| Oracle® SOA Suite Developer's Guide 10g (10.1.3.1.0) Part Number B28764-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® SOA Suite Developer's Guide 10g (10.1.3.1.0) Part Number B28764-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
A web service can be invoked as a synchronous or asynchronous operation. Synchronous web services provide an immediate response to a query, and block the BPEL process for the duration of the operation. Asynchronous web services do not block the BPEL process, and are useful for environments in which a service can take a long time to process a client request. Asynchronous services also provide a more fault-tolerant and scalable architecture than synchronous services.
Both synchronous and asynchronous web services require the following:
Partner link: Defines the location and the role of the web services with which the BPEL process interacts, as well as the variables used to carry information between the web service and the BPEL process. A partner link is required for each web service that the BPEL process calls.
Invoke activity: Opens a port in the BPEL process to send and receive data. A BPEL process uses this port to send the required data and return a response. For a synchronous web service, only one port is needed for both the send and receive functions. Because the BPEL process waits for the reply, nothing that explicitly receives the reply is needed.
An asynchronous web service also requires the following:
Receive activity: Provides another port to receive the reply from the web service.
Correlation ID: Ensures that the response returned corresponds to the request. The correlation ID is unique to the client and partner link initiating the request and is sent to the web service.
The BPEL process in the SOA Order Booking application includes a synchronous web service invocation (to Rapid Manufacturer) and an asynchronous web service invocation (to Select Manufacturer).
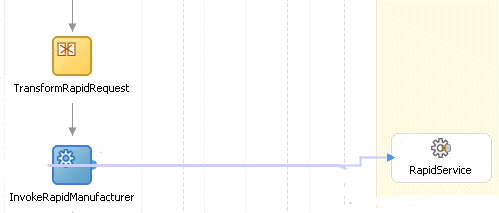
A synchronous invocation is shown in Figure 7-5. The invoke activity (InvokeRapidManufacturer) solicits a quote using the RapidService partner link. The Rapid Manufacturer web service (not shown in the figure) replies immediately to the query.
Figure 7-5 Synchronous Invocation to Rapid Manufacturer
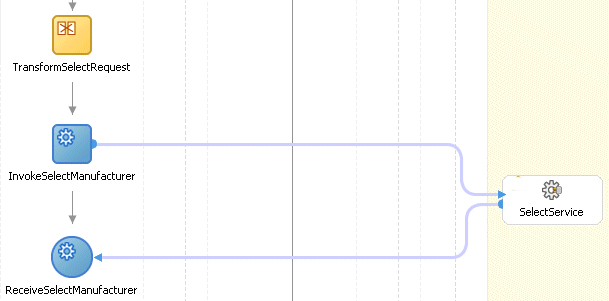
An asynchronous invocation is shown in Figure 7-6. The invoke activity (InvokeSelectManufacturer) solicits a quote using the SelectService partner link. The Select Manufacturer web service (not shown in the figure) processes the request and returns a reply, which is tracked by the correlation ID, to the ReceiveSelectManufacturer activity.
Figure 7-6 Asynchronous Invocation to Select Manufacturer
For both synchronous and asynchronous web service invocations, you add the following activities to a BPEL process:
A partner link activity to define the external web service with which the BPEL process interacts
A scope activity for nesting related activities that can have their own local variables and fault handlers
An invoke activity to specify the operation you want to invoke for the web service (identified by its partner link)
Two assign activities. The first assign activity takes the client query input and contacts the web service. The second assign activity returns the response from the web service.
For an asynchronous web service invocation, you also add the following:
A receive activity after the invoke activity, as shown in Figure 7-6. The receive activity receives the data from the web service. You use the Receive dialog to select the partner link, operation, and variable that are provided by the web service WSDL.
A partner link defines the external services with which the BPEL process interacts.
To create a partner link to a web service:
Create an asynchronous BPEL process.
See Section 7.2.1, "How to Create an Application" for instructions.
Drag and drop a PartnerLink activity under one of the Services swim lanes.
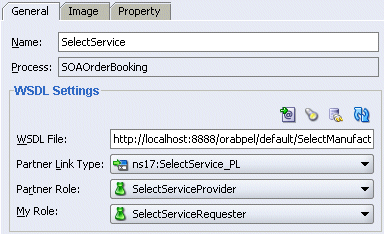
Use the General tab of the Create Partner Link dialog to enter values to create a partner link, as shown in Figure 7-7.
Figure 7-7 Creating a Partner Link for an Asynchronous Web Service
Enter a name for the partner link.
Use the Service Explorer (flashlight icon) to browse for the URL of the web service WSDL file.
This WSDL describes the web service communication endpoints.
Select a partner link type.
This value is supplied by the web service WSDL.
Select a partner role.
This is the provider role of the web service. This value is supplied by the web service WSDL.
For a synchronous web service invocation, skip the My Role field. A role is not required for a partner link to a synchronous web service.
For an asynchronous web service invocation, select a value for the My Role field on the Create Partner Link dialog, as shown in Figure 7-7. This is the requester role of the BPEL process. This value is supplied by the web service WSDL and is needed for the Select Manufacturer web service to return a response to the BPEL process, CallSelectManufacturer.
Click OK.
Save the file.
A scope activity is a container for a group of activities that you want to process as one unit.
To create a scope activity:
Drag and drop a Scope activity between the receiveInput and callbackClient activities.
Double-click the Scope activity.
Select the General tab and enter a name for the Scope activity.
Click OK.
Save the file.
An invoke activity sends information, typically a request, to a web service, which is identified by its partner link, and specifies an operation for the web service to perform.
To create an invoke activity inside a scope activity:
Expand the Scope activity that you just created.
Drag and drop an Invoke activity into the Scope activity.
Double-click the Invoke icon.
Use the Invoke dialog to identify the initial interaction operation between the BPEL process and the web service.
Enter a name for the Invoke activity.
Browse for the partner link that you previously created.
Select an operation.
This value is supplied by the web service WSDL.
Create an input variable with the first icon (the automatic variable creation icon) to the right of the Input Variable field.
A variable named invokeName_operationName_InputVariable is automatically created in the Input Variable field. The variable is automatically assigned a message type of WebServiceNameRequestMessage. This value is supplied by the web service WSDL. This variable holds the contents of the request and is sent to the web service.
Create an output variable with the first icon to the right of the Output Variable field.
A variable named invokeName_operationName_OutputVariable is automatically created in the Output Variable field. This variable is automatically assigned a message type of WebServiceNameResponseMessage. This value is supplied by the web service WSDL. This variable holds the contents of the reply from the web service.
Save the file.
An assign activity transfers data between variables, expressions, and other elements.
To create an initial assign activity inside a scope activity:
Drag and drop an Assign activity to above the Invoke activity and inside the Scope activity.
Double-click the Assign icon.
Use the General tab of the Assign dialog to enter a name for the Assign activity.
Click Apply.
Click the Copy Operation tab.
From the Create list, select Copy Operation.
Use the Create Copy Operation dialog, shown in Figure 7-8, to copy the contents of one variable to another. This Assign activity takes the client's purchase order as input and contacts the Rapid Manufacturer web service for a price quote.
Browse for the From Variable by expanding the tree until you find the client input variable name (as defined in the BPEL process WSDL file).
Browse for the To Variable by expanding the tree until you find the input variable name used by the web service (as defined in the message type definition of the web service WSDL).
Close the Create Copy Operation and Assign windows.
Save the file.
This second assign activity returns a price quote in response to the client's purchase order.
To create a second assign activity inside a scope activity:
Drag and drop a second Assign activity below the Invoke activity and within the Scope activity.
Double-click the Assign icon.
Use the General tab of the Assign dialog to enter a name for the activity.
Click Apply.
Click the Copy Operation tab.
From the Create list, select Copy Operation.
Use the Create Copy Operation dialog to copy the contents of one variable to another.
Browse for the From Variable by expanding the tree until you find the client output variable name (as defined in the BPEL process WSDL file).
Browse for the To Variable by expanding the tree until you find the output variable name used by the web service (as defined in the message type definition of the web service WSDL).
Close the Create Copy Operation and Assign windows.
Save the file.
A receive activity waits for a message from the client or a callback response message from an asynchronous web service.
To create a receive activity:
Drag and drop a Receive activity below the Invoke activity.
Double-click the Receive icon.
Use the General tab to enter values for the receive activity, as shown in Figure 7-9.
Enter a name for the Receive activity.
Use the flashlight icon to browse for the partner link of the web service.
This value is supplied by the web service WSDL.
Select an operation.
This value is supplied by the web service WSDL.
Use the flashlight icon to browse for the variable that holds the response from the web service.
This value is supplied by the web service WSDL.
Save the file.
For a synchronous web service invocation, the following takes place:
The receiveInput receive activity receives input from the user (client), as defined in the WSDL file (bpel_process_name.wsdl).
The first assign activity packages the data from the client so that it can be accepted by the web service.
The partner link sends the repackaged data to the web service and receives a response.
The second assign activity repackages the response into a replyOutput activity so that it can be accepted by the client application.
The replyOutput activity sends the repackaged response back to the client.
Example 7-2 shows the partner link definition and invoke element for a synchronous web service.
Example 7-2 Source Code for the Partner Link Definition and Invoke Element of a Synchronous Web Service
<!-- This section shows where the partner link is defined.-->
<partnerLink name="RapidService" partnerRole="RapidQuote_Role"
partnerLinkType="ns23:RapidQuote_PL"/>
...
<scope name="CallRapidManufacturer">
<variables>
<variable name="manufacturerRequest"
messageType="ns23:RequestQuotePortType_POItemsQuote"/>
</variables>
<sequence name="Sequence_6">
<assign name="TransformRapidRequest">
<bpelx:annotation>
<bpelx:pattern>transformation</bpelx:pattern>
</bpelx:annotation>
<copy>
<from expression="ora:processXSLT('RapidTransformation.xsl',
bpws:getVariableData('inputVariable','payload'))"/>
<to variable="manufacturerRequest" part="parameters"/>
</copy>
</assign>
<invoke name="InvokeRapidManufacturer"
partnerLink="RapidService" portType="ns23:RequestQuote"
operation="POItemsQuote"
inputVariable="manufacturerRequest"
outputVariable="rapidManufacturerResponse"/>
</sequence>
</scope>
For an asynchronous web service invocation, the following takes place:
An assign activity prepares the purchase order.
An invoke activity (InvokeSelectManufacturer) initiates the request. The contents of this request are put into a request variable. The request variable is sent to the asynchronous web service.
When the request is initiated, a correlation ID unique to the client and partner link initiating the request is also sent to the web service. The correlation ID ensures that the correct response is returned to the corresponding requestor.
The web service sends the response to the receive activity (ReceiveSelectManufacturer), which is tracked by the correlation ID.
An assign activity (AssignSelectManufacturer) reads the response.
Example 7-3 shows the source code for the partner link definition and the invoke and receive elements for an asynchronous web service.
Example 7-3 Source Code for the Partner Link Definition and Invoke and Receive Elements of an Asynchronous Web Service
<!-- This section shows where the partner link is defined.-->
<partnerLink myRole="SelectServiceRequester" name="SelectService"
partnerRole="SelectServiceProvider"
partnerLinkType="ns17:SelectService_PL"/>
...
<scope name="GetSelectMfrQuote">
<variables>
<variable name="manufacturerRequest"
messageType="ns17:RequestQuote_processRequestQuote"/>
</variables>
<sequence name="Sequence_15">
<assign name="TransformSelectRequest">
<bpelx:annotation>
<bpelx:pattern>transformation</bpelx:pattern>
</bpelx:annotation>
<copy>
<from expression="ora:processXSLT('SelectTransformation.xsl',bpws:getVariableData
('inputVariable','payload'))"/>
<to variable="manufacturerRequest" part="parameters"/>
</copy>
</assign>
<invoke name="InvokeSelectManufacturer"
partnerLink="SelectService"
portType="ns17:SelectService"
operation="processRequestQuote"
inputVariable="manufacturerRequest"/>
<receive name="ReceiveSelectManufacturer" createInstance="no"
partnerLink="SelectService"
portType="ns17:SelectServiceCallback"
operation="processRequestQuoteResponse"
variable="selectManufacturerResponse"/>
</sequence>
</scope>