle BPEL Process Manager provides a framework for designing, deploying, and managing cross-application business processes based on business process execution language (BPEL) standards. BPEL is an XML-based language for creating business process workflows and orchestrating XML-based web services. The resulting BPEL application supports a service-oriented architecture (SOA) paradigm by leveraging web computing standards to deliver an application that is the business process.
In a BPEL process, every piece of data is in XML format. This includes the messages passed to and from the BPEL process, the messages exchanged with external services, and all variables. You define the types for these messages and variables with the XML schema, in the web services description language (WSDL) file for the BPEL process itself or in the WSDL files for the web services that a BPEL process invokes. The WSDL defines the input and output messages for a BPEL process, the supported client interface and operations, and other features. This functionality enables a BPEL process to be called as a web service. XML variables are manipulated in the BPEL code, including data transformation between different formats required by web services and local manipulation of data (for example, to combine the results from several web service invocations).
When designing a BPEL process, you model the business process by specifying the BPEL building blocks, activities and services, in the order required to execute the business workflow. This chapter describes the key activities and services that you need to understand the BPEL components of the SOA Order Booking application, as well as basic topics such as how to create a BPEL project and invoke a web service. See the following for the context for understanding the activities and services described in this chapter:
See Oracle BPEL Process Manager Developer's Guide for a more complete description of all the BPEL activities and services.
Figure 7-1 shows how a BPEL process receives a request from a client application, invokes a web service to process that request, and returns a value to the client. The figure depicts an asynchronous web service invocation, which returns a result to the client using a callback. Asynchronous processes are good for long-running production environments and do not require the client or partner link to wait for a response.
Figure 7-1 BPEL Process and Asynchronous Service Invocation
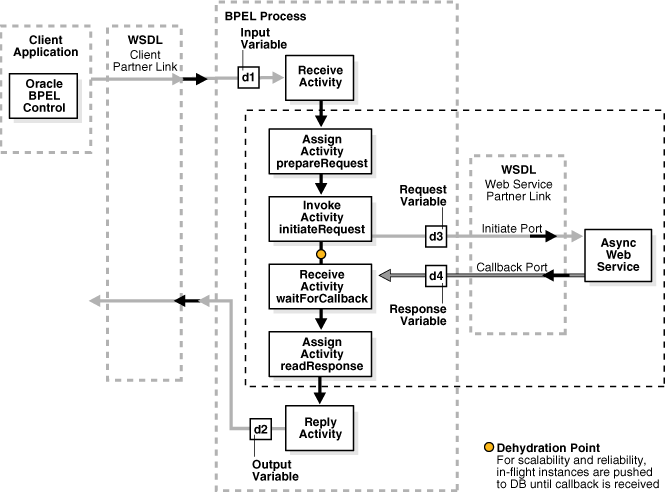
Within the BPEL process, between the receive and reply activities, the BPEL process assigns the client request to an input variable (prepareRequest), invokes the request by putting the contents of this request into a request variable and sending the request to the web service (initiateRequest), receives the response back from the web service (waitForCallback), and assigns the response to an output variable to read the reply (readResponse). Oracle BPEL Process Manager automatically performs dehydration (stores the process in the dehydration store database) after an invoke activity in an asynchronous process, as shown in Figure 7-1. See Oracle BPEL Process Manager Installation Guide for information about setting up a dehydration database.
BPEL processes include partner links to various web services. Partner links define the external services with which the BPEL process interacts. A partner link type characterizes the conversational relationship between two services by defining the roles played by each service in the conversation and specifying the port type provided by each service to receive messages within the context of the conversation. In the SOA Order Booking application, the client partner link kicks off the BPEL process with order information that is routed by Oracle Enterprise Service Bus. See Chapter 2, "The SOA Order Booking Application" for a description of the BPEL processes in the SOA Order Booking application.
See the following for more information about Oracle BPEL Process Manager:
Read this chapter to understand:
How to create BPEL processes
How to communicate with web services
How to deploy and run BPEL processes