Oracle® Retail Tax Integration Layer
Installation Guide
Release 14.1.2.1
E72230-01
February 2016
Oracle®
Retail Tax Integration Layer Installation Guide, Release 14.1.2.1
Copyright © 2016, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Primary Author: Wade Schwarz
Contributors: Nathan Young
This software and related documentation are provided
under a license agreement containing restrictions on use and disclosure and are
protected by intellectual property laws. Except as expressly permitted in your
license agreement or allowed by law, you may not use, copy, reproduce,
translate, broadcast, modify, license, transmit, distribute, exhibit, perform,
publish, or display any part, in any form, or by any means. Reverse
engineering, disassembly, or decompilation of this software, unless required by
law for interoperability, is prohibited.
The information contained herein is subject to change
without notice and is not warranted to be error-free. If you find any errors,
please report them to us in writing.
If this is software or related documentation that is
delivered to the U.S. Government or anyone licensing it on behalf of the U.S.
Government, then the following notice is applicable:
U.S. GOVERNMENT END USERS: Oracle programs, including
any operating system, integrated software, any programs installed on the
hardware, and/or documentation, delivered to U.S. Government end users are
"commercial computer software" pursuant to the applicable Federal
Acquisition Regulation and agency-specific supplemental regulations. As such,
use, duplication, disclosure, modification, and adaptation of the programs,
including any operating system, integrated software, any programs installed on
the hardware, and/or documentation, shall be subject to license terms and
license restrictions applicable to the programs. No other rights are granted to
the U.S. Government.
This software or hardware is developed for general use
in a variety of information management applications. It is not developed or
intended for use in any inherently dangerous applications, including applications
that may create a risk of personal injury. If you use this software or hardware
in dangerous applications, then you shall be responsible to take all
appropriate fail-safe, backup, redundancy, and other measures to ensure its
safe use. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates disclaim any liability for any
damages caused by use of this software or hardware in dangerous applications.
Oracle and Java are registered trademarks of Oracle
and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Intel and Intel Xeon are trademarks or registered
trademarks of Intel Corporation. All SPARC trademarks are used under license
and are trademarks or registered trademarks of SPARC International, Inc. AMD,
Opteron, the AMD logo, and the AMD Opteron logo are trademarks or registered
trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices. UNIX is a registered trademark of The
Open Group.
This software or hardware and documentation may provide
access to or information about content, products, and services from third parties.
Oracle Corporation and its affiliates are not responsible for and expressly
disclaim all warranties of any kind with respect to third-party content,
products, and services unless otherwise set forth in an applicable agreement
between you and Oracle. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates will not be
responsible for any loss, costs, or damages incurred due to your access to or
use of third-party content, products, or services, except as set forth in an
applicable agreement between you and Oracle.
Value-Added
Reseller (VAR) Language
Oracle Retail VAR Applications
The following restrictions and provisions only apply to
the programs referred to in this section and licensed to you. You acknowledge
that the programs may contain third party software (VAR applications) licensed
to Oracle. Depending upon your product and its version number, the VAR
applications may include:
(i) the MicroStrategy Components developed and
licensed by MicroStrategy Services Corporation (MicroStrategy) of McLean, Virginia to Oracle and imbedded in the MicroStrategy for Oracle Retail Data
Warehouse and MicroStrategy for Oracle Retail Planning & Optimization
applications.
(ii) the Wavelink component developed and
licensed by Wavelink Corporation (Wavelink) of Kirkland, Washington, to Oracle
and imbedded in Oracle Retail Mobile Store Inventory Management.
(iii) the software component known as Access Via™
licensed by Access Via of Seattle, Washington, and imbedded in Oracle Retail
Signs and Oracle Retail Labels and Tags.
(iv) the software component known as Adobe Flex™ licensed
by Adobe Systems Incorporated of San Jose, California, and imbedded in Oracle
Retail Promotion Planning & Optimization application.
You acknowledge and confirm that Oracle grants you use
of only the object code of the VAR Applications. Oracle will not deliver source
code to the VAR Applications to you. Notwithstanding any other term or
condition of the agreement and this ordering document, you shall not cause or
permit alteration of any VAR Applications. For purposes of this section,
"alteration" refers to all alterations, translations, upgrades,
enhancements, customizations or modifications of all or any portion of the VAR
Applications including all reconfigurations, reassembly or reverse assembly,
re-engineering or reverse engineering and recompilations or reverse
compilations of the VAR Applications or any derivatives of the VAR
Applications. You acknowledge that it shall be a breach of the agreement to
utilize the relationship, and/or confidential information of the VAR
Applications for purposes of competitive discovery.
The VAR Applications contain trade secrets of Oracle and
Oracle's licensors and Customer shall not attempt, cause, or permit the
alteration, decompilation, reverse engineering, disassembly or other reduction
of the VAR Applications to a human perceivable form. Oracle reserves the right
to replace, with functional equivalent software, any of the VAR Applications in
future releases of the applicable program.
Send Us Your Comments........................................................................................ vii
Preface..................................................................................................................... ix
Audience................................................................................................................................................ ix
Related Documents............................................................................................................................. ix
Customer Support................................................................................................................................ ix
Review Patch Documentation........................................................................................................... x
Improved Process for Oracle Retail Documentation Corrections........................................... x
Oracle Retail Documentation on the Oracle Technology Network........................................ x
Conventions............................................................................................................................................ x
1 Preinstallation Tasks............................................................................................ 1
Implementation Capacity Planning................................................................................................ 1
Requesting Infrastructure Software................................................................................................. 1
Check Database Server Requirements............................................................................................. 1
Check Supported Application Server Requirements.................................................................. 3
Check Supported Web Browser and Client Requirements....................................................... 3
Supported Oracle Retail Products.................................................................................................... 4
Supported Third-Party Products...................................................................................................... 4
Supported Oracle Retail Integration Technologies..................................................................... 4
2 RAC and Clustering.............................................................................................. 5
3 RTIL Installation Tasks......................................................................................... 7
Install Managed Server in WebLogic.............................................................................................. 7
RTIL and TaxWeb Integration................................................................................................ 11
Install Node Manager................................................................................................................ 11
Start the Node Manager............................................................................................................ 15
Load TaxRules (Database Mode)........................................................................................... 16
Extract TaxRules (Jar Mode).................................................................................................... 16
Verify taxcomponent.conf (Database Mode)....................................................................... 17
Verify taxcomponent.conf (Jar Mode)................................................................................... 17
Install Datasource Configuration File.................................................................................. 17
Expand the RTIL Application Distribution................................................................................ 18
Run the RTIL Application Installer............................................................................................... 18
Post Install Steps................................................................................................................................. 20
Resolving Errors Encountered During Application Installation......................................... 23
A Appendix: RTIL Installer Screens........................................................................ 25
B Appendix: Installer Silent Mode.......................................................................... 37
C Appendix: URL Reference................................................................................... 39
JDBC URL for a Database................................................................................................................. 39
LDAP Server URL............................................................................................................................... 39
D Appendix: Common
Installation Errors............................................................... 41
Installer Crashes, Producing Dump Files.................................................................................... 41
Database Installer Hangs on Startup............................................................................................ 41
Warning: Could not create system preferences directory....................................................... 41
Warning: Couldn't find X Input Context..................................................................................... 42
ConcurrentModificationException in Installer GUI................................................................. 42
Error Connecting to Database URL............................................................................................... 42
Multi-Threaded OCI Client Dumps Core after Reconnecting To Database....................... 43
GUI Screens Fail to Open When Running Installer.................................................................. 43
F Appendix: Setting Up Password Stores with
wallets/credential stores................. 45
About Database Password Stores and Oracle Wallet.............................................................. 45
Setting Up Password Stores for Database User Accounts...................................................... 45
Setting up Wallets for Database User Accounts........................................................................ 47
For RMS, RWMS, RPM Batch using sqlplus or sqlldr, RETL, RMS,
RWMS, and ARI 47
Setting up RETL Wallets................................................................................................................... 49
For Java Applications (SIM, ReIM, RPM, RIB, AIP, Alloc, ReSA,
RETL).................... 50
How does the Wallet Relate to the Application?....................................................................... 53
How does the Wallet Relate to Java Batch Program use?....................................................... 53
Database Credential Store Administration................................................................................. 53
Managing Credentials with WSLT/OPSS Scripts.................................................................... 57
listCred........................................................................................................................................... 58
updateCred................................................................................................................................... 59
createCred..................................................................................................................................... 59
deleteCred..................................................................................................................................... 59
modifyBootStrapCredential..................................................................................................... 60
addBootStrapCredential........................................................................................................... 61
Quick Guide for Retail Password Stores (db wallet, java
wallet, DB credential stores) 63
G Appendix: Installation Order............................................................................... 75
Enterprise Installation Order.......................................................................................................... 75
Oracle Retail Tax Integration Layer Installation Guide, Release 14.1.2.1.
Oracle welcomes customers comments and suggestions on the quality
and usefulness of this document.
Your feedback is important, and helps us to best meet your needs
as a user of our products. For example:
§
Are the implementation steps correct and complete?
§
Did you understand the context of the procedures?
§
Did you find any errors in the information?
§
Does the structure of the information help you with your tasks?
§
Do you need different information or graphics? If so, where, and
in what format?
§
Are the examples correct? Do you need more examples?
If you find any errors or have any other suggestions for
improvement, then please tell us your name, the name of the company who has
licensed our products, the title and part number of the documentation and the
chapter, section, and page number (if available).
Note:
Before sending us your comments, you might like to check that you have the
latest version of the document and if any concerns are already addressed. To do
this, access the Online Documentation available on the Oracle Technology
Network Web site. It contains the most current Documentation Library plus all
documents revised or released recently.
Send your comments to us using the electronic mail address: retail-doc_us@oracle.com
Please give your name, address, electronic mail address, and
telephone number (optional).
If you need assistance with Oracle software, then please contact
your support representative or Oracle Support Services.
If you require training or instruction in using Oracle software,
then please contact your Oracle local office and inquire about our Oracle University offerings. A list of Oracle offices is available on our Web site at www.oracle.com.
Oracle Retail Installation Guides contain the requirements and
procedures that are necessary for the retailer to install Oracle Retail
products.
This Installation Guide is written for the following audiences:
§
Database administrators (DBA)
§
System analysts and designers
§
Integrators and implementation staff
You can find more information
about this product in these resources:
§ Oracle Retail
Fiscal Management Release Notes
§
Oracle Retail Merchandising System with Brazil Localization
Installation Guide
§ Oracle Retail
Fiscal Management User Guide and Online Help
§ Oracle Retail
RMS-ReSA User Guide for Brazil Localization and Online Help
§ Oracle Retail
Fiscal Management/RMS Brazil Localization Implementation Guide
§ Oracle Retail
Fiscal Management Data Model
§ Oracle Retail
Merchandising Security Guide
§ Oracle Retail
Licensing Guide
§ Oracle Retail
Merchandising System Documentation
Also see the documentation
library for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition
at this URL: http://www.oracle.com/technology/documentation/bi_ee.html
To contact Oracle
Customer Support, access My Oracle Support at the following URL:
https://support.oracle.com
When contacting
Customer Support, please provide the following:
§
Product version and program/module name
§
Functional and technical description of the problem (include
business impact)
§
Detailed step-by-step instructions to re-create
§
Exact error message received
§
Screen shots of each step you take
When you install the application for the first time, you install
either a base release (for example, 14.1) or a later patch release (for
example, 14.1.2). If you are installing the base release or additional patch
releases, read the documentation for all releases that have occurred since the
base release before you begin installation. Documentation for patch releases
can contain critical information related to the base release, as well as
information about code changes since the base release.
To more quickly address critical corrections to Oracle Retail
documentation content, Oracle Retail documentation may be republished whenever
a critical correction is needed. For critical corrections, the republication of
an Oracle Retail document may at times not be attached to a numbered
software release; instead, the Oracle Retail document will simply be replaced
on the Oracle Technology Network Web site, or, in the case of Data Models, to
the applicable My Oracle Support Documentation container where they reside.
This process will prevent delays in making critical corrections
available to customers. For the customer, it means that before you begin
installation, you must verify that you have the most recent version of the
Oracle Retail documentation set. Oracle Retail documentation is available on
the Oracle Technology Network at the following URL:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/documentation/oracle-retail-100266.html
An updated version of the applicable Oracle Retail document is
indicated by Oracle part number, as well as print date (month and year). An
updated version uses the same part number, with a higher-numbered suffix. For
example, part number E123456-02
is an updated version of a document with part number E123456-01.
If a more recent version of a document is available, that version
supersedes all previous versions.
Oracle Retail product documentation is available on the following
web site:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/documentation/oracle-retail-100266.html
(Data Model documents are not available through Oracle Technology
Network. You can obtain them through My Oracle Support.)
Navigate:
This is a navigate statement. It tells you how to get to the start of the
procedure and ends with a screen shot of the starting point and the statement
“the Window Name window opens.”
This is a code sample
It is used to display examples of code
1
There is significant complexity involved in the deployment of
Oracle Retail applications, and capacity planning is site specific. Oracle
Retail strongly suggests that before installation or implementation you engage
your integrator (such as the Oracle Retail Consulting team) and hardware vendor
to request a disk sizing and capacity planning effort.
Sizing estimates are based on a number of factors, including the
following:
§
Workload and peak concurrent users and batch transactions
§
Hardware configuration and parameters
§
Data sparcity
§
Application features utilized
§
Length of time history is retained
Additional considerations during this process include your high
availability needs as well as your backup and recovery methods.
If you are unable to find the necessary version of the required
Oracle infrastructure software (database server, application server, WebLogic,
etc.) on the Oracle Software Delivery Cloud, you should file a non-technical
‘Contact Us’ Service Request (SR) and request access to the media. For
instructions on filing a non-technical SR, see My Oracle Support Note 1071023.1
– Requesting Physical Shipment or Download URL for Software Media.
Oracle Retail Tax Integration
Layer (RTIL) requires that the RMS 14.1.2.1 database schema be installed. See
the Oracle Retail Merchandising System Installation Guide for the
supported database server requirements.
General Requirements for a database server running RTIL include:
|
Supported on:
|
Versions Supported:
|
|
Database Server OS
|
OS certified with Oracle Database 12cR1 Enterprise
Edition. Options are:
§ Oracle Linux 6 for x86-64 (Actual
hardware or Oracle virtual machine).
§ Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 for x86-64 (Actual hardware or Oracle virtual machine).
§ Oracle Linux 6 for x86-64 (Actual
hardware or Oracle virtual machine).
§ Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 for x86-64 (Actual hardware or Oracle virtual machine).
§ AIX 7.1 (Actual hardware or LPARs)
§ Solaris 11 SPARC (Actual hardware or
logical domains)
§
HP-UX Itanium11.31 Integrity (Actual hardware, HPVM, or vPars)
|
|
Database Server 12cR1
|
Oracle Database Enterprise Edition 12cR1 (12.1.0.2) with
the following specifications:
Components:
§ Oracle Partitioning
§ Examples CD (Formerly the companion
CD)
Oneoff Patches:
§ 19623450: MISSING JAVA CLASSES AFTER UPGRADE TO JDK 7
§ 20406840:
PROC 12.1.0.2 THROWS ORA-600 [17998] WHEN PRECOMPILING BY 'OTHER' USER
Other components:
§ Perl compiler 5.0 or later
§ X-Windows interface
§
JDK 1.7
|
Note: By default,
JDK is at 1.6. After installing the 12.1.0.2 binary, apply the patches
19623450 and 20406840. Then follow the instructions on Oracle Database Java
Developer’s Guide 12c Release 1 to upgrade JDK to 1.7. The Guide is available
here:
http://docs.oracle.com/database/121/JJDEV/chone.htm#JJDEV01000
General requirements for an application server capable of running
RTIL include the following.
|
Supported on
|
Versions Supported
|
|
Application Server OS
|
OS certified with Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g Release1 (11.1.1.7).
Options are:
§ Oracle Linux 6 for x86-64 (Actual
hardware or Oracle virtual machine).
§ Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 for
x86-64 (Actual hardware or Oracle virtual machine).
§ AIX 7.1 (Actual hardware or LPARs)
§ Solaris 11 SPARC (Actual hardware
or logical domains)
§ HP-UX 11.31 Integrity (Actual hardware,
HPVM, or vPars)
|
|
Application Server
|
Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g Release 1 (11.1.1.7)
Components:
§
Oracle WebLogic Server 11g
Release 1 (10.3.6)
Java:
§ JDK 1.7.0+ 64 bit
|
General requirements for client running RMS include the
following.
|
Requirement
|
Version
|
|
Operating system
|
Windows 7
|
|
Display resolution
|
1024x768 or higher
|
|
Processor
|
2.6GHz or higher
|
|
Memory
|
1GByte or higher
|
|
Networking
|
intranet with at least
10Mbps data rate
|
|
Oracle (Sun) Java Runtime
Environment
|
1.7.0+
|
|
Browser
|
Microsoft
Internet Explorer version 11
or Mozilla
Firefox ESR 31
|
|
Product
|
Version
|
|
Oracle Retail Merchandising System (RMS)
|
14.1.2.1
|
|
Product
|
Version
|
|
TaxWeb Tax Rules
(The Tax Rules software is a product of TaxWeb Compliance Software S.A.)
|
§ taxinterfaces.jar – version 1
§ taxcomponent.jar – version 55
§ taxrulesdbplugin.jar – version 2
Note: RTIL was
tested with the above mentioned versions. Please contact TaxWeb for the
latest compatible release (http://www.taxweb.com.br).
|
|
Integration Technology
|
Version
|
|
Oracle Retail Integration Bus (RIB)
|
14.1.2
|
2
The Oracle
Retail Tax Integration Layer has been validated to run in two configurations on
Linux:
§
Standalone Oracle Application Server or Web Logic Server and
Database installations
§
Real Application Cluster Database and Oracle Application Server
or Web Logic Server Clustering
The Oracle Retail products have been validated against a 12.1.0.2
RAC database. When using a RAC database, all JDBC connections should be
configured to use THIN connections rather than OCI connections.
Clustering for Web Logic Server 10.3.6 is managed as an
Active-Active cluster accessed through a Load Balancer. Validation has
been completed utilizing a RAC 12.1.0.2 Oracle Internet Directory database with
the Web Logic 10.3.6 cluster.
References for Configuration:
§
Oracle® Fusion Middleware High Availability Guide 11g Release 1
(11.1.1) Part Number E10106-09
§
Oracle Real Application Clusters Administration and Deployment
Guide
12c Release 1 (12.1) E48838-08
3
Before proceeding, you must install Oracle
WebLogic Server 11g Release 1 (10.3.6), create a separated domain for
RTIL without any other applications not selecting any template like JRF along
with all patches listed in Chapter 1, Preinstallation
Tasks and create a separated domain for RTIL without any other
applications. The RTIL application is deployed to a WebLogic Managed server
within the WebLogic installation.
Before running the application installer, you must install a
managed server for the RTIL application in WebLogic if it was not created
during the domain installation.
1. Log
in to the Administration Console.

2. Click
Lock & Edit.
3. Navigate
to Environment > Servers. Select new tab of the servers on the right side.
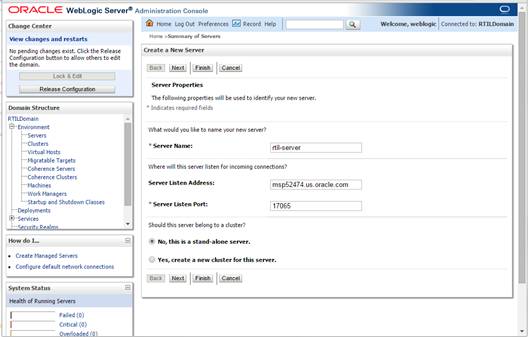
4. Set
the following variables:
§ Server Name:
This value should be specific to your targeted application (for example,
rtil-server).
§ Server Listen
Address: <weblogic server>
(for example, msp52474.us.oracle.com)
§ Server
Listen Port: A free port. Check for
availability.
A suggestion is to increment the AdminServer port by two
and keep incrementing by two for each managed server (for example, 17003,
17005, 17007, and so on.)
5.
Click Next.

6.
Click Finish.

7. Click
Activate Changes on the left side. Once the changes are activated, the
State of the rtil-server should change to SHUTDOWN status.

For this release, it is possible to select the mode where tax
rules will be available; either making the rules available in a database or
archived in a jar file.
RTIL was tested using the database mode, but it is possible to
use the taxrules.jar file provided by TaxWeb.
Note:
Refer to the installation guide provided by TaxWeb for additional information
on using database mode or jar mode.
The steps related to rules when installing RTIL are separated into
database mode and jar mode. Refer to the procedures that are applicable to your
installation decisions about tax rules.
Install Node Manager
Install Node Manager if it was not created during domain install.
The node manager is required so that the managed servers can be started and
stopped through the admin console. Only one node manager is needed per WebLogic
installation.
1. Log
in to the Administration Console.
2. Click
Lock & Edit. Navigate to Environments->Machines. Click New.
3. The
following page is displayed. Set the following variables:
§ Name: Logical
machine name
§ Machine OS:
UNIX

4. Click
Next. The following page is displayed. Set the following variables:
§ Type: Plain
§ Listen Address:
<weblogic server> (for example, msp52478.us.oracle.com)
§ Listen
Port: Assign a port number. Example : 5557
The default port
is 5556.
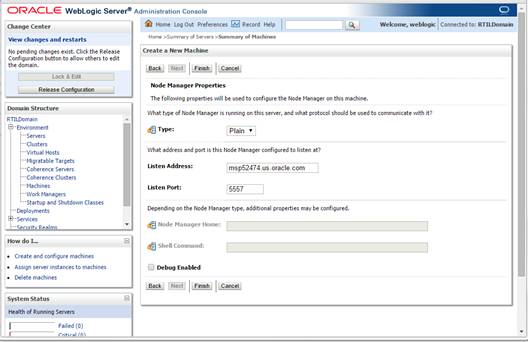
5. Click
Finish.

6.
Click Activate Changes.

7. Click
Lock & Edit.
8.
Navigate to Environments > machines. Click the machine
name. Select the Servers tab. Click Add.
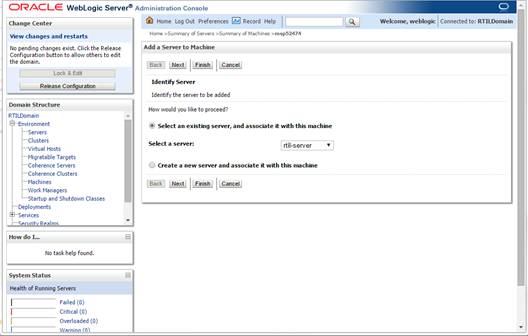
9. Add
the managed servers that need to be configured with the Nodemanager. Save
changes.
§ From the drop down
select the managed server to be added to nodemanager
§ Server:
<app-server> (for example: rtil-server)
10. Click Next.
Click Finish.
11. Go to the managed
server on which RTIL will be deployed and click the Server Start tab. In the
Class Path box, add the following:
<full-path-to-domain>/servers/<managed-server>
For example: /u00/webadmin/product/10.3.x/WLS/user_projects/domains/RTILDomain/servers/rtil-server:$CLASSPATH
12. When using
tax rules in database mode, in the same Server Start Tab referenced in the
above step add the line “-Dtaxcomponent.conf.basedir=[$DOMAIN_HOME]/config” to
the Arguments box. Note that “[DOMAIN_HOME]” needs to be the full path to the
domain, For Example:
-Dtaxcomponent.conf.basedir=/u00/webadmin/product/10.3.x/WLS/user_projects/
domains/RTILDomain /config
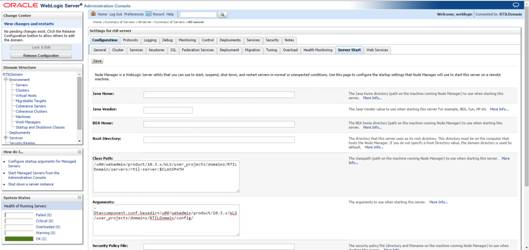
13. Click Save.
14. Click Activate
Changes.
To start the managed servers, complete the following steps.
1. Start
up the nodemanager. Edit the nodemanager.properties file at the following
location with the below values:
$WLS_HOME/wlserver_10.3/common/nodemanager/nodemanager.properties
§ StartScriptEnabled=true
§ StartScriptName=startWebLogic.sh.
2. After
making changes to the nodemanager.properties file, NodeManager must be
restarted.
Note:
The nodemanager.properties file is created after NodeManager is
started for the first time. It is not available before that point.
3. Start
the Node Manager from the command line.
<WLS_HOME>/wlserver_10.3/server/bin
startNodeManager.sh
After the Node Manager is started, the managed servers can
be started through the admin console.
4. Navigate
to Environments > Servers. Select <app-server>
(for example, rtil-server server managed server). Click the Control
tab.
5.
Click Start to start the managed server.

TaxWeb will provide a jar
file (taxrules) with the rules necessary to use in ORFM. For this mode, check
with TaxWeb for the steps used to load rules in their database schema .
For the rules to be extracted as individual Java serialized files,
extraction requires about about 7 GB of free space on the file system. The
amount of space required depends on the number of tax rules in the taxweb drop
and must be verified in the taxweb installation document.
Note: TaxRules
extraction is done through a Java utility, which requires about 5 GB of RAM for
the extraction. The amount of space depends on the number of tax rules in the
taxweb drop and must be verified in the taxweb installation document.
TaxRules extraction can be done in one environment, where the
extracted folder that contains rules can be transferred to all the RTIL
deployment boxes independently. If this method is chosen, the deployment
environment is not required to have five 5 GB of RAM available.
To extract TaxRules, do the following:
1. Create
a folder/directory (for example, taxweb-slim).
Note:
This directory should be created outside of WebLogic domain directory with read
permission for all users (or at least for the Weblogic domain user).
2. Transfer
the taxrules.jar, taxcomponent.jar and the log4j-1.2.15.jar to taxweb-slim
folder. The above mentioned jars are present in the TaxWeb Tax Rules bundle
delivered by TaxWeb
3. From
the command prompt, run the following commands inside the taxweb-slim folder.
$ jar -xf taxrules.jar
$ java –Xmx6120m -cp
log4j-1.2.15.jar:taxcomponent.jar:. erija.taxrules.test.ondemand.RulesToDir
Note:
Verify that a rules folder is created with individual rules in sub directory.
(more than 1 GB).
This config file must be available in the same path defined in step
12 of the Install Node Manager section (Dtaxcomponent.conf.basedir).
Verify the following entries in taxcomponent.conf file.
§
withDBAcess=true
§
driverClass=jndi
§
url=taxrules_component
§
user=taxrules_component
§
taxcomponent.rules.source=database
§
# Taxrules DB plugin config
§
dbplugin.flavor=oracle
§
dbplugin.connection=jndi
§
dbplugin.url=taxrules_data
This file must be available in the config folder from the RTIL
domain.
Verify the following entries in taxcomponent.conf file.
§
onDemand=true
§
dataFiles=<absolute path of the folder created in step 1 of
the Extract TaxRules (Jar Mode) (for
example: taxweb-slim)>
§
withDBAcess=true
§
driverClass=jndi
§
url=<jndi of the taxweb datasource>
The prerequisite for this step is the availability of a TaxWeb Tax
Rules schema which should be installed based on the TaxWeb Tax Rules installation
guide. The datasource should be created in the WebLogic domain in which RTIL will
be installed. Please refer to the TaxWeb Tax Rules installation guide for data
source creation details.
The configured datasource name should be included in the
taxcomponent.conf file supplied in the TaxWeb Tax Rules distribution and placed
in the config folder of the Weblogic domain in which RTIL will be deployed.
To expand the RTIL application distribution, complete the
following steps.
1. Create
a new staging directory for the RTIL application distribution (rtil14application.zip).
Example:
<WLS_HOME> /user_projects/domain/<domain_name>/
servers/<rtil-server>/rtil-staging
This location is referred to as STAGING_DIR for the
remainder of this chapter.
2. Copy
rtil14application.zip to STAGING_DIR and extract its contents.
Once you have a WebLogic instance that is configured and started,
you can run the RTIL application installer. This installer configures and
deploys the RTIL application.
Note:
It is recommended that the installer be run as the same UNIX account that owns
the WebLogic application server ORACLE_HOME files.
1. Change
directories to STAGING_DIR/rtil/application. This directory was created when
the rtil14application.zip file was expanded under STAGING_DIR.
2. Set
and export the following environment variables.
|
Variable
|
Description
|
Example
|
|
ORACLE_HOME
|
The location where Weblogic has been installed
|
ORACLE_HOME= /u00/webadmin/product/10.3.6/WLS
export ORACLE_HOME
|
|
WEBLOGIC_
DOMAIN_HOME
|
The location where the Weblogic domain has been installed
|
WEBLOGIC_DOMAIN_HOME=$ORACLE_
HOME/user_projects/domains/RTILDomain/
export WEBLOGIC_DOMAIN_HOME
|
|
JAVA_HOME
|
Location of a Java 7.0 (1.7.0+) JDK. 64 bit. For Linux and Solaris OS
only). This should be set to the Java being used by the Weblogic server.
|
JAVA_HOME= /u00/webadmin/java/jdk1.7
export JAVA_HOME
|
|
ANT_HOME
|
Location of an Ant 1.9.6.x instance.
|
ANT_HOME=/usr/ant/ant1.9.6/
export ANT_HOME
|
|
DISPLAY
|
Address and port of X server on desktop system of user
running installation. Optional for RTIL application installer.
|
DISPLAY=<IP address>:0
export DISPLAY
|
3. If
you are using an X server (such as Exceed), set the DISPLAY environment
variable so that you can run the installer in GUI mode (recommended). If you
are not using an X server, or the GUI is too slow over your network, do not set
DISPLAY for text mode.
4. If
a secured datasource is going to be configured you also need to set “ANT_OPTS”
so the installer can access the key and trust store that is used for the
datasource security:
export ANT_OPTS="-Djavax.net.ssl.keyStore=<PATH
TO KEY STORE> -Djavax.net.ssl.keyStoreType=jks
-Djavax.net.ssl.keyStorePassword=<KEYSTORE PASSWORD> -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=<PATH
TO TRUST STORE> -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStoreType=jks
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=<TRUSTSTORE PASSWORD>"
An example of this would be:
export ANT_OPTS="-Djavax.net.ssl.keyStore=/u00/webadmin/product/wls_retail /wlserver_10.3/server/lib/orapphost.keystore
-Djavax.net.ssl.keyStoreType=jks -Djavax.net.ssl.keyStorePassword=retail123
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=/
u00/webadmin/product/wls_retail /wlserver_10.3/server/lib/orapphost.keystore
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStoreType=jks -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=retail123"
5. Run
the install.sh script. This launches the installer. After installation is
complete, a detailed installation log file is created (rtil14install.<timestamp>.log).
Note:
The typical usage for GUI mode is no arguments.
./install.sh [text | silent]
Note:If you are running the installer on AIX7.1, please set and export
ANT_OPTS variable with “-Xmso1024k -Xss1024k”, prior to launching the
installer. For example, assuming korn, bourne, or bash shell:
ANT_OPTS=”-Xmso1024k –Xss1024k”
export ANT_OPTS
6.
The installer leaves behind the ant.install.properties file
for future reference and repeat installations. This file contains inputs you
provided. As a security precaution, make sure that the file has restrictive
permissions.
Example:
chmod 600
ant.install.properties
7. Once
the installer is finished, open a web browser and navigate to the URL reported
at the end if the installer logs. You should see something similar to the
following (the text may not be the same):
QtEquwkqJW06jSuzKbk5zGkweNJ6Wy9DdN7ZJagXkJw=
This indicates that RTIL has been deployed and the
application is running and accessible.
1. Once
RTIL installation is complete, set the JTA transaction timeout to 1000 seconds
in the WebLogic Admin console.
§ To override the
default JTA timeout, log in to the WebLogic admin console. Navigate to Services
> JTA link to go to the Configuration section.
§ Replace the default
timeout of 30 seconds with 1000.
§ For the changes to
take effect, bounce the WebLogic Server (for the domain).

2.
Once RTIL installation is complete, configure Xmx and Xms
values in the WebLogic Admin console.
a. Log
in to the admin console.
b. Click
Lock & Edit.
c. Navigate
to Servers -> RTIL Managed Server (for example, rtil-server).
d. Click
the Server Start tab under configuration.
e. Change
the Xmx and Xms as below:
-Xms2g
-Xmx9g

f. Save
the configuration.
g. Click
Activate Changes.

h. Navigate
to Environment à Servers.
i. Click
the Control Tab, under Summary of Servers.

j. Restart
RTIL Managed Server.
IMPORTANT!
IF THE FOLLOWING STEP IS NOT DONE, IT WILL RESULT IN A NON-WORKING APPLICATION!
Add the following in the RTIL database to configure the RTIL URL in the
WebService Consumer.
k. Log
in to the RMS database schema as an RMS user.
l. Add
a record in the retail_service_report_url table with the following column
values.
|
Column Name
|
Value
|
|
RS_CODE
|
RTIL
|
|
RS_NAME
|
Retail Tax Integration
Layer
|
|
RS_TYPE
|
S
|
|
URL
|
<RTIL URL> (for
example, http://<rtilhostname:port>/rtil-web/invokeApp
|
|
SERVER
|
<RTIL_SERVER_NAME>
|
|
PORT
|
<PORT_NUMBER> (for
example, 17065)
|
If the application installer
encounters any errors, execution is halted immediately. You can run the
installer in silent mode so that you do not have to retype the settings for
your environment. See “Appendix: Installer
Silent Mode” for silent mode instructions.
See “Appendix: Common Installation Errors”
for common installation errors.
Because full application installation is required every time, any
previous partial installations are overwritten by the successful installation.
A
Appendix: RTIL Installer Screens
You need the following details about your environment for the
installer to successfully deploy the RTIL application. Depending on the options
you select, you may not see some screens or fields.
Screen: Security Details

|
Field Title
|
Enable SSL for RTIL?
|
|
Field Description
|
Choosing Yes will deploy RTIL using SSL and configure RTIL
to use SSL. In this case, SSL must be configured and the ports must be
enabled for the AdminServer and RTIL managed servers.
Choosing No will deploy and configure RTIL without SSL.
In this case the non-SSL ports must be enabled for the AdminServer and for
the RTIL managed servers.
|
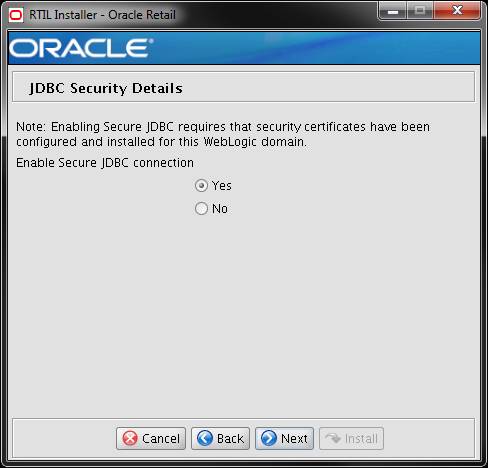
Screen: JDBC Security Details
|
Field Title
|
Enable Secure JDBC
connection
|
|
Field Description
|
Choose Yes to create
secured data sources in WebLogic, otherwise choose No. A secure data base
connection must already be set up if you want to create a secure data source.
|
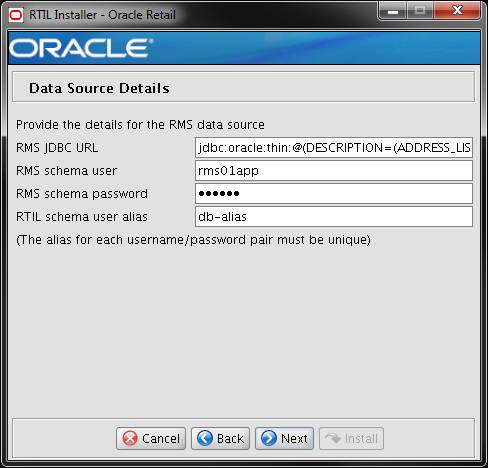
Screen: Data Source Details
|
Field Title
|
RMS JDBC URL
|
|
Field Description
|
URL used by the RTIL
application to access the RMS database schema. See Appendix: URL
Reference for expected syntax.
Note:
The RTIL database tables are
a part of the RMS schema.
|
|
Examples
|
For Non Secure JDBC
Connection: jdbc:oracle:thin:@hostname:1521/dbname
For Secure JDBC Connection: jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS_LIST=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcps)(HOST=dbhostname)(PORT=2484)))(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=mydb)))
|
|
Field Title
|
RMS schema user
|
|
Field Description
|
RMS database user for
accessing the RTIL tables. This should match what was given in the RMS
schema field of the RMS database installer.
|
|
Example
|
rms01app
|
|
Field Title
|
RMS schema password
|
|
Field Description
|
Password for the RMS
database user entered above to access the RTIL tables.
|
|
Field Title
|
RTIL schema user alias
|
|
Field Description
|
The alias to store the
schema credentials.
|
|
Example
|
db-alias
|
|
Notes
|
This alias must be unique.
Do not use the same value for any other alias fields in the installer. If the
same alias is used, entries in the wallet can override each other and cause
problems with the application.
|
Screen: Secure Data Source Details

Note: This screen will appear only
if you select Secure JDBC in the above screens.
|
Field Title
|
Identity Keystore
|
|
Field Description
|
Keystores ensure the
secure storage and management of private keys and trusted certificate
authorities (CAs). This screen lets you provide the keystore to be used for
datasource connection These settings help you to manage the security of
message transmissions. For further information, please refer to the Oracle
Retail Merchandising Operations Management Security Guide.
Location or path where
identity keystore file is stored.
|
|
Example
|
/path/sample.keystore
|
|
Field Title
|
Identity Keystore Type
|
|
Field Description
|
The type of the keystore
used.
|
|
Example
|
jks
|
|
Field Title
|
Identity Keystore
PassPhrase
|
|
Field Description
|
Please provide password to
access the keystore mentioned above.
|
|
Field Title
|
Identity TrustStore
|
|
Field Description
|
This is the path of the
keystore which contains the ssl root and optionally intermediate certificates
as obtained from the certificate authority.
|
|
Example
|
/path/sample.keystore
|
|
Field Title
|
Identity TrustStore Type
|
|
Field Description
|
The type of the truststore
used
|
|
Example
|
Jks
|
|
Field Title
|
Identity TrustStore
PassPhrase
|
|
Field Description
|
Please provide password to
access the truststore mentioned above.
|
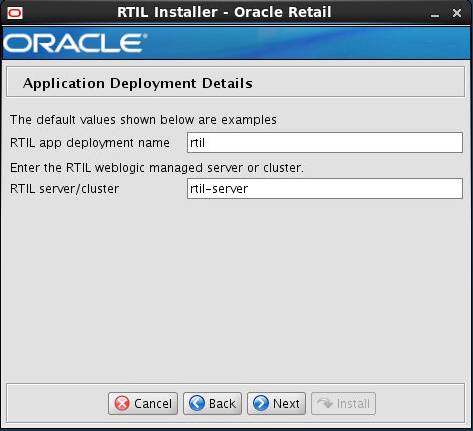
Screen: Application Deployment Details
|
Field Title
|
RTIL app deployment name
|
|
Field Description
|
Name by which this RTIL
application is identified in the application server.
|
|
Example
|
Rtil
|
|
Field Title
|
RTIL server/cluster
|
|
Field Description
|
Name of the server/cluster
that was created for this RTIL application.
The installer deploys the RTIL
application to all instances that are members of this server/cluster. For
this reason, you should not use default_group. A new group dedicated to RTIL
should be created instead.
|
|
Example
|
rtil-server
|
Screen: Weblogic Administrative User

|
Field Title
|
Hostname
|
|
Field Description
|
Hostname of the application
server
|
|
Example
|
apphostname
|
|
Field Title
|
Weblogic admin port
|
|
Field Description
|
Port number of admin
console
|
|
Example
|
17002
|
|
Field Title
|
Weblogic admin user
|
|
Field Description
|
Username of the admin user
for the WebLogic instance to which the RTIL application is being deployed.
|
|
Example
|
weblogic
|
|
Field Title
|
Weblogic admin password
|
|
Field Description
|
Password for the WebLogic
admin user. You chose this password when you created the WebLogic instance or
when you started the instance for the first time.
|
Screen: Log4j logger Details

|
Field Title
|
Log4j Log Level
|
|
Field Description
|
Specifies the level at
which the logging is enabled.
|
|
Example
|
INFO
|
|
Field Title
|
Output to STDOUT
|
|
Field Description
|
Specifies whether the logs
should be routed to the console.
|
|
Field Title
|
Log4j logfile MaxFileSize
(MB)
|
|
Field Description
|
Specifies the file size
threshold beyond which the log file gets rolled over.
|
|
Example
|
5
|
|
Field Title
|
Log4j logfile
MaxBackupIndex
|
|
Field Description
|
Specifies the number of
rolled over log files that will be retained.
|
|
Example
|
30
|
Screen: Turn off the application server’s non-SSL port
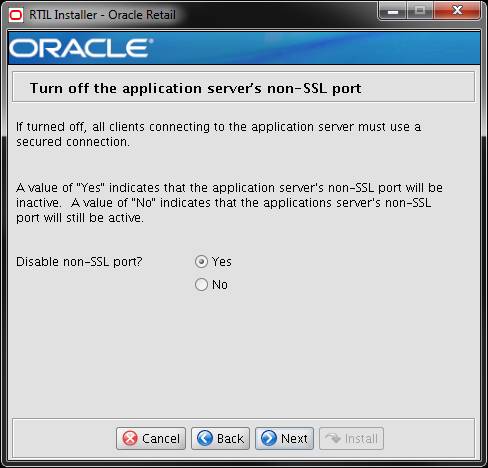
Note: This screen appears only if you have enabled SSL for RTIL.
Ignore this step in case you have not enabled SSL for RTIL.
|
Field Title
|
Disable non-SSL port?
|
|
Field Description
|
Choosing Yes disables the
non SSL port on the managed server.
Choosing no will the leave
the non SSL port of the managed server active.
|
B
In addition to the GUI and text interfaces of the installer,
there is a silent mode that can be run. This mode is useful if you wish to run
a repeat installation without retyping the settings you provided in the
previous installation. It is also useful if you encounter errors in the middle
of an installation and wish to continue.
The installer runs in two distinct phases. The first phase involves
gathering settings from the user. At the end of the first phase, a properties
file named ant.install.properties is created with the settings that were
provided. Then the second phase begins, where this properties file is used to
provide your settings for the installation.
To skip the first phase and re-use the ant.install.properties
file from a previous run, follow these instructions:
1. Edit
the ant.install.properties file and correct any invalid settings that may have
caused the installer to fail in its previous run.
2. Look
for duplicate properties in the ant.install.properties file. Some properties
are set on multiple pages to ensure default values when a page is only
displayed under certain conditions. For example, if there are two instances of
input.property.name, remove all but the last one.
3. Run
the installer again with the silent argument.
Example:
install.sh silent
C
This section provides URL reference information.
Used by the Java application and by the installer to connect to
the database.
Thick Client Syntax: jdbc:oracle:oci:@<sid>
<sid>: system identifier for the database
Example: jdbc:oracle:oci:@mysid
Thin Client Syntax:
jdbc:oracle:thin:@<host>:<port>:<sid>
<host>: hostname of the database server
<port>: database listener port
<sid>: system identifier for the database
Example:
jdbc:oracle:thin:@myhost:1521:mysid
Used by the Java application to connect to the LDAP directory.
Syntax: ldap://<host>:<port>
<host>: hostname of the directory server
<port>: LDAP server port
Example: ldap://myhost:389
D
Appendix: Common Installation Errors
This section provides some common errors encountered during
installation of RTIL.
Symptom:
When the installer is launched on AIX7.1, it may crash during
navigation of the installer screens. The crash produces two binary dump files
(core.<timestamp>.dmp, Snap.<timestamp>.trc) and a javacore text
file (javacore.<timestamp>.txt).
Solution:
Set and export ANT_OPTS variable with "-Xmso1024k
-Xss1024k", prior to launching the installer. For example, assuming korn,
bourne, or bash shell:
ANT_OPTS=”-Xmso1024k –Xss1024k”
export ANT_OPTS
Symptom:
When the database schema installer is run, the following is
written to the console and the installer hangs indefinitely:
Running pre-install checks
Running tnsping to get listener port
Solution:
The installer startup script is waiting for control to return
from the tnsping command, but tnsping is hanging. Type Control+C to
cancel the installer, and investigate and solve the problem that is causing the
tnsping <sid> command to hang. This can be caused by duplicate
database listeners running.
Symptom:
The following text appears in the installer Errors tab:
May 22, 2006 11:16:39 AM java.util.prefs.FileSystemPreferences$3
run
WARNING: Could not create system preferences directory. System preferences
are unusable.
May 22, 2006 11:17:09 AM java.util.prefs.FileSystemPreferences
checkLockFile0ErrorCode
WARNING: Could not lock System prefs. Unix error code -264946424.
Solution:
This is related to
Java bug 4838770. The /etc/.java/.systemPrefs directory may not have been
created on your system. See http://bugs.sun.com
for details.
This is an issue with
your installation of Java and does not affect the Oracle Retail product
installation.
Symptom:
The following text
appears in the console window during execution of the installer in GUI mode:
Couldn't find X Input Context
Solution:
This message is harmless and can be ignored.
Symptom:
In GUI mode, the errors tab shows the following error:
java.util.ConcurrentModificationException
at java.util.AbstractList$Itr.checkForComodification(AbstractList.java:448)
at java.util.AbstractList$Itr.next(AbstractList.java:419)
… etc
Solution:
You can ignore this error. It is related to third-party Java
Swing code for rendering of the installer GUI and does not affect the retail
product installation.
Symptom:
After entering database credentials in the installer screens and
hitting next, a message pops up with an error like this:
Error connecting to database
URL <url> as user <user>
details...
The message prevents you from
moving on to the next screen to continue the installation.
Solution:
This error occurs when the installer fails to validate the user
credentials you have entered on the screen. Make sure that you have entered
the credentials properly. If you receive a message similar to this:
Error connecting to database
URL <url> as user <user>
java.lang.Exception:
UnsatisfiedLinkError encountered when using the Oracle driver.
Please check that the library path is set up properly or
switch to the JDBC thin client.
It may mean that the installer is using the incorrect library path
variables for the platform you are installing on. Open the file
<STAGING_DIR>/rms/dbschema/common/preinstall.sh and toggle the variable “use32bit”
to “true” if it is set to “false” or vice versa. This setting is dependant on
the JRE that is being used.
Symptom
If a multi-threaded Oracle client process that uses OCI to
connect to a remote database loses connectivity with the database, it tries to
reconnect and the client program continues to run. The program then dumps the
core with the following stack trace, when Automatic Diagnostic Repository (ADR)
is enabled.
skgfqio sdbgrfbibf_io_block_file dbgrfrbf_read_block_file
dbgrmflrp_read_page
dbgrmblgmp_get_many_pages dbgrmmdrrmd_read_relation_meta_data
dbgrmmdora_open_record_access_full
dbgriporc_openrel_wcreate dbgrip_open_relation_access dbgrip_start_iterator
dbgrip_relation_iterator dbgruprac_read_adrctl...
Solution
Oracle Retail recommended you disable ADR (diag_adr_enabled=OFF,
a sqlnet.ora parameter) while using multi-threaded OCI/OCCI application.
diag_adr_enabled was introduced in Oracle 11g as a new method of tracing ADR.
This will dump additional trace details.
Disabling 'diag_adr_enabled' does not disturb any functionality.
Therefore, it can safely be unset by doing diag_adr_enabled=off in sqlnet.ora.
However, if you still want tracing, you can have following parameters/variables
set in sqlnet.ora:
trace_level_server=16 -- for server side NET tracing
trace_level_client=16 -- for client side NET tracing
For how to set traditional tracing, see the My Oracle Support
document, “SQL*Net, Net8, Oracle Net Services - Tracing and Logging at a
Glance” (ID 219968.1).
Symptom
When running the installer in GUI mode, the screens fail to open
and the installer ends, returning to the console without an error
message. The ant.install.log file contains this error:
Fatal exception: Width (0) and height (0) cannot be <= 0
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Width (0) and height (0) cannot be <= 0
Solution
This is an error encountered when Antinstaller is used in GUI
mode with certain X Servers. To work around this issue, copy
ant.install.properties.sample to ant.install.properties and rerun the
installer.
F
Appendix: Setting Up Password Stores with wallets/credential
stores
As part of an application installation, administrators must set
up password stores for user accounts using wallets/credential stores. Some password
stores must be installed on the application database side. While the installer
handles much of this process, the administrators must perform some additional
steps.
Password stores for the application and application server user
accounts must also be installed; however, the installer takes care of this
entire process.
ORACLE Retail Merchandising applications now have 3 different
types of password stores. They are database wallets, java wallets, and database
credential stores. Background and how to administer them below are explained in
this appendix
Oracle databases have allowed other users on the server to see
passwords in case database connect strings (username/password@db) were passed
to programs. In the past, users could navigate to ps –ef|grep <username> to see the
password if the password was supplied in the command line when calling a
program.
To make passwords more secure, Oracle Retail has implemented the
Oracle Software Security Assurance (OSSA) program. Sensitive information such
as user credentials now must be encrypted and stored in a secure location. This
location is called password stores or wallets. These password stores are secure
software containers that store the encrypted user credentials.
Users can retrieve the credentials using aliases that were set up
when encrypting and storing the user credentials in the password store. For
example, if username/password@db
is entered in the command line argument and the alias is called db_username,
the argument to a program is as follows:
sqlplus /@db_username
This would connect to the database as it did previously, but it
would hide the password from any system user.
After this is configured, as in the example above, the
application installation and the other relevant scripts are no longer needed to
use embedded usernames and passwords. This reduces any security risks that may
exist because usernames and passwords are no longer exposed.
When the installation starts, all the necessary user credentials
are retrieved from the Oracle Wallet based on the alias name associated with
the user credentials.
There are three different types of password stores. One type
explain in the next section is for database connect strings used in program
arguments (such as sqlplus
/@db_username). The others are for Java application installation
and application use.
After the database is installed and the default database user
accounts are set up, administrators must set up a password store using the
Oracle wallet. This involves assigning an alias for the username and associated
password for each database user account. The alias is used later during the
application installation. This password store must be created on the system
where the application server and database client are installed.
This section describes the steps you must take to set up a wallet
and the aliases for the database user accounts. For more information on
configuring authentication and password stores, see the Oracle
Database Security Guide.
Note: In
this section, <wallet_location>
is a placeholder text for illustration purposes. Before running the command,
ensure that you specify the path to the location where you want to create and
store the wallet.
To set up a password store for the database user accounts,
perform the following steps:
1. Create
a wallet using the following command:
mkstore -wrl <wallet_location> -create
After you run the command, a prompt appears. Enter a
password for the Oracle Wallet in the prompt.
Note: The
mkstore
utility is included in the Oracle Database Client installation.
The wallet is created with the auto-login feature enabled.
This feature enables the database client to access the wallet contents without
using the password. For more information, refer to the Oracle
Database Advanced Security Administrator's Guide.
2. Create
the database connection credentials in the wallet using the following command:
mkstore -wrl <wallet_location>
-createCredential <alias-name> <database-user-name>
After you run the command, a prompt appears. Enter the
password associated with the database user account in the prompt.
3. Repeat
Step 2 for all the database user accounts.
4. Update
the sqlnet.ora file to include the following
statements:
WALLET_LOCATION = (SOURCE = (METHOD =
FILE) (METHOD_DATA = (DIRECTORY = <wallet_location>)))
SQLNET.WALLET_OVERRIDE = TRUE
SSL_CLIENT_AUTHENTICATION = FALSE
5. Update
the tnsnames.ora file to include the following
entry for each alias name to be set up.
<alias-name> =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS_LIST =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)
(HOST = <host>) (PORT = <port>))
)
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVICE_NAME =
<service>)
)
)
In the previous example, <alias-name>, <host>, <port>,
and <service> are
placeholder text for illustration purposes. Ensure that you replace these with
the relevant values.
The following examples show how to set up wallets for database
user accounts for the following applications:
§
For RMS, RWMS, RPM Batch using sqlplus
or sqlldr, RETL, RMS, RWMS, and ARI
To set up wallets for database user accounts, do the following.
1.  Create a new directory called wallet under your folder
structure.
Create a new directory called wallet under your folder
structure.
cd /projects/rms14/dev/
mkdir .wallet
Note: The
default permissions of the wallet allow only the owner to use it, ensuring the
connection information is protected. If you want other users to be able to use
the connection, you must adjust permissions appropriately to ensure only
authorized users have access to the wallet.
2. Create
a sqlnet.ora in the wallet directory with the following content.
WALLET_LOCATION = (SOURCE
= (METHOD = FILE) (METHOD_DATA
= (DIRECTORY = /projects/rms14/dev/.wallet))
)
SQLNET.WALLET_OVERRIDE=TRUE
SSL_CLIENT_AUTHENTICATION=FALSE
Note:
WALLET_LOCATION must be on line 1 in the file.
3. Setup
a tnsnames.ora in the wallet directory. This tnsnames.ora includes the standard
tnsnames.ora file. Then, add two custom tns_alias entries that are only for use
with the wallet. For example, sqlplus /@dvols29_rms01user.
ifile =
/u00/oracle/product/11.2.0.1/network/admin/tnsnames.ora
Examples for a NON pluggable db:
dvols29_rms01user =
(DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = tcp)
(host = xxxxxx.us.oracle.com)
(Port = 1521)))
(CONNECT_DATA
= (SID = <sid_name> (GLOBAL_NAME = <sid_name>)))
dvols29_rms01user.world =
(DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = tcp)
(host = xxxxxx.us.oracle.com)
(Port = 1521)))
(CONNECT_DATA
= (SID = <sid_name>) (GLOBAL_NAME = <sid_name>)))
Examples for a pluggable db:
dvols29_rms01user =
(DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = tcp)
(host = xxxxxx.us.oracle.com)
(Port = 1521)))
(CONNECT_DATA
= (SERVICE_NAME = <pluggable db name>)))
dvols29_rms01user.world =
(DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = tcp)
(host = xxxxxx.us.oracle.com)
(Port = 1521)))
(CONNECT_DATA
= (SERVICE_NAME = <pluggable db name>)))
Note:
It is important to not just copy the tnsnames.ora file because it can quickly
become out of date. The ifile clause (shown above) is key.
4. Create
the wallet files. These are empty initially.
a. Ensure
you are in the intended location.
$ pwd
/projects/rms14/dev/.wallet
b. Create
the wallet files.
$ mkstore -wrl . –create
c. Enter
the wallet password you want to use. It is recommended that you use the same
password as the UNIX user you are creating the wallet on.
d. Enter
the password again.
Two wallet files are created from the above command:
– ewallet.p12
– cwallet.sso
5. Create
the wallet entry that associates the user name and password to the custom tns
alias that was setup in the wallet’s tnsnames.ora file.
mkstore –wrl . –createCredential <tns_alias>
<username> <password>
Example:
mkstore –wrl .
–createCredential dvols29_rms01user rms01user passwd
6. Test
the connectivity. The ORACLE_HOME used with the wallet must be the same version
or higher than what the wallet was created with.
$ export TNS_ADMIN=/projects/rms14/dev/.wallet
/* This is very import to use wallet to point at the alternate tnsnames.ora
created in this example */
$ sqlplus /@dvols29_rms01user
SQL*Plus: Release 12
Connected to:
Oracle Database 12g
SQL> show user
USER is “rms01user”
Running batch programs or shell scripts would be similar:
Ex: dtesys
/@dvols29_rms01user
script.sh
/@dvols29_rms01user
Set the UP unix variable to help with
some compiles :
export UP=/@dvols29_rms01user
for use in RMS batch compiles, and RMS,
RWMS, and ARI forms compiles.
As shown in the example above, users can ensure that passwords
remain invisible.
Additional Database Wallet Commands
The following is a list of additional database wallet commands.
§
Delete a credential on wallet
mkstore –wrl . –deleteCredential dvols29_rms01user
§
Change the password for a credential on wallet
mkstore –wrl . –modifyCredential dvols29_rms01user rms01user
passwd
§
List the wallet credential entries
mkstore –wrl . –list
This command returns values such as the following.
oracle.security.client.connect_string1
oracle.security.client.user1
oracle.security.client.password1
§
View the details of a wallet entry
mkstore –wrl . –viewEntry
oracle.security.client.connect_string1
Returns the value of the entry:
dvols29_rms01user
mkstore –wrl . –viewEntry oracle.security.client.user1
Returns the value of the entry:
rms01user
mkstore –wrl . –viewEntry oracle.security.client.password1
Returns the value of the entry:
Passwd
RETL creates a wallet under $RFX_HOME/etc/security, with the
following files:
§
cwallet.sso
§
jazn-data.xml
§
jps-config.xml
§
README.txt
To set up RETL wallets, perform the following steps:
1. Set
the following environment variables:
§
ORACLE_SID=<retaildb>
§
RFX_HOME=/u00/rfx/rfx-13
§
RFX_TMP=/u00/rfx/rfx-13/tmp
§
JAVA_HOME=/usr/jdk1.6.0_12.64bit
§
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$ORACLE_HOME
§
PATH=$RFX_HOME/bin:$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH
2.
Change directory to
$RFX_HOME/bin.
3. Run setup-security-credential.sh.
§ Enter 1 to add a new
database credential.
§ Enter the
dbuseralias. For example, retl_java_rms01user.
§ Enter the database user
name. For example, rms01user.
§ Enter the database
password.
§ Re-enter the database
password.
§ Enter D to exit the
setup script.
4. Update
your RETL environment variable script to reflect the names of both the Oracle
Networking wallet and the Java wallet.
For example, to configure RETLforRPAS, modify the following
entries in
$RETAIL_HOME/RETLforRPAS/rfx/etc/rmse_rpas_config.env.
§ The RETL_WALLET_ALIAS
should point to the Java wallet entry:
–
export
RETL_WALLET_ALIAS="retl_java_rms01user"
§ The
ORACLE_WALLET_ALIAS should point to the Oracle network wallet entry:
–
export
ORACLE_WALLET_ALIAS="dvols29_rms01user"
§ The SQLPLUS_LOGON
should use the ORACLE_WALLET_ALIAS:
–
export
SQLPLUS_LOGON="/@${ORACLE_WALLET_ALIAS}"
5. To
change a password later, run setup-security-credential.sh.
§ Enter 2 to update a
database credential.
§ Select the credential
to update.
§ Enter the database
user to update or change.
§ Enter the password of
the database user.
§ Re-enter the
password.
For Java applications, consider the following:
§
For database user accounts, ensure that you set up the same alias
names between the password stores (database wallet and Java wallet). You can
provide the alias name during the installer process.
§
Document all aliases that you have set up. During the application
installation, you must enter the alias names for the application installer to
connect to the database and application server.
§ Passwords are
not used to update entries in Java wallets. Entries in Java wallets are stored
in partitions, or application-level keys. In each retail application that has
been installed, the wallet is located in
<WEBLOGIC_DOMAIN_HOME>/retail/<appname>/config Example:
/u00/webadmin/product/10.3.6/WLS/user_projects/domains/14_mck_soa_domain/retail/reim14/config
§ Application
installers should create the Java wallets for you, but it is good to know how
this works for future use and understanding.
§
Scripts are located in <WEBLOGIC_DOMAIN_HOME>/retail/<appname>/retail-public-security-api/bin
for administering wallet entries.
§
Example:
§ /u00/webadmin/product/10.3.6/WLS/user_projects/domains/REIMDomain/retail/reim14/retail-public-security-api/bin
§
In this directory is a script to help you update each alias entry
without having to remember the wallet details. For example, if you set the RPM
database alias to rms01user, you will find a script called update-RMS01USER.sh.
Note:
These scripts are available only with applications installed by way of an
installer.
§
Two main scripts are related to this script in the folder for
more generic wallet operations: dump_credentials.sh and save_credential.sh.
§
If you have not installed the application yet, you can unzip the
application zip file and view these scripts in <app>/application/retail-public-security-api/bin.
§
Example:
§
/u00/webadmin/reim14/application/retail-public-security-api/bin
update-<ALIAS>.sh
update-<ALIAS>.sh updates the wallet entry for this alias.
You can use this script to change the user name and password for this alias.
Because the application refers only to the alias, no changes are needed in
application properties files.
Usage:
update-<username>.sh <myuser>
Example:
/u00/webadmin/product/10.3.x/WLS/user_projects/domains/RPMDomain/retail/rpm14/retail-public-security-api/bin>
./update-RMS01USER.sh
usage: update-RMS01USER.sh <username>
<username>: the username to update into this alias.
Example: update-RMS01USER.sh myuser
Note: this script will ask you for the password for the username
that you pass in.
/u00/webadmin/product/10.3.x/WLS/user_projects/domains/RPMDomain/retail/rpm14/retail-public-security-api/bin>
dump_credentials.sh
dump_credentials.sh is used to retrieve information from wallet. For
each entry found in the wallet, the wallet partition, the alias, and the user
name are displayed. Note that the password is not displayed. If the value of an
entry is uncertain, run save_credential.sh to resave the entry with a known
password.
dump_credentials.sh <wallet location>
Example:
dump_credentials.sh location:/u00/webadmin/product/10.3.x/WLS/user_projects/domains/REIMDomain/retail/reim14/config
Retail Public Security API Utility
=============================================
Below are the credentials found in the wallet at the location:/u00/webadmin/product/10.3.x/WLS/user_projects/domains/REIMDomain/retail/reim14/config
=============================================
Application level key partition name:reim14
User Name Alias:WLS-ALIAS User Name:weblogic
User Name Alias:RETAIL-ALIAS User Name:retail.user
User Name Alias:LDAP-ALIAS User Name:RETAIL.USER
User Name Alias:RMS-ALIAS User Name:rms14mock
User Name Alias:REIMBAT-ALIAS User Name:reimbat
save_credential.sh
save_credential.sh is used to update the information in wallet.
If you are unsure about the information that is currently in the wallet, use
dump_credentials.sh as indicated above.
save_credential.sh -a <alias> -u <user> -p
<partition name> –l <path of the wallet file location where
credentials are stored>
Example:
/u00/webadmin/mock14_testing/rtil/rtil/application/retail-public-security-api/bin>
save_credential.sh -l wallet_test -a myalias -p mypartition -u myuser
=============================================
Retail Public Security API Utility
=============================================
Enter password:
Verify password:
Note: -p in the above
command is for partition name. You must specify the proper partition name used
in application code for each Java application.
save_credential.sh and dump_credentials.sh scripts are the
same for all applications. If using save_credential.sh to add a wallet entry or
to update a wallet entry, bounce the application/managed server so that your
changes are visible to the application. Also, save a backup copy of your
cwallet.sso file in a location outside of the deployment path, because
redeployment or reinstallation of the application will wipe the wallet entries
you made after installation of the application. To restore your wallet entries
after a redeployment/reinstallation, copy the backed up cwallet.sso file over
the cwallet.sso file. Then bounce the application/managed server.
Usage
=============================================
Retail Public Security API Utility
=============================================
usage: save_credential.sh -au[plh]
E.g. save_credential.sh -a rms-alias -u rms_user -p rib-rms -l ./
-a,--userNameAlias <arg> alias for which the
credentials
needs to be stored
-h,--help usage information
-l,--locationofWalletDir <arg> location where the
wallet file is
created.If not specified, it creates the wallet under
secure-credential-wallet directory which is already present under the
retail-public-security-api/ directory.
-p,--appLevelKeyPartitionName <arg> application level
key partition name
-u,--userName <arg> username to be
stored in secure
credential wallet for specified alias*
The ORACLE Retail Java applications have the wallet alias
information you create in an <app-name>.properties file. Below is the
reim.properties file. Note the database information and the user are presented
as well. The property called datasource.credential.alias=RMS-ALIAS uses the ORACLE
wallet with the argument of RMS-ALIAS at the csm.wallet.path and
csm.wallet.partition.name = reim14 to retrieve the password for application
use.
Reim.properties code sample:
datasource.url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@xxxxxxx.us.oracle.com:1521:pkols07
datasource.schema.owner=rms14mock
datasource.credential.alias=RMS-ALIAS
#
=================================================================
# ossa related Configuration
#
# These settings are for ossa configuration to store credentials.
# =================================================================
csm.wallet.path=/u00/webadmin/product/10.3.x/WLS/user_projects/domains/REIMDomain/retail/reim14/config
csm.wallet.partition.name=reim14
Some of the ORACLE Retail Java batch applications have an alias
to use when running Java batch programs. For example, alias REIMBAT-ALIAS maps
through the wallet to dbuser RMS01APP, already on the database. To run a ReIM
batch program the format would be: reimbatchpgmname REIMBAT-ALIAS <other
arguments as needed by the program in question>
The following section describes a domain level database
credential store. This is used in RPM login processing, SIM login processing,
RWMS login processing, RESA login processing and Allocation login processing
and policy information for application permission. Setting up the database
credential store is addressed in the RPM, SIM, ReSA, RWMS, and Alloc 14.1
install guides.
The following sections show an example of how to administer the
password stores thru ORACLE Enterprise Manger Fusion Middleware Control, a
later section will show how to do this thru WLST scripts.
1.
The first step is to use your link to Oracle Enterprise
Manager Fusion Middleware Control for the domain in question. Locate your
domain on the left side of the screen and do a right mouse click on the domain
and select Security > Credentials

2.
Click on Credentials and you will get a screen similar to the
following. The following screen is expanded to make it make more sense. From
here you can administer credentials.
The Create Map add above is to create a new map with keys under it. A map would
usually be an application such as rpm14. The keys will usually represent alias
to various users (database user, WebLogic user, LDAP user, etc). The
application installer should add the maps so you should not often have to add a
map.
Creation of the main keys for an application will also be built
by the application installer. You will not be adding keys often as the
installer puts the keys out and the keys talk to the application. You may be
using EDIT on a key to see what user the key/alias points to and possibly
change/reset its password. To edit a key/alias, highlight the key/alias in
question and push the edit icon nearer the top of the page. You will then get a
screen as follows:
The screen above shows the map (rpm14) that came from the
application installer, the key (DB-ALIAS) that came from the application
installer (some of the keys/alias are selected by the person who did the
application install, some are hard coded by the application installer in
question), the type (in this case password), and the user name and password. This
is where you would check to see that the user name is correct and reset the
password if needed. REMEMBER, a change to an item like a database password WILL
make you come into this and also change the password. Otherwise your application
will NOT work correctly.
This procedure is optional as you can administer the credential
store through the Oracle enterprise manager associated with the domain of your
application install for RPM, SIM, RESA, or Allocation.
An Oracle Platform Security Scripts (OPSS) script is a WLST
script, in the context of the Oracle WebLogic Server. An online
script is a script that requires a connection to a running server. Unless
otherwise stated, scripts listed in this section are online scripts and operate
on a database credential store. There are a few scripts that are offline, that is, they do not require a server to be running
to operate.
Read-only scripts can be performed only by users in the following
WebLogic groups: Monitor, Operator, Configurator, or Admin. Read-write scripts
can be performed only by users in the following WebLogic groups: Admin or
Configurator. All WLST scripts are available out-of-the-box with the
installation of the Oracle WebLogic Server.
WLST scripts can be run in interactive mode or in script mode. In
interactive mode, you enter the script at a command-line prompt and view the
response immediately after. In script mode, you write scripts in a text file
(with a py file name extension) and run it without requiring input, much like
the directives in a shell script.
For platform-specific requirements to run an OPSS script, see http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E21764_01/core.1111/e10043/managepols.htm#CIHIBBDJ
The weakness with the WLST/OPSS scripts is that you have to
already know your map name and key name. In many cases, you do not know or
remember that. The database credential store way through enterprise manager is
a better way to find your map and key names easily when you do not already know
them. A way in a command line mode to find the map name and alias is to run
orapki. An example of orapki is as follows:
/u00/webadmin/product/wls_apps/oracle_common/bin> ./orapki
wallet display –wallet /u00/webadmin/product/wls_apps/user_projects/domains/APPDomain/config/fmwconfig
(where the path above is the domain location of the wallet)
Output of orapki is below. This shows map name of rpm14 and each
alias in the wallet:
Oracle PKI Tool: Version 11.1.1.7.0
Requested Certificates:
User Certificates:
Oracle Secret Store entries:
rpm14@#3#@DB-ALIAS
rpm14@#3#@LDAP-ALIAS
rpm14@#3#@RETAIL.USER
rpm14@#3#@user.signature.salt
rpm14@#3#@user.signature.secretkey
rpm14@#3#@WEBLOGIC-ALIAS
rpm14@#3#@WLS-ALIAS
Trusted Certificates:
Subject: OU=Class 1 Public Primary Certification
Authority,O=VeriSign\, Inc.,C=US
OPSS provides the following scripts on all supported platforms to
administer credentials (all scripts are online, unless
otherwise stated. You need the map name and the key name to run the scripts
below
§
listCred
§
updateCred
§
createCred
§
deleteCred
§
modifyBootStrapCredential
§
addBootStrapCredential
The script listCred returns the list of attribute
values of a credential in the credential store with given map name and key
name. This script lists the data encapsulated in credentials of type password
only.
Script Mode Syntax
listCred.py -map mapName -key keyName
Interactive Mode Syntax
listCred(map="mapName", key="keyName")
The meanings of the arguments (all required) are as follows:
§
map specifies a map name (folder).
§
key specifies a key name.
Examples of Use:
The following invocation returns all the information (such as user
name, password, and description) in the credential with map name myMap
and key name myKey:
listCred.py -map myMap -key myKey
The following example shows how to run this command and similar
credential commands with WLST:
/u00/webadmin/product/wls_apps/oracle_common/common/bin>
sh wlst.sh
Initializing WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST)...
Welcome to WebLogic Server Administration Scripting Shell
wls:/offline>
connect('weblogic','password123','xxxxxx.us.oracle.com:17001')
Connecting to t3://xxxxxx.us.oracle.com:17001 with userid
weblogic ...
Successfully connected to Admin Server 'AdminServer' that belongs
to domain 'APPDomain'.
wls:/APPDomain/serverConfig>
listCred(map="rpm14",key="DB-ALIAS")
Already in Domain Runtime Tree
[Name : rms01app, Description : null, expiry Date : null]
PASSWORD:retail
*The above means for map rpm14 in APPDomain, alias DB-ALIAS
points to database user rms01app with a password of retail
The script updateCred modifies the type, user name,
and password of a credential in the credential store with given map name and
key name. This script updates the data encapsulated in credentials of type
password only. Only the interactive mode is supported.
Interactive Mode Syntax
updateCred(map="mapName", key="keyName", user="userName",
password="passW", [desc="description"])
The meanings of the arguments (optional arguments are enclosed by
square brackets) are as follows:
§
map specifies a map name (folder) in the credential
store.
§
key specifies a key name.
§
user specifies the credential user name.
§
password specifies the credential password.
§
desc specifies a string describing the credential.
Example of Use:
The following invocation updates the user name, password, and
description of the password credential with map name myMap and key
name myKey:
updateCred(map="myMap", key="myKey",
user="myUsr", password="myPassw")
The script createCred creates a credential in the
credential store with a given map name, key name, user name and password. This
script can create a credential of type password only. Only the interactive mode
is supported.
Interactive Mode Syntax
createCred(map="mapName", key="keyName",
user="userName", password="passW", [desc="description"])
The meanings of the arguments (optional arguments are enclosed by
square brackets) are as follows:
§
map specifies the map name (folder) of the
credential.
§
key specifies the key name of the credential.
§
user specifies the credential user name.
§
password specifies the credential password.
§
desc specifies a string describing the credential.
Example of Use:
The following invocation creates a password credential with the
specified data:
createCred(map="myMap", key="myKey",
user="myUsr", password="myPassw")
The script deleteCred removes a credential with
given map name and key name from the credential store.
Script Mode Syntax
deleteCred.py -map mapName -key keyName
Interactive Mode Syntax
deleteCred(map="mapName",key="keyName")
The meanings of the arguments (all required) are as follows:
§
map specifies a map name (folder).
§
key specifies a key name.
Example of Use:
The following invocation removes the credential with map name myMap
and key name myKey:
deleteCred.py -map myMap -key myKey
The offline script modifyBootStrapCredential
modifies the bootstrap credentials configured in the default jps context, and
it is typically used in the following scenario: suppose that the policy and
credential stores are LDAP-based, and the credentials to access the LDAP store
(stored in the LDAP server) are changed. Then this script can be used to seed
those changes into the bootstrap credential store.
This script is available in interactive mode only.
Interactive Mode Syntax
modifyBootStrapCredential(jpsConfigFile="pathName",
username="usrName", password="usrPass")
The meanings of the arguments (all required) are as follows:
§
jpsConfigFile specifies the location of the file jps-config.xml
relative to the location where the script is run. Example location: /u00/webadmin/product/wls_apps/user_projects/domains/APPDomain/config/fmwconfig.
Example location of the bootstrap wallet is /u00/webadmin/product/wls_apps/user_projects/domains/APPDomain/config/fmwconfig/bootstrap
§
username specifies the distinguished name of the
user in the LDAP store.
§
password specifies the password of the user.
Example of Use:
Suppose that in the LDAP store, the password of the user with
distinguished name cn=orcladmin has been changed to welcome1,
and that the configuration file jps-config.xml is located in the
current directory.Then the following invocation changes the password in the
bootstrap credential store to welcome1:
modifyBootStrapCredential(jpsConfigFile='./jps-config.xml',
username='cn=orcladmin', password='welcome1')
Any output regarding the audit service can be disregarded.
The offline script addBootStrapCredential adds a
password credential with given map, key, user name, and user password to the
bootstrap credentials configured in the default jps context of a jps
configuration file.
Classloaders contain a hierarchy with parent classloaders and
child classloaders. The relationship between parent and child classloaders is
analogous to the object relationship of super classes and subclasses. The
bootstrap classloader is the root of the Java classloader hierarchy. The Java
virtual machine (JVM) creates the bootstrap classloader, which loads the Java
development kit (JDK) internal classes and java.* packages
included in the JVM. (For example, the bootstrap classloader loads java.lang.String.)
This script is available in interactive mode only.
Interactive Mode Syntax
addBootStrapCredential(jpsConfigFile="pathName",
map="mapName", key="keyName", username="usrName",
password="usrPass")
The meanings of the arguments (all required) are as follows:
§
jpsConfigFile specifies the location of the file jps-config.xml
relative to the location where the script is run. Example location: /u00/webadmin/product/wls_apps/user_projects/domains/APPDomain/config/fmwconfig
§
map specifies the map of the credential to add.
§
key specifies the key of the credential to add.
§
username specifies the name of the user in the
credential to add.
§
password specifies the password of the user in the
credential to add.
Example of Use:
The following invocation adds a credential to the bootstrap
credential store:
addBootStrapCredential(jpsConfigFile='./jps-config.xml',
map='myMapName', key='myKeyName', username='myUser', password =’myPass’)
|
Retail app
|
Wallet type
|
Wallet loc
|
Wallet partition
|
Alias name
|
User name
|
Use
|
Create by
|
Alias Example
|
Notes
|
|
RMS batch
|
DB
|
<RMS batch install dir (RETAIL_HOME)>/.wallet
|
n/a
|
<Database SID>_<Database schema owner>
|
<rms schema owner>
|
Compile, execution
|
Installer
|
n/a
|
Alias hard-coded by installer
|
|
RMS forms
|
DB
|
<forms install dir>/base/.wallet
|
n/a
|
<Database SID>_<Database schema owner>
|
<rms schema owner>
|
Compile
|
Installer
|
n/a
|
Alias hard-coded by installer
|
|
ARI forms
|
DB
|
<forms install dir>/base/.wallet
|
n/a
|
<Db_Ari01>
|
<ari schema owner>
|
Compile
|
Manual
|
ari-alias
|
|
|
RMWS forms
|
DB
|
<forms install dir>/base/.wallet
|
n/a
|
<Database SID>_<Database schema owner>
|
<rwms schema owner>
|
Compile forms, execute batch
|
Installer
|
n/a
|
Alias hard-coded by installer
|
|
RPM batch plsql and sqlldr
|
DB
|
<RPM batch install dir>/.wallet
|
n/a
|
<rms schema owner alias>
|
<rms schema owner>
|
Execute batch
|
Manual
|
rms-alias
|
RPM plsql and sqlldr batches
|
|
RWMS auto-login
|
JAVA
|
<forms install dir>/base/.javawallet
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
<RWMS Installation name>
|
<RWMS database user alias>
|
<RWMS schema owner>
|
RWMS forms app to avoid dblogin screen
|
Installer
|
rwms14inst
|
|
|
|
|
|
<RWMS Installation name>
|
BI_ALIAS
|
<BI Publisher administrative user>
|
RWMS forms app to connect to BI Publisher
|
Installer
|
n/a
|
Alias hard-coded by installer
|
|
AIP app
|
JAVA
|
<weblogic domain home>/retail/<deployed aip app
name>/config
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Each alias must be unique
|
|
|
|
|
aip14
|
<AIP weblogic user alias>
|
<AIP weblogic user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
aip-weblogic-alias
|
|
|
|
|
|
aip14
|
<AIP database schema user alias>
|
<AIP database schema user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
aip01user-alias
|
|
|
|
|
|
aip14
|
<rib-aip weblogic user alias>
|
<rib-aip weblogic user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
rib-aip-weblogic-alias
|
|
|
RPM app
|
DB credential store
|
|
Map=rpm14 or what you called the app at install time.
|
Many for app use
|
|
|
|
|
<weblogic
domain home>/config/fmwconfig/jps-config.xml has info on the credential
store. This directory also has the domain cwallet.sso file.
|
|
RPM app
|
JAVA
|
<weblogic domain home>/retail/<deployed rpm app
name>/config
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Each alias must be unique
|
|
|
|
|
rpm14
|
<rpm weblogic user alias>
|
<rpm weblogic user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
rpm-weblogic-alias
|
|
|
|
|
|
rpm14
|
<rpm batch user name> is the alias. Yes, here alias
name = user name
|
<rpm batch user name>
|
App, batch use
|
Installer
|
RETAIL.USER
|
|
|
|
JAVA
|
<retail_home>/orpatch/config/javaapp_rpm
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Each alias must be unique
|
|
|
|
|
retail_installer
|
<rpm weblogic user alias>
|
<rpm weblogic user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
weblogic-alias
|
|
|
|
|
|
retail_installer
|
<rms shema user alias>
|
<rms shema user name>
|
App, batch use
|
Installer
|
rms01user-alias
|
|
|
|
|
|
retail_installer
|
<reim batch user alias>
|
<reim batch user name>
|
App, batch use
|
Installer
|
reimbat-alias
|
|
|
|
|
|
retail_installer
|
<LDAP-ALIAS>
|
cn=rpm.admin,cn=Users,dc=us,dc=oracle,dc=com
|
LDAP user use
|
Installer
|
LDAP_ALIAS
|
|
|
ReIM app
|
JAVA
|
<weblogic domain home>/retail/<deployed reim app
name>/config
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Each alias must be unique
|
|
|
|
|
<installed app name, ex: reim14>
|
<reim weblogic user alias>
|
<reim weblogic user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
weblogic-alias
|
|
|
|
|
|
<installed app name, ex: reim14>
|
<rms shema user alias>
|
<rms shema user name>
|
App, batch use
|
Installer
|
rms01user-alias
|
|
|
|
|
|
<installed app name, ex: reim14>
|
<reim webservice validation user alias>
|
<reim webservice validation user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
reimwebservice-alias
|
|
|
|
|
|
<installed app name, ex: reim14>
|
<reim batch user alias>
|
<reim batch user name>
|
App, batch use
|
Installer
|
reimbat-alias
|
|
|
|
|
|
<installed app name, ex: reim14>
|
<LDAP-ALIAS>
|
cn=REIM.ADMIN,cn=Users,dc=us,dc=oracle,dc=com
|
LDAP user use
|
Installer
|
LDAP_ALIAS
|
|
|
|
JAVA
|
<retail_home>/orpatch/config/javaapp_reim
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Each alias must be unique
|
|
|
|
|
retail_installer
|
<reim weblogic user alias>
|
<reim weblogic user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
weblogic-alias
|
|
|
|
|
|
retail_installer
|
<rms shema user alias>
|
<rms shema user name>
|
App, batch use
|
Installer
|
rms01user-alias
|
|
|
|
|
|
retail_installer
|
<reim webservice validation user alias>
|
<reim webservice validation user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
reimwebservice-alias
|
|
|
|
|
|
retail_installer
|
<reim batch user alias>
|
<reim batch user name>
|
App, batch use
|
Installer
|
reimbat-alias
|
|
|
|
|
|
retail_installer
|
<LDAP-ALIAS>
|
cn=REIM.ADMIN,cn=Users,dc=us,dc=oracle,dc=com
|
LDAP user use
|
Installer
|
LDAP_ALIAS
|
|
|
RESA app
|
DB credential store
|
|
Map=resa14 or what you called the app at install time
|
Many for login and policies
|
|
|
|
|
<weblogic
domain home>/config/fmwconfig/jps-config.xml has info on the credential
store. This directory also has the domain cwallet.sso file. The bootstrap
directory under this directory has bootstrap cwallet.sso file.
|
|
RESA app
|
JAVA
|
<weblogic domain home>/retail/<deployed resa app
name>/config
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Each alias must be unique
|
|
|
|
|
<installed app name>
|
<resa weblogic user alias>
|
<resa weblogic user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
wlsalias
|
|
|
|
|
|
<installed app name>
|
<resa schema
db user alias>
|
<rmsdb shema user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
Resadb-alias
|
|
|
|
|
|
<installed app name>
|
<resa schema user alias>
|
<rmsdb shema user name>>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
resa-alias
|
|
|
|
JAVA
|
<retail_home>/orpatch/config/javaapp_resa
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Each alias must be unique
|
|
|
|
|
retail_installer
|
<resa weblogic user alias>
|
<resa weblogic user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
wlsalias
|
|
|
|
|
|
retail_installer
|
<resa schema
db user alias>
|
<rmsdb shema user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
Resadb-alias
|
|
|
|
JAVA
|
<retail_ home>/orpatch/config/javaapp_rasrm
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Each alias must be unique
|
|
|
|
|
retail_installer
|
<alloc weblogic user alias>
|
<alloc weblogic user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
weblogic-alias
|
|
|
Alloc app
|
DB credential store
|
|
Map=alloc 14 or what you called the app at install time
|
Many for login and policies
|
|
|
|
|
<weblogic
domain home>/config/fmwconfig/jps-config.xml has info on the credential
store. This directory also has the domain cwallet.sso file. The bootstrap
directory under this directory has bootstrap cwallet.sso file.
|
|
Alloc app
|
JAVA
|
<weblogic domain home>/retail/config
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Each alias must be unique
|
|
|
|
|
<installed app name>
|
<alloc weblogic user alias>
|
<alloc weblogic user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
weblogic-alias
|
|
|
|
|
|
<installed app name>
|
<rms schema user alias>
|
<rms schema user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
dsallocAlias
|
|
|
|
|
|
<installed app name>
|
<alloc batch user alias>
|
<SYSTEM_ADMINISTRATOR>
|
Batch use
|
Installer
|
alloc14
|
|
|
|
JAVA
|
<retail_ home>/orpatch/config/javaapp_alloc
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Each alias must be unique
|
|
|
|
|
retail_installer
|
<alloc weblogic user alias>
|
<alloc weblogic user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
weblogic-alias
|
|
|
|
|
|
retail_installer
|
<rms schema user alias>
|
<rms schema user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
dsallocAlias
|
|
|
|
|
|
retail_installer
|
<alloc batch user alias>
|
<SYSTEM_ADMINISTRATOR>
|
Batch use
|
Installer
|
alloc14
|
|
|
|
JAVA
|
<retail_ home>/orpatch/config/javaapp_rasrm
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Each alias must be unique
|
|
|
|
|
retail_installer
|
<alloc weblogic user alias>
|
<alloc weblogic user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
weblogic-alias
|
|
|
SIM app
|
DB credential store
|
|
Map=oracle.retail.sim
|
Aliases required for SIM app use
|
|
|
|
|
<weblogic
domain home>/config/fmwconfig/jps-config.xml has info on the credential
store. This directory also has the domain cwallet.sso file.
|
|
|
JAVA
|
<weblogic domain home>/retail/<deployed sim app
name>/batch/resources/conf
|
oracle.retail.sim
|
<sim batch user alias>
|
<sim batch user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
BATCH-ALIAS
|
|
|
|
JAVA
|
<weblogic domain home>/retail/<deployed sim app
name>/wireless/resources/conf
|
oracle.retail.sim
|
<sim wireless user alias>
|
<sim wireless user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
WIRELESS-ALIAS
|
|
|
RETL
|
JAVA
|
<RETL home>/etc/security
|
n/a
|
<target application user alias>
|
<target application db userid>
|
App use
|
Manual
|
retl_java_rms01user
|
|
|
RETL
|
DB
|
<RETL home>/.wallet
|
n/a
|
<target application user alias>
|
<target application db userid>
|
App use
|
Manual
|
<db>_<user>
|
|
|
RIB
|
JAVA
|
<RIBHOME DIR>/deployment-home/conf/security
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
<app> is one of aip, rfm, rms, rpm, sim, rwms, tafr
|
|
JMS
|
|
|
jms<1-5>
|
<jms user alias> for jms<1-5>
|
<jms user name> for jms<1-5>
|
Integra-
tion use
|
Installer
|
jms-alias
|
|
|
WebLogic
|
|
|
rib-<app>-app-server-instance
|
<rib-app weblogic user alias>
|
<rib-app weblogic user name>
|
Integra-
tion use
|
Installer
|
weblogic-alias
|
|
|
Admin GUI
|
|
|
rib-<app>#web-app-user-alias
|
<rib-app admin gui user alias>
|
<rib-app admin gui user name>
|
Integra-
tion use
|
Installer
|
admin-gui-alias
|
|
|
Application
|
|
|
rib-<app>#user-alias
|
<app weblogic user alias>
|
<app weblogic user name>
|
Integra-
tion use
|
Installer
|
app-user-alias
|
Valid only for aip, rpm, sim
|
|
DB
|
|
|
rib-<app>#app-db-user-alias
|
<rib-app database schema user alias>
|
<rib-app database schema user name>
|
Integra-
tion use
|
Installer
|
db-user-alias
|
Valid only for rfm, rms, rwms, tafr
|
|
Error Hospital
|
|
|
rib-<app>#hosp-user-alias
|
<rib-app error hospital database
schema user alias>
|
<rib-app error hospital database schema user name>
|
Integra-
tion use
|
Installer
|
hosp-user-alias
|
|
|
RFI
|
Java
|
<RFI-HOME>/retail-financial-integration-solution/service-based-integration/conf/security
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
<installed app name>
|
rfiAppServerAdminServerUserAlias
|
<rfi weblogic user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
rfiAppServerAdminServerUserAlias
|
|
|
|
|
|
<installed app name>
|
rfiAdminUiUserAlias
|
<ORFI admin user>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
rfiAdminUiUserAlias
|
|
|
|
|
|
<installed app name>
|
rfiDataSourceUserAlias
|
<ORFI schema user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
rfiDataSourceUserAlias
|
|
|
|
|
|
<installed app name>
|
ebsDataSourceUserAlias
|
<EBS schema user name>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
ebsDataSourceUserAlias
|
|
|
|
|
|
<installed app name>
|
smtpMailFromAddressAlias
|
<From email address>
|
App use
|
Installer
|
smtpMailFromAddressAlias
|
|
G
This section provides a guideline as
to the order in which the Oracle Retail applications should be installed. If a
retailer has chosen to use some, but not all, of the applications the order is
still valid less the applications not being installed.
Note:
The installation order is not meant to imply integration between products.
Enterprise Installation
Order
1. Oracle
Retail Merchandising System (RMS), Oracle Retail Trade Management (RTM)
2. Oracle
Retail Sales Audit (ReSA)
3. Oracle
Retail Extract, Transform, Load (RETL)
4. Oracle
Retail Active Retail Intelligence (ARI)
5. Oracle
Retail Warehouse Management System (RWMS)
6. Oracle
Retail Invoice Matching (ReIM)
7. Oracle
Retail Price Management (RPM)
8. Oracle
Retail Allocation
9. Oracle
Retail Central Office (ORCO)
10. Oracle
Retail Returns Management (ORRM)
11. Oracle
Retail Back Office (ORBO)
12. Oracle
Retail Store Inventory Management (SIM)
13. Oracle
Retail Predictive Application Server (RPAS)
14. Oracle
Retail Demand Forecasting (RDF)
15. Oracle
Retail Category Management (RCM)
16. Oracle
Retail Replenishment Optimization (RO)
17. Oracle
Retail Analytic Parameter Calculator Replenishment Optimization (APC RO)
18. Oracle
Retail Regular Price Optimization (RPO)
19. Oracle
Retail Merchandise Financial Planning (MFP)
20. Oracle
Retail Size Profile Optimization (SPO)
21. Oracle
Retail Assortment Planning (AP)
22. Oracle
Retail Item Planning (IP)
23. Oracle
Retail Item Planning Configured for COE (IP COE)
24. Oracle
Retail Advanced Inventory Planning (AIP)
25. Oracle
Retail Analytics
26. Oracle
Retail Advanced Science Engine (ORASE)
27. Oracle
Retail Integration Bus (RIB)
28. Oracle
Retail Service Backbone (RSB)
29. Oracle
Retail Financial Integration (ORFI)
30. Oracle
Retail Point-of-Service (ORPOS)
§ Oracle Retail Mobile
Point-of-Service (ORMPOS) (requires ORPOS)
31. Oracle
Retail Markdown Optimization (MDO)
32. Oracle
Retail Clearance Optimization Engine (COE)
33. Oracle
Retail Analytic Parameter Calculator for Markdown Optimization
(APC-MDO)
34. Oracle
Retail Analytic Parameter Calculator for Regular Price Optimization
(APC-RPO)
35. Oracle
Retail Macro Space Planning (MSP)
The Oracle Retail Enterprise suite includes Macro Space
Planning. This can be installed independently of and does not affect the
installation order of the other applications in the suite. If Macro Space
Planning is installed, the installation order for its component parts is:
§ Oracle Retail Macro
Space Management (MSM)
§ Oracle Retail
In-Store Space Collaboration (ISSC) (requires MSM)
§ Oracle Retail Mobile
In-Store Space Collaboration (requires MSM and ISSC)




























