Reference Materials
The Web GUI offers extensive online help. Through the GUI help, you can find details about performing all administrative tasks that the GUI helps you perform, plus reference information for all configuration tool folders.
Accessing the Control Panel Applet
To open the control panel applet, select Start![]() Control Panel
Control Panel![]() BEA TUXEDO.
BEA TUXEDO.
Figure 3-1 BEA TUXEDO System for Windows NT Control Panel

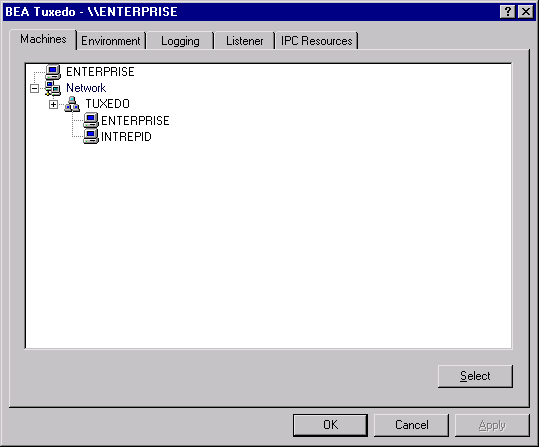
Accessing Machines on a Network
The MACHINES page enables the BEA TUXEDO administrator to access any machine on the Microsoft Windows Network running Windows NT, where the administrator has logon privileges. The administrator can then set environment variables remotely, determine the location of BEA TUXEDO event logging, add/start/remove tlisten services, and tune IPC resources. The administrator can access a remote machine by locating the machine on a network tree.
Figure 3-2 BEA TUXEDO System for Windows NT Machines Page
If you know a machine's name, but not its work group, click Select. Then type the name of the remote machine on the Enter Machine Name window and click OK.
Figure 3-3 BEA TUXEDO System for Windows NT Enter Machine Name Box

All subsequent actions on other folders in the control panel applet take place on the selected machine.
Modifying Environment Variables
Modifying BEA TUXEDO environment variables is almost identical to modifying Windows NT environment variables. The Variable field contains a list of the most commonly used BEA TUXEDO environment variables.
To add or edit a variable, select the variable, enter its value in its Value field, and click Set. To delete a variable, click the variable you want to delete and click Delete. Clicking OK or Apply saves any changes made to the BEA TUXEDO environment.
Figure 3-4 BEA TUXEDO System for Windows NT Environment Page

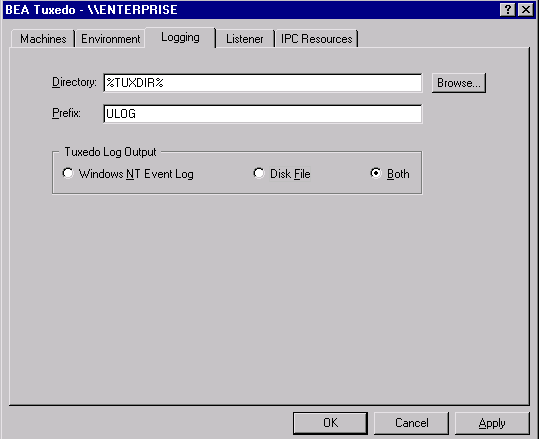
Directing BEA TUXEDO Messages to the Windows NT Event Log
You can direct BEA TUXEDO system messages to the Windows NT Event Log by setting the LOGGING page. You can select the Logging option (Windows NT Event Log) or the traditional ULOG (Disk File), or both. If you want traditional ULOG messages, select the directory into which ULOG messages will be written, as well as the prefix for the filename. The default prefix is ULOG, and the default filename is ULOG.mmddyy.
Figure 3-5 BEA TUXEDO System for Windows NT Logging Page
To view Event Log entries, select Start![]() Programs
Programs![]() Administrative Tools
Administrative Tools ![]() Event Viewer. From the Event Viewer Log window, verify that Application is checked.
Event Viewer. From the Event Viewer Log window, verify that Application is checked.
Figure 3-6 BEA TUXEDO System for Windows NT Event Detail Window

Each message identifies the message number and catalog that you can use to look up the description and recommended action in the BEA TUXEDO System Message Manual. Messages also have a type (that is, Information, Warning, or Error) and brief description.
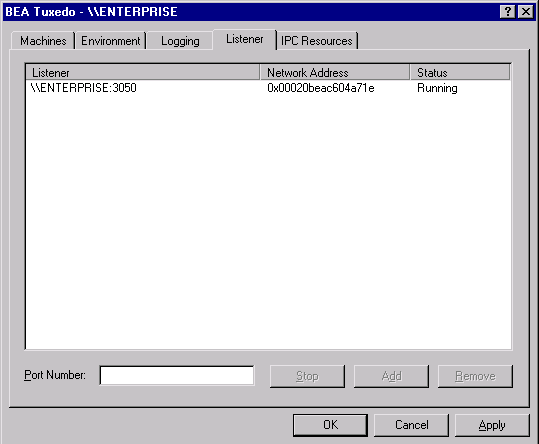
Configuring tlisten Processes to Start Automatically
You can configure one or more tlisten processes to start automatically when you boot up your system. On the Listener page, enter a port number in the Port Number field and click Add to add the service to the list. After you click OK or Apply, and reopen the control panel, you can start or stop tlisten services right on the LISTENER page. You can also use the Windows NT Services control panel to start or stop a tlisten service or to configure the service to start automatically.
Figure 3-7 BEA TUXEDO System for Windows NT Listener Page
You can use the tlisten program to perform administrative actions in an application across multiple computers. You must start the tlisten program on each computer before running the application. Generally, you need one tlisten for each BEA TUXEDO application running on the computer.
Maximizing System Performance
The BEA TUXEDO system for Windows NT provides you with BEA TUXEDO IPC Helper (TUXIPC), an interprocess communication subsystem, installed with the product. On most systems, IPC Helper runs as installed; however, you can use the RESOURCES page of the control panel applet to tune the TUXIPC subsystem and maximize performance.
With the IPC RESOURCES page of the control panel, you can set a variety of IPC resources to the right of each box. In the Select IPC Resources field, you can name a set of resources. Selecting the default Medium disables any changes to the parameters. If you backspace over Medium (a single backspace removes the whole string), the parameters are made available for changes. To add a new configuration, type New, edit the BEA TUXEDO IPC parameters as needed, and click Set to associate the name with the revised set of resources. Clicking Apply saves the changes in the Registry Table. You must then stop and then restart the tuxipc.exe service for the changes to take effect.
Figure 3-8 BEA TUXEDO System for Windows NT IPC Resources Page

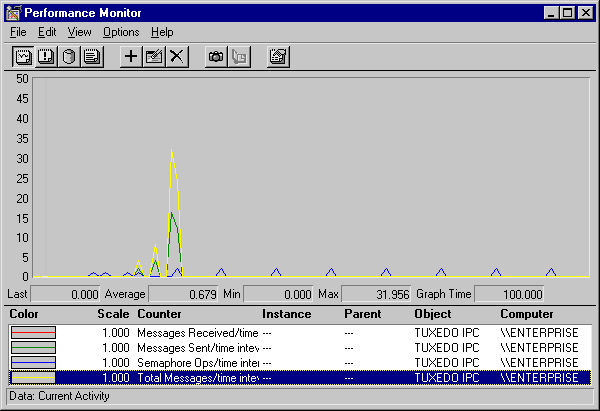
You can view the performance of a running BEA TUXEDO application on the NT Performance Monitor.
Figure 3-9 BEA TUXEDO System for Windows NT Performance Monitor