| Oracle® Retail Store Inventory Management Store User Guide Release 16.0 E76179-08 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
| Oracle® Retail Store Inventory Management Store User Guide Release 16.0 E76179-08 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
This chapter covers security features. The following topics are covered:
Overview: Introduction to security features.
Role Maintenance: Description of screens for maintaining roles.
User Maintenance: Description of screens for maintaining users.
Technical: Information on user/role security.
SIM provides role-based user access control in order to manage application functionality and data available to users. This role-based user access control allows security to be managed in a way that corresponds closely to the organization's structure.
Security is handled by assigning privileges (permissions) to a role in SIM. These roles are assigned to users and can be different roles for different stores (in LDAP or SIM). If the user does not have permission, the feature will not be available for user.
SIM secures buttons, drop-down values, and menu options on the PC, handheld, and MAF. Additionally, permissions are validated on the Server side.
To allow flexibility on how security is implemented, three modes of deployment exist:
External Authentication/Authorization
An external system controls security (LDAP). Users and role/store assignments are administered in LDAP. Authentication is performed in LDAP. Note that Oracle LDAP (for example, OID) is the only supported LDAP. This is the default and recommended model of deployment.
Internal Authentication/Authorization
SIM controls all aspects of security. Users, roles, user/role/store/group assignments are all administered in SIM. Authentication is performed in SIM.
External/Internal Authentication/Authorization
A hybrid approach is used for authentication. Users may be stored in either external LDAP or the internal database. Users that are created in LDAP behave the same way as the external authentication mode, but can be assigned additional roles in the internal database through the SIM management screens. After successful authentication, the external user is granted the permissions associated with roles assigned in both the LDAP and database. Users that are created in the database behave the same way as the internal authentication mode.
| Deployment Mode | Controlled by? | What is controlled? |
|---|---|---|
| External Authentication/Authorization
Default |
LDAP |
|
| Internal Authentication/Authorization | SIM |
|
| External/Internal Authentication/Authorization | LDAP + SIM | LDAP:
SIM: Additional roles |
SIM's security model allows for very flexible UI authorization allowing to control user create, edit, and approval as a very granular level. It also is built in a flexible way to allow assignment autonomy to store users without compromising corporate security.
Use Case 1
Everyone in the store can create inventory adjustments, but if inventory has to be removed from stock, it requires special authorization by a store manager. Data security allows users to get permission to use specific inventory adjustment reason codes. Two different roles can be created, one role has data permissions that only allow inventory to move from available to unavailable and from unavailable back into available. The second role has those reason codes that allow the user to move inventory from unavailable to be removed from stock. The associates in the store all get the first role assigned, while the first and second roles are assigned to the store manager.
This allows associates to move inventory into a bucket of unavailable and complete the inventory adjustment. The manager then can review the items in the unavailable bucket and move them to out of stock.
Use Case 2
A retailer requires store managers to approve all store shipment dispatches. However, they do not want to manage the day to day vacation and schedules of their managers. Since dispatching still needs to happen, the store managers are put in charge to give this privilege to other users when they are out.
This process is supported by creating a store level role that has a required expiration date. The store managers have limited security privileges for their store only as well as the dispatch store role.
When they go on vacation or schedules are conflicting, they can assign the store role to a user for their store. In this process they also have to put in an expiration date for when they will be back.
The ability to define if a role is corporate or store level allows the implementation of this very flexible process.
This section covers system parameters, notifications, and security.
Default Days for Temporary Role End Date
Values: 0 - 999
Default: 5
Topic: Security
Editable: Yes
For roles defined as temporary, this parameter defaults the end date to the role.
If the value is zero, the temporary role can have any end date.
Maximum Days for Temporary Users End Date
Values: 0 - 999
Default: 5
Topic: Security
Editable: Yes
For roles defined as temporary, this parameter limits the time before deactivating a temporary user.
If the value is zero, the temporary user account can have any end date.
User Security Mode
Values: External Authentication/Authorization, Internal Authentication/Authorization, External/Internal Authentication and Internal Authorization, External/Internal Authentication/Authorization
Default: Internal Authentication/Authorization
Topic: Security
Editable: No
Defines which type of authentication is used.
If an email address is provided for the user at the time the new user is created or during an edit of the user (password assignment selected), the new one time password is sent in email to the user. A check is performed to ensure the system is set up to allow emails to newly created users. With hardening of security, the user email notification option not part of the SIM PC UI, but can be accessed by an Administrator through the database or a tool such as JConsole.
Security permissions exist for:
Accessing, creating, editing, and deleting roles and users
Assigning individual store and mass assigning store and roles to users
Data permissions exist around role types and user types:
A user must have proper permissions to create users as a Corporate or Store User.
A user must have proper permissions to create, edit, or look up super users, temporary users, or store users.
This section describes the available screens for maintaining roles.
The Role List screen displays a list of roles already defined in the system. It is accessed within the Security dialog by clicking the Role Maintenance button from the Security menu. The filter for this screen allows the user to filter by role name, description, role type, topic or permission.
Roles contain permissions which indicate what the functions a user has access to and can execute. As an example of functions consider creating an inventory adjustment or the dispatching of a return.
Roles may be created, edited or deleted from this screen. However, a role may not be deleted if there are users currently assigned the role.
The Role List Filter screen is accessed by clicking the Filter button from the Role List screen. The user can filter on various search criteria. After applying the filter, the user will be returned to the Role List screen with the roles displayed per the entered criteria.
The Role Detail screen displays the assigned permissions for a specific role. It is accessed within the Security dialog by clicking a role from the Role List Screen.
The user with permissions to define roles will be able to assign or remove permission for new or existing roles. Many times, roles will be created based on the type of employee - District Manager, Store Manager, Sales Associate, Stocker, and so on. Roles may also be broken out by duties performed, such as Shipping, Receiving, Inventory Management, and so on.
When a role is created, the Role Type must be specified. There are two role types:
Corporate: this type of role will typically perform tasks for the entire enterprise such as assigning roles to users, setting up corporate wide system/store options, creating templates, and so on.
Store: this type of role will typically perform tasks for one or more stores such as receiving, inventory management, and so on.
A demo set of Corporate and Store roles is loaded during install and will have default values provided.
If the "End Date Required" is checked, when the role is assigned to a user, the system will require an end date be specified when granting the role to a user.
Permissions are used for all device types.
For a full list of permissions and email alerts, see the Oracle Retail Store Inventory Management Configuration Guide.
Specific Data Permissions may also be added to a role and can be accessed by clicking the data permissions button.
The Data Permissions screen displays the assigned data permissions for a specific role. It is accessed within the Security dialog by clicking the data permissions button from the Role Detail screen.
Secured Data Value Types contain a list of all data types where security can be applied. This provides a way to limit the data values displayed to a user in a drop-down list. For example: A Store User may only have access to use the RTV Reason Code: Damage which will apply to items returned in a store. However, other Corporate Users may need access to additional reason codes for returning other items which are not sold in the store, such as Overstock.
The following various secured data value types are available:
Container Items Limited To
Counting Method
Display a List of Diff Types
Inventory Adjustment Reason Code
Item Request Delivery Timeslot
Item Ticket Batch Reason
Location Type
Product Group Type
Role Type
RTV Reason Code
RTV Shipment Reason Code
Security Group
Shelf Adjustment Type
Shelf Replenishment Type
Ticket Print Reason
Transfer Shipment Reason Code
User Type
For details on the secured data value types, see the various functional areas.
Role Type data permissions, are used to control which roles a user is allowed to assign based on their permissions. A user with permission to assign store roles is not allowed to assign corporate roles without additional permissions.
User Type data permissions, are used to control which user type a user is allowed to manage based on their permissions. A user with the Temporary user permission may create and manage temporary users but is not allowed to manage a Super User or Store User without additional permissions.
Security Group permissions are assigned to a user role. For additional information around security groups, see "Group Assignments."
This section describes the available screens for maintaining roles.
The User List screen displays a list of users already defined in the system for the store the Security Administrator is logged into. The filter can be used to reduce the list displayed by selecting any combination of the following: Username, First Name, Last Name, Role, Type, Status, Group, Create Date, Start Date, Store, Default Store, or Comments.
A new user can be created from this screen by clicking the Create button. If the Security Administrator clicks a user, the User Detail screen opens with the selected user information displayed on the screen. The user can be edited by selecting the user to go into the User Detail screen. Finally, the Security Administrator can select one or more users to delete from the system. If the users are set up externally, they will not be eligible for deletion.
The User Filter screen is accessed by clicking the Filter button from the User List screen. The user can filter on various search criteria. After applying the filter, the user will be returned to the User List screen with the users displayed per the entered criteria.
The User Detail screen allows the Security Administrator to create new users, edit existing users, assign passwords, assign stores, assign groups, and assign roles to the selected user. It is accessed within the Security dialog by clicking a user from the User List Screen or pressing the Create button.
It is possible to edit any user type by the Security Administrator as long as it was originally created in SIM. The Copy Assignments button is only available when a user is setting up a new user. It allows the user to copy over the assignments from one user to another.
The Assign Groups button is used to assign security groups to a user. The security administrator creating or updating the user will only be able to add the groups to the user in which they have data permissions associated to their role. For more details, see "Data Permissions" and the Oracle Retail Store Inventory Management Security Guide.
The User Type of Super User will have access to all locations within SIM. Super Users are often set up to manage security (roles, user and role/store assignments) and setup only, but typically have no access to transactions. New stores will automatically be assigned to the super user, but roles are not auto assigned. This allows the super user to still log in to the store and assign roles to users, but not necessarily execute any transactions.
The User Type of Store User will have access to one or more stores assigned to them. If the Store User is assigned to more than one store, they will need to select the store if they want to work in any other store than their default store.
|
Note: There are a few areas in which they may be able to work with any store they are assigned to regardless of the store they are logged into. |
The User Type of Temporary User will have limited access for a set period of time. The maximum number of days for a temporary user to be active are set up in System Administration. This feature can be used to support a temporary influx of employees during special events where employees are hired at a very quick pace by the store manager and do not need to roll onto other corporate systems.
|
Note: The assignment of the language (locale) is not tied with the user, but rather with the store the user is logged into. The language displayed on the screen will default based on the locale of the store the user is logged into. If the store is locale=French, the user language is displayed in French; if they switch to a Dutch store, the language is displayed in Dutch. |
The Assign Password popup allows a user to set up an initial password for a specific user. It is accessed within the Security dialog by clicking the Assign Password button from the User Detail Screen.
The Security Administrator will be allowed to enter an initial password for the user or to have the system generate a password. SIM can be configured to include specific min/max password length and special characters. This is set up on the Password Configuration screen.
The Store Assignments screen allows a user to assign the stores to which a user will have access. It is accessed within the Security dialog by clicking the Assign Stores button from the User Detail screen.
A Super User is always required to have all stores assigned with a default store. It is not possible to remove any stores for a Super User from the Assigned Stores list.
The Role Assignments screen allows a Security Administrator to assign roles to a user. It is accessed within the Security dialog by clicking the Assign Roles button from the User Detail screen.
A role may be granted to a user for a specific time period. If the role assigned was set up with an attribute requiring the end date, the system will place an asterisk in each of the corresponding End Date fields in the table. This will visibly alert the user to enter in a date for each of the roles.
The store list will be reduced to only those stores the user has access to and the role list will only display those role types (corporate or store) where the user has data permissions.
The User Lookup popup allows a user to copy the store, role, and group assignments from a user already set up. It is accessed within the Security dialog by clicking the Copy Assignments button from the User Detail screen.
If the store, role, and group assignments are copied, additional changes can still be made for the new user being set up. Roles can be assigned by a user only if they possess that role as well.
The Group Assignments screen allows a user to assign permission groups to a user already set up. It is accessed within the Security dialog by clicking the Assign Groups button from the User Detail screen.
The groups available to assign to the user are available based upon the data permissions assigned to the role of the person creating the group.
Security functions are broken out into the following groups:
Administrator User (sim_admin_users - Group for administrator operation users.)
Batch User (sim_batch_users - Group for batch operation users)
Integration User (sim_integration_users - Group for integration operation users)
MPS Ops User (sim_mps_users - Group for MPS operation users)
Security Ops User (sim_security_users - Group for security operation users.)
Server Ops User (sim_server_users - Group for server operation users.)
The Mass Assign Stores screen allows a user to assign stores to a selected group of users. It is accessed within the Security dialog by clicking the mass assign stores button from the Security Menu.
A Super User will always have all stores assigned. It is not possible to remove any stores for a Super User.
The Mass Assign Roles screen which allows a user to assign one or more roles to a selected group of users. It is accessed within the Security dialog by clicking the mass assign roles button from the Security Menu.
If a role selected requires an end date, the system will require an end date to be entered for the role/users selected.
Authentication refers to verification of who the user is, typically through t the user ID and password. Authorization refers to what that user is authorized to do as well, as it refers to role-based authorization. Users are assigned to roles and roles have permissions. Permissions allow users to perform actions through menus and buttons.
Oracle Internet Directory (OID) is the only supported LDAP with SIM. Oracle recommends "External Authentication / Authorization" as the mode to use. It is the default installation mode.
To change the security model to use internal security, use a preferred MBean browser. Under SystemConfig MBean, change SECURITY_AUTHENTICATION_METHOD value to 0.
For information on how to use a MBean browser, see the Oracle Retail Store Inventory Management Configuration Guide.
Once the security method is changed to internal security, the authentication provider needs to be changed to SIM Database Authentication provider. For details, see the "SIM Database Authentication Provider set up" section in the Oracle Retail Store Inventory Management Installation Guide.
For internal security, use the installation user created during application installation to set up SIM configuration and user/role management:
The default algorithm used to store passwords in SIM is Secure Hashing Algorithm (SHA).
This can be configured in the server.cfg file to be any algorithm recognized by the Java encryption API.
When creating roles, job functions, and corporate hierarchies must be considered and taken into account.
Authenticate the user:
Authenticate the user name and password for SSO or Non-SSO login.
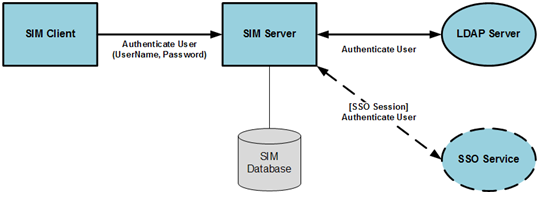
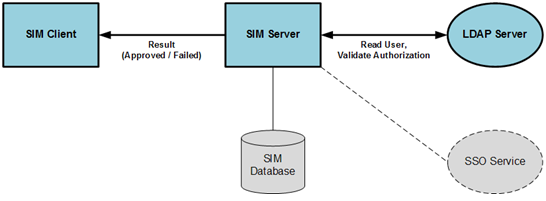
Validate the user login. If the user login is successful, the SIM application is opens.
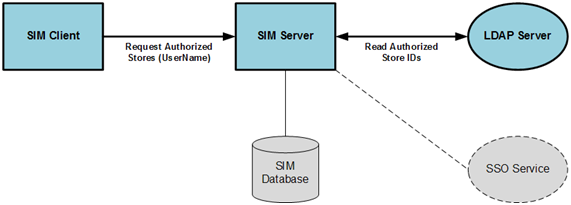
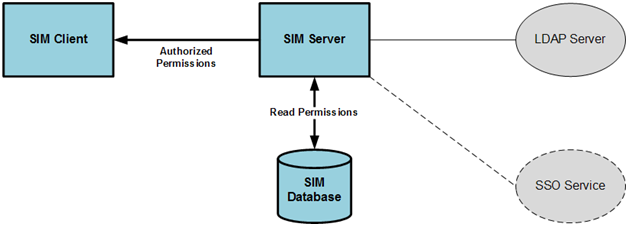
Request the authorized stores:
Read the authorized stores for the user.
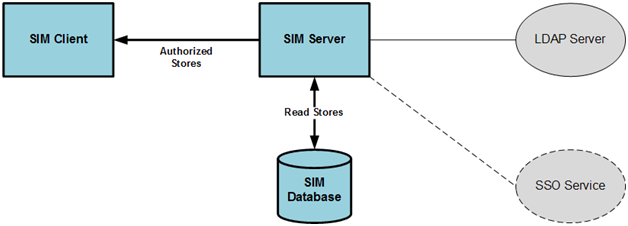
Set the list of authorized stores for the user.
Request the authorized permissions:
Request the authorized permissions for the user-store-role.
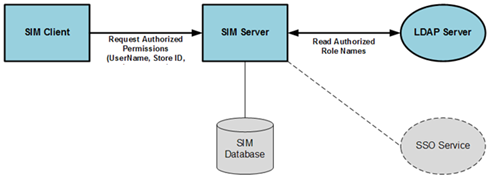
Read the permissions for the user-store-role from the SIM database.
Roles are a collection of permissions which can be assigned to a user. They act as job-functions with specific authority-levels.
Roles can be created and maintained using Role Maintenance:
Each role has a role type and a set of permissions associated with it.
Role types are used to control which roles a user is allowed to assign based on their permissions. By default, the role types that exist in SIM application are Store and Corporate. A user with permission to assign store roles is not allowed to assign corporate roles without additional permissions.
Role assignments can include start and/or end dates.
Roles are created and edited in SIM using the security administration screens, and are stored in the SECURITY_ROLE, SECURITY_ROLE_PERMISSION tables. When using external security, the role header information is also stored in LDAP as a simRole, although only the roleName is used by SIM and the role information is retrieved from the SIM database. Roles can contain any combination of available permissions and can overlap with other roles.
Roles are associated with a role type, which is defined in the SECURITY_ROLE_TYPE table. The default role types include Store and Corporate. Role types are used to control which roles a user is allowed to assign based on their permissions. A user with permission to assign store roles is not allowed to assign corporate roles without additional permissions.
The Role Detail screen also allows the assignment of data permissions, which control access to specific types of data. For example, data permissions can be used to control access to specific inventory adjustment reason codes, item request timeslots, role types, or product group types.
In case external/internal authentication/authorization is used, LDAP will only need to store those roles assigned to users that are controlled by LDAP.
User maintenance is used for creation and maintenance of all SIM user records. SIM users are assigned one or more roles which have permissions associated with them. This role-based security model controls which user can perform specific tasks or have access to specific data based on the permissions associated with the role/roles assigned to the user:
A user is associated with a status that controls the account access of the user. Only an Active user is allowed to access the application.
A user can have a start and/or end date to control the account access.
Users also require store assignments in addition to roles.
Each user is associated with a user type. The valid user types are:
Store user: Can have access to more than one store.
Temporary user: Must have an end date.
Super user: Has access to all the stores, but requires role assignments to gain access to functionality.
Users are granted access to secure interfaces by assigning groups to the user in the SIM UI.
All SIM users require the authenticated group assignment in order to access SIM (default group name: sim_secure_users). The following table lists the SIM user group assignments.
| Group | User for? |
|---|---|
| SIMSecureUsers | Provided by internal authentication / must be set up when using LDAP authentication |
| Admin | Accessing configuration management functionality |
| Security Ops | Accessing user and security management functionality |
| MPS | Accessing MPS (staging table) admin functionality |
| Batch | For triggering batch clients |
| Integration | Accessing external integration end points (for example, RIB, POS, third-party manifest) |
| Server Ops | Internal server operations |
This list represents application groups.
SIMSecureUsers: This is required for all users who need to access SIM. This is automatically provided for users authenticated with internal database security. For LDAP users, this needs to be set up. This is mandatory. Note that anyone using SIM, needs to have this application group.
The following three groups can be assigned as needed to users:
Admin: Required for administrator operation, such as configuration management.
Security: Required for security management operation, such as user and role management.
MPS: Required for MPS management operation, such as staged messages and work type screens (intended for use by system administrator).
The following three groups are not meant to be used for store-users:
Integration: Required for accessing integration end points. RIB is a default integration user.
Batch: Required for batch job operation (batch client).
Server: Used for internal server operation, not used by remote or external clients.
Additional special purpose groups should be assigned to users as needed for accessing special interfaces such as administrator operations or security management operations. Oracle Software Security Assurance (OSSA) Sensitive information, such as user credentials, must be encrypted and stored in a secure location, known as credential stores. These credential stores are secure software containers that store the encrypted user credentials.
SIM has implemented using credential store alias names in the following areas:
LDAP connection credentials
RIB service credentials (publish and subscribe)
BIP service credentials
Web service consumer credentials (OMS, manifest)
WebLogic user credentials (batch, server, wireless users)
SIM uses external secure credential stores for the SIM client to look up SIM remote services:
SIM stores the database password in a secure credential store for the database standalone program which invokes sqlplus or sqlldr.
SIM stores the application remote login password in a secure credential store for Java application programs.
SIM also modifies programs to use security alias names for accessing database or remote applications:
The data seeding (import) program passes the user and password when invoking the sqlplus and sql loader (sqlldr) inside the program.
Any other data import utility or adhoc batch program uses SIM standard Java wrapper to call the stored procedure; if using Java wrapper is not applicable, and if connecting to the database through a database client utility such as sqlplus or sqlldr, then the secure pass store is used and tnsalias for database connection credential stored in the wallet must be used.
For more information, see the "Appendix: Setting Up Password Stores with Oracle Wallet" in the Oracle Retail Store Inventory Management Installation Guide.
SIM is intended to work with any Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) product. Out of the box, SIM ships sample .ldif files that can be used to create data in an LDAP system. Oracle expects customers to use these files as examples to create their own data load files and hook into their own pre-existing corporate LDAP authentication system.
|
Note: A simUser can have more than one simStore by simply repeating the userStores line, but should only have one defaultStore. A simUserRole can also have more than one simStore by repeating the userRoleStores line. |
Business objects are used throughout the application code for all business processing.
| Business Object | Description |
|---|---|
| Permission | Contains information about a specific permission in SIM. It is mostly used when managing roles as it contains additional information used for assignment to roles, such as description, device type, and permission group. Permissions with no device type apply to all devices. Permissions are primarily identified by their name instead of their database ID. |
| PermissionGroup | Object that contains information about a defined grouping of permissions in SIM. Permission groups are used to categorize and filter permissions for filtering and display purposes. It is mostly used for security management operations. |
| PermissionSet | Object that contains a various set of permissions. This class represents a set of permissions and any associated parameters. It is used to hold the set of permissions that have been assigned to a role. Permission sets are also used to hold the union of permissions for multiple roles that a user has been authorized to access. This class includes methods to test for the presence and absence of permissions in the set. |
| Role | Object containing information about a role. This class represents the header information for a role. It contains the role name, description, role type, and whether an end date is required for assignment to a user. It is mostly used for security management operations. Roles are primarily identified by their name instead of their database ID. |
| RoleType | Object containing information about a type of role. Role types are used for filtering and display purposes but are also used with data permissions to restrict access to functionality for certain types of roles. It is mostly used for security management operations. |
| Group | Object container information about a group. Groups are used for restricting access to application interfaces such as remote services. Services with special purposes or restricted operation require additional group assignment for access to be authorized. |
| User | Object containing user information. User objects are used to hold both internal and external user data. Users are primarily identified by their username instead of their database ID. |
| UserPassword | Object containing information about a user's password. It contains information for an individual password record such as date and status. It is used for both current passwords and password history. User password objects are used to hold internal password records. |
| PasswordConfiguration | Object containing information about a password configuration. |
| UserRole | Object containing information about a role assigned to a user. It includes information such as start/end date, store ID, and other state information. User role objects are used to hold both internal and external assignments. A role assignment with no specified store ID applies to all available stores. |
| UserStore | Object containing information about a user's assignment to a store. Store assignments do not exist for super users as they have implicit access to all stores. User store objects are used to hold both internal and external assignments. |
| UserGroup | Object container information about a group assignment for a user. |
The following database tables are used by SIM:
| Table Name | Description |
|---|---|
| SECURITY_USER_ROLE | This table contains role assignments for users. This table includes cached data in fail-over mode. |
| SECURITY_USER_STORE | This table contains store assignments for users. This table includes cached data in fail-over mode. |
| SECURITY_PERMISSION | This table contains permissions that can be associated to roles. |
| SECURITY_PERMISSION_GROUP | This table contains permission groups that are used to categorize permissions. |
| SECURITY_ROLE | This table contains role information. |
| SECURITY_ROLE_PERMISSION | This table contains the relationship between roles and permissions, and includes permission parameters where appropriate. |
| SECURITY_ROLE_TYPE | This table contains the role types that are used to define roles. |
| SECURITY_USER | This table contains user information for access control purposes. This table includes cached data in fail-over mode. |
| SECURITY_USER_PASSWORD | This table contains user passwords, including the current password and password history. This table includes cached data in fail-over mode. |