14 Configuring Listening Channels
A listening channel is used to send messages to Oracle B2B. A listening channel listens on an endpoint for messages. If a listening channel is marked as internal, then it can be used by any internal business application. If it is used as an external channel, then any trading partner can send a message to Oracle B2B using this channel.
This chapter contains the following topics:
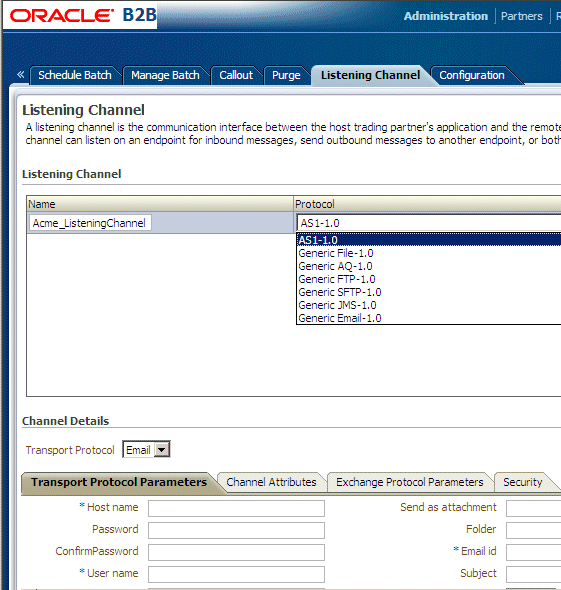
14.1 Adding a Listening Channel and Protocol
Listening channels are used globally. You do not need to select a listening delivery channel in an agreement. Listening channels are used for any trading partner to send inbound messages to Oracle B2B or for any back-end business application to send outbound messages to Oracle B2B.
When you add a listening channel, you also specify the protocol that the channel uses, as shown in Figure 14-1.
By using a global listening channel, you can keep all messages in one directory from which Oracle B2B pulls. This approach is useful for File, FTP, and SFTP (SSH FTP) exchanges.
Table 14-1 describes the listening channel protocols supported by Oracle B2B.
Table 14-1 Listening Channel Protocols
| Protocol | Description |
|---|---|
|
AS1-1.0 |
Applicability Statement 1 (AS1) provides S/MIME and uses SMTP to transmit data using e-mail. Security, authentication, message integrity, and privacy are assured by the use of encryption and digital signatures. Use nonrepudiation to make it impossible for the intended recipient of a message to deny having received it. AS1 works with almost any type of data. AS1-1.0 is in preview mode for this release. |
|
Generic File, Generic AQ, Generic FTP, Generic SFTP, Generic JMS, Generic Email |
Using the Generic options, you can send messages with or without security. The Generic exchange protocol supports MIME and S/MIME, including S/MIME 3.0-based signing and encryption. There is no receipt acknowledgment support with the Generic protocols (acknowledgment mode must be set to None). |
14.2 Using Transport Protocols
The transport protocol used to send the message is determined by the listening channel you select, as shown in the Channel Details area in Figure 14-2.
Figure 14-2 Channel Details: The Transport Protocol
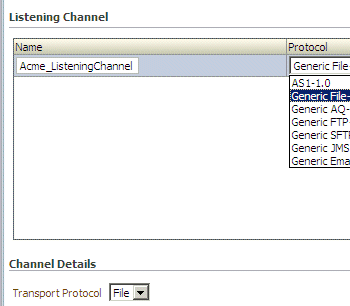
Description of "Figure 14-2 Channel Details: The Transport Protocol"
Table 14-2 describes the transport protocols available in Oracle B2B.
Table 14-2 Transport Protocols Available in Oracle B2B
| Protocol | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Use Email for AS1 and Email listening channels. |
|
File |
The File transport enables files to be picked up from a shared file directory. |
|
AQ |
Oracle AQ provides secure, bidirectional, asynchronous communication. The location of the application location is transparent, using any number of Oracle connectivity options, including OCI, JDBC, or PL/SQL. Both XML and non-XML message payloads are supported. |
|
FTP |
FTP enables files to be passed with FTP between applications. FTP runs on default port 21. To change to another port, provide the value in the Control Port field. To enable SSL, use the Channel Mask field. The default is None (no SSL). |
|
SFTP |
SFTP enables files to be passed using SSH FTP. SFTP runs on default port 22, which can be changed to another port. SFTP supports two modes of authentication, password authentication and public key authentication. To use password authentication, provide a password, which is used for authentication. To use public key authentication, provide the private key file location. You may also need to provide a pass phrase if the private key file is pass-phrase protected. |
|
JMS |
JMS enables applications to send and receive messages to and from the queues and topics administered by any Java Message Service (JMS) provider, including Oracle WebLogic JMS and non-Oracle providers such as MQSeries JMS (IBM). |
14.3 Adding Listening Channel Details
Listening channel details include transport protocol parameters, channel attributes, exchange protocol parameters, and security specifications. Table 14-3 describes these details.
Table 14-3 Listening Channel Details and Associated Protocols
| Protocol/Parameter | Description | Protocol Used With |
|---|---|---|
|
Transport Protocol Parameters |
A transport protocol defines the properties specific to a given use of a protocol endpoint. The transport is responsible for message delivery using the selected transport protocol, mode (synchronous or asynchronous), server, and protocol endpoint address (trading partner address, such as a URI). |
- |
|
Channel mask |
To enable SSL for FTP, enter one of the following:
The default is None (no SSL). |
FTP (optional) |
|
Cipher suites |
Sets of ciphers defined in SSL. |
FTP (optional) |
|
Connection factory |
The JNDI location or Java class name for the connection factory, as in |
JMS (optional) |
|
Consumer |
The client that receives the message. |
AQ (optional) |
|
Content type |
The content type of the payload being sent over e-mail. The default content type is |
AS1 (optional) Email (optional) |
|
Control port |
Provide a value to change the default FTP port value (21) |
FTP (optional) |
|
Data port |
For active FTP connections, use this option to configure the static/fixed data port of the FTP server. |
FTP (optional) |
|
Data source |
The JNDI name of the JDBC data source to access AQ queues. |
AQ (optional) |
|
Destination name |
The JMS destination name. |
JMS (optional) |
|
Email ID |
The e-mail address to which messages are delivered (similar to specifying the path for a file channel or queues in AQ or JMS). |
AS1 (required) Email (required) |
|
Email Server |
Select IMAP or POP3. |
AS1 (required) Email (required) |
|
Encoding |
The encoding used in B2B to convert the contents of the inbound files. |
FTP (optional) |
|
Filename format |
The following filename formats can be used: %FROM_PARTY% %TO_PARTY% %DOCTYPE_NAME% %DOCTYPE_REVISION% %MSG_ID% %TIMESTAMP% This filename format can be used for ebMS documents only: %ACTIONNAME% These formats can be used in any combination; for example, %TO_PARTY%_%DOCTYPE_NAME%_%DOCTYPE_REVISION%.dat produces something like |
File (optional) FTP (optional) SFTP (optional) |
|
Folder |
An absolute directory path is recommended. |
AS1 (optional) Email (optional) |
|
Folder name |
An absolute directory path is recommended. |
File (required) FTP (required) |
|
Host name |
The trading partner's transport or e-mail server exchanging messages. |
AS1 (required) AQ (optional) FTP (required) SFTP (required) Email (required) |
|
Is Map Payload Alone |
Indicates that the payload is sent alone as part of a JMS message of type j |
JMS (optional) |
|
Is topic |
Select to indicate that JMS is communicating with a topic (not a queue). |
JMS (optional) |
|
Message type |
Select a JMS messages type: BYTES, TEXT, or MAP. |
JMS (optional) |
|
Pass phrase and Confirm pass phrase |
If you enter a private key file location, and if the private key file is pass-phrase protected, then enter the pass phrase. |
SFTP (optional) |
|
Password and Confirm Password |
To use password authentication, provide a key store password, which is used for authentication. |
AS1 (optional) AQ (optional) FTP (optional) SFTP (optional) JMS (optional) Email (optional) |
|
Path |
The absolute directory path where messages are sent from or received. |
SFTP (required) |
|
Polling interval |
The time interval in milliseconds during which Oracle B2B polls the server for inbound messages. |
AS1 (optional) File (optional) AQ (optional) FTP (optional) SFTP (optional) JMS (optional) Email (optional) |
|
Port number |
AQ runs on default port 1521. SFTP runs on default port 22, which can be changed to another port. FTP runs on default port 21, which is not displayed. See the description of Control Port for how to change this port number. |
AQ (optional) SFTP (required) |
|
Private key |
To use public key authentication, provide the private key file location. You may also need to provide a pass phrase if the private key file is pass-phrase protected. |
SFTP (optional) |
|
Queue name |
The AQ queue name. |
AQ (optional) |
|
Recipient |
The value used when delivering a message to the AQ queue. For example, if you set the recipient to |
AQ (optional) |
|
Send as attachment |
If enabled, the message (payload) is sent as an e-mail attachment instead of the typical delivery in which the payload is the message body. |
AS1 (optional) Email (optional) |
|
SID |
System ID to identify an Oracle database. |
AQ (optional) |
|
Subject |
The subject header of the e-mail message. |
AS1 (optional) Email (optional) |
|
Subscriber ID |
The JMS subscriber ID is required if JMS is communicating with a topic. |
JMS |
|
User name |
The user name (login name) to connect to the target servers. This value is optional for AQ and JMS because B2B can use the configured JNDI data sources to connect to queues. |
AS1 (required) AQ (optional) FTP (required) SFTP (required) JMS (optional) Email (required) |
|
Use proxy |
Select this option if a proxy server is used. |
FTP (optional) SFTP (optional) |
|
Channel Attributes |
The channel is the communication interface between the host trading partner's host application and its installation. |
|
|
Ack Mode |
Select Sync, Async, or None for the mode in which the trading partner receives messages. Select None for all generic exchanges. |
AS1 (optional) |
|
Description |
Provide an optional description. |
AS1 (optional) File (optional) AQ (optional) FTP (optional) SFTP (optional) JMS (optional) Email (optional) |
|
Enable/Disable Channel |
The channel is the communication interface between the host trading partner's host application and its installation. |
AS1 (required) File (required) AQ (required) FTP (required) SFTP (required) JMS (required) Email (Required) |
|
Internal |
Select this option if the channel is internal to the host trading partner's enterprise. (This feature is disabled for AS1.) |
File (optional) AQ (optional) FTP (optional) SFTP (optional) JMS (optional) Email (optional) |
|
Response Mode |
Select Sync, Async, or None, |
AS1 (required) |
|
Retry Count |
The number of times that Oracle B2B retries sending the message. |
AS1 (optional) File (optional) AQ (optional) FTP (optional) SFTP (optional) JMS (optional) Email (optional) |
|
Retry Interval |
The time interval in seconds during which Oracle B2B attempts to resend the message. A time interval of 2 minutes increments the HH:MM:SS timestamp as follows: If the sent timestamp is 3:42:58, then 42 seconds is incremented by 2 minutes and the retry is sent at 3:44:00. The seconds are dropped in the retry increment. Subsequent retries are at 2 minute intervals. For protocols with acknowledgments, B2B waits for the acknowledgment (formerly called the Time to Acknowledge parameter). If it is not received, the retry interval setting causes B2B to retry |
AS1 (optional) File (optional) AQ (optional) FTP (optional) SFTP (optional) JMS (optional) Email (optional) |
|
Exchange Protocol Parameters |
The exchange protocol defines the headers, acknowledgments, and packaging that puts the headers and payload together (the message exchange mechanism). The exchange protocol also defines signing and compression. |
- |
|
Signed and Compressed |
Select to enable these options. |
AS1 (optional) |
|
Security Parameters |
- |
- |
|
Ack Signed |
Select this option to ensure that the responder acknowledges receipt of the messages; nothing needs to be provided. |
AS1 |
|
Digital Signature |
If Message Signed is selected, then select one of the following: SMIME 3.0 with MD5 - RSA SMIME 3.0 with SHA1 - RSA |
AS1 |
|
Encryption |
If Message Encrypted is selected, then select one of the following: SMIME 3.0 with DES SMIME 3.0 with 3DES SMIME 3.0 with RC2 - 40 SMIME 3.0 with RC2 - 64 SMIME 3.0 with RC2 - 128 |
AS1 |
|
Message Encrypted |
Select this option to enable message encryption. This option requires you to select an encryption schema in the Encryption field. |
AS1 |
|
Message Signed |
Select this option to provide one of the digital signatures in the Digital Signature field. |
AS1 |
14.4 Configuring a Listening Channel
To configure a listening channel, add a listening channel protocol, and then transport protocol parameters, channel attributes, exchange protocol parameters, and security parameters, depending on the channel protocol you selected.
To add a listening channel protocol:
-
Click the Administration link.
-
Click the Listening Channel tab.
-
Click Add.
-
Provide a name for the listening channel.
-
Select a protocol.
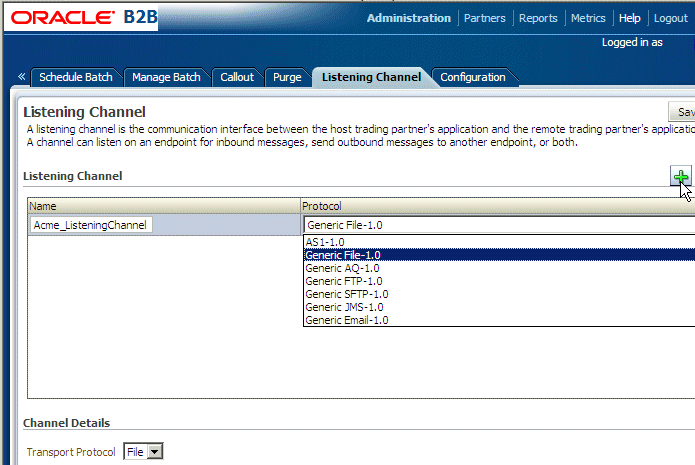
Description of the illustration bb_listen_chan1.gif
See Table 14-1 for a description of the protocols.
The transport protocol that appears under Channel Details is based on your protocol selection in Step 5.
-
Click Save.
To add transport protocol parameters:
-
Click the Transport Protocol Parameters tab.
-
Provide transport protocol parameters, depending on the channel/transport protocols.
Table 14-3 describes the transport protocol parameters (listed in alphabetical order within the transport protocol parameters category) and the protocols to which the parameters apply.
-
Click Save.
-
Click the Channel Attributes tab.
-
Provide channel attributes, depending on the channel/transport protocols selected.
Table 14-3 describes the channel attributes (listed in alphabetical order within the channel attributes category) and the protocols to which the attributes apply.
-
Click Save.
To add exchange protocol parameters:
-
Click the Exchange Protocol Parameters tab.
-
Provide exchange protocol parameters, depending on the channel/transport protocols selected.
Table 14-3 describes the exchange protocol parameters (listed in alphabetical order within the exchange protocol parameters category) and the protocols to which the attributes apply.
-
Click Save.
-
Click the Security Parameters tab.
-
Provide security parameters, depending on the channel/transport protocols selected.
Table 14-3 describes the security parameters (listed in alphabetical order within the security parameters category) and the protocols to which the attributes apply.
-
Click Save.