A Oracle ADF XML Files
This appendix provides reference for the Oracle ADF metadata files that you create in your data model and user interface projects. You may use this information when you want to edit the contents of the metadata these files define.
This appendix includes the following sections:
A.1 Introduction to the ADF Metadata Files
Metadata files in the Oracle Fusion web application are structured XML files used by the application to:
-
Specify the parameters, methods, and return values available to your application's Oracle ADF data control usages
-
Create objects in the Oracle ADF binding context and define the runtime behavior of those objects
-
Define configuration information about the UI components in JSF and ADF Faces
-
Define application configuration information for the Java EE application server
In the case of ADF bindings, you can use the binding-specific editors to customize the runtime properties of the binding objects. You can open a binding editor when you display the Structure window for a page definition file and choose Properties from the context menu.
Additionally, you can view and edit the contents of any metadata file in JDeveloper's XML editor. The easiest way to work with these file is through the Structure window and Property Inspector. In the Structure window, you can select an element and in the Property Inspector, you can define attribute values for the element, often by choosing among dropdown menu choices. Use this reference to learn the choices you can select in the case of the Oracle ADF-specific elements.
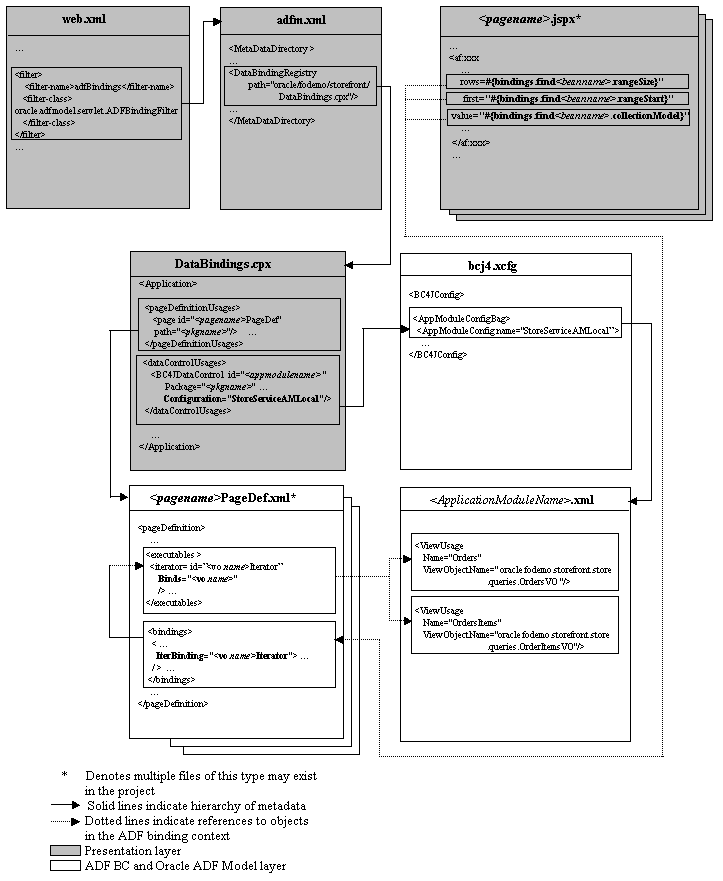
A.2 ADF File Overview Diagram
The relationship between the Oracle ADF metadata files defines dependencies between the model data and the user interface projects. The dependencies are defined as file references within XML elements of the files.
Figure A-1 illustrates the hierarchical relationship of the XML metadata files that you might work with in a Fusion web application that uses an ADF Business Components application module as a service interface to JSF web pages.
A.2.1 Oracle ADF Data Control Files
In an ADF Business Components application, the data control implementation files are contained within the application. The application module and view object XML component descriptor files provide the references for the data control. These files, in conjunction with the bc4j.xcfg file, provide the necessary information for the data control.
An application that uses ADF Business Components in one project and a non-ADF Business Components data control in another project may have a DataControls.dcx file, as well as supporting <sessionbeanname>.xml and <beanname>.xml files.
A.2.2 Oracle ADF Data Binding Files
These standard XML configuration files for a Fusion web application appear in your user interface project:
-
adfm.xml: This file lists theDataBindings.cpxfile that is available in the current project.See Section A.4, "adfm.xml" for more information.
-
DataBindings.cpx: This file contains the page map, page definitions references, and data control references. The file is created the first time you create a data binding for a UI component (either from the Structure window or from the Data Controls Panel). TheDataBindings.cpxfile defines the Oracle ADF binding context for the entire application. The binding context provides access to the bindings and data controls across the entire application. TheDataBindings.cpxfile also contains references to the<pagename>PageDef.xmlfiles that define the metadata for the Oracle ADF bindings in each web page.For more information, see Section A.7, "DataBindings.cpx".
-
<pagename>PageDef.xml: This is the page definition XML file. It associates web page UI components with data, or data controls. JDeveloper creates this file each time you design a new web page using the Data Controls Panel or Structure window. These XML files contain the metadata used to create the bindings that populate the data in the web page's UI components. For every web page that refers to an ADF binding, there must be a corresponding page definition file with binding definitions.For more information, see Section A.8, "pageNamePageDef.xml".
A.2.3 Web Configuration Files
These standard XML configuration files required for a JSF application appear in your user interface project:
-
web.xml: Part of the application's configuration is determined by the contents of its Java EE application deployment descriptor,web.xml. Theweb.xmlfile defines everything about your application that a server needs to know. The file plays a role in configuring the Oracle ADF data binding by setting up theADFBindingFilter. Additional runtime settings include servlet runtime and initialization parameters, custom tag library location, and security settings.For more information about ADF data binding and JSF configuration options, see Section A.13, "web.xml".
An ADF Faces application typically uses its own set of configuration files in addition to
web.xml. For more information, see the "Configuration in trinidad-config.xml" section in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Web User Interface Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework. -
adfc-config.xml:The configuration file for an ADF unbounded task flow. The configuration file contains metadata about the activities and control flows contained in the unbounded task flow. The default name for this file isadfc-config.xml, but an end user can change the name.For more information, see Section A.9, "adfc-config.xml".
-
task-flow-definition.xml: The configuration file for an ADF bounded task flow. The configuration file contains metadata about the activities and control flows contained in the bounded task flow. The default name for this file can be task-flow-defintion.xmlor whatever an end user specifies in the Create ADF Task Flow dialog. The same application can contain multiple task flow definition files.For more information, see Section A.10, "task-flow-definition.xml".
A.3 ADF File Syntax Diagram
Figure A-2 illustrates the hierarchical relationship of the XML metadata files that you might work with in a web application that uses an ADF application module as a service interface to ADF Business Components. At runtime, the objects created from these files interact in this sequence:
-
When the first request for an ADF databound web page occurs, the servlet registers the Oracle ADF servlet filter
ADFBindingFilternamed in theweb.xmlfile. -
The binding filter creates an empty binding context.
-
When a page is rendered, the binding filter asks the binding context to load a corresponding
PageDef.xmlfor the page. -
The binding context creates the binding container by loading the
<page>file as referenced by the<pagemap>element in theDataBindings.cpxfile. -
The
adfm.xmlfile loads theDataBindings.cpxcontents and finds the rightPageDef.xmlbased on the<pagemap>element reference to the<pageDefinitionUsage>element. -
The binding container's
prepareModelphase prepares and refreshes all relevant executables (most are markeddeferredby default). -
An iterator binding gets executed by referencing the named method on the data control found through the data control factory named in the case of ADF Business Components in the
bc4j.xcfgfile. -
The binding container also creates the bindings defined in the
<bindings>section of thepagenamePageDef.xmlfile for the mapped web page. -
The web page references to ADF bindings through EL using the expression
#{bindings}are resolved by accessing the binding container of the page. -
The page pulls the available data from the bindings in the binding container.
A.4 adfm.xml
The adfm.xml file contains the classpath-relative paths for the .cpx, .dcx, .jpx, and .xcfg files in each design time project that is included in the runtime deployed application. The adfm.xml file operates as a dynamically maintained "Registry of Registries" that is used to quickly find all .cpx, .dcx, .jpx, and .xcfg files (which are themselves registries of metadata).
The file registry is used extensively by the ADF Library resource catalog browsing implementations, by the ADF model layer design time, and at runtime during merge and discovery.
When a developer creates a binding on a page, JDeveloper adds metadata files (for example, page definitions) in the project source tree. The adfm.xml file then notes the location of each.
When a project is built, the adfm.xml file is put in project-root/adfmsrc/META-INF/adfm.xml. The project-level archive deployment profiles locate the file at META-INF/adfm.xml.
At runtime, the application classpath is scanned to build the list of .cpx files that comprise the application. The application then loads each.cpx as needed to create the binding context. For details about the ADF model layer usage, see Section 12.3.2, "What Happens When You Use the Data Controls Panel".
Four types of sub registries are recorded by the adfm.xml file:
-
DataBindingRegistry(.cpx) -
DataControlRegistry(.dcx) -
BusinessComponentServiceRegistry(.xcfg) -
BusinessComponentProjectRegistry(.jpx)
A.5 modelProjectName.jpx
The.jpx file contains configuration information that JDeveloper uses in the design time to allow you to create the data model project with ADF Business Components. It also contains metadata that defines how a shared application module is used at runtime. Because the shared application module can be accessed by any data model project in the same Fusion web application, JDeveloper maintains the scope of the shared application module in the ADF Business Components project configuration file.
This file is saved in the src directory of the project. For example, if you look at the StoreFrontService.jpx file in the ./src/model subdirectory of the Fusion Order Demo application's StoreFrontService project, you will see the SharedLookupService application module's usage definition. For details about the shared application module usage, see Section 10.2.2, "What Happens When You Define a Shared Application Module".
Example A-2 displays a sample default.jpx file.
<JboProject
xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/bc4j"
Name="StoreFrontService"
Version="11.1.1.49.73"
SeparateXMLFiles="true"
PackageName="">
<DesignTime>
<Attr Name="_appModuleNames0"
Value="oracle.fodemo.storefront.lookups.LookupServiceAM"/>
<Attr Name="_domainNames0"
Value="oracle.fodemo.storefront.entities.formatters.UppercaseOracleStyleDate"/>
<Attr Name="_jprName" Value="../StoreFrontService.jpr"/>
<Attr Name="_appModuleNames1"
Value="oracle.fodemo.storefront.store.service.StoreServiceAM"/>
<Attr Name="_NamedConnection" Value="FOD"/>
</DesignTime>
<Containee
Name="links"
FullName="oracle.fodemo.storefront.account.queries.links.links"
ObjectType="JboPackage">
<DesignTime>
<Attr Name="_VO" Value="true"/>
<Attr Name="_VL" Value="true"/>
</DesignTime>
</Containee>
<Containee
Name="queries"
FullName="oracle.fodemo.storefront.account.queries.queries"
ObjectType="JboPackage">
<DesignTime>
<Attr Name="_VO" Value="true"/>
</DesignTime>
</Containee>
<Containee
Name="associations"
FullName="oracle.fodemo.storefront.entities.associations.associations"
ObjectType="JboPackage">
<DesignTime>
<Attr Name="_AS" Value="true"/>
</DesignTime>
</Containee>
<Containee
Name="entities"
FullName="oracle.fodemo.storefront.entities.entities"
ObjectType="JboPackage">
<DesignTime>
<Attr Name="_EO" Value="true"/>
</DesignTime>
</Containee>
<Containee
Name="formatters"
FullName="oracle.fodemo.storefront.entities.formatters.formatters"
ObjectType="JboPackage">
<DesignTime>
<Attr Name="_DO" Value="true"/>
</DesignTime>
</Containee>
<Containee
Name="lookups"
FullName="oracle.fodemo.storefront.lookups.lookups"
ObjectType="JboPackage">
<DesignTime>
<Attr Name="_VO" Value="true"/>
<Attr Name="_AM" Value="true"/>
</DesignTime>
</Containee>
<Containee
Name="links"
FullName="oracle.fodemo.storefront.store.queries.links.links"
ObjectType="JboPackage">
<DesignTime>
<Attr Name="_VL" Value="true"/>
</DesignTime>
</Containee> <Containee
Name="queries"
FullName="oracle.fodemo.storefront.store.queries.queries"
ObjectType="JboPackage">
<DesignTime>
<Attr Name="_VO" Value="true"/>
</DesignTime>
</Containee>
<Containee
Name="service"
FullName="oracle.fodemo.storefront.store.service.service"
ObjectType="JboPackage">
<DesignTime>
<Attr Name="_AM" Value="true"/>
</DesignTime>
</Containee>
<AppModuleUsage
Name="SharedLookupService"
FullName="oracle.fodemo.storefront.lookups.LookupServiceAM"
ConfigurationName="oracle.fodemo.storefront.lookups.null"
SharedScope="1"/>
</JboProject>
A.6 bc4j.xcfg
The bc4j.xcfg file contains metadata information about application module names, the database connection used by the application module, and the runtime parameters the user has configured for the application module.
The bc4j.xcfg file is located in the ./common subdirectory relative to the application module's XML component definition. All of the configurations for all of the application modules in a single Java package are saved in that same file. For example, if you look at the bc4j.xcfg file in the ./classes/oracle/fodemo/storefront/store/service/common directory of the Fusion Order Demo application's StoreFront project, you will see the three named configurations for its StoreServiceAM application module. For details about editing the configurations, see Section 9.3.4, "How to Change Your Application Module's Runtime Configuration" and Section 41.2, "Setting Pool Configuration Parameters".
Example A-2 displays a sample bc4j.xcfg file from the Fusion Order Demo application.
Example A-2 Sample bc4j.xcfg File
<BC4JConfig version="11.1" xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/bc4j/configuration">
<AppModuleConfigBag ApplicationName="oracle.fodemo.storefront.store.service.StoreServiceAM">
<AppModuleConfig
DeployPlatform="LOCAL"
JDBCName="FOD"
jbo.project="StoreFrontService"
name="StoreServiceAMLocal"
ApplicationName="oracle.fodemo.storefront.store.service.StoreServiceAM">
<Database jbo.locking.mode="optimistic"/>
<Security AppModuleJndiName="oracle.fodemo.storefront.store.service.StoreServiceAM"/>
</AppModuleConfig>
<AppModuleConfig
DeployPlatform="LOCAL"
JDBCName="FOD"
jbo.project="StoreFrontService"
name="StoreServiceAMLocalWeb"
ApplicationName="oracle.fodemo.storefront.store.service.StoreServiceAM">
<AM-Pooling jbo.ampool.initpoolsize="1"/>
<Database jbo.locking.mode="optimistic"/>
<Security AppModuleJndiName="oracle.fodemo.storefront.store.service.StoreServiceAM"/>
<Custom fod.application.issoaenabled="true"/>
</AppModuleConfig>
<AppModuleConfig
name="StoreFrontService"
ApplicationName="oracle.fodemo.storefront.store.service.StoreServiceAM"
jbo.project="StoreFrontService"
DeployPlatform="SI">
<AM-Pooling jbo.ampool.resetnontransactionalstate="true"/>
<Database jbo.SQLBuilder="ORACLE" jbo.locking.mode="optimistic"
jbo.TypeMapEntries="Java"/>
<Security AppModuleJndiName="oracle.fodemo.storefront.store.service.StoreServiceAM"/>
<Custom JDBCDataSource="java:comp/env/jdbc/FODDS"/>
</AppModuleConfig>
</AppModuleConfigBag>
</BC4JConfig>
A.7 DataBindings.cpx
The DataBindings.cpx file is created in the user interface project the first time you drop a data control usage onto a web page in the visual editor. The DataBindings.cpx file defines the Oracle ADF binding context for the entire application and provides the metadata from which the Oracle ADF binding objects are created at runtime. It is used extensively by the ADF Library Resource Palette browsing implementations, and also by the .cpx and .dcx design time and runtime merge and discovery. When you insert a databound UI component into your document, the page will contain binding expressions that access the Oracle ADF binding objects at runtime.
If you are familiar with building Fusion web applications in earlier releases of JDeveloper, you'll notice that the.cpx file no longer contains all the information copied from the DataControls.dcx file, but only a reference to it. If you need to make changes to the.cpx file, you must edit the DataControls.dcx file.
The DataBindings.cpx file appears in the /src directory of the user interface project. When you double-click the file node, the binding context description appears in the XML source editor. (To edit the binding context parameters, use the Property Inspector and select the desired parameter in the Structure window.)
A.7.1 DataBindings.cpx Syntax
The top level element of the DataBindings.cpx file is <DataControlConfigs>:
<?xml version = '1.0' encoding = 'UTF-8'?> <BC4JConfig version="11.0" xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/bc4j/configuration">
where the XML namespace attribute (xmlns) specifies the URI to which the data controls bind at runtime. Only the package name is editable; all other attributes should have the values shown.
Figure A-3 displays the child element hierarchy of the <DataControlConfigs> element. Note that each business service for which you have created a data control will have its own <dataControlUsages> definition.
The child elements have the following usages:
-
<definitionFactories>registers a factory class to create the ADF binding objects associated with a particular namespace at runtime. The factory class is specific to the namespace associated with the type of ADF binding (for instance, a task flow binding). -
<pageMap>maps all user interface URLs and the corresponding page definition usage name. This map is used at runtime to map a URL to its page definition. -
<pageDefinitionUsages>maps a page definition usage (BindingContainerinstance) name to the corresponding page definition. Theidattribute represents the usage ID. The path attribute represents the full path to the page definition. -
<dataControlUsages>declares a list of data control usages (shortnames) and corresponding path to the data control definition entries in the.dcxor.xcfgfile.
Table A-1 describes the attributes of the DataBindings.cpx elements.
Table A-1 Attributes of the DataBindings.cpx File Elements
A.7.2 DataBindings.cpx Sample
Example A-3 shows the syntax for the DataBindings.cpx file in the Fusion Order Demo application.
The ADF executable definition factory (factory element) is named by a className attribute and is associated with a namespace. At runtime, the factory class creates the executable definition objects that leads to the creation of the binding objects for the ADF binding container associated with a particular page definition. The factory locates the page definition through two DataBindings.cpx file elements: the pageMap element that maps the page URL to the page definition ID (usageId attribute) assigned at design time and the pageDefinitionUsages element that maps the ID to the location of the page definition from the project or project classpath.
Additionally, the ADF Business Components data control (BC4JDataControl element) is named by the id attribute. The combination of the Package attribute and the Configuration attribute is used to locate the bc4j.xcfg file in the ./common subdirectory of the indicated package. The configuration contains the information of the application module name and all the runtime parameters the user has configured.
Example A-3 Sample DataBindings.cpx File
<Application xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adfm/application"
version="11.1.1.44.61" id="DataBindings" SeparateXMLFiles="false"
Package="oracle.fodemo.storefront" ClientType="Generic"
ErrorHandlerClass="oracle.fodemo.frmwkext.FODCustomErrorHandler">
<definitionFactories>
<factory nameSpace="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/controller/binding"
className="oracle.adf.controller.internal.binding.
TaskFlowBindingDefFactoryImpl"/>
<factory nameSpace="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adfm/dvt"
className="oracle.adfinternal.view.faces.dvt.model.binding.
FacesBindingFactory"/>
</definitionFactories>
<pageMap>
<page path="/home.jspx" usageId="homePageDef"/>
...
</pageMap>
<pageDefinitionUsages>
<page id="homePageDef"
path="oracle.fodemo.storefront.pageDefs.homePageDef"/>
...
</pageDefinitionUsages>
<dataControlUsages>
<BC4JDataControl id="StoreServiceAMDataControl"
Package="oracle.fodemo.storefront.store.service"
FactoryClass="oracle.adf.model.bc4j.DataControlFactoryImpl"
SupportsTransactions="true" SupportsFindMode="true"
SupportsRangesize="true" SupportsResetState="true"
SupportsSortCollection="true"
Configuration="StoreServiceAMLocalWeb" syncMode="Immediate"
xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adfm/datacontrol"/>
...
</dataControlUsages>
</Application>
A.8 pageNamePageDef.xml
The pageNamePageDef.xml files are created each time you insert a databound component into a web page using the Data Controls Palette or Structure window. These XML files define the Oracle ADF binding container for each web page in the application. The binding container provides access to the bindings within the page. You will have one XML file for each databound web page.
Caution:
TheDataBindings.cpx file maps JSF pages to their corresponding page definition files. If you change the name of a page definition file or a JSF page, JDeveloper does not automatically refactor the DataBindings.cpx file. You must manually update the page mapping in the DataBindings.cpx file.The PageDef.xml file appears in the /src/view directory of the user interface project. The Application Navigator displays the file in the view package of the Application Sources node. When you double-click the file node, the page description appears in the XML source editor. To edit the page description parameters, use the Property Inspector and select the desired parameter in the Structure window.
For more information, see Chapter 12, "Working with Page Definition Files".
There are important differences in how the page definitions are generated for methods that return a single value and a collection.
A.8.1 PageDef.xml Syntax
The top-level element of the PageDef.xml file is <pageDefinition>:
<pageDefinition xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adfm/uimodel"
version="10.1.3.35.83" id="<pagename>PageDef"
Package="oracle.fod.view.pageDefs">
where the XML namespace attribute (xmlns) specifies the URI to which the ADF binding container binds at runtime. Only the package name is editable; all other attributes should have the values shown.
Example A-4 displays the child element hierarchy of the <pageDefinition> element. Note that each business service for which you have created a data control will have its own <AdapterDataControl> definition.
Example A-4 PageDef.xml Element Hierarchy
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<pageDefinition>
<parameters>
...
</parameters>
<executables>
...
</executables>
<bindings>
...
</bindings>
</pageDefinition>
The child elements have the following usages:
-
<parameters>defines page-level parameters that are EL accessible. These parameters store information local to the web page request and may be accessed in the binding expressions. -
<executables>defines the list of items (methods, view objects, and accessors) to execute during theprepareModelphase of the ADF page lifecycle. Methods to be executed are defined by<methodIterator>. The lifecycle performs the execute in the sequence listed in the<executables>section. Whether or not the method or operation is executed depends on its refresh orrefreshConditionattribute value. Built-in operations on the data control are defined by:-
<page>- definition for a nested page definition (binding container)-
<iterator>- definition to a named collection inDataControls-
<accessorIterator>- definition to get an accessor in a data control hierarchy-
<methodIterator>- definition to get to an iterator returned by an invoked method defined by amethodActionin the same file-
<variableIterator>- internal iterator that contains variables declared for the binding container-
<invokeAction>- definition of which method to invoke as an executable -
<bindings>refers to an entry in<executables>to get to the collection from which bindings extract/submit attribute level data.
Table A-2 describes the attributes of the top-level <pageDefinition> element.
Table A-2 Attributes of the PageDef.xml File <pageDefinition> Element
| Element Syntax | Attributes | Attribute Description |
|---|---|---|
|
ControllerClass |
Fully qualified class name to create when controller requests a |
|
|
EnableTokenValidation |
Enables currency validation for this bindingContainer when a postback occurs. This is to confirm that the web tier state matches the state that particular page was rendered with. |
|
|
FindMode |
FindMode is for legacy (10.1.2) use only and indicates whether this bindingContainer should start out in findMode when initially prepared. |
|
|
MsgBundleClass |
Fully qualified package name. Identifies the class which contains translation strings for any bindings. |
|
|
SkipValidation |
Determines if data validation occurs. The supported values are:
Setting a value for this attribute can be useful if you want to skip data validation on, for example, a train component. For more information see the "How to Create the Train Model" section of the Oracle Fusion Middleware Web User Interface Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework |
|
|
Viewable |
An EL expression that should resolve at runtime to whether this binding and the associated component should be rendered or not. |
Table A-3 describes the attributes of the child element of <parameters>.
Table A-3 Attributes of the PageDef.xml File <parameters> Element
| Element Syntax | Attributes | Attribute Description |
|---|---|---|
|
evaluate |
Specifies when the parameter should be evaluated: |
|
|
id |
Unique identifier. May be referenced by ADF bindings. |
|
|
option |
Indicates the usage of the variable within the binding container:
|
|
|
readonly |
Indicates whether the parameter value may be modified or not. Set to |
|
|
|
A default value, which can be an EL expression. |
Table A-4 describes the attributes of the PageDef.xml <executables> elements.
Table A-4 Attributes of the PageDef.xml File <executables> Element
| Element Syntax | Attributes | Attribute Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Specifies any other accessor defined by this binding. |
|
|
Specifies the view or action to which the iterator is bound. |
|
|
|
Identifies the Java type of beans in the associated iterator or collection. |
|
|
|
If |
|
|
|
Specifies the rate of events when a component is wired to data via this iterator and is in polling event mode. |
|
|
|
Interprets and returns the collection referred to by this iterator binding. |
|
|
|
Unique identifier. May be referenced by any ADF value binding. |
|
|
|
Reference to the |
|
|
|
Used for ADF Business Components only. A boolean value determines whether the collection is an object type or not. |
|
|
|
Specifies the number of data objects in a range to fetch from the bound collection. The range defines a window you can use to access a subset of the data objects in the collection. By default, the range size is set to a range that fetches just ten data objects. Use |
|
|
|
Determines when and whether the executable should be invoked. Set one of the following properties as required:
|
|
|
|
An EL expression that when resolved, determines when and whether the executable should be invoked. For example, |
|
|
|
Specifies the condition after which the page should be refreshed. |
|
|
|
Specify a value to determine if a result set returns the number of rows you specify as a value. If you set Set |
|
|
|
Specifies whether the iterator is sortable or not. |
|
|
|
Determines the action to invoke. This may be on any
|
|
|
|
Unique identifier. May be referenced by any ADF action binding. |
|
|
|
See |
|
|
|
See |
|
|
|
Identifies the Java type of beans in the associated iterator or collection. |
|
|
|
This is for backward compatibility to indicate which class implements the runtime for this binding definition. Not used in current JDeveloper release. |
|
|
|
See |
|
|
|
See |
|
|
|
Specifies the rate of events when a component is wired to data via this iterator and is in polling event mode. |
|
|
|
Name of the |
|
|
|
Used internally by ADF. |
|
|
|
Unique identifier. May be referenced by any ADF value binding. |
|
|
|
Not used by EJB session facade data control (used by ADF Business Components only). |
|
|
|
See |
|
|
|
See |
|
|
|
Specifies the condition after which the page should be refreshed. |
|
|
|
See |
|
|
|
See |
|
|
|
Unique identifier. In the case of |
|
|
|
Specifies the rate of events when a component is wired to data via this iterator and is in polling event mode. |
|
|
|
Used by |
|
|
|
See |
|
|
|
Specifies the condition after which the page should be refreshed. |
|
|
|
See |
Table A-5 describes the attributes of the PageDef.xml <bindings> element.
Table A-5 Attributes of the PageDef.xml File <bindings> Element
| Element Syntax | Attributes | Attribute Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Fully qualified package name. Identifies the class for which the data control is created. In the case of the EJB session facade, this is the session bean. |
|
|
|
This is for backward compatibility to indicate which class implements the runtime for this binding definition. This is used by earlier versions of JDeveloper. |
|
|
|
Name of the |
|
|
|
Used by default when you drop an operation from the Data Controls Panel in the automatically configured |
|
|
|
Specifies the instance name for the action. |
|
|
|
Specifies the |
|
|
|
Use if you want to use the result of a method action binding (once converted to a |
|
|
|
Set to |
|
|
|
This is for backward compatibility to indicate which class implements the runtime for this binding definition. This is used by earlier versions of JDeveloper. |
|
|
|
Specifies the event strategy for the component when run with ADS (Active Data Services). Can be specified as push poll ppr none |
|
|
|
Used internally by ADF. |
|
|
|
This is the class name for a o |
|
|
|
Used internally by ADF. |
|
|
|
Unique identifier. May be referenced by any ADF action binding. |
|
|
|
Refers to the |
|
|
|
Refers to the entry in the message bundle for this |
|
|
|
Set to |
|
|
|
This is for backward compatibility to indicate which class implements the runtime for this binding definition. This is used by earlier versions of JDeveloper. |
|
|
|
Identifies whether the value at the zero index in the static value list in this boolean list binding represents |
|
|
|
Used internally by ADF. |
|
|
|
This is the class name for a |
|
|
|
Used internally by ADF. |
|
|
|
Unique identifier. May be referenced by any ADF action binding. |
|
|
|
Refers to the |
|
|
|
Refers to the |
|
|
|
Determines whether this list binding is for navigation, contains a static list of values or is an LOV type list. |
|
|
|
Describes whether this list binding has a null value and, if so, whether it should be displayed at the beginning or the end of the list. |
|
|
|
Refers to the entry in the message bundle for this |
|
|
|
Maps the data binding XML for an ADF Faces gantt component. |
|
|
|
Maps the data binding XML for an ADF Faces gauge component. |
|
|
|
Set to |
|
|
|
This is for backward compatibility to indicate which class implements the runtime for this binding definition. This is used by earlier versions of JDeveloper. |
|
|
|
Identifies whether the value at the zero index in the static value list in this boolean list binding represents |
|
|
|
The name of the accessor to invoke to get the next level of nodes for a given hierarchical node type in a tree. |
|
|
|
Used internally by ADF. |
|
|
|
This is the class name for a |
|
|
|
Used internally by ADF. |
|
|
|
An XML file that specifies the type of graph to use, for example, pie chart or bar graph. This XML file can be used to customize the visual properties of the graph. It contains graph attributes such as title, subtitle, footnote, graph type, legend area, and plot area. The default filename is |
|
|
|
For master-detail forms, specifies the attribute that will be used to group data. |
|
|
|
Unique identifier. May be referenced by any ADF action binding. |
|
|
|
Refers to the |
|
|
|
Refers to the entry in the message bundle for this |
|
|
|
Defines the attribute, based on which data will be clubbed. |
|
|
|
Determines whether graph is for |
|
|
|
Wraps the data binding XML for an ADF Faces graph component. |
|
|
|
Set to |
|
|
|
This is for backward compatibility to indicate which class implements the runtime for this binding definition. This is used by earlier versions of JDeveloper. |
|
|
|
Used internally by ADF. |
|
|
|
This is the class name for a |
|
|
|
Used internally by ADF. |
|
|
|
Unique identifier. May be referenced by any ADF action binding. |
|
|
|
Refers to the |
|
|
|
Refers to the |
|
|
|
Determines whether this list binding is for navigation, contains a static list of values, or is an LOV type list. |
|
|
|
Specifies the number of items to display in a choice list when you want to provide a shortcut for the end-user to display their most recent selections. For example, a form might display a choice list of supplier ID values to drive a purchase order form. In this case, you can allow users to select from a list of their most recently view suppliers, where the number of supplier choices is determined by the count you enter. The default for the choice list is to display all values for the attribute and is specified by the count 0 (zero)." |
|
|
|
Specifies the |
|
|
|
Describes whether this list binding has a null value and, if so, whether it should be displayed at the beginning of the list or the end. |
|
|
|
Refers to the entry in the message bundle for this |
|
|
|
Defines a static list of values that will be rendered in the bound list component. |
|
|
|
Wraps the data binding XML for an ADF Data Visualization geographic map component. |
|
|
|
Fully qualified package name. Identifies the class for which the data control is created. In the case of the EJB session facade, this is the session bean. |
|
|
|
This is for backward compatibility to indicate which class implements the runtime for this binding definition. This is used by earlier versions of JDeveloper. |
|
|
|
This is the class to which the method being invoked belongs. |
|
|
|
Name of the |
|
|
|
Used internally by ADF. |
|
|
|
Unique identifier. May be referenced by any ADF action binding. |
|
|
|
A dot-separated EL path to a Java object instance on which the associated method is to be invoked. |
|
|
|
Set to |
|
|
|
Set to |
|
|
|
Indicates the name of the operation on the given instance or class that needs to be invoked for this |
|
|
|
Whether this action requires that the model be updated before the action is to be invoked. |
|
|
|
The EL path of the result returned by the associated method. |
|
|
|
Wraps the data binding XML for an ADF Faces pivot table component. |
|
|
|
Set to |
|
|
|
This is for backward compatibility to indicate which class implements the runtime for this binding definition.This is used by earlier versions of JDeveloper. |
|
|
|
Accesses the |
|
|
|
Used internally for testing purposes. |
|
|
|
This is the class name for a |
|
|
|
Used internally by ADF. |
|
|
|
Indicates the discriminator value for a hierarchical type binding (type definition for a tree node). This value is used to determine whether a given row in a collection being rendered in a polymorphic tree binding should be rendered using the containing hierarchical type binding. |
|
|
|
Unique identifier. May be referenced by any ADF action binding. |
|
|
|
Refers to the |
|
|
|
The data model used by ADF Tree components. |
A.9 adfc-config.xml
The default name for an ADF unbounded task flow's XML source file is adfc-config.xml. Each Fusion web application optionally contains a single ADF unbounded task flow. The adfc_config.xml file contains activities, control flow rules, and managed beans interacting to allow a user to complete a task.
The adfc-config.xml file is located in the /public_html/WEB-INF directory relative to the ADF application's user interface project.
For more information, see Section 14.1.2.1, "Unbounded Task Flows".
A.10 task-flow-definition.xml
The XML source file for an ADF bounded task flow is called a task flow definition. The name for this source file is taken from the value specified in the Task Flow ID field of the Create ADF Task Flow wizard. By default, JDeveloper proposes the following filename when you invoke the Create ADF Task Flow wizard: task-flow-definition.xml. A Fusion web application can contain one or more ADF bounded task flows. Each bounded task flow has its own task flow definition source file. For more information about bounded task flows, see Section 14.1.2.2, "Bounded Task Flows".
A.11 adf-config.xml
JDeveloper generates the adf-config.xml file when you create an application using the Fusion Web Application (ADF) template. It stores the file in the following directory:
application_root\.adf\META-INF
The adf-config.xml file specifies application-level settings that are usually determined at deployment and are often changed at runtime. You can use a deployment profile to specify settings that are used at application deploy time. You can change some of the settings at runtime using Oracle Enterprise Manager.
Changing settings in the adf-config.xml file allow you to, for example, enable or disable the validation of ADF Controller metadata. Another example is where you need to replicate memory scope if you deploy your Fusion web application in a clustered environment.
You can also change settings in the adf-config.xml file to manage the caching of resource bundles where your application uses EL expressions to retrieve strings at runtime from resource bundles. The properties that you can configure to do this are:
-
initial-sizeSpecifies the initial number of resource bundles that your application can cache. The default value is
100. -
max-sizeSpecifies the maximum number of resource bundles that your application can cache. The default value is
100. -
load-factorThe default value is
0.75. -
expire-timeThe default value is
43200seconds (12 hours).You specify these properties as attribute values of the
<resource-bundle-cache>element in theadf-config.xmlfile. Example A-5 demonstrates how you might configure these values for your application in theadf-config.xmlfile.
As an alternative to configuring the caching of resource bundles in the adf-config.xml file, you can specify the resource bundle caching properties as parameters for the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). If you specify the properties as parameters for the JVM, the changes apply to all applications managed by the JVM. For this reason, we recommend that you configure the resource bundle caching properties in the adf-config.xml file for you application. Use the following property names if you decide to specify the resource bundle caching properties as parameters for the JVM:
-
resource-bundle-cache-initial-size -
resource-bundle-cache-max-size -
resource-bundle-cache-load-factor -
resource-bundle-cache-expire-time
At runtime, the Fusion web application loads the adf-config.xml file from the META-INF directory. If the Fusion web application finds more than one adf-config.xml file, it stops loading the file and logs a warning.
The following tasks also modify or require you to modify the adf-config.xml file:
-
Creating task flows
For more information, see Chapter 14, "Getting Started with ADF Task Flows".
-
Enabling implicit save points
For more information, see Section 18.7.9, "How to Enable Implicit Save Points".
-
Persisting saved searches in MDS
For more information, see Section 27.2.3, "How to Persist Saved Searches into MDS".
-
Configure ADF Business Components global settings
For more information, see Section 39.1.1, "Limiting the View Object Max Fetch Size to Fetch the First n Rows" and see Section 3.3.1, "Choosing a Connection, SQL Flavor, and Type Map."
-
Enabling ADF Security
For more information, see Section 30.3.2, "What Happens When You Enable ADF Security".
-
Enabling seeded customizations
For more information, Section 34.2.4, "How to Enable Seeded Customizations for View Projects" and Section 34.2.5, "How to Enable Seeded Customizations in Existing Pages".
-
Configuring change persistence
For more information, see Section 35.2.1, "How to Enable User Customizations".
-
Enabling user customizations
For more information, see Section 35.2.2, "What Happens When You Enable User Customizations".
Example A-5 shows extracts from the Fusion Order Demo application's adf-config.xml file.
Example A-5 Sample adf-config.xml File
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="windows-1252" ?>
<adf-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/config"
xmlns:sec="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/security/config">
<sec:adf-security-child xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/security/config">
<JaasSecurityContext initialContextFactoryClass="oracle.adf.share.security.JAASInitialContextFactory"
jaasProviderClass="oracle.adf.share.security.providers.jps.JpsSecurityContext"
authorizationEnforce="true"
authenticationRequire="true"/>
<CredentialStoreContext credentialStoreClass="oracle.adf.share.security.providers.jps.CSFCredentialStore"
credentialStoreLocation="../../src/META-INF/jps-config.xml"/>
</sec:adf-security-child>
<adf-controller-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/controller/config">
<savepoint-datasource>java:comp/env/jdbc/FODDS</savepoint-datasource>
<enable-implicit-savepoints>true</enable-implicit-savepoints>
</adf-controller-config>
<adf-faces-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/faces/config">
<persistent-change-manager>
<persistent-change-manager-class>oracle.adf.view.rich.change.MDSDocumentChangeManager</persistent-change-manager-class>
</persistent-change-manager>
<taglib-config>
<taglib uri="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/faces/rich">
<tag name="calendar">
<attribute name="activeDay">
<persist-changes>true</persist-changes>
</attribute>
</tag>
<!-- Additional tags omitted to make this example concise -->
<tag name="table">
<attribute name="filterVisible">
<persist-changes>true</persist-changes>
</attribute>
</tag>
</taglib>
</taglib-config>
</adf-faces-config>
<adf-mds-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/mds/config">
<mds-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/mds/config" version="11.1.1.000">
<cust-config>
<match path="/">
<customization-class name="oracle.adf.share.config.UserCC"/>
</match>
</cust-config>
</mds-config>
</adf-mds-config>
<adf-adfm-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adfm/config">
<defaults rowLimit="100"/>
<startup>
<amconfig-overrides>
<config:Database jbo.SQLBuilder="Oracle" jbo.locking.mode="optimistic"/>
</amconfig-overrides>
</startup>
</adf-adfm-config>
<!-- Properties to manage the caching of a resource bundle in your application -->
<adf-resourcebundle-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/resourcebundle/config">
<applicationBundleName>
path-to-resource-bundle/bundle-name
</applicationBundleName>
<resource-bundle-cache initial-size="20" max-size="100" expire-time="30000" load-factor=".75"/>
<bundleList>
<bundleId override="true">
package.BundleID
</bundleId>
</bundleList>
</adf-resourcebundle-config>
</adf-config>
A.12 adf-settings.xml
The adf-settings.xml file holds project-level and library-level settings such as ADF Faces help providers and ADF Controller phase listeners.
The configuration settings for adf-settings.xml are fixed and cannot be changed during or after application deployment. There can be multiple adf-settings.xml files in an application. The users of adf-settings.xml files are responsible for merging the contents of their configuration.
The following tasks modify or require you to modify the adf-settings.xml file:
-
Registering a phase listener
For more information, see Section 21.4.2, "How to Register a Listener Globally".
-
Creating help for ADF Faces components
For more information, see the "Displaying Help for Components" section in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Web User Interface Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
For information about how to create and edit the adf-settings.xml file, see the "How to Configure for ADF Faces in adf-settings" section in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Web User Interface Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
Example A-6 shows a sample adf-setting.xml file with settings configured for a phase listener and a help provider.
Example A-6 Sample adf-settings.xml File
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="windows-1252" ?>
<adf-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/config">
<adfc-controller-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/controller/config">
<lifecycle>
<phase-listener>
<listener-id>FODPhaseListener</listener-id>
<class>oracle.fodemo.storefront.listeners.FODPhaseListener</class>
</phase-listener>
</lifecycle>
<help-provider prefix="MYAPP">
<help-provider-class>oracle.fodemo.storefront.MyHelpProvider</help-provider-class>
<property>
<property-name>myCustomProperty</property-name>
<value>someValue</value>
</property>
</help-provider>
</adfc-controller-config>
</adf-config>
A.13 web.xml
Oracle ADF has specific configuration settings for the standard web.xml deployment descriptor file.
When you create a project in JDeveloper that uses JSF technology, a starter web.xml file with default settings is created for you in the /WEB-INF folder. To edit the file, double-click web.xml in the Application Navigator to open it in the XML editor.
The following must be configured in web.xml for all applications that use JSF and ADF Faces:
-
JSF servlet and mapping: The servlet
javax.faces.webapp.FacesServletthat manages the request-processing lifecycle for web applications utilizing JSF to construct the user interface. -
ADF Faces filter and mapping: A servlet filter to ensure that ADF Faces is properly initialized by establishing a
AdfFacesContextobject. This filter also processes file uploads. -
ADF resource servlet and mapping: A servlet to serve up web application resources (images, style sheets, JavaScript libraries) by delegating to a
ResourceLoader.
The JSF servlet and mapping configuration settings are automatically added to the starter web.xml file when you first create a JSF project. When you insert an ADF Faces component into a JSF page for the first time, JDeveloper automatically inserts the configuration settings for ADF Faces filter and mapping, and resource servlet and mapping.
For more information, see the "ADF Faces Configuration" appendix in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Web User Interface Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
A.14 logging.xml
ADF Logger is a diagnostic tool that you can use in JDeveloper to capture runtime traces messages when you debug an application. You configure the use of this tool by editing the logging.xml file.
For more information about the logging.xml file and using the ADF Logger, see Section 31.5, "Using the ADF Logger".