3 Getting Started Managing Oracle Fusion Middleware
When you install Oracle Fusion Middleware, you install the binary files, such as executable files, jar files, and libraries. Then, you use configuration tools to configure the software. This chapter provides information you need to get started managing Oracle Fusion Middleware, including information about the tools you use.
This chapter includes the following topics:
-
Getting Started Using Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control
-
Getting Started Using Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console
-
Getting Started Using the Fusion Middleware Control MBean Browsers
-
Basic Tasks for Configuring and Managing Oracle Fusion Middleware
3.1 Setting Up Environment Variables
When you installed Oracle Fusion Middleware, you were logged in to your operating system as a particular user. You should always log in as this user to manage your installation because this user has permission to view and modify the files in your installation's Oracle home.
To use Oracle Fusion Middleware, you must set environment variables as shown in the following tables:
Table 3-1 Environment Variables for Linux and UNIX
Table 3-2 shows the environment variables for Windows.
Table 3-2 Environment Variables for Windows
Best Practices for Multiple Installations on a UNIX Host
If you have multiple installations of Oracle Fusion Middleware on a UNIX host, it is very important to completely set your environment when managing a particular installation.
Some Oracle Fusion Middleware commands use the MW_HOME and ORACLE_HOME environment variables to determine which installation to operate on, and some use the directory location of the command. It is, therefore, not sufficient to simply reset your environment variables or change directories to a different Oracle home as you move between installations. You must fully change to the new installation as follows:
-
Log in as the user who installed Oracle Fusion Middleware.
On UNIX hosts, you may also use the
sucommand to switch to the user, but be sure to use the dash (-) option so that your environment is set the same as it would have been had you actually logged in as that user. For example:su - user -
Set the correct environment variables for the installation, as described in Table 3-1.
-
Execute commands in the Middleware home and Oracle home of the correct installation.
Multiple Installations by the Same User If you installed multiple installations as the same user, ensure that you are in the correct Middleware home and Oracle home and have the correct environment variables set when working on a particular installation. You may want to set up some scripts to make it easy to change from one installation to another.
3.2 Overview of Oracle Fusion Middleware Administration Tools
After you install and configure Oracle Fusion Middleware, you can use the graphical user interfaces or command-line tools to manage your environment.
Oracle offers the following primary tools for managing your Oracle Fusion Middleware installations:
-
Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control. See Section 3.3.
-
Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console. See Section 3.4
-
The Oracle Fusion Middleware command-line tools. See Section 3.5.
-
The Fusion Middleware Control MBean Browser. See Section 3.6.
Note that you should use these tools, rather than directly editing configuration files, to perform all administrative tasks unless a specific procedure requires you to edit a file. Editing a file may cause the settings to be inconsistent and generate problems.
Both Fusion Middleware Control and Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console are graphical user interfaces that you can use to monitor and administer your Oracle Fusion Middleware environment. You can perform some tasks with either tool, but for other tasks, you can only use one of the tools. Table 3-3 lists some common tasks with the recommended tool.
Table 3-3 Comparing Fusion Middleware Control and WebLogic Server Administration Console
| Task | Tool to Use |
|---|---|
|
Manage Oracle WebLogic Server |
Use: |
|
Create additional Managed Servers |
WebLogic Server Administration Console |
|
Clone Managed Servers |
WebLogic Server Administration Console |
|
Cluster Managed Servers |
WebLogic Server Administration Console |
|
Start and stop Oracle WebLogic Server |
Fusion Middleware Control or WebLogic Server Administration Console |
|
Add users and groups |
WebLogic Server Administration Console if using the default embedded LDAP; if using another LDAP server, use the LDAP server's tool |
|
Manage Data Sources |
Use: |
|
Create data sources |
WebLogic Server Administration Console |
|
Create connection pools |
WebLogic Server Administration Console |
|
Manage JMS Resources |
Use: |
|
Create JMS queues |
WebLogic Server Administration Console |
|
Configure advanced queuing |
WebLogic Server Administration Console |
|
Manage SOA environment |
Use: |
|
Deploy SOA Composite applications |
Fusion Middleware Control |
|
Monitor SOA Composite applications |
Fusion Middleware Control |
|
Modify Oracle BPEL Process Manager MBean properties |
Fusion Middleware Control |
|
Debug applications such as Oracle BPEL Process Manager applications |
Fusion Middleware Control |
|
ADF Applications |
Use: |
|
Deploy ADF applications |
Fusion Middleware Control |
|
Java EE applications |
Use: |
|
Deploy Java EE applications |
WebLogic Server Administration Console or Fusion Middleware Control |
|
Security |
Use: |
|
Configure and manage auditing |
Fusion Middleware Control |
|
Configure SSL |
WebLogic Server Administration Console for Oracle WebLogic Server Fusion Middleware Control for Java components and system components. See Chapter 6. |
|
Change passwords |
WebLogic Server Administration Console |
|
Manage Components |
Use: |
|
View and manage log files |
Fusion Middleware Control for most log files WebLogic Server Administration Console for the following logs: DOMAIN_HOME/servers/server_name/logs/access.log DOMAIN_HOME/servers/server_name/data/ldap/log/EmbeddedLDAP.log DOMAIN_HOME/servers/server_name/data/ldap/log/EmbeddedLDAPAccess.log |
|
Change ports |
WebLogic Server Administration Console for Oracle WebLogic Server and Java components For some system components, Fusion Middleware Control. See the Administration Guide for the component. |
|
Manage Oracle HTTP Server |
Fusion Middleware Control |
|
Manage Oracle Web Cache |
Fusion Middleware Control |
|
Start and stop components |
Fusion Middleware Control |
|
Start and stop applications |
Fusion Middleware Control |
3.3 Getting Started Using Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control
Fusion Middleware Control is a Web browser-based, graphical user interface that you can use to monitor and administer a farm.
A farm is a collection of components managed by Fusion Middleware Control. It can contain a Oracle WebLogic Server domain, one Administration Server, one or more Managed Servers, clusters, and the Oracle Fusion Middleware components that are installed, configured, and running in the domain.
Fusion Middleware Control organizes a wide variety of performance data and administrative functions into distinct, Web-based home pages for the farm, domain, servers, components, and applications. The Fusion Middleware Control home pages make it easy to locate the most important monitoring data and the most commonly used administrative functions—all from your Web browser.
The following topics are discussed in this section:
3.3.1 Displaying Fusion Middleware Control
To display Fusion Middleware Control, you enter the Fusion Middleware Control URL, which includes the name of the host and the administration port number assigned during the installation. The following shows the format of the URL:
http://hostname.domain:port/em
For some installation types, such as SOA or Web Tier, if you saved the installation information by clicking Save on the last installation screen, the URL for Fusion Middleware Control is included in the file that is written to disk (by default to your home directory).
For other installation types, the information is displayed on the Create Domain screen of the Configuration Wizard when the configuration completes.
The port number is the number of the Administration Server. By default, the port number is 7001.
To display Fusion Middleware Control:
-
Enter the URL in your Web browser. For example:
http://host1.example.com:7001/em
The following shows the login page:
Description of the illustration welcome.gif
-
Enter the Oracle Fusion Middleware administrator user name and password and click Login.
The default user name for the administrator user is
weblogic. This is the account you can use to log in to Fusion Middleware Control for the first time. The password is the one you supplied during the installation of Oracle Fusion Middleware.
3.3.2 Using Fusion Middleware Control Help
At any time while using the Fusion Middleware Control Console, you can click Help at the top of the page to get more information. In most cases, the Help window displays a help topic about the current page. Click Contents in the Help window to browse the list of help topics, or click Search to search for a particular word or phrase.
3.3.3 Navigating Within Fusion Middleware Control
Fusion Middleware Control displays the target navigation pane on the left and the content pane on the right. For example, when you first log in to Fusion Middleware Control, the farm home page is displayed on the right.
From the target navigation pane, you can expand the tree and select an Oracle WebLogic Server domain, an Oracle WebLogic Server Managed Server, a component, an application, or a Metadata Repository.
When you select a target, such as a Managed Server or a component, the target's home page is displayed in the content pane and that target's menu is displayed at the top of the page, in the context pane. For example, if you select a Managed Server, the WebLogic Server menu is displayed. You can also view the menu for a target by right-clicking the target in the navigation pane.
The following figure shows the target navigation pane and the home page of an Managed Server. Because a Managed Server was selected, the dynamic target menu listed in the context pane is the WebLogic Server menu.
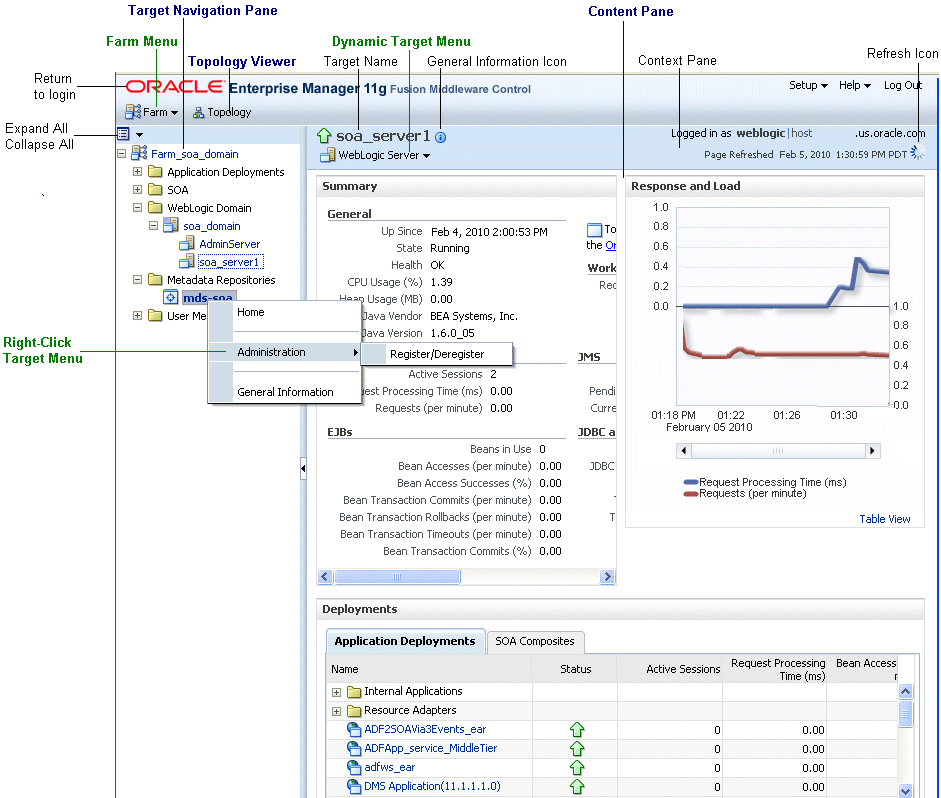
Description of the illustration nav.gif
In the preceding figure, the following items are called out:
-
Target Navigation Pane lists all of the targets in the farm in a navigation tree.
-
Content Pane shows the current page for the target. When you first select a target, that target's home page is displayed.
-
Farm Menu provides a list of operations that you can perform on the farm. The Farm menu is always available.
-
Dynamic Target Menu provides a list of operations that you can perform on the currently selected target. The menu that is displayed depends on the target you select. The menu for a specific target contains the same operations as those in the Right-Click Target Menu.
-
Right-Click Target Menu provides a list of operations that you can perform on the currently selected target. The menu is displayed when you right-click the target name in the target navigation pane. In the figure, even though the WebLogic Server is selected and its home page is displayed, the right-click target menu displays the operations for a metadata repository because the user has right-clicked the metadata repository.
The menu for a specific target contains the same operations as those in the Dynamic Target Menu.
-
General Information Icon provides information about the target. For example, for a domain, it displays the target name, the version, and the domain home.
-
Context Pane provides the name of the target, the name of the current user, the host name, and the time of the last page refresh, as well as the Refresh icon.
-
Expand All/Collapse All lets you expand or collapse the navigation tree.
-
Refresh indicates when the page is being refreshed. Click it to refresh a page with new data. (Refreshing the browser window refreshes the page but does not retrieve new data.)
-
Return to login takes you to the login page when you click the Oracle Enterprise Manager logo.
In addition, from Fusion Middleware Control, from the home pages of targets such as the Administration Server or Managed Servers, you can access the WebLogic Server Administration Console. For information about configuring Single Sign-On between Fusion Middleware Control and the WebLogic Server Administration Console, see "Configuring Single Sign-On for Administration Consoles" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Enterprise Deployment Guide for Oracle Identity Management.
Table 3-4 describes some common ways you can navigate within Fusion Middleware Control.
Table 3-4 Navigating Within Fusion Middleware Control
| To: | Take This Action: |
|---|---|
|
View all of the targets in the farm |
Click the Expand All icon at the top of the target navigation pane. |
|
Navigate to the farm |
Select the farm from the target navigation pane. The farm's home page is displayed in the content pane. |
|
Operate on the farm |
Select the Farm menu, which is always available at the top left of Fusion Middleware Control. |
|
Operate on a target |
Right-click the target in the target navigation pane. The target menu is displayed. Alternatively, you can select the target and use the dynamic target menu in the context pane. |
|
Return to the target's home page |
Click the target name at the top left-hand corner of the context pane. |
|
Refresh a page with new data |
Click the Refresh icon in the top right of the context pane. |
|
Return to a previous page |
Click the breadcrumbs, which appear below the context pane. The breadcrumbs appear when you drill down in a target. For example, choose Logs from the WebLogic Server menu, then View Log Messages. Select a log file and click View Log File. The breadcrumbs show: Log Messages > Log Files > View Log File: logfile_name |
|
View the host on which the target is running |
Select the target in the target navigation pane and view the host name in the target's context pane. You can also view the host name by clicking the General Information icon. |
|
Return to the login page |
Click the Oracle Enterprise Manager logo at the top left of the page. |
|
View the topology |
Click Topology. |
|
View a server log file |
Right-click the server name in the target navigation pane. Choose Logs, and then View Log Messages to see a summary of log messages and to search log files. |
3.3.4 Understanding Users and Roles for Fusion Middleware Control
To access Fusion Middleware Control and perform tasks, you must have the appropriate role. Fusion Middleware Control uses the Oracle WebLogic Server security realm and the roles defined in that realm. If a user is not granted one of these roles, the user cannot access Fusion Middleware Control.
Each role defines the type of access a user has. For example, a user with the role Admin has full privileges. A user with the role Operator has privileges to perform essential day-to-day operations. A user with the role Monitor has privileges only to view the configuration.
3.3.5 Viewing and Managing the Farm
When you log in to Fusion Middleware Control, the first page you see is the Farm home page. You can also view this page at any time by selecting the farm in the target navigation pane.
The following figure shows the Farm home page:

Description of the illustration farmhome.gif
The Farm menu is displayed at the top of the page. From the Farm menu, you can take the following actions:
-
Create and delete components and create clusters
-
View log messages.
-
Specify monitoring credentials
The Farm menu is always displayed, even if you have selected other entities.
You can view the farm topology by selecting Topology. The Topology Viewer provides you with a high-level view of the topology, including Managed Servers, deployed applications, and the routing configuration. See Section 10.3.
3.3.6 Viewing and Managing Components
From the target navigation pane, you can drill down to view and manage the components in your farm.
For example, to view and manage Oracle SOA Suite, take the following steps:
-
In the target navigation pane, expand the farm, then SOA.
-
Select the SOA instance.
The home page for the SOA instance is displayed, as shown in the following figure:
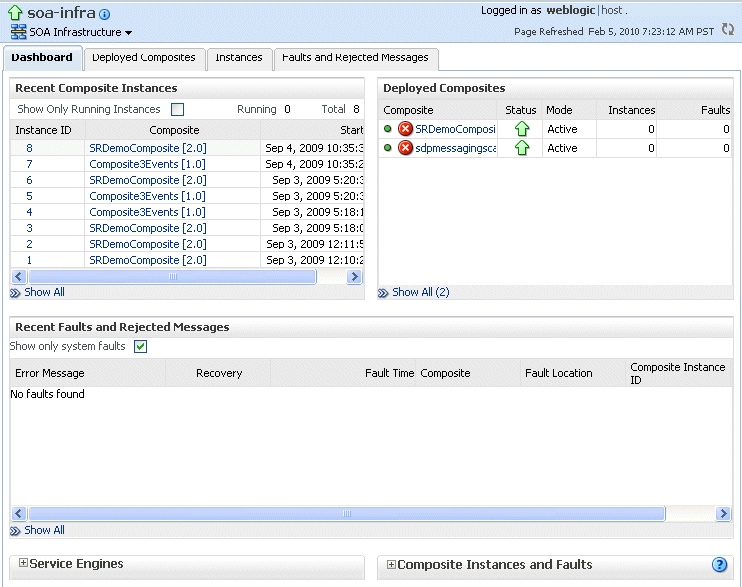
Description of the illustration soa_home.gif
-
From the SOA Infrastructure menu, you can perform many administrative tasks, such as starting, stopping, and monitoring Oracle SOA Suite and deploying SOA composite applications.
As another example, to view and manage Oracle HTTP Server, take the following steps:
-
In the target navigation pane, expand the farm, then Web Tier.
-
Select the Oracle HTTP Server instance, for example, ohs1.
The home page for the Oracle HTTP Server ohs1 is displayed, as shown in the following figure:
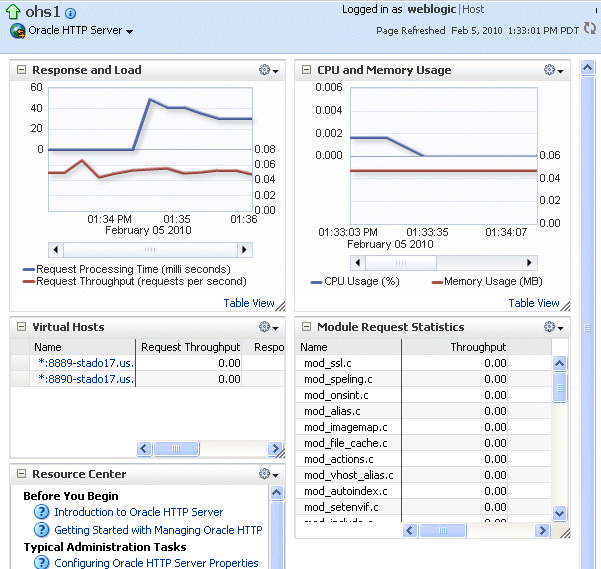
Description of the illustration ohs_home.gif
-
From the HTTP Server menu, you can perform many administrative tasks, such as starting, stopping, and monitoring Oracle HTTP Server.
See Also:
Section 10.1.5 for more information about monitoring components3.3.7 Viewing the Status of Applications
From the target navigation pane, you can drill down to view and manage the applications in your farm.
To view Java EE applications:
-
From the target navigation pane, expand the farm and then Application Deployments.
-
Select the application that you want to view.
The application's home page is displayed. In this page, you can view a summary of the application's status, entry points to the application, Web Services and modules associated with the application, and the response and load.
To view SOA Composite Applications:
-
From the target navigation pane, expand the farm, then SOA, and then soa-infra.
-
Select the application that you want to view.
The application's home page is displayed. It shows information about the application, such as the recent instances of the application, the faults and rejected messages and the policies.
3.4 Getting Started Using Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console
Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console is a Web browser-based, graphical user interface that you use to manage an Oracle WebLogic Server domain. It is accessible from any supported Web browser with network access to the Administration Server.
Use the Administration Console to:
-
Configure, start, and stop WebLogic Server instances
-
Configure WebLogic Server clusters
-
Configure WebLogic Server services, such as database connectivity (JDBC) and messaging (JMS)
-
Configure security parameters, including creating and managing users, groups, and roles
-
Configure and deploy Java EE applications
-
Monitor server and application performance
-
View server and domain log files
-
View application deployment descriptors
-
Edit selected run-time application deployment descriptor elements
3.4.1 Displaying the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console
To display the Administration Console:
-
Enter the following URL in a browser:
http://hostname:port_number/console
The port number is the number of the Administration Server. By default, the port number is 7001.
The login page is displayed.
-
Log in using the user name and password supplied during installation or another administrative user that you created.
Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console is displayed:
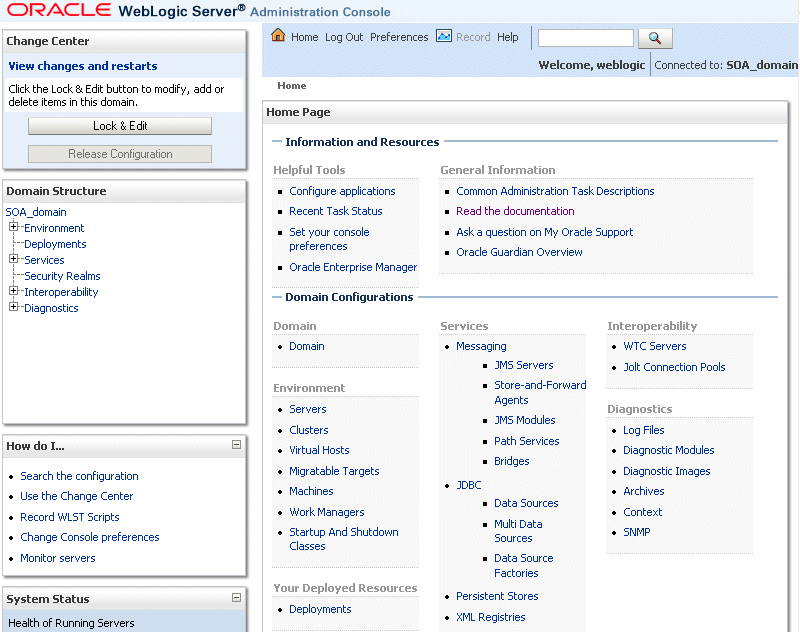
Description of the illustration wls_admin.gif
Alternatively, you can access the Administration Console from Fusion Middleware Control, from the home pages of targets such as the Administration Server or Managed Servers.
3.4.2 Locking the WebLogic Server Configuration
Before you make configuration changes, lock the domain configuration, so you can make changes to the configuration while preventing other accounts from making changes during your edit session. To lock the domain configuration:
-
Locate the Change Center in the upper left of the Administration Console screen.
-
Click Lock & Edit to lock the configuration edit hierarchy for the domain.
As you make configuration changes using the Administration Console, you click Save (or in some cases Finish) on the appropriate pages. This does not cause the changes to take effect immediately. The changes take effect when you click Activate Changes in the Change Center. At that point, the configuration changes are distributed to each of the servers in the domain. If the changes are acceptable to each of the servers, then they take effect. If any server cannot accept a change, then all of the changes are rolled back from all of the servers in the domain. The changes are left in a pending state; you can then either edit the pending changes to resolve the problem or revert to the previous configuration.
3.5 Getting Started Using Command-Line Tools
Oracle Fusion Middleware provides the following primary command-line tools to manage most Oracle Fusion Middleware components:
-
WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST). See Section 3.5.1.
-
Oracle Process Manager and Notification Server (OPMN). See Section 3.5.2.
3.5.1 Getting Started Using the Oracle WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST)
The Oracle WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) is a command-line scripting environment that you can use to create, manage, and monitor Oracle WebLogic Server domains. It is based on the Java scripting interpreter, Jython. In addition to supporting standard Jython features such as local variables, conditional variables, and flow control statements, WLST provides a set of scripting functions (commands) that are specific to WebLogic Server. You can extend the WebLogic scripting language to suit your needs by following the Jython language syntax.
You can use WLST commands in the following ways:
-
Interactively, on the command line
-
In script mode, supplied in a file
-
Embedded in Java code
For example, to invoke WLST interactively, and connect to the WebLogic Server, use the following commands:
java weblogic.WLST
connect('username', 'password', 'localhost:7001')
To display information about WLST commands and variables, enter the help command. For example, to display a list of categories for online commands, enter the following:
wls:/base_domain/serverConfig> help('online')
help('activate') Activate the changes.
help('addListener') Add a JMX listener to the specified MBean.
help('adminHome') Administration MBeanHome.
help('cancelEdit') Cancel an edit session.
help('cd') Navigate the hierarchy of beans.
help('cmo') Current Management Object.
.
.
.
To monitor the status, you use the WLST state command, using the following format:
state(name, type)
For example to get the status of the Managed Server soa_server1, use the following command:
wls:/SOA_domain/serverConfig> state('soa_server1', 'Server')
Current state of 'soa_server1' : RUNNING
3.5.1.1 Using Custom WLST Commands
Many components, such as Oracle SOA Suite, Oracle Platform Security Services (OPSS), Oracle Fusion Middleware Audit Framework, and MDS, and services such as SSL and logging, provide custom WLST commands.
To use those custom commands, you must invoke the WLST script from the appropriate Oracle home. Do not use the WLST script in the WebLogic Server home.
-
For the following components and services, invoke WLST from the Oracle Common home:
-
Oracle Access Manager
The script is located at:
(UNIX) ORACLE_COMMON_HOME/common/bin/wlst.sh (Windows) ORACLE_COMMON_HOME\common\bin\wlst.cmd
-
For other components, such as Oracle HTTP Server, Oracle SOA Suite, or Oracle WebCenter, invoke WLST from the Oracle home in which the component has been installed. The script is located at:
The script is located at:
(UNIX) ORACLE_HOME_for_component/common/bin/wlst.sh (Windows) ORACLE_HOME_for_component\common\bin\wlst.cmd
For example, to run the custom WLST commands for Oracle SOA Suite on a Linux system, use the following commands:
cd ORACLE_HOME_for_SOA/common/bin ./wlst.sh
3.5.1.2 Using WLST Commands for System Components
In addition to the commands provided by WLST for Oracle WebLogic Server, WLST provides a subset of commands to manage system components. These commands are:
-
startproc(componentName [, componentType] [, componentSet): Starts the specified component
-
stopproc(componentName [, componentType] [, componentSet): Stops the specified component
-
status(componentName [, componentType] [, componentSet): Obtains the status of the specified component
-
proclist(): Obtain the list of components
To use these custom commands, you must invoke the WLST script from the Oracle home in which the component has been installed. Do not use the WLST script in the WebLogic Server home. The script is located at:
(UNIX) ORACLE_HOME_for_component/common/bin/wlst.sh (Windows) ORACLE_HOME_for_component\common\bin\wlst.cmd
3.5.2 Getting Started Using Oracle Process Manager and Notification Server
Oracle Process Manager and Notification Server (OPMN) manages and monitors the following Oracle Fusion Middleware components, referred to as system components:
-
Oracle HTTP Server
-
Oracle Web Cache
-
Oracle Internet Directory
-
Oracle Virtual Directory
-
Oracle Forms Services
-
Oracle Reports
-
Oracle Business Intelligence Discoverer
-
Oracle Business Intelligence
OPMN provides the opmnctl command. The executable file is located in the following directory, which you should add to your PATH environment variable:
(UNIX) ORACLE_HOME/opmn/bin (Windows) ORACLE_HOME\opmn\bin
To view the status of all system components in an Oracle instance, use the following command:
opmnctl status Processes in Instance: webtier_inst ---------------------------------+--------------------+---------+--------- ias-component | process-type | pid | status ---------------------------------+--------------------+---------+--------- webcache1 | WebCache-admin | 19556 | Alive webcache1 | WebCache | 19555 | Alive ohs1 | OHS | 7249 | Alive
To view the status of a particular component or component type, use the following command:
opmnctl status componentName [, componentType] [, componentSet]
For example, to view the status of an Oracle Virtual Directory instance named ovd1, use the following command:
opmnctl status ias-component=ovd1
You can use OPMN to start and stop system components, monitor system components, and perform many other tasks related to process management. For example, you can use the following commands to start and stop OPMN and all OPMN-managed processes, such as Oracle HTTP Server and Oracle Web Cache:
opmnctl startall opmnctl stopall
To start a component, use the following command:
opmnctl startproc componentName [, componentType] [, componentSet
For example, to start an Oracle HTTP Server instance named ohs1, use the following command:
opmnctl startproc ias-component=ohs1
See Also:
-
Chapter 4 for information about starting and stopping your Oracle Fusion Middleware environment
-
Chapter 10 for more information about monitoring your Oracle Fusion Middleware environment
-
Oracle Fusion Middleware Oracle Process Manager and Notification Server Administrator's Guide
3.6 Getting Started Using the Fusion Middleware Control MBean Browsers
A managed bean (MBean) is a Java object that represents a JMX manageable resource in a distributed environment, such as an application, a service, a component or a device.
MBeans are defined in the Java EE Management Specification (JSR-77), which is part of Java Management Extensions, or JMX, a set of specifications that allow standard interfaces to be created for managing applications in a Java EE environment. For information about JSR-77, see:
http://java.sun.com/j2ee/tools/management/
You can create MBeans for deployment with an application into Oracle WebLogic Server, enabling the application or its components to be managed and monitored through Fusion Middleware Control.
See Also:
"Understanding WebLogic Server MBeans" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing Custom Management Utilities With JMX for Oracle WebLogic ServerFusion Middleware Control provides a set of MBean browsers that allow to you browse the MBeans for an Oracle WebLogic Server or for a selected application. You can also perform specific monitoring and configuration tasks from the MBean browser.
The following topics describe how to view the MBeans:
3.6.1 Using the System MBean Browser
To view the System MBean Browser specific to a particular Oracle WebLogic Server Managed Server and to configure and use the MBeans:
-
From the target navigation pane, expand the farm, then WebLogic Domain, and then the domain.
-
Select the Managed Server.
-
From the WebLogic Server menu, choose System MBean Browser.
The System MBean Browser page is displayed.
-
Expand a node in the MBean navigation tree and drill down to the MBean you want to access. Select an MBean instance.
-
To view the MBean's attributes, select the Attributes tab. Some attributes allow you to change their values. To do so, enter the value in the Value column.
-
To view the available operations, select the Operations tab. To perform an operation, click the operation. The Operations page appears. Enter any applicable values and click Invoke.
See Also:
The Fusion Middleware Control online help3.6.2 Using the MBeans for a Selected Application
You can view, configure, and use the MBeans for a specific application by taking the steps described in Section 3.6.1, and drilling down to the application. As an alternative, you can navigate to an application's MBeans using the following steps:
-
From the target navigation pane, expand the farm, then Application Deployments.
-
Select the application.
-
From the Application Deployments menu, choose System MBean Browser.
The System MBean Browser page is displayed, along with the MBean information for the application.
-
To view the MBean's attributes, select the Attributes tab. Some attributes allow you to change their values. To do so, enter the value in the Value column.
-
To view the available operations, select the Operations tab. To perform an operation, click the operation. The Operations page appears. Enter any applicable values and click Invoke.
3.7 Managing Components
Oracle Fusion Middleware components include Oracle WebLogic Server, Java components that are part of Oracle SOA Suite and WebCenter, such as Oracle BPEL Process Manager or Oracle Business Activity Monitoring, and system components such as Oracle Web Cache.
To manage the Oracle WebLogic Server and Java components, you can use WLST, Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console, or Fusion Middleware Control.
To manage system components, you can use OPMN, WLST, or Fusion Middleware Control.
See:
-
Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Planning Guide and the individual installation guides for information about installing and configuring components
-
Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Guide for Oracle WebLogic Server for installing and configuring Oracle WebLogic Server
-
The administration guide for each component or suite for more information about managing these components.
3.8 Changing the Administrative User Password
During the Oracle Fusion Middleware installation, you must specify a password for the administration account. Then, you can use this account to log in to Fusion Middleware Control and the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console for the first time. You can create additional administrative accounts using the WLST command line or the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
You can change the password of the administrative user using the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console or the WLST command line.
3.8.1 Changing the Administrative User Password Using the Command Line
To change the administrative user password or other user passwords using the command line, you invoke the UserPasswordEditorMBean.changeUserPassword method, which is extended by the security realm's AuthenticationProvider MBean.
For more information, see the changeUserPassword method in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Oracle WebLogic Server MBean Reference.
3.8.2 Changing the Administrative User Password Using the Administration Console
To change the password of an administrative user using the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console:
-
Navigate to the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console. (For example, from the home page of the domain in Fusion Middleware Control, select To configure and managed this WebLogic Domain, use the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.)
-
From the target navigation pane, select Security Realms.
The Summary of Security Realms page is displayed.
-
Select a realm, such as myrealm.
The Settings for the realm page is displayed.
-
Select the Users and Groups tab, then the Users tab. Select the user.
The Settings for user page is displayed.
-
Select the Passwords tab.
-
Enter the new password, then enter it again to confirm it.
-
Click Save.
3.9 Basic Tasks for Configuring and Managing Oracle Fusion Middleware
The following provides a summary of the steps you need to take to configure and manage a basic Oracle Fusion Middleware environment after you have installed the software:
-
Configure Oracle WebLogic Server. See Oracle Fusion Middleware Creating Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
-
Configure components, such as Oracle SOA Suite, Oracle HTTP Server, or Oracle Web Cache. See Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Planning Guide.
-
Configure SSL. See Chapter 6.
-
Create and manage metadata repositories, including the MDS repository.
-
Deploy an application. See Chapter 9.
-
Configure load balancing. You can configure load balancing between different components or applications. See the Oracle Fusion Middleware High Availability Guide.
-
Back up your environment. See Chapter 15.
-
Monitor your environment and manage log files. See Chapter 10 and Chapter 11.
-
Expand your environment. See Chapter 18.
This guide also describes other tasks that you may need to perform, depending on your Oracle Fusion Middleware environment.