| Oracle® SOA Suite Developer's Guide 10g (10.1.3.1.0) Part Number B28764-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® SOA Suite Developer's Guide 10g (10.1.3.1.0) Part Number B28764-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
After you define the data model, you can create rules to define business policies based on the data model. For example, in the SOA Order Booking application, we define several rules that specify the business policies for an incoming order. In this rules application, the rules determine if an order requires manual credit approval.
In general, you use rules to define your business policies. For example, in the SOA Order Booking application, the rules specify that manual approval is not required if the status of the customer is platinum. For the non-platinum customers, rules specify that when the dollar amount of the order is greater than or equal to $1000, the order requires manual approval and when the order is under $1000, the order is approved automatically.
To define business policies in your application, you need to define rule sets and then create rules.
Before you can create a rule, you must create a rule set. A rule set is a container for rules.
To create a rule set:
Click the Rulesets tab.
Click the RuleSet node in the navigation tree. This displays the RuleSet Summary page.
On the Ruleset Summary page, click Create. This displays the Ruleset page.
In the Name field, enter a a name. For example, for the ruleset for the SOA Order Booking application, enter ApproveOrderRequired.
(Optional) Enter text in the Description field.
Click OK.
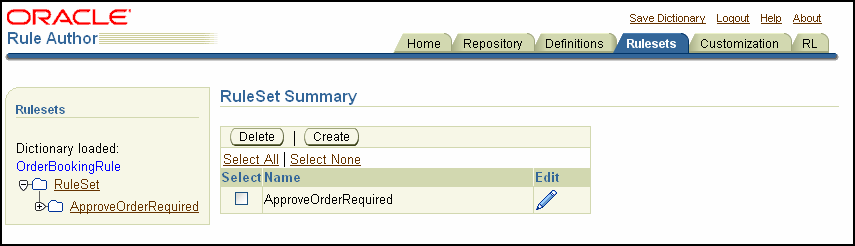
The rule set is created. After you create the rule set, the new entry appears in the Rulesets tree under RuleSet, as shown in Figure 8-11.
Save the dictionary.
Figure 8-11 Rule Author Rule Set Summary Page
After creating a rule set, you can create a rule within the ruleset. The rules determine your business policies. For example, in the SOA Order Booking application, the rules for the following business policies were defined:
belowLimit: if the order is under $1000, then the order is approved automatically.
overLimit: for non-platinum customers, if the dollar amount of the order is greater than or equal to $1000, then the order requires manual approval.
platinumMember: if the customer's status is platinum, then the order is approved automatically, regardless of the dollar amount of the order.
To create a rule:
Click the RuleSets tab. The navigation pane displays the RuleSet folder. For example, for the SOA Order Booking application, the ruleset folder contains the ApproveOrderRequired rule.
Click a node in the ruleset folder. For example, click the ApproveOrderRequired node in the navigation tree. This displays the Ruleset page, with the Rules table (see Figure 8-12).
|
Note: If you have not yet created rules, then the Rules table is empty. |
Figure 8-12 Rule Author RuleSet Page Showing the Create Button
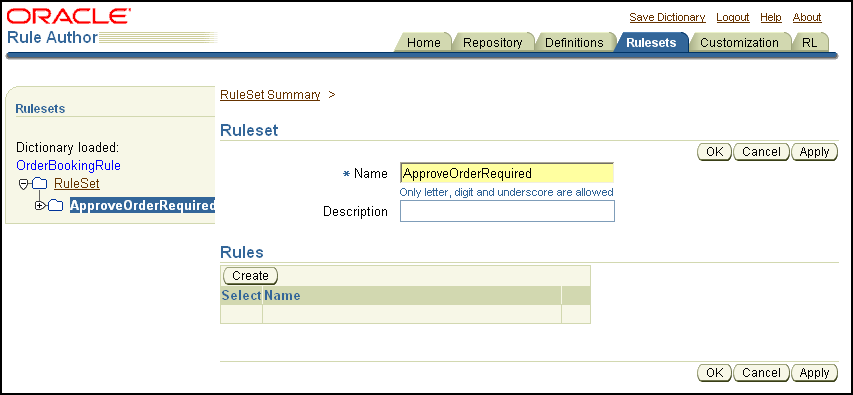
Click Create. This displays the Rule page.
On the Rule page, in the Name field, enter a name for the rule. For example, enter belowLimit.
On the Rule page in the Priority field, enter the rule priority for the rule. For example, enter 0 (0 is the default priority).
|
Note: The Priority field determines which rule to act upon, and in what order, if more than one rule applies. Often, in applications that use rules, the rules are applied in any order until a decision is reached, so setting a priority is not required. |
(Optional) In the Description field, enter a description. For example, see Figure 8-13.
When the rules engine runs, it uses the rules to check the available facts for matching patterns. You must add a pattern to a rule to allow the rules engine to match patterns.
To add a pattern for the rule:
In the If box on the Rule page click New Pattern.
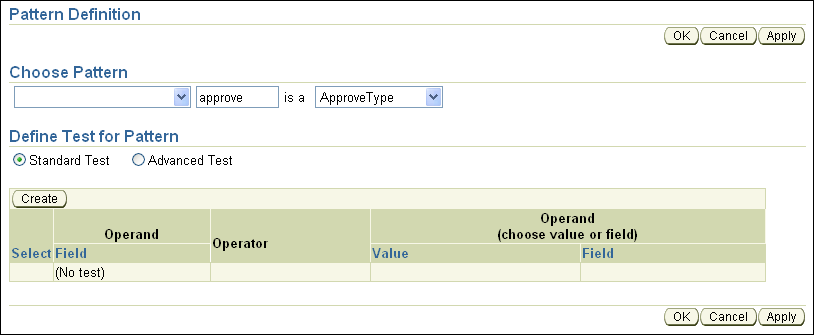
The Pattern Definition page appears. The Pattern Definition page contains two areas: Choose Pattern and Define Test for Pattern.
Under Choose Pattern, in the first list select the first entry, which is blank.
This list specifies that the rule should fire each time there is a match. One alternative value, There is at least one case, selects one firing of the rule if there is at least one match (one such driver). The other alternate value, There is no case, specifies that the rule fires once if there are no such matches.
The next text box under Choose Pattern lets you enter a temporary name for the matched fact.
For example, enter approve in this field (this defines the "pattern bind variable name").
This field lets you test multiple instances of the same type in a single rule.
The last list contains the text, <make a choice>, this list shows the available fact types. In this list select ApproveType (see Figure 8-14).
Click OK on the pattern definition page to save the pattern definition and close the Pattern Definition page.
Click OK on the RuleSet page to save the rule.
|
Note: Changes made to the pattern are not added to the rule until you click OK or Apply on the Rule page. If you navigate to a different rule set or select a different tab before you click OK or Apply, Rule Author discards your pattern definition changes. |
Save the dictionary.
Figure 8-14 Pattern Definition for Below Limit Rule
Without any tests defined on the pattern, any action that you define would apply to all approveTypes. To define tests for patterns, continue, as shown in Section 8.7.2.2. For information on rule actions, see Section 8.7.2.3, "Add an Action for a Rule".
Tests on patterns allow the rules engine to limit a rule match to a data item that meets the test requirements. For example, for the belowLimit rule, Global Company used a test to specify that the price associated with an order was below the specified approval limit.
To add a pattern test for a rule:
From the Rulesets tab, in the navigation tree click the rule where you want to add a test. For example, click the belowLimit rule.
In the If table on the rule page, select the pencil icon to display the Pattern Definition page for this rule.
On the Pattern Definition page, select Standard Test, then click Create (see Figure 8-15).
Figure 8-15 Rule Author Rule Pattern Definition Page with Standard Test Fields
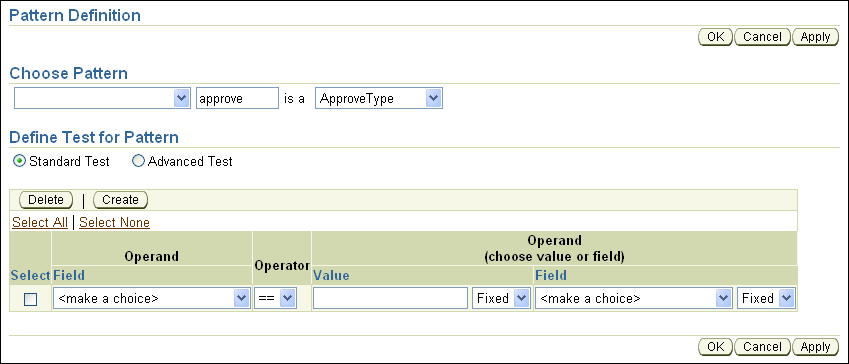
In the Operand column, select a field from the list (for example, approve.price).
In the Operator column, select < (less than).
In the Operand (choose value or field) column, select a field from the list (for example, AUTOMATED_ORDER_LIMIT).
Next to the Value and Field boxes is a list containing the values Any and Fixed (see Figure 8-16). Select Fixed for both of these fields (this is the default).
Figure 8-16 Rule Author Pattern Definition Page with Values for the belowLimit Rule
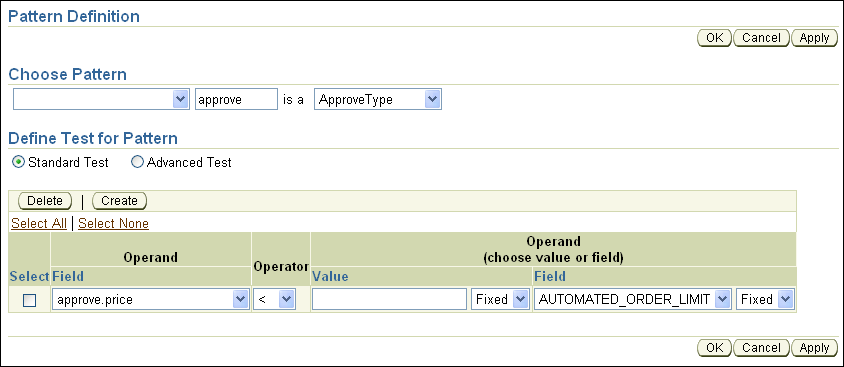
Click OK on the Pattern Definition page to save your changes and close the Pattern Definition page.
On the Rule page, click OK or Apply.
|
Note: Changes made to the pattern are not added to the rule until you click OK or Apply on the Rule page. If you do not click OK or Apply, Rule Author does not save your work on the rule. |
Save the dictionary.
Actions are associated with pattern matches. At runtime, when the "If" portion of a rule matches, the rules engine executes the "Then" portion to run the action or actions associated with the rule. Table 8-1 shows the Rule Author action types for actions that you can use when you create a rule.
Table 8-1 Action Types
| Action Type | Description |
|---|---|
|
Assert |
Asserts a fact used in a pattern. If a fact matched in a pattern is changed, that fact must be asserted again to notify the rules engine that the fact has changed. |
|
Assert New |
Creates a new fact type instance and asserts that instance to the rules engine. |
|
Assign |
Assigns a value to a variable or fact property. If a new value is assigned to a fact property, the fact must be asserted again in order for the rules to be re-evaluated with the new value. |
|
Call |
Allows you to call a function to perform an action. |
|
Retract |
Retracts a fact used in a pattern. You might want to retract a fact for a number of reasons, including:
|
|
RL |
Creates free form RL Language text that is executed directly. The syntax of the RL Language text is not validated by the SDK, so creating RL actions may result in the generation of invalid RL code from the ruleset. |
To add an action that assigns values associated with a rule pattern match:
Click the Rulesets tab.
In the tree, click the node for the rule you want.
On the Rule page, in the Then box, click New Action. This displays the Add Action page.
From the Action Type box select the Assign item. This shows the Action Parameters box.
From the Name field, select the action variable you want.
In the Expression field, enter the expression value.
Click OK to save your changes and close the Add Action page.
On the Rule page, click OK or Apply.
Save the dictionary.
For example, to add the action for the belowLimit rule:
To add the action that assigns values associated with the belowLimit rule pattern match:
Click the Rulesets tab.
In the tree, under ApproveOrderRequired, click the belowLimit node.
On the Rule page, in the Then box, click New Action. This displays the Add Action page.
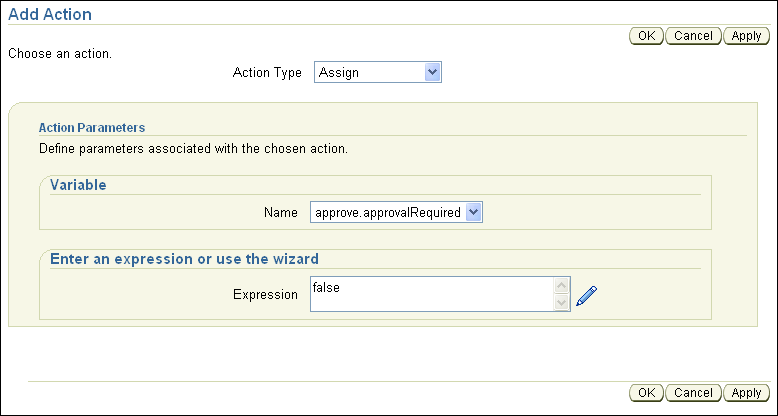
From the Action Type box select the Assign item. This shows the Action Parameters box.
From the Name field, choose approve.approvalRequired.
In the Expression field, enter the expression value false (see figure Figure 8-17).
Click OK to save your changes and close the Add Action page.
On the Rule page, click OK or Apply.
Save the dictionary.
Figure 8-17 Rule Author Add Action Page for the belowLimit Rule
When you define a ruleset and rules, you specify business policies for your application. For example, in the SOA Order Booking application the rules specify the business policies to determine if an order requires manual credit approval based on the size of the order and the customer status. At runtime, the application runs the rules against asserted facts in the rules engine, and returns results or performs actions based on the rules that match the facts. For information on using a BPEL Decision Service, see Section 7.8, "Using Business Rules and a Decide Activity".
When you work with BPEL and a Decision Service, you can only pass information to and from the Decision Service using an XML Document. When you develop other types of rules applications, you can pass information to and from the rules engine using either Java objects or XML documents.