| Oracle® TopLink Developer's Guide 10g Release 3 (10.1.3.1.0) Part Number B28218-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® TopLink Developer's Guide 10g Release 3 (10.1.3.1.0) Part Number B28218-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
Oracle TopLink is an advanced, object-persistence and object-transformation framework that provides development tools and run-time capabilities that reduce development and maintenance efforts, and increase enterprise application functionality.
This chapter describes the following topics:
Oracle TopLink builds high-performance applications that store persistent object-oriented data in a relational database. It successfully transforms object-oriented data into either relational data or Extensible Markup Language (XML) elements.
Using TopLink, you can integrate persistence and object-transformation into your application, while staying focused on your primary domain problem by taking advantage of an efficient, flexible, and field-proven solution (see "Solving the Object-Persistence Impedance Mismatch").
TopLink is suitable for use with a wide range of Java 2 Enterprise Edition (J2EE) and Java application architectures (see "TopLink Application Architectures"). Use TopLink to design, implement, deploy, and optimize an advanced, object-persistence and object-transformation layer that supports a variety of data sources and formats, including the following:
Relational–for transactional persistence of Java objects to a relational database accessed using Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) drivers.
Object-Relational–for transactional persistence of Java objects to special purpose structured data source representations optimized for storage in object-relational databases such as Oracle Database.
Enterprise information system (EIS)–for transactional persistence of Java objects to a nonrelational data source accessed using a J2EE Connector architecture (J2C) adapter, and any supported EIS record type, including indexed, mapped, or XML.
XML–for nontransactional, nonpersistent (in-memory) conversion between Java objects and XML Schema Document (XSD)-based XML documents using Java Architecture for XML Binding (JAXB).
TopLink includes support for container-managed persistence (CMP) containers from a variety of vendors–such as Oracle Containers for J2EE (OC4J), IBM WebSphere application server, and BEA WebLogic Server–and support for base classes that simplify bean-managed persistence (BMP) development.
The extensive suite of development tools that TopLink provides, including Oracle TopLink Workbench, lets you quickly capture and define object-to-data source and object-to-data representation mappings in a flexible, efficient metadata format (see "Understanding TopLink Metadata").
The TopLink runtime lets your application exploit this mapping metadata with a simple session facade that provides in-depth support for data access, queries, transactions (both with and without an external transaction controller), and caching.
For more information about TopLink, see "TopLink Key Features".
Java-to-data source integration is a widely underestimated problem when creating enterprise Java applications. This complex problem involves more than simply reading from and writing to a data source. The data source elements include tables, rows, columns, and primary and foreign keys. The Java and J2EE include entity classes (regular Java classes or Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB) entity beans), business rules, complex relationships, and inheritance. In a nonrelational data source, you must match your Java entities with EIS records or XML elements and schemas. These differences (as shown in Figure 1-2) are known as the object-persistence impedance mismatch.
Figure 1-2 Solving Object-Persistence Impedance Mismatch
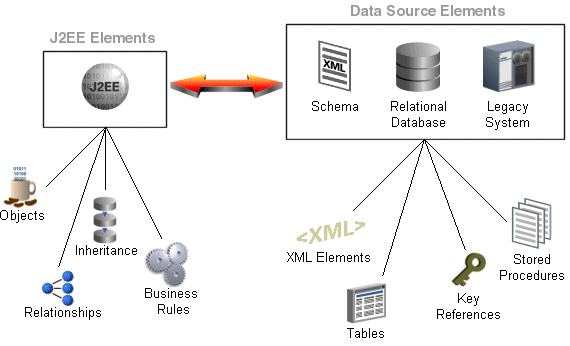
Successful solution requires bridging these different technologies, and solving the object-persistence impedance mismatch–a challenging and resource-intensive problem. To solve this problem, you must resolve the following issues between J2EE and data source elements:
Fundamentally different technologies
Different skill sets
Different staff and ownership for each of the technologies
Different modeling and design principles
Application developers need a product that enables them to integrate Java applications with any data source, without compromising ideal application design or data integrity. In addition, Java developers need the ability to store (that is, persist) and retrieve business domain objects using a relational database or a nonrelational data source as a repository.
TopLink Solution
TopLink addresses the disparity between Java objects and data sources. TopLink is a persistence framework that manages relational, object-relational, EIS, and XML mappings in a seamless manner. This allows developers to rapidly build applications that combine the best aspects of object technology and the specific data source. TopLink lets you do the following:
Persist Java objects to virtually any relational database supported by a JDBC-compliant driver.
Persist Java objects to virtually any nonrelational data source supported by a J2EE Connector architecture (J2C) adapter using indexed, mapped, or XML enterprise information system (EIS) records.
Perform in-memory conversions between Java objects and XML Schema (XSD) based XML documents using JAXB.
Map any object model to any relational or nonrelational schema, using the Oracle TopLink Workbench graphical mapping tool.
Use TopLink successfully, even if you are unfamiliar with SQL or JDBC, because TopLink offers a clear, object-oriented view of data sources.
TopLink provides an extensive and thorough set of features. Java developers can use these features to rapidly build high-performance enterprise applications that are both scalable and maintainable.
Some of the primary features of TopLink are the following:
Nonintrusive, flexible, metadata-based architecture (see "Understanding TopLink Metadata")
Comprehensive visual TopLink Workbench
Advanced mapping support and flexibility (relational, object-relational, EIS, and XML)
Object caching support
Query flexibility
Just-in-time reading
Caching
Object-level transaction support and integration
Locking
Multiple performance tuning options
Architectural flexibility
For additional information, see the TopLink page on OTN:
http://www.oracle.com/technology/products/ias/toplink/index.html
You can use TopLink in a variety of application architectures, including three- and two-tier architectures, with or without J2EE, to access a variety of data types on both relational and nonrelational data sources.
Figure 1-3 TopLink and Your Application Architecture
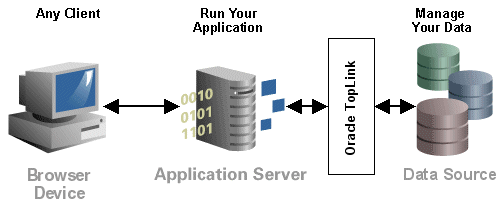
For more information on strategies for incorporating TopLink into your application architecture, see "Designing Your Application With TopLink".
This section introduces some of the following common enterprise architectures used by TopLink applications:
The three-tier (or J2EE Web) application is one of the most common TopLink architectures. This architecture is characterized by a server-hosted environment in which the business logic, persistent entities, and the Oracle TopLink Foundation Library all exist in a single Java Virtual Machine (JVM). See "Understanding the Three-Tier Architecture" for more information.
The most common example of this architecture is a simple three-tier application in which the client browser accesses the application through servlets, JavaServer Pages (JSP) and HTML. The presentation layer communicates with TopLink through other Java classes in the same JVM, to provide the necessary persistence logic. This architecture supports multiple servers in a clustered environment, but there is no separation across JVMs from the presentation layer and the code that invokes the persistence logic against the persistent entities using TopLink.
A popular variation on the three-tier application involves wrapping the business logic, including the TopLink access, in EJB session beans. This architecture provides a scalable deployment and includes integration with transaction services from the host application server. See "Understanding the EJB Session Bean Facade Architecture" for more information.
Communication from the presentation layer occurs through calls to the EJB session beans. This architecture separates the application into different tiers for the deployment. The session bean architecture can persist either Java objects or EJB entity beans.
EJB 3.0 Entities with JPA
The EJB 3.0 specification includes an additional persistence specification called the Java Persistence API (JPA). You can use this API for creating, removing and querying across lightweight Java objects both within a compliant EJB 3.0 container and a standard Java SE 5 environment. TopLink Essentials is the open-source community edition of TopLink. It provides the JPA functionality for the EJB 3.0 reference implementation.
|
Note: TopLink Essentials is the default JPA implementation in OC4J. |
When using TopLink JPA, you can access the API through extensions. The extensions allow you to reach down to the TopLink API and modify the JPA implementation.
To obtain more information, see the following:
TopLink provides CMP support for applications that require the use of EJB entity beans. This support is available on the leading application servers. TopLink CMP support provides you with an EJB 1.0, 1.1, 2.0 and 2.1 CMP solution transparent to the application code, but still offers all the TopLink run-time benefits. See "Understanding the EJB Entity Beans With CMP Architecture" for more information.
Applications can access TopLink-enabled entity beans with container-managed persistence directly from the client, or from within a session bean layer. TopLink also offers the ability to use regular Java objects in relationships with enterprise entity beans.
|
Note: Even though TopLink fully supports EJB 1.0, 1.1, 2.0, 2.1 and, preliminarily EJB 3.0, this version of Oracle TopLink Developer's Guide only focuses on EJB 2.0 and 2.1. For detailed information on TopLink support for EJB 1.0 and 1.1, refer to the earlier versions of Oracle TopLink Developer's Guide. |
Another option for using EJB entity beans is to use TopLink BMP in the application. This architecture enables developers to access the persistent data through the EJB application programming interface (API), but is platform independent. See "Understanding the EJB Entity Beans With BMP Architecture" for complete information.
The BMP approach is portable–that is, after you create an application, you can move it from one application server platform to another.
A Web services architecture is similar to the three-tier or session-bean architecture. However, in a Web services architecture you encapsulate business logic (the service) in a Web service instead of (or in addition to) using session beans. In a Web services architecture, clients communicate with your application using XML.
As in any architecture, you can use TopLink to persist objects to relational or EIS data sources. However, in a Web services architecture you can also use TopLink to map your object model to an XML schema for use with the Web service or as the Web service XML serializer.
See "Understanding the Web Services Architecture" for more information
A two-tier (or client/server) application is one in which the TopLink application accesses the database directly. Although less common than the other architectures discussed here, TopLink supports this architecture for smaller or embedded data processing applications. See "Understanding the Two-Tier Architecture" for more information.