| Oracle® Identity Manager Connector Guide for IBM RACF Advanced Release 9.0.4 Part Number E10451-04 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Identity Manager Connector Guide for IBM RACF Advanced Release 9.0.4 Part Number E10451-04 |
|
|
View PDF |
This appendix describes the IBM RACF Advanced connector functionality in detail in the following sections:
The architecture for Oracle Identity Manager Advanced connector begins with the Oracle Identity Manager LDAP Gateway. The LDAP Gateway is built on Java 1.4.2, allowing for portability across different platforms and operating systems and complete integration with the Oracle Identity Manager system.
The LDAP Gateway works transparently with Oracle Identity Manager to communicate with IBM RACF facilities in a z/OS environment. The LDAP Gateway is installed along with Oracle Identity Manager on the same server. In addition, the Reconciliation Agent enables the LDAP Gateway server to become a subscriber to security and identity events from IBM RACF.
Oracle Identity Manager maps mainframe authentication repositories by the LDAP DN. By changing the LDAP DN, different authentication repositories and different mainframe resources can be addressed.
The Provisioning Agent is a mainframe component, receiving native mainframe IBM RACF provisioning commands from the LDAP Gateway. These requests are processed against the IBM RACF authentication repository with the response parsed and returned to the LDAP Gateway.
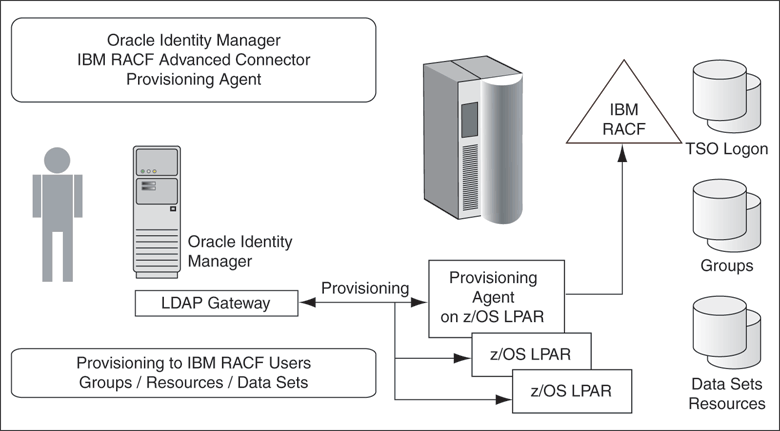
The Provisioning Agent includes LDAP bind and authorization requests. In addition to traditional provisioning functions, the Provisioning Agent can also build the necessary TSO logon functions, including building CLIST files, and working to replicate existing mainframe user profile scenarios. The Provisioning Agent can also extend authorization to data sets, groups, and resources through enterprise rules set in Oracle Identity Manager.
Mainframe architecture includes significant communication of connector resources and internal mainframe memory subpools for enterprise loads at peak times, supporting over a million transactions per day. The entire Provisioning Agent is protected by AES 128 encryption and APF authorized resources.
The Provisioning Agent receives Identity and Authorization change events, and effects requested changes on the z/OS mainframe authentication repository, IBM RACF Advanced. The Provisioning Agent is a mainframe-installed component that receives native mainframe requests from the LDAP Gateway.
An important architectural feature of the Provisioning Agent is that provisioning updates are made from the LDAP Gateway to the IBM RACF Advanced authentication repository. As such, the Provisioning Agent needs to be installed on at least one z/OS LPAR. Provisioning commands sent from Oracle Identity Manager then change authentication and authorization across all LPARS serviced by the IBM RACF Advanced authentication repository. Within this framework, multiple IBM RACF Advanced systems that are not externally synchronized will require a second Provisioning connector.
While most provisioning commands are designed around direct access to IBM RACF Advanced, some LDAP provisioning commands are executed in multiple mainframe commands. For example, to provision for TSO access, some systems require modification to a CLIST profile. The type of command depends on which mainframe process is to be accessed.
When an event occurs on the mainframe, independent of any custom installed technology, the event is processed through an appropriate mainframe exit. Because the Reconciliation Agent uses exit technology, there are no hooks in the z/OS mainframe operating system.
Identity events that arise from a user at TSO login, changes by an administrator from the command prompt, or events resulting from batch jobs are detected and notification messages are securely sent in real time. The Reconciliation Agent captures changes to user attributes (any ALTUSER change), changes to a user account (REVOKE, RESUME), and certain changes to user authorization for groups and resources. If a user account is created or deleted on the mainframe, the Reconciliation Agent will notify Oracle Identity Manager and even create a corresponding account in Oracle Identity Manager.
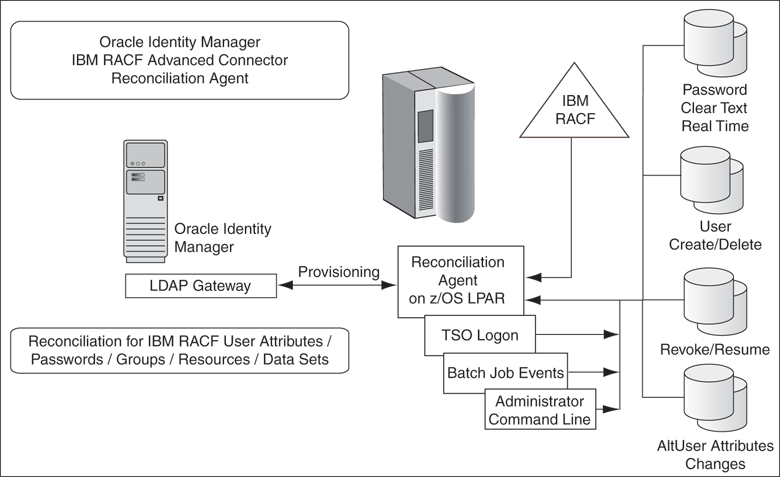
Passwords fall into a special category. If business rules permit, a password change will be passed to Oracle Identity Manager in real time. Within other business rules, only a notification that the password has been changed will be passed.
Internal to mainframe architecture is significant communication of connector resources and internal mainframe memory subpools for enterprise loads at peak times. The Reconciliation Agent was specifically designed to handle peak loads from a mainframe batch job. If 1 MB of mainframe memory is allocated to the messaging subpools, they can hold up to 50,000 identity event messages. These messages are then spooled to the LDAP Gateway, which supplies the messages to Oracle Identity Manager for subsequent processing (typically over the next hour). The entire Reconciliation Agent is protected by AES 128 encryption and APF authorized resources.
The Reconciliation Agent sends notification events to the Oracle Identity Manager LDAP Gateway from the z/OS mainframe. A command execution is passed through an exit, just before full completion of the native mainframe command. A common use of this technology is to require user accounts or passwords to be formatted to a proper length or that they must contain at least one letter and one number. If the exit fails, the command fails and returns an error message. By capturing identity or authentication events at an exit, the Reconciliation Agent captures these events outside the operating system, just prior to completing the command and storing the results in the IBM RACF authentication repository.
As with the Provisioning Agent, there is an architectural dependence based on the LPAR. When a user account is created, is authorized to something, or works on the mainframe, they do this on an LPAR. Since all actions are within the LPAR and the Reconciliation Agent detected events from an LPAR exit, the Reconciliation Agent must be installed on each LPAR. This is a scheduled event, usually done with a maintenance schedule, because an LPAR exit change is only recognized after an IPL.
The message transport layer is the process where the messages are exchanged between the LDAP Gateway and the IBM RACF Advanced Provisioning and Reconciliation Agent.
The LDAP Gateway uses TCP/IP as a message transport layer to the Provisioning and Reconciliation Agent. This protocol is layered with an internal Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption using 128-bit cryptographic keys. This encryption protocol is internal between the LDAP Gateway and Provisioning/Reconciliation Agent, and does not depend on platform-specific programs or libraries.
The LDAP Gateway, Provisioning Agent, and Reconciliation Agent all coordinate bidirectional synchronization to a single IBM RACF authentication repository. Internally, the LDAP Gateway has 20 AES cryptographic keys which are randomly selected for a given message, 10 of which are dedicated for bidirectional messages between the Provisioning Agent and the other 10 are used for the Reconciliation Agent.
Messages between the LDAP Gateway and the Provisioning Agent have a very short life span. The provisioning process that arises for Oracle Identity Manager expects a pass or fail LDAP message quickly.
The Reconciliation Agent has been engineered for the following:
If the TCP/IP connection has not been established between the Reconciliation Agent and the LDAP Gateway, up to 50,000 messages are kept in a secure mainframe memory subpool prior to message processing.
During the message generation process, the Reconciliation Agent places both a time stamp and a sequential serial number to each message. An archive of the message is kept in an encrypted format in an APF authorized VSIM file, with both serial and time/date stamps.
Once transmitted, the messages are logged internally within the LDAP Gateway, again in an encrypted format.