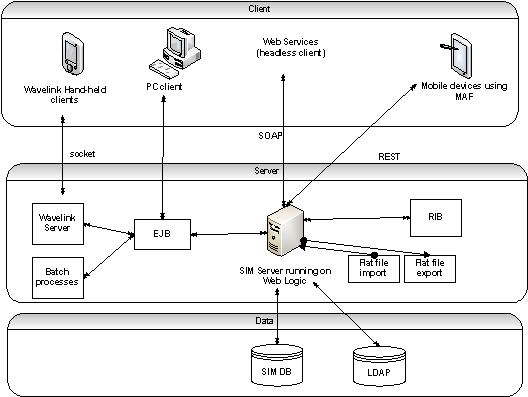
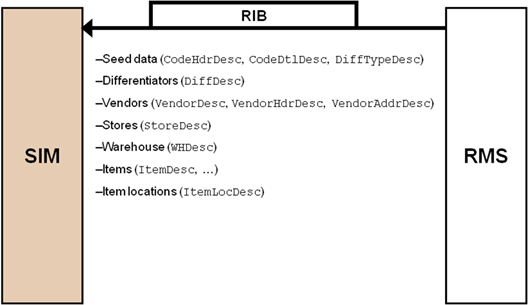
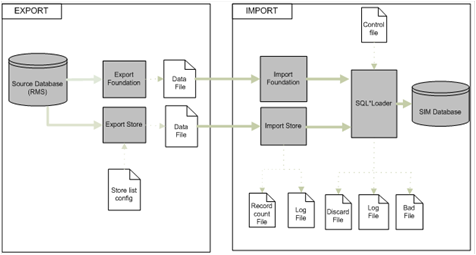
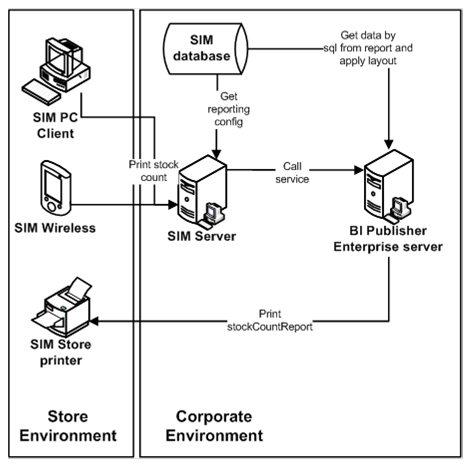
|
Permission
|
Topic
|
Usage
|
|
Access Admin
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Admin button on the SIM Login screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Auto-Receive Stores
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Auto-Receive Stores button on the Store Admin screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Buddy Store
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Buddy Store button on the Store Admin screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Container Lookup
|
Admin
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Container Lookup menu option on the Lookups menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the user will have access to functionality
within Container Lookups .
Without this permission, the user will not have access to Container Lookup
functions.
On the PC, with this permission, the Container Lookup button on the Lookups
screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Customize Translations
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Customize Translations button on the UI Config screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Extended Attribute
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the Ext.
Attribute button on the Setup screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Extended Attribute Dept. Assign
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Assign to Dept. button on the Extended Attributes screen is displayed and
enabled. Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Extended Attribute Setup
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Setup Attributes button on the Extended Attributes screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Finisher Lookup
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Finisher Lookup button on the Lookups screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission the button is not displayed.
|
|
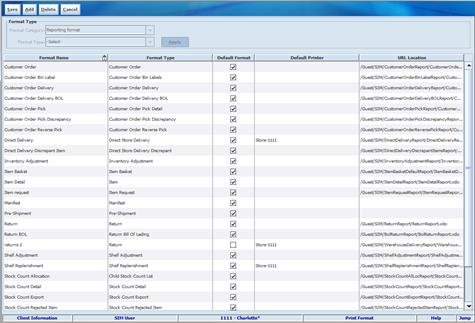
Access Formats
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Print Format button on the Print Setup screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Hierarchy Format
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Hierarchy Format button on the Print Setup screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Inventory Adjustment Reason
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the Inv.
Adj. Reason button on the Setup screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Inventory Management
|
Admin
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Inv.
Management menu option on the Main menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the user will have access to functionality
within Inventory Management.
Without this permission, the user will not have access to Inventory
Management functions.
On the PC, with this permission, the Inventory Mgmt button on the SIM Login
screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Item Lookup
|
Admin
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Item
Lookups menu option on the Lookups menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the user will have access to functionality within
Item Lookups.
Without this permission, the user will not have access to Item Lookup
functions.
On the PC, with this permission, the Item Lookup button on the Lookups screen
is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Lookup
|
Admin
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Lookups menu option on the Main menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the user will have access to functionality
within Lookups.
Without this permission, the user will not have access to Lookup functions.
On the PC, with this permission, the Lookups button on the SIM Login screen
is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access MPS Staged Messages
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the MPS
Staged Messages button on the Technical Maintenance screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access MPS Work Types
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the MPS
Worker Types button on the Technical Maintenance screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Operational Views
|
Admin
|
On MAF, with this permission, the
Operational Viewed menu option in the Drawer/menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Access Print
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Print button on the SIM Login screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Printers
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Printers button on the Print Setup screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Product Groups
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Product Group button on the Admin screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Product Group Schedules
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Product Group Schedule button on the Admin screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Report
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Reports button on the SIM Login screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Session Printer
|
Admin
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Session Printer menu option on the Main menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Session Printer button on the Print
Setup screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Setup
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Setup button on the Admin screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Shipment Reasons
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Shipment Reason button on the Setup screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Shipping Receiving
|
Admin
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Shipping/Receiving menu option on the Main menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the user will have access to functionality
within Shipping/Receiving.
Without this permission, the user will not have access to Shipping/Receiving
functions.
On the PC, with this permission, the Shipping/Receiving button on the SIM
Login screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access SIM Managed Store
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the SIM
Managed Stores button on the SIM Stores screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access SIM Store
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the SIM
Stores button on the Setup screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Store Admin
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Store Admin button on the Setup screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Store Defaults Admin
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Store Defaults Admin button on the Setup screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Supplier Lookup
|
Admin
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Supplier Lookup menu option on the Lookups menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the user will have access to functionality
within Supplier Lookup.
Without this permission, the user will not have access to Supplier Lookup
functions.
On the PC, with this permission, the Supplier Lookup button on the Lookups
screen is displayed and enabled. It also is required to display the Primary
Supplier button on the Item Detail screen.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access System Admin
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
System Admin button on the Setup screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Technical Maintenance
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Technical Maintenance button on the Admin screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Tolerances
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Tolerances button on the Setup screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Transaction History
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission the Tran
History button on the Lookups screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access UDAs
|
Admin
|
On the HH, with this permission, the View
UDAs menu option is enabled on the Item Lookup menu.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the UDA option button on the Item Lookup
screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the option button is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the UDA Print Setup button on the Print
Setup screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission the screen is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the UDA Detail button on the Item Detail
screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access UI Configuration
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the UI
Configuration button on the Technical Maintenance screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Add Extended Attribute Department
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the Add
button on the Assign Attributes screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Add Inventory Adjustment Reason
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the Add
button on the Inventory Adjustment Reason Maintenance screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Add Shipment Reasons
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the Add
button on the Shipment Reason Maintenance screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Create Product Groups
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Create button on the Product Group List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Create Product Group Schedules
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Create button on the Product Group Schedule List screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Create Translations
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Create button on the Translation Details screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete Extended Attribute Department
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Remove button on the Assign Attributes screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete Inventory Adjustment Reason
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Delete button on the Inventory Adjustment Reason Maintenance screen is
displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete Product Groups
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Delete button on the Product Group List screen with be displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed. If the button is
displayed, the user must also have the necessary data permission for the
product group the user is attempting to delete. If the user is not authorized
for the product group type, User is not authorized to delete this type of
Product Group.
|
|
Delete Product Group Schedules
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Delete button on the Product Group Schedule List screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed. If the button is
displayed, the user must also have the necessary data permission for the
product group that is associated to the product group schedule that is
attempted to be deleted. If the user is not authorized for the product group
type, User is not authorized to delete this type of Product Group Schedule.
|
|
Delete Shipment Reasons
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Delete button on the Shipment Reason Maintenance screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete Staged Messages
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Delete button on the MPS Staged Message Lookup screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Display Stock Locator
|
Admin
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Stock Locator option on the Item Lookup menu is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Stock Locator button on the Item Lookup
screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Edit Extended Attribute Setup
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, the Save
and Cancel buttons on the Setup Attributes screen are displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the buttons are not displayed.
|
|
Edit Product Groups
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, when a
user double-clicks on an existing Product Group, the Product Group Detail
screen will open. If the user also has the correct data permission for the
product group type, the screen will open in Edit mode.
Without the necessary data permission for the type, the screen will open in
View-only mode. The user must also have this permission for each store that
is included on the product group. If the user does, then the user can edit
the product group; if the user does not, then the screen will open in
View-only mode.
|
|
Edit Product Group Schedules
|
Admin
|
On the PC, with this permission, when a
user double-clicks on an existing Product Group Schedule, the Product Group
Schedule Detail screen will open. If the user also has the correct data
permission for the product group type, the screen will open in Edit mode.
Without the necessary data permission for the type, the screen will open in
View only mode. The user must also have this permission for each store that
is included on the schedule. If the user does, then the user can edit the
schedule; if the user does not then the screen will open in View-only mode.
|
|
Access Customer Details
|
Customer Order
|
On MAF, with this permission, the
Customer Details menu option in the footer menu on the Cust Order Items
Screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Customer button on the Customer Order
Detail screen. This permission is needed to access the customer details such
as name, address for a customer order.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Customer Order
|
Customer Order
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Customer Orders menu option on the Cust Ord Mgmt menu and Item Lookup menu is
displayed. Without this permission the option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Customer Order menu option in the
drawer/menu is available under the Customer Order Mgmt menu. Without
this permission, the option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Customer Order button on the Customer
Order Management List screen is displayed and enabled. Without this
permission, the button is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, when a user double-clicks on an existing
customer order on the Customer Order Management List screen, the Customer
Order Detail screen will open. Without this permission, the user is not
allowed to access the transaction.
On the PC, with this permission, the Customer Orders button on the Item
Lookup pop-up search screen is displayed and enabled. Without this permission
the tab will be disabled.
On the PC, with this permission, the Customer Orders button on the Item
Detail screen is displayed and enabled. Without this permission, the button
is not displayed.
|
|
Access Customer Order Delivery
|
Customer Order
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Deliver
Cust Order menu option on the Cust Ord Mgmt menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Delivery menu option in the footer menu on
the Cust Order Items Screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Delivery button on the Customer Order
List and Customer Order Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, when a user double-clicks on an existing
customer order delivery on the Customer Order Management List screen, the
Customer Order Detail screen will open.
Without this permission, when a user double clicks on an existing customer
order on the Customer Order Management List screen, the user is not allowed
to access the transaction.
|
|
Access Customer Order Delivery Attribute
|
Customer Order
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Add
Ext Attribute menu option on the Customer Order Summary menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Attributes screen on the Item Detail
screen, is displayed.
Without this permission, the screen is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Ext. Attributes button on the Delivery
Summary screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Customer Order Management
|
Customer Order
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Customer Order Mgmt menu option on the Main menu is displayed.
Without this permission the option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Customer Order Mgmt menu option in the
Drawer/menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Customer Order Mgmt button on the SIM
Login screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Customer Order Pick
|
Customer Order
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Customer Order Pick menu option on the Cust Ord Mgmt menu is displayed.
Without this permission the option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Customer Order Picking menu option will be
dislayed in the drawer.
Without this permission, the menu is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Pick button on the Customer Order
Management List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Customer Order Reverse Pick
|
Customer Order
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Reverse Pick button on the Customer Order Detail screen is displayed and
enabled. Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
With this permission, the Reverse Pick button on the Customer Order List
screen is displayed and enabled. Without this permission, the button is not
displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, when a user double-clicks on an existing
customer order reverse pick record on the Customer Order Management List
screen, the Customer Order Detail screen will open.
Without this permission, when a user double clicks on an existing customer
order reverse pick record on the Customer Order Management List screen, the
user is not allowed to access the transaction.
|
|
Cancel Submit Customer Order Delivery
|
Customer Order
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Cancel Submit menu option on the Delivery Summary menu is displayed.
Without this permission the option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Cancel Submit menu option in the footer
menu on the Delivery Items Screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Cancel Submit button on the Customer
Order Delivery Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Confirm Customer Order Pick
|
Customer Order
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Confirm Now menu option on the Pick Summary menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Confirm menu option in the footer menu on
the Pick Items Screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Confirm button on the Customer Order
Pick List Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Confirm Customer Order Reverse Pick
|
Customer Order
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Confirm button on the Customer Order Reverse Pick Detail screen is displayed
and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Create Customer Order Delivery For Pickup
|
Customer Order
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Create Delivery menu option on the Deliver Cust Order menu is displayed. In
addition, the option will only be available for orders with a Reservation
Type 'Web Orders' and Delivery Type 'Pickup'.
Without this permission, the option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Create button on the Delivery List screen
is displayed. In addition, the button will only be available for orders with
a Delivery Type 'Pickup'.
Without this permission, the menu is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Create button on the Customer Order
Delivery List screen is displayed and enabled. In addition, the button will
only be available for orders with a Reservation Type 'Web Orders' and
Delivery Type 'Pickup'.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Create Customer Order Delivery for
Shipment
|
Customer Order
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Create Delivery menu option on the Deliver Cust Order menu is displayed. In
addition, the option will only be available for orders with a Reservation
Type 'Web Orders' and Delivery Type 'Shipment'.
Without this permission the option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Create button on the Delivery List screen
is displayed. In addition, the button will only be available for orders with
a Reservation Type 'Web Orders' and Delivery Type 'Shipment'.
Without this permission, the menu is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Create button on the Customer Order
Delivery List screen is displayed and enabled. In addition, the button will
only be available for orders with a Reservation Type 'Web Orders' and
Delivery Type 'Shipment'.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Create Customer Order Pick
|
Customer Order
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Create Pick menu option on the Customer Order Pick menu is displayed.
Without this permission the option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Create button on the Pick List Screen is
displayed and enabled. Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Pick menu option in the footer menu on the
Cust Order Items Screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Create button on the Customer Order Pick
List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Create Customer Order Reverse Pick
|
Customer Order
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Create button on the Customer Order Reverse Pick List screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete Customer Order Delivery
|
Customer Order
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Delete Delivery menu option on the Delivery Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Delete menu option in the footer menu on
the Delivery Items Screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Delete button on the Customer Order
Delivery List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete Customer Order Pick
|
Customer Order
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Delete Pick menu option on the Pick Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Delete menu option in the footer menu on
the Pick Items Screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Delete button on the Customer Order Pick
List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete Customer Order Reverse Pick
|
Customer Order
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Delete button on the Customer Order Reverse Pick List screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Dispatch Customer Order Delivery
|
Customer Order
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Dispatch Now menu option on the Delivery Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Dispatch menu option in the footer menu on
the Delivery Items Screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Dispatch button on the Customer Order
Delivery Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Dispatch Incomplete Customer Order
Delivery
|
Customer Order
|
On the HH, with this permission, when the
Dispatch Now has been selected on the Delivery Summary screen and the
customer order is incomplete a warning message is displayed to the user and
allowed to cancel or continue.
Without this permission, when the Dispatch Now has been selected on the
Delivery Summary screen when the customer order is incomplete, an error
message is displayed to the user and the user cannot continue.
On MAF, with this permission, when the Dispatch menu option on the Delivery
Items screen has been selected and the customer order is incomplete, a
warning message is displayed to the user and allowed to cancel or continue.
Without this permission, when the Dispatch menu option has been selected on
the Delivery Items, an error message is displayed and the user cannot
continue.
On the PC, with this permission, when the Dispatch button on the Customer
Order Delivery Detail screen has been selected and the customer order is
incomplete, a warning message is displayed to the user and allowed to cancel
or continue.
Without this permission, when the Dispatch button has been selected on the
Delivery Summary screen when the customer order is incomplete, an error
message is displayed to the user and the user cannot continue.
|
|
Edit Customer Order BOL
|
Customer Order
|
On MAF, with this permission, the Edit
Delivery menu option in the footer menu on the Delivery Items screen is
displayed.
Without this permission, the menu is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the BOL Detail screen will open in Edit
mode. In addition, the View Customer Order BOL permission is required to gain
access to the screen.
Without this permission, the BOL Detail screen is View-only.
|
|
Edit Customer Order Delivery Attribute
|
Customer Order
|
On MAF, with this permission, the Add
Attributes button and Remove Attributes (Trash can) on the Attributes screen
of the Item Detail screen are displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button and trash can are not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Apply, Add, Remove and Cancel buttons on
the Extended Attribute Data Entry screen are displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the buttons are not displayed.
|
|
Edit Customer Order Delivery For Pickup
|
Customer Order
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Edit
Delivery menu option on the Deliver Cust Order menu is displayed. In
addition, the option will only be available for orders with a Reservation
Type 'Web Orders' and Delivery Type 'Pickup'.
Without this permission, the option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, when a user selects on an existing Customer
Order Delivery record, the Delivery Items screen and Item Detail screen will
be editable. In addition, only the orders with a Delivery Type ‘In Store
Pickup' will be editable.
Without this permission, the screen will open in View-only mode.
On the PC, with this permission, when a user double-clicks on an existing
Customer Order Delivery record, the Customer Order Delivery Detail screen
will open. In addition, only the orders with a Reservation Type 'Web Orders'
and Delivery Type 'Pickup' will be editable.
Without this permission, the screen will open in View-only mode.
|
|
Edit Customer Order Delivery For Shipment
|
Customer Order
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Edit
Delivery menu option on the Deliver Cust Order menu is displayed. In
addition, the option will only be available for orders with a Reservation
Type 'Web Orders' and Delivery Type 'Shipment'.
Without this permission, the option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, when a user selects on an existing Customer
Order Delivery record, the Delivery Items screen and Item Detail screen will
be editable. In addition, only the orders with a Delivery Type 'Ship to
Customer' will be editable.
Without this permission, the screen will open in View-only mode.
On the PC, with this permission, when a user double-clicks on an existing
Customer Order Delivery record, the Customer Order Delivery Detail screen
will open. In addition, only the orders with a Reservation Type 'Web Orders'
and Delivery Type 'Shipment' will be editable.
Without this permission, the screen will open in View-only mode.
|
|
Edit Customer Order Pick
|
Customer Order
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Review Pick menu option on the Pick Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, when the user selects a Customer Order Pick,
the Pick Items screen and the Item Details screen will open in edit mode.
Without this permission, the screens will open in a view-only mode.
On the PC, with this permission, when a user double-clicks on an existing
Customer Order Pick record, the Customer Order Pick Detail screen will open
in an edit mode.
Without this permission, the screen will open in View-only mode.
|
|
Edit Customer Order Reverse Pick
|
Customer Order
|
On the PC, with this permission, when a
user double-clicks on an existing Customer Order Reverse Pick record, the
Customer Order Reverse Pick Detail screen will open in edit mode.
Without this permission, the screen will open in View-only mode.
|
|
Edit Quantity Deliveries
|
Customer Order
|
On MAF, with this permission, the
Delivery quantity field and quantity widget on the Item Detail screen is
enabled.
Without this permission, the field and quantity widget is not enabled and
only scanning is allowed.
|
|
Edit Quantity Picking
|
Customer Order
|
On MAF, with this permission, the Picking
quantity field and quantity widget on the Item Detail screen is enabled.
Without this permission, the field and quantity widget is not enabled and
only scanning is allowed.
|
|
Item Substitution For Picking
|
Customer Order
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Item
Substitution option on the Pick Detail screen is enabled.
Without this permission, the option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Item Substitution menu option in the footer
menu on the Item Detail Screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Item Substitution button on the Customer
Order Pick Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Reject Customer Order
|
Customer Order
|
On MAF, with this permission, the Reject
menu option in the footer menu on the Cust Order Items Screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Reject button on the Customer Order
Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Submit Customer Order Delivery
|
Customer Order
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Submit menu option on the Delivery Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Submit menu option in the footer menu on
the Delivery Items Screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Submit button on the Customer Order
Delivery Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
View Customer Order BOL
|
Customer Order
|
On MAF, with this permission, the BOL
Info menu option in the footer menu on the Delivery Items Screen is
displayed.
Without this permission, the menu is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the BOL button on the Customer Order
Delivery Detail screen is displayed and enabled. The BOL Detail screen will
open in View-only mode.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Adjust Container DSD Receiving
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Adjust menu option on the Container Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Adjust button on the DSD Receiving
Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Confirm Container DSD Receiving
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Confirm menu option on the Container Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Confirm button on the DSD Receiving
Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Confirm DSD Receipt
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Confirm menu option on the Receipt Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Confirm button on the DSD Receiving Detail
screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Create Container
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Create Container menu option on the Receipt Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Create Container button on the DSD
Receiving Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Customer Order
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Customer Orders button on the DSD Receiving Detail screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Default Qty in All Containers
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Default Qty menu option on the Receipt Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Default Qty button on the DSD Receiving
Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Default Qty in Container
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Default Qty menu option on the Receipt Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Default Qty button and the Clear Qty
button on the DSD Receiving Detail Container screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Delete Container
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Delete Container menu option on the Container Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Delete button on the DSD Receiving
Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Delete Receipt
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Delete Receipt menu option on the Receipt Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Delete Delivery button on the DSD
Receiving Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Document DSD Receiving
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Document button on the DSD Receiving Container Detail screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access DSD Receiving
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the DSD
Receiving menu option on the Shipping/Receiving screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the DSD Receiving button on the
Shipping/Receiving screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access DSD Receiving Ext. Attribute
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Add
Ext Attribute menu option on the Container Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Ext. Attributes button on the DSD
Receiving Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Item Receiving
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Item
Receiving menu option on the Container Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Access Purchase Order
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Purchase Order menu option on the DSD Receiving screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Purchase Order button on the
Shipping/Receiving screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Reject Delivery
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Reject Delivery menu option on the Receipt Summary screen is displayed. The
menu option is only displayed when applying an ASN to a delivery.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Reject Delivery button on the DSD
Receiving Detail screen is displayed and enable. The button is only displayed
when applying an ASN to a delivery.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Remove Item DSD Receiving
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Remove Item menu option on the Container Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Remove Item button on the DSD Receiving
Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Review Items
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Review Item menu option on the Container Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Add New Item DSD Receiving
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Add
New Item menu option on the Container Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed. An item can
always be added when creating a receipt on the fly.
On the PC, with this permission, an item can be added to the transaction.
Without this permission, an item cannot be added to the transaction from the
DSD Receiving Container Detail screen or Advanced Item Entry screen. An Item
can always be added when creating a receipt on the fly.
|
|
Allow DSD Receiving Without PO
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Create Receipt menu option on the DSD Receiving screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Create Receipt menu option on the DSD
Receiving List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Allow DSD Receiving With PO
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Create Receipt menu option on the PO Detail screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Create Receipt button on the Purchase
Order Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Allow Over Receiving for DSD Receiving
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the user
is allowed to over-receive quantities for a DSD Receipt.
Without this permission, the user is not allowed to over-receive quantities
and a message is displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the user is allowed to over-receive
quantities.
Without this permission, the user is not allowed to over-receive quantities
and will be prompted when damaged and received quantity is larger than the
expected quantity.
|
|
Allow Receiving Damages
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Record Damages menu option on the Container Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the damaged column on the DSD Receiving
Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the damaged column is not displayed.
|
|
Display Expected Quantity
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
expected quantity on the Item Detail screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the quantity is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the expected quantity column on the DSD
Receiving Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the column is not displayed.
|
|
Edit Container
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Edit
Container menu option on the Receipt Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, when the user double-clicks on an existing
Container in the DSD Receiving Detail screen, the DSD Receiving Container
Detail screen will open in edit mode.
Without this permission, the screen will open in view-only mode.
|
|
Edit Container Info
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Additional Details option on the Container Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Container Info screen will open in edit
mode.
Without this permission, the screen will open in view-only mode.
|
|
Edit Delivery Info
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Additional Details menu option on the Receipt Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Direct Delivery Info screen will open in
edit mode.
Without this permission, the screen will open in view-only mode.
|
|
Edit DSD Receiving
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the PC, with this permission, when the
user double-clicks on an existing Receipt in the DSD Receiving List screen,
the DSD Receiving Detail screen will open in edit mode.
Without this permission, the screen will open in view-only mode.
|
|
Edit DSD Receiving Ext. Attribute
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Apply, Add Attributes, Remove Attributes and Cancel buttons on the Extended
Attributes Entry screen are displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the Close button is displayed and enabled.
|
|
Override Supplier Discrepancies
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the user
can override the supplier discrepancies check during the DSD receipt.
Without this permission, the message “Quantity received is larger than
expected, reduce the quantity received” is displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the user can override the supplier
discrepancies check during the direct delivery receipt.
Without this permission, the message “Quantity received is larger than
expected, reduce the quantity received” is displayed.
|
|
Receive Direct Delivery on Shop Floor
|
DSD Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Receive on Shop Floor prompt on the DSD Receiving Detail screen will be
displayed.
Without this permission the prompt is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Receive on Shop Floor check box on the
DSD Container Info screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the check box is not enabled.
|
|
Email Alert - Customer Order Pick
Reminder
|
Email
|
With this permission, the user will be
notified, if the pick list has been created but not actioned.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Email Alert - Customer Order Receipt
|
Email
|
With this permission, the user will be
notified when customer orders are received.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Email Alert - Customer Order Reminder
|
Email
|
With this permission, the user will be
notified when the customer order has not been fulfilled.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Email Alert – Damaged Delivery
|
Email
|
With this permission, the user will be
notified when the delivery includes damaged items.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Email Alert – Finisher Delivery Unable to
Auto-Receive
|
Email
|
With this permission, the user will be
notified when the finisher delivery UIN qty discrepancy exists on an incoming
ASN during batch processing.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Email Alert – Finisher UIN Discrepancy
|
Email
|
With this permission, the user will be
notified when a finisher return received quantity does not match the number
of serial numbers on the return.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Email Alert – Misdirected Container
|
Email
|
With this permission, the user will be
notified when a container has been received in another location.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Email Alert - New Customer Order
|
Email
|
With this permission, the user will be
notified when customer orders are created.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Email Alert – Over Received Quantity
|
Email
|
With this permission, the user will be
notified when the number of pre-populated serial numbers exceeds the received
quantity.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Email Alert – Receiving UIN Discrepancy
|
Email
|
With this permission, the user will be
notified when the number of pre-populated serial numbers does not match the
received quantity.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Email Alert –RTV Request Expiration
Approaching
|
Email
|
With this permission, the user will be
notified if the supplier return request expiration date is approaching.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Email
Alert – RTV Unavailable request quantity
|
Email
|
With
this permission, the user will be notified if there is not enough inventory
in the unavailable bucket to send back to supplier from a return request.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Email
Alert – Shipped Delivery Overdue
|
Email
|
With
this permission, the user will be notified when the shipped delivery has not
been received and has passed the expected date.
Without this permission, the will not be notified.
|
|
Email
Alert – Store Delivery Unable to Auto-Receive
|
Email
|
With
this permission, the user will be notified when a store delivery has
discrepancies and cannot be auto received.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Email
Alert – Store Receiving Over/Under
|
Email
|
With
this permission, the user will be notified when a store transfer has
over/under received quantities.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Email
Alert - Transfer Request
|
Email
|
With
this permission, the user will be notified when a transfer request is
created.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Email
Alert – Transfer Request Approved
|
Email
|
With
this permission, the user will be notified when a transfer request is
approved.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Email
Alert – Transfer Request Expiration Approaching
|
Email
|
With
this permission, the user will be notified when a transfer request has not
been approved and the request is about to expire. This is based on the not
after date set.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Email
Alert – Transfer Request Rejected
|
Email
|
With
this permission, the user will be notified when a transfer request is
rejected.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Email
Alert – Transfer Unavailable Request Quantity
|
Email
|
With
this permission, the user will be notified when the requested quantity is no
longer available at the requested source location.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Email
Alert – UIN Items on Incoming ASN Failed
|
Email
|
With
this permission, the user will be notified if an Auto Generated SN item is on
the ASN with pre-generated numbers when processing thru the RIB.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Email
Alert - Unexpected UIN (Store Changed)
|
Email
|
With
this permission, the user will be notified when UINs are discovered at a
store where they should not be.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Email
Alert – Warehouse Delivery Unable to Auto-Receive
|
Email
|
With
this permission, the user will be notified when the delivery includes
pre-populated serial numbers and cannot be automatically received.
Without this permission, the user will not be notified.
|
|
Access
Notifications
|
Home
Page
|
On
MAF, with this permission, the bell notification icon will be enabled.
Without this permission, it will be disabled.
|
|
Send
Notification
|
Home
Page
|
On
MAF, with this permission, the user will be able to swipe an open transaction
and send a notification.
Without this permission, the notify function will not be available.
|
|
View
Transactions
|
Home
Page
|
On
MAF, with this permission, the user will be able to view all of the open
transactions on the home page (depending on data permissions).
Without this permission, the home page will still display (just without the
transactions listed) allowing for changing the store and the access to
notifications; however the list of open transactions will be empty.
|
|
Access
Inventory Adjustment
|
Inventory
Adjustments
|
On
the HH, with this permission, the Inventory Adjustments menu option on the
Inv. Management menu is displayed.
Without this permission the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Inventory Adjustment menu option will
display in the Drawer.
Without this permission, the menu option will not display.
On the PC, with this permission, the Inventory Adjustment button on the
Inventory Management screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access
Inventory Adjustment Attribute
|
Inventory
Adjustments
|
On
the HH, with this permission, the Add Ext Attribute menu option on the
Inventory Adj. Summary menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Attributes screen on the Inventory
Adjustment Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the Attributes screen is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Ext. Attributes button on the Inventory
Adjustment Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Complete
Inventory Adjustment
|
Inventory
Adjustments
|
On
the HH, with this permission, the Confirm Now menu option on the Inventory
Adjustment Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed. The Confirm Later
menu option will be available to save the transaction.
On MAF, User must have this permission in order for the Confirm action to
appear on the footer menu on the Inventory Adjustment Detail Screen.
Without this permission, the user will not be able to confirm the
transaction, but only be able to Save the transaction.
On the PC, with this permission, the Confirm button on the Inventory
Adjustment Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed. The Save button will be
enabled to save the transaction.
|
|
Create
Inventory Adjustment
|
Inventory
Adjustments
|
On
the PC, with this permission, the Create button on the Inventory Adjustment
List Screen will be displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button will not be displayed.
On MAF, the permission must exist in order for the Copy action to be
available to the user. This action is available in the footer menu and allows
the user to copy ‘Completed’ adjustments.
On the PC, with this permission, the Create button on the Inventory
Adjustment List screen is displayed and enabled. The Copy button is also
enabled with this permission when the user is copying completed adjustments.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete
Inventory Adjustment
|
Inventory
Adjustments
|
On
the HH, with this permission, the Delete Inv. Adj. menu option on the
Inventory Adj. Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Delete menu option in the footer menu on
the Inventory Adjustment List screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Delete button on the Inventory
Adjustment List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Edit Inventory Adjustment
|
Inventory Adjustments
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Edit
Inv. Adj. menu option in the Inventory Adj. menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, when the user selects an inventory adjustment
it will be editable and the user is allowed to make changes.
Without this permission, the inventory adjustment is view only.
On the PC, with this permission, when the user double-clicks on an existing
Inventory Adjustment in the Inventory Adjustment List screen, the Inventory
Adjustment Detail is editable.
Without this permission, the screen will open in View-only mode.
|
|
Edit Inventory Adjustment Attribute
|
Inventory Adjustments
|
On MAF, with this permission, Attributes
can be added/removed: The Add Attributes and Remove Attributes (Trash can)
buttons will be available on the Attributes screen of the Inventory
Adjustment Detail.
Without this permission, attributes cannot be added or removed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Apply, Add Attributes, Remove Attributes
and Cancel buttons on the Extended Attributes Entry screen are displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the Close button is displayed and enabled.
|
|
Edit Quantity
|
Inventory Adjustments
|
On MAF, with this permission, the user
will be able to tap on the item quantity and the quantity widget will open to
edit the quantity.
Without this permission, the quantity is not editable and only scanning is
allowed.
|
|
Access Item Basket
|
Item Basket
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Item
Basket menu option on the Inv. Management menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Add Item to Item Basket
|
Item Basket
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Add
Item option on the Item Basket summary menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Create Item Basket
|
Item Basket
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Create Item Basket menu option on the Item Basket menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Delete Item Basket
|
Item Basket
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Delete Item Basket option on the Item Basket summary menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Delete Item from Item Basket
|
Item Basket
|
On the HH, with this permission the
Delete Item option on the Item Basket summary menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Print Item Basket
|
Item Basket
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Print Ticket option on the Item Basket summary is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Save Item Basket
|
Item Basket
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Save
Basket option on the Item Basket summary is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Access Item Request
|
Item Requests
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Item
Requests menu option on the Inv. Management menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Item Request button on the Inventory
Management screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Add Items To Item Request
|
Item Requests
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Add/Edit Item menu option on the Item Requests Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
This permission does not apply when creating an Item Request. Add/Edit Item
menu is always available when creating.
On the PC, with this permission and the Edit Item Requests permission, the
Add Item button on the Item Request Detail Screen is displayed and enabled
when editing an existing Item Request.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
This permission does not apply when creating an Item Request. Add Item
button is always available when creating.
|
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Add/Edit Item menu option on the Item Requests Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission the menu option is not displayed when editing an Item
Request.
On the HH, with this permission, the message “Item is not on the request.
Would you like to add it?” and the Yes and No menu options are displayed.
Without this permission, the message screen is not displayed. This permission
does not apply when creating an item request. Users will always be able to
add and edit items when creating an item request.
On the PC, with this permission and the Edit Item Requests permission, the
Add Item button on the Item Request Detail screen is displayed and enabled
when editing an existing Item Request.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed. This permission does
not apply when creating an Item Request. Add Item button will always be
available when creating.
|
|
Create Item Request
|
Item Requests
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Create Item Request menu option on the Item Requests menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Create button on the Item Request List
screen is displayed and enabled. The Add Items button will also be enabled on
the Item Request Detail screen.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete Item Request
|
Item Requests
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Delete Item Request menu option on the Item Requests menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Delete button on the Item Request List
screen is displayed and enabled. Without this permission, the button is not
displayed.
With this permission, the Item Remove button on the Item Request Detail
screen is displayed and enabled. Without this permission, the button is not
displayed.
|
|
Edit Item Request
|
Item Requests
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Edit
Item Request menu option on the Item Requests menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, when the user double clicks on an existing
Item Request in the Item Request List screen, the Item Request Detail screen
will open in edit mode.
Without this permission, the screen will open in View-only mode.
|
|
Request Items
|
Item Requests
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Request Item Request menu option on the Item Requests menu is displayed.
Without this permission the menu option is not displayed.
On the HH, with this permission, the Request Now menu option on the Item
Requests Summary screen is displayed. Without this permission the menu option
is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Request button on the Item Request
Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Item Ticket
|
Item Tickets
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Ticket Printing menu option on the Main menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Item Ticket button on the Print Menu
screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Item Ticket Batch
|
Item Tickets
|
On the PC, with this permission, the Item
Ticket Batch button in the Print Menu screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Item Ticket Price Override
|
Item Tickets
|
On the HH, with this permission the
Ticketing Price Override menu is displayed and the user can override the
price on the Ticket Detail screen.
Without this permission, the menu is not displayed and the user cannot
override the price.
|
|
Create Item Ticket
|
Item Tickets
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Create button on the Item Tickets List screen and the Add Ticket button on
the Item Ticket Batch Detail screen are displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the buttons are not displayed.
|
|
Create Item Ticket Batch
|
Item Tickets
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Create Batch button on the Item Ticket Batch List screen and Generate Tickets
button on the Add Transaction screen are displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete Item Ticket
|
Item Tickets
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Delete button on the Item Tickets List, Item Ticket Batch List screens and
the Remove Ticket button on the Item Ticket Batch Detail screens are
displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the buttons are not displayed.
|
|
Edit Item Ticket
|
Item Tickets
|
On the PC, with this permission, when the
user double clicks on an existing Item Ticket in the Item Ticket List or Item
Ticket Batch Detail screen, the Item Ticket Detail screen will open in edit
mode.
On the PC, with this permission, when the user double clicks on an existing
item ticket batch on the Item Ticket Batch List screen, the Item Ticket Batch
Detail screen will open in edit mode.
Without this permission, the screens will open in View-only mode.
|
|
Print Item Tickets
|
Item Tickets
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Print Tickets button on the Item Ticket List, Item Ticket Detail, Item Ticket
Batch List and Item Ticket Batch Detail screens are displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Update Format Item Ticket
|
Item Tickets
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Update Format button on the Item Ticket List, Item Tickets Batch List and
Item Ticket Batch Detail screens are displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the buttons are not displayed.
|
|
Update SOH Item Ticket
|
Item Tickets
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Refresh Qty button on the Item Tickets List, Item Ticket Batch List and Item
Ticket Batch Detail screens are displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the buttons are not displayed.
|
|
Access Price Change
|
Price Changes
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Price Change button on the Inventory Management screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Create Price Change
|
Price Changes
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Create button on the Price Change List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Print Item Tickets For Price Changes
|
Price Changes
|
On the PC, with this permission, the Item
Tickets button on the Price Change List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Print Shelf Labels For Price Changes
|
Price Changes
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Shelf Labels button on the Price Change List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Accept RTV
|
RTV
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Accept button on the RTV Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access RTV
|
RTV
|
On the PC, with this permission, the RTV
button on the Shipping/Receiving screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Add Items To RTV
|
RTV
|
On the PC, with this permission, an item
can be added to the transaction. on the RTV Detail screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the item cannot be added from the RTV Detail screen
or Advanced Item Entry screen. If the user is creating an RTV, the item can
be added to the transaction.
|
|
Approve RTV
|
RTV
|
On the PC, with this permission, the Approve
button on the RTV Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Close RTV
|
RTV
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Close RTV button on the RTV Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Create RTV
|
RTV
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Create RTV button on the RTV List Screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Remove Item
|
RTV
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Remove Item button on the RTV Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete RTV
|
RTV
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Delete button on the RTV Detail Screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Edit RTV
|
RTV
|
On the PC, with this permission, when the
user double-clicks on an existing RTV in the RTV List screen, the RTV Detail
screen will open in edit mode.
Without this permission, the screen will open in view-only mode.
|
|
Reject RTV
|
RTV
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Reject button on the RTV Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Shipment Create RTV
|
RTV
|
On the PC, with this permission, the Ship
button on the RTV Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access RTV Shipment
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the RTV
Shipment button on the Shipping/Receiving menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the RTV Shipment button on the
Shipping/Receiving screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access RTV Shipment Attribute
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Add
Ext Attribute menu option on the RTV Container Detail screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Ext. Attributes button on the RTV
shipment Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Add Items to RTV Shipment
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, an item
can be added to the transaction.
Without this permission, an item cannot be added. If the user is creating an
RTV, an item can always be added.
On the PC, with this permission, an item can be added to the transaction on
the RTV shipment Container Detail screen or Advanced Item Entry screen.
Without this permission, an item cannot be added to the transaction. If the
user is creating an RTV, an item can always be added.
|
|
Allow Non Document Items RTV Shipment
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the user
is allowed to add items not existing on the RTV selected.
Without this permission, the user can only ship items already existing on the
RTV document.
On the PC, with this permission, the user is allowed to add items not
existing on the RTV selected.
Without this permission, the user can only ship items already existing on the
RTV document.
|
|
Allow over shipping RTV Shipment
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the user
is allowed to ship more products than approved on the RTV.
Without this permission, the user will not be allowed to overship.
On the PC, with this permission, the user is allowed to ship more products
than approved on the RTV.
Without this permission, the user will not be allowed to overship.
|
|
Cancel Submit RTV Shipment
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Cancel Submit menu option on the RTV Shipment Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Cancel Submit button on the RTV shipment
Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Confirm RTV Shipment Container
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Confirm Container menu option on the RTV shipment Container Summary screen is
displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Confirm button on the RTV shipment
Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Create RTV Shipment
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Create menu option on the RTV Shipment menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Create button on the RTV Shipment List
screen and the Add Item button on the RTV Shipment Detail screen is displayed
and enabled.
Without this permission, the buttons are not displayed.
|
|
Create RTV Shipment Container
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Add
Container menu option on the RTV Shipment Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Create Container button on the RTV
Shipment Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Default Items to RTV Shipment
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Default Item menu option on the RTV Shipment menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Default Item button on the RTV shipment
Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Remove Item
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Delete Item menu option on the RTV shipment Container Summary screen is
displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Remove Item button on the RTV shipment
Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Delete RTV Shipment
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Delete option on the RTV Shipment Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Delete button on the RTV Shipment Detail
screen is displayed and enabled.
Without the permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete RTV Shipment Container
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Delete container menu option on the RTV shipment Container Summary screen is
displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Delete button on the RTV shipment
Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Dispatch RTV Shipment
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Dispatch Now menu option on the RTV Shipment Summary menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Dispatch button on the RTV Shipment
Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Edit Container RTV Shipment
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Edit
Container menu option on the RTV Shipment Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, when the user double-clicks on an existing
container on the RTV Shipment Detail screen, the RTV Shipment Container
Detail screen will open in edit mode.
Without this permission, the screen will open in view-only mode.
|
|
Edit RTV Shipment
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Edit
menu option on the RTV Shipment screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, when the user double-clicks on an existing
RTV Shipment on the RTV Shipment List screen, the RTV Shipment Detail screen
will open in edit mode.
Without this permission, the screen will open in view-only mode.
|
|
Edit RTV Shipment Attribute
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Apply, Add, Remove and Cancel buttons on the Extended Attribute Entry screen
is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the buttons are not displayed.
|
|
Edit RTV Shipment BOL
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the PC, with this permission, the BOL
button on the RTV Shipment Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Edit RTV Shipment Info
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Additional Details menu option on the RTV Shipment Summary screen is
displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Info button on the RTV Shipment Detail
screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Edit RTV Container Info
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Additional Details menu option on the RTV Container Summary screen is
displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Info button on the RTV Shipment
Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Adjust Container RTV Shipment
|
RTV Shipment
|
With this permission, the Adjust
Container menu option on the RTV shipment Container Summary screen is
displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Open button on the RTV Shipment
Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Review Container RTV Shipment
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Review Container menu option on the RTV Container Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Submit RTV Shipment
|
RTV Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Submit menu option on the RTV Shipment Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Submit button on the RTV Shipment Detail
screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Role Maintenance
|
Security
|
On the PC, with this permission, the Role
Maintenance button on the Security menu is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Security
|
Security
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Security button on the Admin menu is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access User Maintenance
|
Security
|
On the PC, with this permission, the User
Maintenance button on the Security menu is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Assign Password
|
Security
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Assign Password button on the User Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Assign User Group
|
Security
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Assign Group button on the User Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Assign User Role
|
Security
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Assign Roles button on the User Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Assign User Store
|
Security
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Assign Stores button on the User Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Create User
|
Security
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Create button on the User List is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete Role
|
Security
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Delete button on the Role List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete User
|
Security
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Delete button on the User List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Edit User
|
Security
|
On the PC, with this permission, when the
user double-clicks on an existing user in the User List screen, the User
Detail screen will open in edit mode.
Without this permission, the User Detail screen will open in view-only mode.
|
|
Mass Assign User Role
|
Security
|
On the PC, with this permission, the Mass
Assign Roles button on the Security menu is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Mass Assign User Store
|
Security
|
On the PC, with this permission, the Mass
Assign Stores button on the Security menu is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Sequencing
|
Sequencing
|
On the HH, with this permission the
Sequencing menu option on the Inv. Management menu is displayed.
Without this permission the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Sequencing button on the Inventory
Management menu is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Add Item to Location
|
Sequencing
|
On the PC, with this permission, an item
can be added to the transaction.
Without this permission, an item cannot be added from the Micro Sequence Edit
screen or Advanced Item Entry screen.
|
|
Add Locations For An Item
|
Sequencing
|
On the PC, with this permission, the Add
Location button on the Item Locations List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Add Sequencing Locations
|
Sequencing
|
On the PC, with this permission, the Add
Location button on the Macro Sequence Edit screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Apply Class List To Location
|
Sequencing
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Apply Class List button on the Macro Sequence Edit screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Apply Item List to Location
|
Sequencing
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Apply Item List button on the Micro Sequence Edit screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Arrange Items Within Location
|
Sequencing
|
On the PC, with this permission, the Move
Up and Move Down buttons on the Micro Sequence Edit screen are displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the buttons are not displayed.
|
|
Arrange Sequencing Locations
|
Sequencing
|
On the PC, with this permission, the Move
Up and Move Down buttons on the Macro Sequence Edit screen are displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the buttons are not displayed.
|
|
Delete Items from a Location
|
Sequencing
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Remove Item button on the Micro Sequence Edit screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, this button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete Locations For An Item
|
Sequencing
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Remove Item button on the Item Location List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete Sequencing Locations
|
Sequencing
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Remove Item button on the Macro Sequence Edit screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Edit Items Within A Location
|
Sequencing
|
On the PC, with this permission, when the
user double- clicks on an existing Sequencing Location in the Macro Sequence
List screen, the Micro Sequence List screen will open in edit mode.
Without this permission, the Micro Sequence List screen will open in
view-only mode.
On the PC, with this permission, when the user double-clicks on an existing
Item in the Micro Sequence List screen, the Item Location List screen will
open in edit mode. Without this permission, the Micro Sequence List screen
will open in view-only mode.
On the PC, with this permission, the Edit Items button on the Micro Sequence
List screen is displayed and enabled. Without this permission, the button is
not displayed.
|
|
Edit Sequencing Locations
|
Sequencing
|
On the PC, with this permission, the Edit
Locations button on the Macro Sequence List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Sequence Items
|
Sequencing
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Sequence Item menu option on the Sequencing menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Sequence Items Within A Location
|
Sequencing
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Sequence all items in a location menu option on the Sequencing menu is
displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Access Shelf Adjustment
|
Shelf Replenishment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Shelf Adjustment menu option on the Shelf Replenishment menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Create Shelf Adjustment
|
Shelf Replenishment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Create menu option on the Shopfloor Adjust, Backroom Adjust, Display List and
Ad Hoc Replenish menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Access Shelf Replenishment
|
Shelf Replenishment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Shelf Replenishment menu option on the Inv. Management menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Shelf Replenishment button on the
Inventory Management menu is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Action Shelf Replenishment
|
Shelf Replenishment
|
On the HH, with this permission the
Action Shelf Replen menu option on the Shelf Replenishment menu is displayed.
Without this permission the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Create
Shelf Replenishment
|
Shelf
Replenishment
|
On
the HH, with this permission, the Within Day and the End Of Day menu options
on the Shelf Replenishment menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu options is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Create button on the Shelf Replenishment
List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete
Shelf Replenishment
|
Shelf
Replenishment
|
On
the PC, with this permission, the Delete button on the Shelf Replenishment
screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Replenishment
Item Substitution
|
Shelf
Replenishment
|
On
the HH, with this permission, the Item Substitution option on the Pick Detail
screen is enabled.
Without this permission, the option is not displayed.
Note: This permission only applies when the user has selected to allow item
substitution when prompted.
On the PC, with this permission, the Allow Substitute Item check box on the
Shelf Replenishment Create screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the check box is not enabled.
|
|
Access
Adhoc Stock Counts
|
Stock
Counts
|
On
the HH, with this permission, the Ad Hoc Stock Count menu option on the Stock
Counting menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Access
Stock Count
|
Stock
Counts
|
On
the HH, with this permission the Stock Counts menu option on the Inv.
Management menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Stock Count menu option will appear in the
drawer.
Without this permission, the menu option will not be displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Stock Counts button on the Inventory
Management menu is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access
Stock Count Attribute
|
Stock
Counts
|
On
the HH, with this permission, the Add Ext Attribute menu option on the Stock
Counting menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Attribute screen on the Item Details screen
is displayed.
Without this permission, the screen is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Ext. Attributes button on the Stock
Count Detail and Stock Re-count Detail screen are displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Amend
Stock Count
|
Stock
Counts
|
On
the HH, with this permission, the <amend> option (or Shift-5 function)
on the Stock Counting screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the option is not displayed and the Shift-5 function
is not available.
|
|
Amend
Stock Recount
|
Stock
Counts
|
On
the HH, with this permission, the <amend> option (or Shift-5 function)
for stock re-counts is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the option is not displayed and the Shift-5 function
is not available.
|
|
Authorize
Stock Count
|
Stock
Counts
|
On
the PC, with this permission, the Authorize button on the Child Stock Count
List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Complete
Stock Count
|
Stock
Counts
|
On
the HH, with this permission, the Complete Count menu option on the Stock
Counting menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Complete menu option in the footer
menu of the Stock Count Items and Stock Re-count Items screen is
available.
Without this permission, the menu option is not available.
On the PC, with this permission, the Complete button on the Child Stock Count
List, the Stock Count Detail and the Stock Re-Count Detail Screens is
displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Confirm
Authorization Stock Count
|
Stock
Counts
|
On
the PC, with this permission, the Confirm Authorization button on the Child
Stock Count List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Confirm
Child Stock Count
|
Stock
Counts
|
On
the PC, with this permission, the Confirm Child button on the Stock Count
Authorization screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Count
Stock Count
|
Stock
Counts
|
On
the HH, with this permission, the Stock Count menu option on the Stock
Counting menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Create
Adhoc Stock Count
|
Stock
Counts
|
On
the HH, with this permission, the Create New Count menu option on the Ad-Hoc
Stock Count menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Create Ad hoc button on the Stock Count
List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete Stock Count
|
Stock Counts
|
On MAF, with this permission, the Delete
menu option in the footer menu of the Child Count List screen is
available.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Delete button on the Stock Count List
screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Edit Adhoc Stock Count
|
Stock Counts
|
On MAF, with this
permission, when the user selects an Ad Hoc Stock Count in the
Stock Count List screen, the Child Count List screen will open in edit mode.
Without this permission, the screen will open in view-only mode.
On the PC, with this permission, when the user double-clicks on an existing
Ad Hoc Stock Count in the Stock Count List screen, the Child Stock Count List
screen will open in edit mode.
Without this permission, the Child Stock Count List screen will open in
view-only mode.
|
|
Edit Stock Count Attribute
|
Stock Counts
|
On MAF, with this permission, the Add
Attributes button and Remove Attributes (Trash can) on the Attributes screen
of the Item Detail screen are displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button and trash can are not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Apply, Add, Remove and Cancel button on
the Extended Attribute Entry screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Edit Quantity Stock Count
|
Stock Counts
|
On MAF, with this permission, the Qty
field and quantity widget on the Item Detail and Review Item screens are
enabled.
Without this permission, the Qty field and quantity widget is not
enabled and only scanning is allowed.
|
|
Edit Unit Amount Stock Count
|
Stock Counts
|
On MAF, with this
permission, when the user selects a Unit and Amount Stock Count in
the Stock Count List screen, the Child Count List screen will open in edit
mode.
Without this permission, the screen will open in view-only mode.
On the PC, with this permission, when the user double-clicks on an existing
Unit and Amount Stock Count in the Stock Count List screen, the Child Stock
Count List screen will open in edit mode.
Without this permission, the Child Stock Count List screen will open in
view-only mode.
|
|
Edit Unit Stock Count
|
Stock Counts
|
On MAF, with this
permission, when the user selects a Unit Stock Count in the
Stock Count List screen, the Child Count List screen will open in edit mode.
Without this permission, the screen will open in view-only mode.
On the PC, with this permission, when the user double-clicks on an existing
Unit Stock Count in the Stock Count List screen, the Child Stock Count List
screen will open in edit mode.
Without this permission, the Child Stock Count List screen will open in
view-only mode.
|
|
Recount Stock Count
|
Stock Counts
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Stock Re-Count menu option on the Stock Counting menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, when the user selects a stock count
in the Stock Count List screen and the stock count is in 'Recount'
status, the Recount Items screen will open in edit mode.
Without this permission, the screen will not be displayed.
|
|
Rejected Item Stock Count
|
Stock Counts
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Rejected Items button on the Child Stock Count List screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Save Child Stock Count
|
Stock Counts
|
On MAF, with this
permission, the Save button, Save menu option and Save &
Continue menu option on the Stock Count Items and Stock Re-count
Items screens are displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button and menu options are not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Save Child button on the Stock Count
Authorization screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Snapshot Stock Count
|
Stock Counts
|
On MAF, with this permission, the
Snapshot button on the Child Count List screens is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Take Snapshot button on the Child Stock
Count List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Snapshot Stock Count Child
|
Stock Counts
|
On MAF, with this
permission, the Snapshot button on the Stock Count Items screens is
displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Take Snapshot button on the Stock Count
Detail and the Stock Re-Count Detail screens is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Update Authorization Quantity Stock Count
|
Stock Counts
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Update Auth Qty button on the Child Stock Count List and the Stock Count
Authorization Screens is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Store Order
|
Store Orders
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Store Orders button on the Inventory Management screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Add Item Store Order
|
Store Orders
|
On the PC, with this permission, an item
can be added to the transaction.
Without this permission, an item cannot be added from the Store Order Detail
or Advanced Item Entry screen. An item can always be added when creating a
Store Order.
|
|
Approve Store Order
|
Store Orders
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Approve button on the Store Order Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Cancel Item Store Order
|
Store Orders
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Remove Item button on the Store Order Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Cancel Store Order
|
Store Orders
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Delete button on the Store Orders screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Create Store Order
|
Store Orders
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Create button on the Store Orders screen is displayed and enabled. The Add
Item button the Store Order Detail screen will also be enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Edit Store Order
|
Store Orders
|
On the PC, with this permission, when the
user double-clicks on an existing Store Order in the Store Orders screen, the
Store Detail screen will open in edit mode.
Without this permission, the Store Order Detail screen will open in view-only
mode
|
|
Access Templates
|
Templates
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Template button on the Inventory Adjustment List screen is displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Apply Templates
|
Templates
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Apply Template menu option on the Inventory Adj. menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the 'FromTemplate' option on the Create Inventory
Adjustment popup is displayed.
Without this permission, the option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Apply Template button on the Inventory
Adjustment Detail screen is displayed and enabled. The template dropdown and
multiplier is also enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete Templates
|
Templates
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Delete button on the Template List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Accept Transfer Request
|
Transfers
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Accept Request menu option on the Pick Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Accept button on the Transfer Detail
screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Accept Reject Request
|
Transfers
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Accept/Reject Tsf Request menu option on the Transfer menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Access Transfer
|
Transfers
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Transfers button on the Shipping/Receiving screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Transfer Context Field
|
Transfers
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Context Field menu option on the Request Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the HH, with this permission, the Enter Context Value is displayed when
the Context Type is PROM.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Context Type dropdown on the Transfer
Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the dropdown is not enabled.
On the PC, with this permission and the Context Type selected is PROM, the
Context Value field on the Transfer Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the field is not enabled.
|
|
Access Transfer Request
|
Transfers
|
On the HH, with this permission the Tsf
Request menu option on the Shipping/Receiving menu is displayed.
Without this permission the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Add Item To Transfer
|
Transfers
|
On the HH, with this permission, an item
can be added to the transaction.
Without this permission, an item cannot be added.
On the PC, with this permission, an item can be added to the transaction.
Without this permission, an item cannot be added thru the Transfer Detail
screen or Advanced Item Entry screen. An item can always be added when
creating a transfer.
|
|
Approve Transfer
|
Transfers
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Approve button on the Transfer Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Close Transfer
|
Transfers
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Close Transfer button on the Transfer Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Create Request
|
Transfers
|
On the HH, with this permission the
Create Tsf Request menu option on the Transfer menu is displayed.
Without this permission the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Create Request button on the Transfer
List screen is displayed and enabled. The Add Item button on the Transfer
Detail screen will also be enabled.
Without this permission, the buttons are not displayed.
|
|
Create Transfer
|
Transfers
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Create Transfer button on the Transfer List screen is displayed and enabled.
The Add Item button on the Transfer Detail screen will also be enabled.
Without this permission, the buttons are not displayed.
|
|
Remove Item
|
Transfers
|
On the HH, with this permission, when the
user enters a zero on the Request Review screen a confirmation message is
displayed.
Without this permission, an error message is displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Remove Item button on the Transfer
Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete Request
|
Transfers
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Delete Request menu option on the Request Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Delete Transfer
|
Transfers
|
On the PC, with this permission, the Delete
button on the Transfer Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Edit Transfer
|
Transfers
|
On the PC, with this permission, when the
user double-clicks on an existing Transfer in the Transfer List screen, the
Transfer Detail screen will open in edit mode.
Without this permission, the screen will open in view-only mode.
|
|
Edit Transfer Request
|
Transfers
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Edit
Tsf Request menu option on the Transfer menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, when the user double-clicks on an existing
Transfer Request in the Transfer List screen, the Transfer Detail screen will
open in edit mode.
Without this permission, the screen will open in view-only mode.
|
|
Reject Transfer Request
|
Transfers
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Reject Request menu option the Pick Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Reject button on the Transfer Detail
screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Request Transfer
|
Transfers
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Request Now menu option on the Request Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Request button on the Transfer Detail
screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Review Item
|
Transfers
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Review Item menu option on the Request Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
View Details
|
Transfers
|
On the HH, with this permission, the View
Details menu option on the Request Summary screen is displayed. Without this
permission the menu option is not displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Access Container Attribute
|
Transfer Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the Add
Ext Attribute menu option on the Container Summary menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Attributes screen on the Tsf Ship Item
Detail screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the Attributes screen is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Ext. Attributes button on the Transfer
Shipment Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Shipment
|
Transfer Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Transfer Shipment menu option on the Shipping/Receiving menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Transfer Shipment menu option will appear
in the drawer.
Without this permission, the Transfer Shipment option will not be displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Transfer Shipment button on the
Shipping/Receiving is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Add Items with No Document
|
Transfer Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the No
Document menu option on the Document Selection menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the No Document button on the Select Document
screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the No Document button on the Document
Selection screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not enabled.
|
|
Add Item to Transfer Shipment
|
Transfer Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, an item
can be added to the transaction.
Without this permission, an item cannot be added to the transaction.
On MAF, the permission must exist in order to Add Items on the Container
Items and Item Detail screens.
Without this permission, items cannot be added.
On the PC, with this permission, an item can be added to the transaction.
Without this permission, an item cannot be added from the Transfer Shipment
Container Detail screen or Advanced Item Entry screen.
|
|
Adjust Container
|
Transfer Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Adjust menu option on the Container Summary menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Adjust menu option in the footer menu on
the Container Items screen is available.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Adjust button on the Transfer Shipment
Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Cancel Submit Shipment
|
Transfer Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Cancel Submit menu option on the Shipment Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Cancel Submit menu option in the footer
menu of the Tsf Ship Containers screen is available.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Cancel Submit button on the Transfer
Shipment Detail screen are displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the buttons are not displayed.
|
|
Confirm Container
|
Transfer Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Confirm Container menu option on the Container Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Confirm menu option in the footer menu of
the Container Items screen is available.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Confirm button on the Transfer Shipment
Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Create Shipment
|
Transfer Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Create Shipment menu option on the Shipment Menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Create button on the Tsf Ship List screen
is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Create button on the Transfer Shipment
List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete Shipment
|
Transfer Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Delete Shipment menu option on the Shipment Summary menu, the Delete
Container on the Container Summary menu on the Container Detail menu is
displayed.
Without this permission the menu options are not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Delete menu option in the footer menu of
the Tsf Ship Containers screen is available.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Delete button on the Transfer Shipment
Detail and the Delete button on the Transfer Shipment Container Detail screen
are displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the buttons are not displayed.
|
|
Dispatch Shipment
|
Transfer Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Dispatch menu option on the Shipment Summary menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Dispatch menu option in the footer menu of
the Tsf Ship Containers screen is available.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Dispatch button on the Transfer Shipment
Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Edit Container
|
Transfer Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the user
can edit a container within a transfer shipment.
Without this permission, the container is view-only.
On MAF, with this permission, the user can edit a container within a transfer
shipment.
Without this permission, the container is view-only.
On the PC, with this permission, the user can edit a container within a
transfer shipment.
Without this permission, the container is view-only.
|
|
Edit Container Attribute
|
Transfer Shipment
|
On MAF, with this permission, extended
attributes can be added/removed: The Add Attributes and Remove
Attributes (Trash can) buttons will be available on the Attributes screen of
the Transfer Shipment Item Detail.
Without this permission, attributes cannot be added or removed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Apply, Add Attributes, Remove Attributes
and Cancel buttons on the Extended Attributes Entry screen are displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the Close button is displayed and enabled.
|
|
Edit Container Info
|
Transfer Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Additional Details menu option on the Container Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Edit Container menu option in the footer
menu on the Container Items screen is available.
Without this permission, the option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, when the user clicks the Info button on the
Transfer Shipment Container Detail screen, the Container Info screen will
open in edit mode.
Without this permission, the screen will open in view-only mode.
|
|
Edit Quantity Transfer Shipment
|
Transfer Shipment
|
On MAF, with this permission, the Shipped
Qty field and quantity widget on the Item Detail screen is enabled.
Without this permission, the Shipped Qty field and quantity widget is
not enabled and only scanning is allowed.
|
|
Edit Shipment
|
Transfer Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the user
is able to edit an existing transfer shipment.
Without this permission the shipment is view only.
On MAF, with this permission, the user is able to edit an existing transfer
shipment.
Without this permission, the transfer shipment is view-only.
On the PC, with this permission, with this permission, the user is able to
edit an existing transfer shipment.
Without this permission, the transfer shipment is view-only.
|
|
Edit Shipment BOL
|
Transfer Shipment
|
On MAF, with this permission, the user is
able to edit shipment carrier details on the Edit Shipment screen.
Without this permission, the carrier details are view only.
On the PC, with this permission, the Save button on the BOL Detail screen is
displayed and enabled. Additionally, the screen opens in edit mode.
Without this permission, the screen is view only.
|
|
Edit Shipment Info
|
Transfer Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Additional Details menu option on the Shipment Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the user is able to edit shipment authorization
details on the Edit Shipment screen for a shipment to a warehouse or
finisher.
Without this permission, the details are view only.
On the PC, with this permission, when the user clicks the Info button on the
Transfer Shipment Detail screen, the Shipment Info screen will open in edit
mode.
Without this permission, the screen will open in view-only mode.
|
|
Remove Item
|
Transfer Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Remove Item menu option on the Container Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, the permission must exist in order to Remove Items on the Container
Items and Item Detail screens.
Without this permission, items cannot be removed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Remove Item button on the Transfer
Shipment Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Review Item
|
Transfer Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Review Item menu option on the Container Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Select Container Document
|
Transfer Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the user
can toggle to access the Select Document screen from the Scan Item screen.
Without this permission, the toggle option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, when the user taps the Document on the Info Bar
of the Container Items screen, the user will navigate to the Select Document
screen.
Without this permission, the user will remain on the Container Items screen.
On the PC, with this permission, when the user clicks the Document button on
the Transfer Shipment Container Detail screen, the Document Selection screen
is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Submit Shipment
|
Transfer Shipment
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Submit menu option on the Shipment Summary menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Submit menu option in the footer menu on
the Tsf Ship Containers screen is available.
Without this permission, the option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Submit button on the Transfer Shipment
Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Quick Receiving
|
Transfer Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission the Quick
Receiving menu option on the Shipping/Receiving menu is displayed.
Without this permission the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Quick Receiving menu
option will appear in the drawer.
Without this permission, the Quick Receiving option will not display.
|
|
Access Transfer Receiving
|
Transfer Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Transfer Receiving menu option on the Shipping/Receiving screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Transfer Receiving menu
option will appear in the drawer.
Without this permission, the Transfer Receiving option will not display.
On the PC, with this permission, the Transfer Receiving button on the
Shipping/Receiving is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access Transfer Receiving Attribute
|
Transfer Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission and the
system parameter Enable Extended Attributes is set to Yes, the Add Ext Attrib
menu option on the Container Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option does not display.
On MAF, with this permission, the Attributes screen on the Tsf Rcv Item
Detail screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the Attributes screen is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission and the system parameter Enable Extended
Attributes is set to Yes, the Ext Attributes button is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Add Item to Transfer Receipt
|
Transfer Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the user
is allowed to add an unexpected item to a receipt. The system will prompt
the user to confirm.
Without this permission, the user is not allowed to add the item. The system
will prompt the user, the item is unexpected and cannot be received.
On MAF, this permission must exist in order to Add Items on the
Container Items and Item Detail screens.
Without this permission, the user cannot add items.
On the PC, with this permission, an item can be added to the transaction.
Without this permission, an item cannot be added to the Transfer Receiving
Container Detail screen or Advanced Item Entry screen.
|
|
Adjust Container
|
Transfer Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission and the
container status is ‘Received’, the Adjust menu option on the Container
Summary menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, this permission, the Adjust menu option in the footer menu on the
Container Items screen is available.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission and the container status is ‘Received’, the
Adjust button on the Transfer Receiving Container Detail screen is displayed
and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Confirm Container
|
Transfer Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Confirm menu option on the Container Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Confirm menu option in the footer menu
on the Container Items screen is available.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Confirm button on the Transfer Receiving
Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Confirm
Receipt
|
Transfer
Receiving
|
On
the HH, with this permission, the Confirm Receipt menu option on the Receipt
Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Confirm menu option in the footer menu on
the Tsf Rcv Containers screen is available.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Confirm button on the Transfer Receiving
Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Create
Container
|
Transfer
Receiving
|
On
the HH, with this permission, the Add Container menu option on the Receipt
Summary Menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Create menu option in the footer menu on
the Tsf Rcv Containers screen is available.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Create Container button on the Transfer
Receiving Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Default
Qty in All Containers
|
Transfer
Receiving
|
On
the HH, with this permission, the Default Qty menu option on the Receipt
Summary menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Default Qty button and Default Qty
menu option on the Tsf Rcv Containers screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button and menu option are not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the Default Qty button on the Transfer
Receiving Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Default
Quantity in Container
|
Transfer
Receiving
|
On
the HH, with this permission, the Default Qty menu option on the Container Summary
menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Default Qty and Clear Qty menu
option on the Container Items screen is available.
Without this permission, the menu options do not display.
On the PC, with this permission, the Default Qty button on the Transfer
Receiving Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Delete
Container
|
Transfer
Receiving
|
On
the HH, with this permission, the Delete Container menu option on the
Container Summary is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Delete menu option on the Container items
screen is available.
Without this permission, the menu option will not display.
On the PC, with this permission, the Delete Container button on the Transfer
Receiving Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
|
|
Display
Expected Qty
|
Transfer
Receiving
|
On
the HH, with this permission, the expected quantity will display on the Item
Receive screen.
Without this permission, the expected quantity will not be displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Expected Qty field and label will display
on the Container Items screen and Item Detail screen.
Without this permission, the field and label will not display.
On the PC, with this permission, the expected quantity will display on the
Transfer Receiving Container Detail screen.
Without this permission, the expected quantity will not be displayed.
|
|
Edit
Container
|
Transfer
Receiving
|
On
the HH, with this permission, the user is able to edit an existing container
for a transfer receipt.
Without this permission, the container is view only.
On MAF, with this permission, the user is able to edit an existing
container for a transfer receipt.
Without this permission, the container is view-only.
On the PC, with this permission, the user is able to edit an existing
container for a transfer receipt.
Without this permission, the container is view-only.
|
|
Edit
Container Info
|
Transfer
Receiving
|
On
the HH, with this permission, the Additional Details menu option on the
Container Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option will not display.
On MAF, with this permission, the Edit Container menu option on the Container
Items screen is available.
Without this permission, the menu option will not display.
On the PC, with this permission, when the user clicks the Info button on the
Transfer Receiving Detail screen, the Container Info screen will open in edit
mode.
Without this permission, the screen will open in view-only mode.
|
|
Edit
Quantity Transfer Receiving
|
Transfer
Receiving
|
On
MAF, with this permission, the Received Qty field, Damaged Qty and
Quantity widget field on the Item Detail screen is enabled.
Without this permission, the Received Qty, Damaged Qty fields and
Quantity widget is not be enabled and only scanning is allowed.
|
|
Edit
Receipt
|
Transfer
Receiving
|
On
MAF, with this permission, the user is able to edit an existing transfer
receipt.
Without this permission, the transfer receipt is view-only.
On the PC, with this permission, the user is able to edit an existing
transfer receipt.
Without this permission, the transfer receipt is view-only.
|
|
Edit Receiving Info
|
Transfer Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Additional Details menu option on the Receipt Summary screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Edit Receipt menu option in the footer menu
on the Tsf Rcv Containers screen is available.
Without this permission, the menu option will not display.
On the PC, with this permission, when the user clicks the Info button on the
Transfer Receiving Detail screen, the Receiving Info screen will open in edit
mode.
Without this permission, the screen will open in view-only mode.
|
|
Edit Transfer Receiving Attribute
|
Transfer Receiving
|
On MAF, with this permission, extended
attributes can be added/removed: The Add Attributes and Remove
Attributes (Trash can) buttons will be available on the Attributes screen
of the Transfer Receiving Item Detail.
Without this permission, the menu option will not display.
On the PC, with this permission the Apply, Add Attributes, Remove Attributes
and Cancel buttons on the Extended Attributes Entry screen are displayed and
enabled.
Without this permission, the Close button is displayed and enabled.
|
|
Misdirected Container
|
Transfer Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Misdirected Container menu option on the Receipt summary menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Copy button on the Misdirected
Items screen is available.
Without this permission, the button will not display.
On the PC, with this permission, the Misdirected Container button on the
Transfer Receiving Detail screen, is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Receive On Shop Floor
|
Transfer Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Receive on Shop floor prompt on the Confirm screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the prompt is not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Receive On Shop Floor checkbox on the Edit
Container screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the checkbox is view-only.
On the PC, with this permission, the Receive on Shop Floor check box on the
Transfer Receiving Container Info screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the check box is disabled.
|
|
Record Receipt Damages
|
Transfer Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Damage by Item and Damage Remaining menu options on the Receipt Summary
screen are displayed.
Without this permission, the menu options are not displayed.
On MAF, with this permission, the Damaged Qty field on the Item Detail screen
and the Damages Receiving and Regular Receiving menu options in the footer
menu on the Container Items screen is available.
Without this permission, the menu options will not display.
On the PC, with this permission, the damaged field on the Transfer Receiving
Container Detail screen and the damaged field, the dropdown includes ‘damage’
and the Damage All button on the UIN popup is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the fields, selections and buttons are not
available.
|
|
Remove Item
|
Transfer Receiving
|
On the HH, with this permission, the user
is allowed to remove an unexpected item to a receipt. The system will prompt
the user to confirm.
Without this permission, the user is not allowed to remove the item. Note:
Items that are not unexpected are never allowed to be removed regardless of
the permission.
On MAF, this permission must exist in order to Remove Items on the
Container Items and Item Detail screens.
Without this permission, the user cannot remove items. Note: Items that are
not unexpected are never allowed to be removed regardless of the permission.
On the PC, with this permission, the Remove Item button on the Transfer
Receiving Container Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed. Note: Items that are
not unexpected are never allowed to be removed regardless of the permission.
|
|
Access UIN Attribute
|
UIN
|
On the PC, with this permission, the UIN Attributes
button on the Setup screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Access UIN Resolution
|
UIN
|
On the PC, with this permission, the UIN
Resolution button on the Admin screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Create UIN AGSN Ticket
|
UIN
|
On the HH, with this permission, the New
AGSN menu option on the Ticketing Options menu is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
Note: The Re-print AGSN Ticket is controlled by the Print Auto Generated SN
permission.
On the PC, with this permission, the Auto-Generate SN box on the Item Ticket
Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the check box is disabled.
|
|
Create UIN on the Fly
|
Inventory Adjustments
|
On the HH, with this permission, the user
is allowed to create a UIN on the fly when creating an inventory adjustment
using a reason code of Disposition Movement from Out (Dist) to Available to
Sell (ATS) = UIN Status in Stock.
Without this permission, the user will not be able to create a new UIN.
On MAF, with this permission, the user is allowed to create a UIN on the fly
when creating an inventory adjustment using a reason code of Disposition
Movement from Out (Dist) to Available to Sell (ATS) = UIN Status in Stock.
Without this permission, the user will not be able to create a new UIN.
On the PC, with this permission, the user is allowed to create a UIN on the
fly when creating an inventory adjustment using a reason code of Disposition
Movement from Out (Dist) to Available to Sell (ATS) = UIN Status in Stock.
Without this permission, the user will not be able to create a new UIN.
|
|
Print UIN Auto Generate Serial Number
|
UIN
|
On the HH, with this permission and the
Format Type is Auto Generate SN, the Re-print AGSN menu option on the
Ticketing Select Options screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
Note: The New AGSN print option is controlled by the Create UIN AGSN Ticket
permission.
On the PC, with this permission and the UIN type is AGSN, the Print Ticket
button on the UIN Detail screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission and the Format type is Auto Generate SN, the
Auto Generate check box on the Item Ticket Detail screen is enabled.
Without this permission, the checkbox is disabled.
Note: This permission controls whether the user can generate additional
serial numbers/tickets
|
|
Resolve UIN Exceptions
|
UIN
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Resolve button on the UIN Resolution List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|
|
Update UIN Status
|
UIN
|
On the PC, with this permission, the
Update Status dropdown on the UIN History screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the dropdown is not enabled.
|
|
View UIN Detail
|
UIN
|
On the HH, with this permission, the
Serial Number menu option on the Item Lookup screen is displayed.
Without this permission, the menu option is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, if the item is a UIN item the UIN Detail
button on the Item Lookup screen is displayed and enabled. Without this
permission, the button is not displayed.
Note: There will not be a UIN Detail tab on the Item Lookup popup, which is
available from within a transaction.
|
|
View UIN History
|
UIN
|
On the PC, with this permission, the View
History button on the UIN Resolution List screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
On the PC, with this permission, the View History button on the UIN Detail
screen is displayed and enabled.
Without this permission, the button is not displayed.
|