1 About the Connector
Oracle Identity Manager automates access rights management, security, and provisioning of IT resources. Oracle Identity Manager connectors are used to integrate Oracle Identity Manager with third-party applications. This guide discusses the procedure to deploy the connector that is used to integrate Oracle Identity Manager with Microsoft Windows.
This chapter contains the following sections:
Note:
In this guide, the term Oracle Identity Manager host computer refers to the computer on which Oracle Identity Manager is installed.
At some places in this guide, Microsoft Windows has been referred to as the target system.
-
Section 1.4, "Lookup Definitions Used During Connector Operations"
-
Section 1.7, "Roadmap for Deploying and Using the Connector"
1.1 Certified Components
Table 1-1 lists the certified components for this connector.
Table 1-1 Certified Components
| Item | Requirement |
|---|---|
|
You can use one of the following releases of Oracle Identity Manager:
|
|
|
JDK |
The JDK version can be one of the following:
|
|
The target system can be any one of the following:
|
|
|
Oracle Identity Manager host platform |
The Oracle Identity Manager host platform can be any one of the following:
|
|
Infrastructure requirements |
An additional computer running any one of the following:
This computer is meant for use as a file server. |
|
Other applications |
A release of the Microsoft Active Directory User Management connector that supports the GUID user attribute |
|
Target system user account |
The target system user account can be any one of the following:
You provide the credentials of this user account while configuring the IT resource. The procedure is described later in this guide. |
1.2 Certified Languages
The connector supports the following languages:
-
Arabic
-
Chinese Simplified
-
Chinese Traditional
-
Danish
-
English
-
French
-
German
-
Italian
-
Japanese
-
Korean
-
Portuguese (Brazilian)
-
Spanish
See Also:
For information about supported special characters
-
On Oracle Identity Manager release 9.1.0.x, see Oracle Identity Manager Globalization Guide.
-
On Oracle Identity Manager releases 11.1.1 and 11.1.2, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle Identity Manager
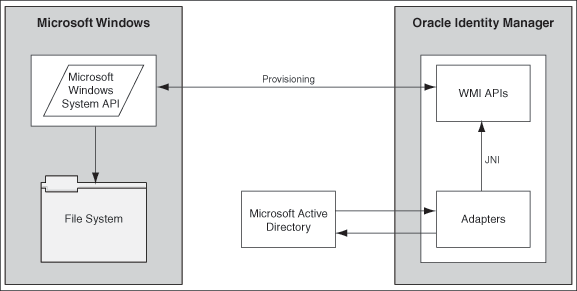
1.3 Connector Architecture
The connector enables the creation of shared folders on Microsoft Windows Server through a provisioning operation on Oracle Identity Manager. This provisioning operation consists of the following steps:
-
For the specified OIM User, the connector fetches the GUID from the Microsoft Active Directory resource records stored in Oracle Identity Manager.
-
From the GUID, the connector determines the user name in the Microsoft Active Directory resource record.
-
The connector uses the Microsoft Windows System APIs on the target system to create the shared folder. The user name obtained from Microsoft Active Directory is set as the owner of the shared folder.
Figure 1-1 shows the basic architecture of the connector.
After you create a shared folder, you can also perform the following additional provisioning operations:
-
Set and modify permissions assigned to the user on the folder.
-
Set a new share path for the folder.
-
Hide the folder.
1.4 Lookup Definitions Used During Connector Operations
The Lookup.Windows.Configuration lookup definition is automatically created when you install the connector. This lookup definition holds the following entries:
-
ADGUIDColumnName
-
ADROName
Section 2.3.1, "Setting Up the Lookup.Windows.Configuration Lookup Definition" provides information about setting values in this lookup definition.
1.5 User Attributes for Provisioning
Table 1-2 provides information about user attribute mappings for provisioning.
Table 1-2 User Attributes for Provisioning
| Process Form Field | Target System Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Share Path |
Folder Path |
This attribute is used to specify the path of the shared folder. |
|
Hidden |
Hidden |
This attribute is used to specify that the shared folder must be hidden. |
|
New Share Path |
New Share Name |
This attribute is used to assign a new share name to an existing shared folder. |
|
Full Control |
Full Control |
This attribute is used to grant full control of the folder to the user. |
|
Change |
Modify |
This attribute is used to grant the user permission to modify the contents of the folder. |
|
Read |
Read |
This attribute is used to grant the user permission to view the contents of the folder. |
|
Write |
Write |
This attribute is used to grant the user permission to add contents to the folder. |
|
None |
On the target system, the check boxes in the Deny column are selected. Alternatively, the check boxes in the Allow column are not selected. |
This attribute is used to deny the user access to the folder. |
1.6 Provisioning Functions
Table 1-3 lists the provisioning functions that are supported by the connector. The Adapter column gives the name of the adapter that is used when each function is performed.
Table 1-3 Provisioning Functions
| Function | Description | Adapter |
|---|---|---|
|
Create folder for a user |
Creates a folder, shares it for the user, and adds the user to the shared folder. Note: The folder that the connector creates is not the home folder for the user. When the user is added to the shared folder, only the permissions selected on the process form are granted. When you create a share for a user, the share name assigned is the user ID. Therefore, you cannot directly create another share for the user. As a workaround, you can specify a new share name for the first share and then create another share for the user. The second share is assigned the user ID as its name. You can follow this approach to create multiple shares for a user. |
Win2K Create Directory Win2K Create Share Win2K Add User To Folder |
|
Create hidden folder for a user |
Creates a hidden folder, shares it for the user, and adds the user to the shared hidden folder. Note: The folder that the connector creates is not the home folder for the user. When the user is added to the shared folder, only the permissions selected on the process form are granted. |
Win2K Create Hide Option |
|
Delete share attribute |
Stops sharing a folder. |
Win2K Delete Share |
|
Update access permissions for user |
Updates the permissions granted to a user on the shared folder. |
Win2K Add User To Folder |
|
Revoke access permissions from user |
Revokes the permissions granted to a user on a shared folder. |
Win2K Remove User From Folder |
|
Add new share name |
Assigns a new share name to an existing shared folder. |
Win2K Update Share Path |
1.7 Roadmap for Deploying and Using the Connector
The following is the organization of information in the rest of this guide:
-
Chapter 2, "Deploying the Connector" describes procedures that you must perform on Oracle Identity Manager and the target system during each stage of connector deployment.
-
Chapter 3, "Configuring the Connector" describes guidelines on using the connector.
-
Chapter 4, "Testing and Troubleshooting" describes the procedure to test the connector.
-
Chapter 5, "Known Issues" lists known issues associated with this release of the connector.