| Oracle® Secure Enterprise Search Administrator's Guide 11g Release 1 (11.1.2.0.0) Part Number E14130-04 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Secure Enterprise Search Administrator's Guide 11g Release 1 (11.1.2.0.0) Part Number E14130-04 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter discusses the Oracle SES crawler. It contains the following topics:
See Also:
"Tuning the Crawl Performance" and "Tuning Search Performance"
The Oracle Secure Enterprise Search tutorials at
The Oracle Secure Enterprise Search (Oracle SES) crawler is a Java process activated by a set schedule. When activated, the crawler spawns processor threads that fetch documents from sources. The crawler caches the documents, and when the cache reaches the maximum batch size of 250 MB, the crawler indexes the cached files. This index is used for searching.
The document cache, called Secure Cache, is stored in Oracle Database in a compressed SecureFile LOB. Oracle Database provides excellent security and compact storage.
In the Oracle SES Administration GUI, you can create schedules with one or more sources attached to them. Schedules define the frequency at which the Oracle SES index is kept up to date with existing information in the associated sources.
In the process of crawling, the crawler maintains a list of URLs of the discovered documents that are fetched and indexed in an internal URL queue. The queue is persistently stored, so that crawls can be resumed after the Oracle SES instance is restarted.
A display URL is a URL string used for search result display. This is the URL used when users click the search result link. An access URL is an optional URL string used by the crawler for crawling and indexing. If it does not exist, then the crawler uses the display URL for crawling and indexing. If it does exist, then it is used by the crawler instead of the display URL for crawling. For regular Web crawling, only display URLs are available. But in some situations, the crawler needs an access URL for crawling the internal site while keeping a display URL for the external use. For every internal URL, there is an external mirrored URL.
For example, for file sources with display URLs, end users can access the original document with the HTTP or HTTPS protocols. These provide the appropriate authentication and personalization and result in better user experience.
Display URLs can be provided using the URL Rewriter API. Or, they can be generated by specifying the mapping between the prefix of the original file URL and the prefix of the display URL. Oracle SES replaces the prefix of the file URL with the prefix of the display URL.
For example, if the file URL is
file://localhost/home/operation/doc/file.doc
and the display URL is
https://webhost/client/doc/file.doc
then specify the file URL prefix as
file://localhost/home/operation
and the display URL prefix as
https://webhost/client
You can alter the crawler's operating parameters at two levels:
At the global level for all sources
At the source level for a particular defined source
Global parameters include the default values for language, crawling depth, and other crawling parameters, and the settings that control the crawler log and cache.
To configure the crawler:
Click the Global Settings tab.
Under Sources, click Crawler Configuration.
Make the desired changes on the Crawler Configuration page. Click Help for more information about the configuration settings.
Click Apply.
To configure the crawling parameters for a specific source:
From the Home page, click the Sources secondary tab to see a list of sources you have created.
Click the edit icon for the source whose crawler you want to configure, to display the Edit Source page.
Click the Crawling Parameters subtab.
Make the desired changes. Click Help for more information about the crawling parameters.
Click Apply.
Note that the parameter values for a particular source can override the default values set at the global level. For example, for Web sources, Oracle SES sets a default crawling depth of 2, irrespective of the crawling depth you set at the global level.
Also note that some parameters are specific to a particular source type. For example, Web sources include parameters for HTTP cookies.
This section describes crawler settings and other mechanisms to control the scope of Web crawling:
See Also:
"Tuning the Crawl Performance" for more detailed information on these settings and other issues affecting crawl performanceFor initial planning purposes, you might want the crawler to collect URLs without indexing. After crawling is finished, examine the document URLs and status, remove unwanted documents, and start indexing. The crawling mode is set on the Home - Schedules - Edit Schedules page.
See Also:
Appendix B, "URL Crawler Status Codes"Note:
If you are using a custom crawler created with the Crawler Plug-in API, then the crawling mode set here does not apply. The implemented plug-in controls the crawling mode.These are the crawling mode options:
Automatically Accept All URLs for Indexing: This crawls and indexes all URLs in the source. For Web sources, it also extracts and indexes any links found in those URLs. If the URL has been crawled before, then it is reindexed only if it has changed.
Examine URLs Before Indexing: This crawls but does not index any URLs in the source. It also crawls any links found in those URLs.
Index Only: This crawls and indexes all URLs in the source. It does not extract any links from those URLs. In general, select this option for a source that has been crawled previously under "Examine URLs Before Indexing".
URL boundary rules limit the crawling space. When boundary rules are added, the crawler is restricted to URLs that match the indicated rules. The order in which rules are specified has no impact, but exclusion rules always override inclusion rules.
This is set on the Home - Sources - Boundary Rules page.
Specify an inclusion rule that a URL contain, start with, or end with a term. Use an asterisk (*) to represents a wildcard. For example, www.*.example.com. Simple inclusion rules are case-insensitive. For case-sensitivity, use regular expression rules.
An inclusion rule ending with example.com limits the search to URLs ending with the string example.com. Anything ending with example.com is crawled, but http://www.example.com.tw is not crawled.
If the URL Submission functionality is enabled on the Global Settings - Query Configuration page, then URLs that are submitted by end users are added to the inclusion rules list. You can delete URLs that you do not want to index.
Oracle SES supports the regular expression syntax used in Java JDK 1.4.2 Pattern class (java.util.regex.Pattern). Regular expression rules use special characters. The following is a summary of some basic regular expression constructs.
A caret (^) denotes the beginning of a URL and a dollar sign ($) denotes the end of a URL.
A period (.) matches any one character.
A question mark (?) matches zero or one occurrence of the character that it follows.
An asterisk (*) matches zero or more occurrences of the pattern that it follows. You can use an asterisk in the starts with, ends with, and contains rules.
A backslash (\) escapes any special characters, such as periods (\.), question marks (\?), or asterisks (\*).
See Also:
http://java.sun.com for a complete description in the Sun Microsystems Java documentationYou can specify an exclusion rule that a URL contains, starts with, or ends with a term.
An exclusion of uk.example.com prevents the crawling of Example hosts in the United Kingdom.
Default Exclusion Rules
The crawler contains a default exclusion rule to exclude non-textual files. The following file extensions are included in the default exclusion rule.
Image: jpg, gif, tif, bmp, png
Audio: wav, mp3, wma
Video: avi, mpg, mpeg, wmv
Binary: bin, exe, so, dll, iso, jar, war, ear, tar, wmv, scm, cab, dmp
To crawl a file with these extensions, modify the following section in the ORACLE_HOME/search/data/config/crawler.dat file, removing any file type suffix from the exclusion list.
# default file name suffix exclusion list RX_BOUNDARY (?i:(?:\.jar)|(?:\.bmp)|(?:\.war)|(?:\.ear)|(?:\.mpg)|(?:\.wmv)|(?:\.mpeg)|(?:\.scm)|(?:\.iso)|(?:\.dmp)|(?:\.dll)|(?:\.cab)|(?:\.so)|(?:\.avi)|(?:\.wav)|(?:\.mp3)|(?:\.wma)|(?:\.bin)|(?:\.exe)|(?:\.iso)|(?:\.tar)|(?:\.png))$
Then add the MIMEINCLUDE parameter to the crawler.dat file to crawl any multimedia file type, and the file name is indexed as title.
For example, to crawl any audio files, remove .wav, .mp3, and .wma, and add the MIMEINCLUDE parameter:
RX_BOUNDARY (?i:(?:\.gif)|(?:\.jpg)|(?:\.jar)|(?:\.tif)|(?:\.bmp)|(?:\.war)|(?:\.ear)|(?:\.mpg)|(?:\.wmv)|(?:\.mpeg)|(?:\.scm)|(?:\.iso)| (?:\.dmp)|(?:\.dll)|(?:\.cab)|(?:\.so)|(?:\.avi)|(?:\.bin)|(?:\.exe)|(?:\.iso)|(?:\.tar)|(?:\.png))$ MIMEINCLUDE audio/x-wav audio/mpeg
Note:
Only the file name is indexed when crawling multimedia files, unless the file is crawled using a crawler plug-in that provides a richer set of attributes, such as the Image Document Service plug-in.The following example uses several regular expression constructs that are not described earlier, including range quantifiers, non-grouping parentheses, and mode switches. For a complete description, see the Sun Microsystems Java documentation.
To crawl only HTTPS URLs in the example.com and examplecorp.com domains, and to exclude files ending in .doc and .ppt:
Inclusion: URL regular expression
^https://.*\.example(?:corp){0,1}\.com
Exclusion: URL regular expression (?i:\.doc|\.ppt)$
You can customize which document types are processed for each source. By default, PDF, Microsoft Excel, Microsoft PowerPoint, Microsoft Word, HTML and plain text are always processed.
To add or remove document types:
On the Home page, click the Sources secondary tab.
Choose a source from the list and select Edit to display the Customize Source page.
Select the Document Types subtab.
The listed document types are supported for the source type.
Move the types to process to the Processed list and the others to the Not Processed list.
Click Apply.
Keep the following in mind about graphics file formats:
For graphics format files (JPEG, JPEG 2000, GIF, TIFF, DICOM), only the file name is searchable. The crawler does not extract any metadata from graphics files or make any attempt to convert graphical text into indexable text, unless you enable a document service plug-in. See "Configuring Support for Image Metadata".
Oracle SES allows up to 1000 files in zip files and LHA files. If there are more than 1000 files, then an error is raised and the file is ignored. See "Crawling Zip Files Containing Non-UTF8 File Names".
See Also:
Oracle Text Reference Appendix B for supported document typesCrawling depth is the number of levels to crawl Web and file sources. A Web document can contain links to other Web documents, which can contain more links. Specify the maximum number of nested links for the crawler to follow. Crawling depth starts at 0; that is, if you specify 1, then the crawler gathers the starting (seed) URL plus any document that is linked directly from the starting URL. For file crawling, this is the number of directory levels from the starting URL.
Set the crawling depth on the Home - Sources - Crawling Parameters page.
You can control which parts of your sites can be visited by robots. If robots exclusion is enabled (default), then the Web crawler traverses the pages based on the access policy specified in the Web server robots.txt file. The crawler also respects the page-level robot exclusion specified in HTML metatags.
For example, when a robot visits http://www.example.com/, it checks for http://www.example.com/robots.txt. If it finds it, then the crawler checks to see if it is allowed to retrieve the document. If you own the Web sites, then you can disable robots exclusions. However, when crawling other Web sites, always comply with robots.txt by enabling robots exclusion.
Set the robots parameter on the Home - Sources - Crawling Parameters page.
By default, Oracle SES processes dynamic pages. Dynamic pages are generally served from a database application and have a URL that contains a question mark (?). Oracle SES identifies URLs with question marks as dynamic pages.
Some dynamic pages appear as multiple search results for the same page, and you might not want them all indexed. Other dynamic pages are each different and must be indexed. You must distinguish between these two kinds of dynamic pages. In general, dynamic pages that only change in menu expansion without affecting its contents should not be indexed.
Consider the following three URLs:
http://example.com/aboutit/network/npe/standards/naming_convention.html http://example.com/aboutit/network/npe/standards/naming_convention.html?nsdnv=14z1 http://example.com/aboutit/network/npe/standards/naming_convention.html?nsdnv=14
The question marks (?) in two URLs indicate that the rest of the strings are input parameters. The three results are essentially the same page with different side menu expansion. Ideally, the search yields only one result:
http://example.com/aboutit/network/npe/standards/naming_convention.html
Note:
The crawler cannot crawl and index dynamic Web pages written in Javascript.Set the dynamic pages parameter on the Home - Sources - Crawling Parameters page.
The URL Rewriter is a user-supplied Java module for implementing the Oracle SES UrlRewriter interface. The crawler uses it to filter or rewrite extracted URL links before they are put into the URL queue. The API enables ultimate control over which links extracted from a Web page are allowed and which ones should be discarded.
URL filtering removes unwanted links, and URL rewriting transforms the URL link. This transformation is necessary when access URLs are used and alternate display URLs must be presented to the user in the search results.
Set the URL rewriter on the Home - Sources - Crawling Parameters page.
You can override a default document title with a meaningful title if the default title is irrelevant. For example, suppose that the result list shows numerous documents with the title "Daily Memo". The documents had been created with the same template file, but the document properties had not been changed. Overriding this title in Oracle SES can help users better understand their search results.
Title fallback can be used for any source type. Oracle SES uses different logic for each document type to determine which fallback title to use. For example, for HTML documents, Oracle SES looks for the first heading, such as <h1>. For Microsoft Word documents, Oracle SES looks for text with the largest font.
If the default title was collected in the initial crawl, then the fallback title is only used after the document is reindexed during a re-crawl. This means if there is no change to the document, then you must force the change by setting the re-crawl policy to Process All Documents on the Home - Schedules - Edit Schedule page.
This feature is not currently supported in the Oracle SES Administration GUI. Override a default document title with a meaningful title by adding the keyword BAD_TITLE to the ORACLE_HOME/search/data/config/crawler.dat file. For example:
BAD_TITLE Daily Memo
Where Daily Memo is the title string to be overridden. The title string is case-insensitive and can use multibyte characters in UTF8 character set.
You can specify multiple bad titles, each one on a separate line.
Special considerations with title fallback
With Microsoft Office documents:
Font sizes 14 and 16 in Microsoft Word correspond to normalized font sizes 4 and 5 (respectively) in converted HTML. The Oracle SES crawler only picks up strings with normalized font size greater than 4 as the fallback title.
Titles should contain more than five characters.
When a title is null, Oracle SES automatically indexes the fallback title for all binary documents (for example, .doc, .ppt, .pdf). For HTML and text documents, Oracle SES does not automatically index the fallback title. This means that the replaced title on HTML or text documents cannot be searched with the title attribute on the Advanced Search page. You can turn on indexing for HTML and text documents in the crawler.dat file. For example, set NULL_TITLE_FALLBACK_INDEX ALL.
The crawler.dat file is not included in the backup available on the Global Settings - Configuration Data Backup and Recovery page. Ensure you manually back up the crawler.dat file.
See Also:
"Crawler Configuration File"This feature enables the crawler to automatically detect character set information for HTML, plain text, and XML files. Character set detection allows the crawler to properly cache files during crawls, index text, and display files for queries. This is important when crawling multibyte files (such as files in Japanese or Chinese).
This feature is not currently supported in the Oracle SES Administration GUI, and by default, it is turned off. Enable automatic character set detection by adding a line in the crawler configuration file: ORACLE_HOME/search/data/config/crawler.dat. For example, add the following as a new line:
AUTO_CHARSET_DETECTION
You can check whether this is turned on or off in the crawler log under the "Crawling Settings" section.
To crawl XML files for a source, be sure to add XML to the list of processed document types on the Home - Source - Document Types page. XML files are currently treated as HTML format, and detection for XML files may not be as accurate as for other file formats.
The crawler.dat file is not included in the backup available on the Global Settings - Configuration Data Backup and Recovery page. Ensure that you manually back up the crawler.dat file.
See Also:
"Crawler Configuration File"With multibyte files, besides turning on character set detection, be sure to set the Default Language parameter. For example, if the files are all in Japanese, select Japanese as the default language for that source. If automatic language detection is disabled, or if the crawler cannot determine the document language, then the crawler assumes that the document is written in the default language. This default language is used only if the crawler cannot determine the document language during crawling.
If your files are in multiple languages, then turn on the Enable Language Detection parameter. Not all documents retrieved by the crawler specify the language. For documents with no language specification, the crawler attempts to automatically detect language. The language recognizer is trained statistically using trigram data from documents in various languages (for instance, Danish, Dutch, English, French, German, Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish). It starts with the hypothesis that the given document does not belong to any language and ultimately refutes this hypothesis for a particular language where possible. It operates on Latin-1 alphabet and any language with a deterministic Unicode range of characters (like Chinese, Japanese, Korean, and so on).
The crawler determines the language code by checking the HTTP header content-language or the LANGUAGE column, if it is a table source. If it cannot determine the language, then it takes the following steps:
If the language recognizer is not available or if it cannot determine a language code, then the default language code is used.
If the language recognizer is available, then the output from the recognizer is used.
Oracle Text MULTI_LEXER is the only lexer used for Oracle Secure Enterprise Search.
The Default Language and the Enable Language Detection parameters are on the Global Settings - Crawler Configuration page (globally) and also the Home - Sources - Crawling Parameters page (for each source).
Note:
For file sources, the individual source setting for Enable Language Detection remains false regardless of the global setting. In most cases, the language for a file source should be the same, and set from, the Default Language setting.For sources created before Oracle SES 11g, the document cache remains in the cache directory. Sources are not stored in Secure Cache in the database until they are migrated to use Secure Cache. You can manage the cache directory for these older sources the same as in earlier releases.
You can manage the Secure Cache either on the global level or at the data source level. The data source configuration supersedes the global configuration.
The cache is preserved by default and supports the Cached link feature in the search result page. If you do not use the Cache link, then you can delete the cache, either for specific sources or globally for all of them. Without a cache, the Cached link in a search result page returns a File not found error.
To delete the cache for all sources:
Select the Global Settings tab in the Oracle SES Administration GUI.
Choose Crawler Configuration.
Set Preserve Document Cache to No.
Click Delete Cache Now to remove the cache from all sources, except any that are currently active under an executing schedule. The cache is deleted in the background, and you do not have to wait for it to complete.
Click Apply.
To delete the cache for an individual source:
Select the Sources secondary tab on the Home page.
Click Edit for the source.
Click the Crawling Parameters subtab.
Set Preserve Document Cache to No.
Click Apply.
Oracle SES provides an XML connector framework to crawl any repository that provides an XML interface to its contents. The connectors for Oracle Content Server, Oracle E-Business Suite 12, and Siebel 8 use this framework.
Every document in a repository is known as an item. An item contains information about the document, such as author, access URL, last modified date, security information, status, and contents.
A set of items is known as a feed or channel. To crawl a repository, an XML document must be generated for each feed. Each feed is associated with information such as feed name, type of the feed, and number of items.
To crawl a repository with the XML connector, place data feeds in a location accessible to Oracle SES over one of the following protocols: HTTP, FTP, or file. Then generate an XML Configuration File that contains information such as feed location and feed type. Create a source with a source type that is based on this XML connector and trigger the crawl from Oracle SES to crawl the feeds.
There are two types of feeds:
Control feed: Individual feeds can be located anywhere, and a single control file is generated with links to the feeds. This control file is input to the connector through the configuration file. A link in control feed can point to another control feed. Control feed is useful when data feeds are distributed over many locations or when the data feeds are accessed over diverse protocols such as FTP and file.
Directory feed: All feeds are placed in a directory, and this directory is input to the connector through the configuration file. Directory feed is useful when the data feeds are available in a single directory.
Guidelines for the target repository generating the XML feeds:
XML feeds are generated by the target repository, and each file system has a limit on how many files it can hold. For directory feeds, the number of documents in each directory should be less than 10,000. There are two considerations:
Feed files: The number of items in each feed file should be set such that the total number of feed files in the feed directory is kept under 10,000.
Content files: If the feed files specify content through attachment links and the targets of these links are stored in the file system, then ensure that the targets are distributed in multiple directories so that the total number of files in each directory is kept under 10,000.
When feeds are generated real-time over HTTP, ensure that the component generating the feeds is sensitive to time out issues of feed requests. The feed served as the response for every request should be made available within this time out interval; otherwise, the request from Oracle SES times out. The request is retried as many times as specified while setting up the source in Oracle SES. If all these attempts fail, then the crawler ignores this feed and proceeds with the next feed.
See Also:
The courses in the Oracle E-Business Suite Learning Management application can be crawled and indexed to readily search the courses offered, location and other details pertaining to the courses.
To crawl and index courses in Oracle E-Business Suite Learning Management:
Generate XML feed containing the courses. Each course can be an item in the feed. The properties of the course such as location and instructor can be set as attributes of the item.
Move the feed to a location accessible to Oracle SES through HTTP, FTP, or file protocol.
Generate a control file that points to that feed.
Generate a configuration file to point to this feed. Specify the feed type as control, the URL of the control feed, and the source name in the configuration file.
Create an Oracle E-Business Suite 12 source in Oracle SES, specifying in the parameters the location of the configuration file, the user ID and the password to access the feed.
The configuration file is an XML file conforming to a set schema.
The following is an example of a configuration file to set up an XML-based source:
<rsscrawler xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/search/rsscrawlerconfig">
<feedLocation>ftp://my.host.com/rss_feeds</feedLocation>
<feedType>directoryFeed</feedType>
<errorFileLocation>/tmp/errors</errorFileLocation>
<securityType>attributeBased</securityType>
<sourceName>Contacts</sourceName>
<securityAttribute name="EMPLOYEE_ID" grant="true"/>
</rsscrawler>
Where
feedLocation is one of the following:
URL of the directory, if the data feed is a directory feed
This URL should be the FTP URL or the file URL of the directory where the data feeds are located. For example:
ftp://example.domain.com/relativePathOfDirectory file://example.domain.com/c:\dir1\dir2\dir3 file://example.domain.com//private/home/dir1/dir2/dir3
File URL if the data feeds are available on the same computer as Oracle SES. The path specified in the URL should be the absolute path of the directory.
FTP URL to access data feeds on any other computer. The path of the directory in the URL can be absolute or relative. The absolute path should be specified following the slash (/) after the host name in the URL. The relative path should be specified relative to the home directory of the user used to access FTP feeds.
The user ID used to crawl the source should have write permissions on the directory, so that the data feeds can be deleted after crawl.
URL of the control file, if the data feed is a control feed
This URL can be HTTP, HTTPS, file, or FTP URL. For example:
http://example.com:7777/context/control.xml
The path in FTP and file protocols can be absolute or relative.
feedType indicates the type of feed. Valid values are directoryFeed, controlFeed, and dataFeed.
errorFileLocation (optional) specifies the directory where status feeds should be uploaded.
A status feed is generated to indicate the status of the processing feed. This status feed is named data_feed_file_name.suc or data_feed_file_name.err depending on whether the processing was successful. Any errors encountered are listed in the error status feed. If a value is specified for this parameter, then the status feed is uploaded to this location. Otherwise, the status feed is uploaded to the same location as the data feed.
The user ID used to access the data feed should have write permission on the directory.
If feedLocation is an HTTP URL, then errorFileLocation also should be an HTTP URL, to which the status feeds are posted. If no value is specified for errorFileLocation, then the status feeds are posted to the URL given in feedLocation.
If an error occurs while processing a feed available over file or FTP protocol, then the erroneous feed is renamed filename.prcsdErr in the same directory.
sourceName (optional) specifies the name of the source.
securityType (optional) specifies the security type. Valid values are the following:
noSecurity: There is no security information associated with this source at the document level. This is the default value.
identityBased: Identity-based security is used for documents in the feed.
attributeBased: Attribute-based security is used for documents in the feed. With this security model, security attributes should be specified in the securityAttribute tag, and the values for these attributes should be specified for each document.
securityAttribute specifies attribute-based security. One or more tags of this type should be specified, and each tag should contain the following attributes:
name: Name of the security attribute.
grant: Boolean parameter indicating whether this is a grant/deny attribute. The security attribute is considered a grant attribute if the value is true and a deny attribute if the value is false.
The Oracle SES crawler initially is set to search only text files. You can change this behavior by configuring an image document service connector to search the metadata associated with image files. Image files can contain rich metadata that provide additional information about the image itself.
The Image Document Service connector integrates Oracle Multimedia (formerly Oracle interMedia) images with Oracle SES. This connector is separate from any specific data source.
The following table identifies the metadata formats (EXIF, IPTC, XMP, DICOM) that can be extracted from each supported image format (JPEG, TIFF, GIF, JPEG 2000, DICOM).
| JPEG | TIFF | GIF | JPEG2000 | DICOM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXIF | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| IPTC | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| XMP | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| DICOM | No | No | No | No | Yes |
See Also:
Oracle Multimedia User's Guide and Oracle Multimedia Reference for more information about image metadataImage files can contain metadata in multiple formats, but not all of it is useful when performing searches. A configuration file in Oracle SES enables you to control the metadata that is searched and published to an Oracle SES Web application.
The default configuration file is named attr-config.xml. Note that if you upgraded from a previous release, then the default configuration file remains ordesima-sample.xml.
You can either modify the default configuration file or create your own file. The configuration file must be located at ORACLE_HOME/search/lib/plugins/doc/ordim/config/. Oracle recommends that you create a copy of the default configuration file before editing it. Note that the configuration file must conform to the XML schema ORACLE_HOME/search/lib/plugins/doc/ordim/xsd/ordesima.xsd.
Oracle SES indexes and searches only those image metadata tags that are defined within the metadata element (between <metadata>...</metadata>) in the configuration file. By default, the configuration file contains a set of the most commonly searched metadata tags for each of the file formats. You can add other metatags to the file based on your specific requirements.
Image files can contain metadata in multiple formats. For example, an image can contain metadata in the EXIF, XMP, and IPTC formats. An exception to this are DICOM images, which contain only DICOM metadata. Note that for IPTC and EXIF formats, Oracle Multimedia defines its own image metadata schemas. The metadata defined in the configuration file must conform to the Oracle Multimedia defined schemas.
Because different metadata formats use different tags to refer to the same attribute, it is necessary to map metatags and the search attributes they define. Table 4-1 lists some of the commonly used metatags and how they are mapped in Oracle SES.
Table 4-1 Metatag Mapping
| Oracle SES Attribute Name | Oracle SES Predefined Name | EXIF Metatag | IPTC Metatag | XMP Metatag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Author |
Author |
Artist |
Author |
photoshop:Creator |
|
AuthorTitle |
X |
X |
AuthorTitle |
photoshop:AuthorsPosition |
|
Description |
Description |
ImageDescription |
Caption |
dc:Description |
|
Title |
Title |
X |
ObjectName |
dc:Title |
|
DescriptionWriter |
X |
X |
captionWriter |
photoshop:CaptionWriter |
|
Headline1 |
Headline1 |
X |
Headline |
photoshop:Headline |
|
Category |
X |
X |
Category |
photoshop:Category |
|
Scene |
X |
X |
X |
Iptc4xmpCore:Scene |
|
Publisher |
X |
X |
X |
dc:Publisher |
|
Source |
X |
X |
Source |
photoshop:Source |
|
Copyright |
X |
Copyright |
Copyright |
dc:rights |
|
Keywords |
Keywords |
X |
Keyword |
dc:subject |
|
Provider |
X |
X |
Credit |
photoshop:Credit |
|
City |
X |
X |
City |
photoshop:City |
|
State |
X |
X |
provinceState |
photoshop:State |
|
Country |
X |
X |
Country |
photoshop:Country |
|
Location |
X |
X |
location |
Iptc4xmpCore:Location |
|
EquipmentMake |
X |
Make |
X |
tiff:Make |
|
EquipmentModel |
X |
Model |
X |
tiff:Model |
Oracle SES provides this mapping in the configuration file attr-config.xml. You can edit the file to add other metatags. Oracle recommends that you make a copy of the original configuration file before editing the settings. The configuration file defines the display name of a metatag and how it is mapped to the corresponding metadata in each of the supported formats.
This is done using the searchAttribute tag, as shown in the example below:
<searchAttribute> <displayName>Author</displayName> <metadata> <value format="iptc">byline/author</value> <value format="exif">TiffIfd/Artist</value> <value format="xmp">dc:creator</value> <value format="xmp">tiff:Artist</value> </metadata> </searchAttribute>
For each search attribute, the value of displayName is an Oracle SES attribute name that is displayed in the Oracle SES web application when an Advanced Search - Attribute Selection is performed. If any of the listed attributes are detected during a crawl, then Oracle SES automatically publishes the attributes to the SES web application.
For the element value, format must take the value of one of the supported formats such as iptc, exif, xmp, or dicom.
The value defined within the element, for example, byline/author, is the XML path when the image format is IPTC, EXIF, or XMP. For DICOM, this value must be the standard tag number or value locator.
For IPTC and EXIF formats, the XML path must conform to the metadata schemas defined by Oracle Multimedia. These schemas are defined in the files ordexif.xsd and ordiptc.xsd located at ORACLE_HOME/search/lib/plugins/doc/ordim/xsd/.
You do not need to specify the root elements defined in these schemas (iptcMetadata, exifMetadata) in the configuration file. For example, you can specify byline/author as the xmlPath value of the author attribute in IPTC format. Oracle Multimedia does not define XML schemas for XMP metadata, so refer to the Adobe XMP specification for the xmlPath value.
Within the <searchAttribute> tag, you can also specify an optional <dataType> tag if the attribute carries a date or numerical value. For example,
<searchAttribute>
<displayName>AnDateAttribute</displayName>
<dataType>date</dataType>
<metadata>
...
</metadata>
</searchAttribute>
The default data type is string, so you do not have to explicitly specify a string.
Oracle SES supports both standard and custom XMP metadata searches. Because all XMP properties share the same parent elements <rdf:rdf><rdf:description>, you must specify only the real property schema and property name in the configuration file. For example, specify photoshop:category instead of rdf:rdf/rdf:description/photoshop:category. The same rule applies to XMP custom metadata also. However, for XMP structure data, you must specify the structure element in the format parent/child 1/child 2/…child N, where child N is a leaf node. For example, Iptc4xmpCore:CreatorContactInfo/Iptc4xmpCore:CiPerson. Note that the image plug-in does not validate the metadata value for XMP metadata.
XMP metatags consist of 2 components separated by a colon(:). For example, photoshop:Creator, which corresponds to the Author attribute (see Table 4-1). In this, photoshop refers to the XMP schema namespace. The other common namespaces include dc, tiff, and Iptc4xmpCore.
Before defining any XMP metadata in the configuration file, you must ensure that the namespace is defined. For example, before defining the metadata photoshop:Creator, you must include the namespace photoshop in the configuration file. This rule applies to both the standard and custom XMP metadata namespaces. As a best practice, Oracle recommends that you define all the namespaces at the beginning of the configuration file. If the namespace defined in the configuration file is different from the one in the image, then Oracle SES cannot find the attributes associated with this namespace. You can define namespaces as shown:
<xmpNamespaces> <namespace prefix="Iptc4xmpCore">http://iptc.org/std/Iptc4xmpCore/1.0/xmlns/</namespace> <namespace prefix="dc">http://purl.org/dc/elements/1.1/</namespace> <namespace prefix="photoshop">http://ns.adobe.com/photoshop/1.0/</namespace> <namespace prefix="xmpRights">http://ns.adobe.com/xap/1.0/rights/</namespace> <namespace prefix="tiff">http://ns.adobe.com/tiff/1.0/</namespace> </xmpNamespaces>
Note that the Adobe XMP Specification requires that XMP namespaces end with a slash (/) or hash (#) character.
See Also:
Adobe Extensible Metadata Platform (XMP) Specification for the XMP metadata schema and a list of standard XMP namespace values:Custom XMP metadata must be explicitly added to attr-config.xml. An example of a custom metadata is:
<xmpNamespaces>
<namespace prefix="hm">http://www.oracle.com/ordim/hm/</namespace>
</xmpNamespaces>
<searchattribute>
<displayname>CardTitle</displayname>
<metadata>
<value format="xmp">hm:cardtitle</value>
</metadata>
</searchattribute>
Oracle SES 11g supports DICOM metatags, and these metatags are available in the default configuration file attr-config.xml. Note that the configuration file ordesima-sample.xml, which is the default configuration file if you upgraded from a previous release, does not contain DICOM metatags. Therefore, you must manually add DICOM metatags to the ordesima-sample.xml file. To do this, you can copy the DICOM metatags from attr-config.xml, which is available in the same directory. You can also reference the DICOM standard and add additional DICOM tags.
DICOM metatags are either DICOM standard tags or DICOM value locators.
DICOM standard tags are 8-digit hexadecimal numbers, represented in the format ggggeeee where gggg specifies the group number and eeee specifies the element number. For example, the DICOM standard tag for the attribute performing physician's name is represented using the hexadecimal value 00081050.
Note that the group number gggg must take an Even value, excepting 0000, 0002, 0004, and 0006, which are reserved group numbers.
The DICOM standard defines over 2000 standard tags.
The file attr-config.xml contains a list of predefined DICOM standard metatags. You can add new metatags to the file as shown in the following example:
<searchAttribute>
<displayName>PerformingPhysicianName</displayName>
<metadata>
<value format="dicom">00081050</value>
</metadata>
</searchAttribute>
Note:
The image connector does not support SQ, UN, OW, OB, and OF data type tags. Therefore, do not define such tags in the configuration file.See Also:
http://medical.nema.org for more information about the standard tags defined in DICOM images, and the rules for defining metatagsValue locators identify an attribute in the DICOM content, either at the root level or from the root level down.
A value locator contains one or more sublocators and a tag field (optional). A typical value locator is of the format:
sublocator#tag_field
Or of the format:
sublocator
Each sublocator represents a level in the tree hierarchy. DICOM value locators can include multiple sublocators, depending on the level of the attribute in the DICOM hierarchy. Multiple sublocators are separated by the dot character (.). For example, value locators can be of the format:
sublocator1.sublocator2.sublocator3#tag_field
Or of the format:
sublocator1.sublocator2.sublocator3
A tag_field is an optional string that identifies a derived value within an attribute. A tag that contains this string must be the last tag of a DICOM value locator. The default is NONE.
A sublocator consists of a tag element and can contain other optional elements. These optional elements include definer and item_num. Thus, a sublocator can be of the format:
tag
Or it can be of the format
tag(definer)[item_num)
Table 4-2 Sub Components of a Sublocator
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
|
tag |
A DICOM standard tag represented as an 8-digit hexadecimal number. |
|
definer |
A string that identifies the organization creating the tag. For tags that are defined by the DICOM standard, the default value (which can be omitted) is Note that Oracle SES supports DICOM standard tags alone. It does not support private tags. |
|
item_num |
An integer that identifies a data element within an attribute, or a wildcard character ("*") that identifies all data elements within an attribute. It takes a default value of 1, the first data element of an attribute. This parameter is optional. |
The following example shows how to add a value locator to the attr-config.xml file:
<searchAttribute> <displayName>PatientFamilyName</displayName> <metadata> <value format="dicom">00100010#UnibyteFamily</value> </metadata> </searchAttribute>
where UnibyteFamily is a tag_field of person name.
The following example shows how to define a value locator from the root level.
<searchAttribute>
<displayName>AdmittingDiagnosisCode</displayName>
<metadata>
<value format="dicom">00081084.00080100</value>
</metadata>
</searchAttribute>
<searchAttribute>
<displayName>AdmittingDiagnosis</displayName>
<metadata>
<value format="dicom">00081084.00080104</value>
</metadata>
</searchAttribute>
In the above example, the tag 00081084 represents the root tag Admitting Diagnoses Code Sequence. This tag includes four child tags: code value (0008, 0100), coding scheme designator (0008, 0102), coding scheme version (0008, 0103) and code meaning (0008, 0104). In this example, we define the value locators for code value: 00081084.00080100 and code meaning: 00081084.00080104.
Note:
The image connector does not support SQ, UN, OW, OB, and OF data type value locators. Therefore, ensure that the last sublocator of a value locator does not specify such data types.See Also:
Oracle Multimedia DICOM Developer's Guide for more information about DICOM value locatorsTo search for information about image caption writer:
Open Oracle SES Administration GUI and create the DescriptionWriter attribute:
Specify DescriptionWriter as an Oracle SES attribute name (shown on the Advanced Search - Attribute Selection page).
Examine the following sources for information relevant to modifying the default attr-config.xml file:
Oracle Multimedia IPTC schema at ORACLE_HOME/search/lib/plugins/doc/ordim/xsd/ordiptc.xsd. The IPTC metadata for image caption writer is shown as captionWriter.
Adobe XMP Specification for XMP Metadata. The XMP path for this property is defined as photoshop:CaptionWriter.
Oracle Multimedia EXIF schema. There is no caption writer metadata in EXIF.
Add the following section to attr-config.xml:
<searchAttribute>
<displayName>DescriptionWriter</displayName>
<metadata>
<xmlPath format="iptc">captionWriter</xmlPath>
<xmlPath format="xmp">photoshop:CaptionWriter</xmlPath>
</metadata>
</searchAttribute>
If the photoshop XMP namespace is not registered in the configuration file, then add the namespace element to xmpNamespaces as shown here:
<xmpNamespaces> <namespace prefix="photoshop">http://ns.adobe.com/photoshop/1.0/</namespace>
.
. existing namespaces
.
</xmpNamespaces>
A default Image Document Service connector instance is created during the installation of Oracle SES. You can configure the default connector or create a new one.
To create an Image Document Service instance:
In the Oracle SES Administration GUI, click Global Settings.
Under Sources, click Document Services to display the Global Settings - Document Services page.
To configure the default image service instance:
Click Expand All
Click Edit for the default image service instance.
or
To create a new image service instance:
Click Create to display the Create Document Service page.
For Select From Available Managers, choose ImageDocumentService. Provide a name for the instance.
Provide a value for the attributes configuration file parameter.
The default value of attributes configuration file is attr-config.xml. The file is located at ORACLE_HOME/search/lib/plugins/doc/ordim/config/, where ORACLE_HOME refers to ORACLE_BASE/seshome, the directory which stores the Oracle SES specific components. If you create a new configuration file, then you must place the file at the same default location.
Click Apply.
Click Document Services in the locator links to return to the Document Services page.
Add the Image Document Service plug-in to either the default pipeline or a new pipeline.
To add the default Image Document Service plug-in to the default pipeline:
Under Document Service Pipelines, click Edit for the default pipeline.
Move the Image Document Service instance from Available Services to Used in Pipeline.
Click Apply.
To create a new pipeline for the default Image Document Service plug-in:
Under Document Service Pipelines, click Create to display the Create Document Service Pipeline page.
Enter a name and description for the pipeline.
Move the Image Document Service instance from Available Services to Used in Pipeline.
Click Create.
You must either create a source to use the connector or enable the connector for an existing source.
To enable the connector for an existing source:
Click Sources on the Home page.
Click the Edit icon for the desired source.
Click Crawling Parameters.
Select the pipeline that uses the Image Document Service and enable the pipeline for this source.
Click Document Types. From the Not Processed column, select the image types to search and move them to the Processed column. The following sources are supported: JPEG, JPEG2000, GIF, TIFF, DICOM.
You can search image metadata from either the Oracle SES Basic Search page or the Advanced Search - Attribute Selection page.
For Basic Search, Oracle SES searches all the metadata defined in the configuration file for each supported image document (JPEG, TIFF, GIF, JPEG 2000, and DICOM). It returns the image document if any matching metadata is found.
Advanced Search enables you to search one or more specified attributes. It also supports basic operations for date and number attributes. Oracle SES returns only those image documents that contain the specified metadata.
Note that Oracle SES does not display the Cache link for image search results.
If the Image Document Service Connector fails, then check the following:
Is the pipeline with an Image Document Service connector instance enabled for the source?
Are the image types added to the source?
For a web source, are the correct MIME types included in the HTTP server configuration file?
For example, if you use Oracle Application Server, then check the file ORACLE_HOME/Apache/Apache/conf/mime.types. If the following media types are missing, then add them:
| MIME Type | Extensions |
|---|---|
| image/jp2 | jp2 |
| application/dicom | dcm |
If a connection is established, and all the image files are not crawled, then check whether the recrawl policy is set to Process Documents That Have Changed. If so, change this to Process All Documents.
To do this, go to Home - Schedules, and under Crawler Schedules, click Edit for the specific source. This opens the Edit Schedule page. Under Update Crawler Recrawl Policy, select Process All Documents.
Note that you can change the recrawl policy back to Process Documents That Have Changed, after the crawler has finished crawling all the documents in the new source.
Each source has its own set of document attributes. Document attributes, like metadata, describe the properties of a document. The crawler retrieves values and maps them to a search attributes. This mapping lets users search documents based on their attributes. Document attributes in different sources can be mapped to the same search attribute. Therefore, users can search documents from multiple sources based on the same search attribute.
After you crawl a source, you can see the attributes for that source. Document attribute information is obtained differently depending on the source type.
See Also:
"Customizing the Appearance of Search Results" for a list of Oracle internal attributes
Document attributes can be used in tasks such as document management, access control, or version control. Different sources can have different attribute names that are used for the same idea; for example, version and revision. It can also have the same attribute name for different ideas; for example, "language" as in natural language in one source but as programming language in another. Document attribute information is obtained differently depending on the source type.
Oracle SES has several default search attributes. They can be incorporated in search applications for a more detailed search and richer presentation.
Search attributes are defined in the following ways:
System-defined search attributes, such as title, author, description, subject, and mimetype.
Search attributes created by the Oracle SES administrator.
Search attributes created by the crawler. During crawling, the crawler plug-in maps the document attribute to a search attribute with the same name and data type. If not found, then the crawler creates a new search attribute with the same name and type as the document attribute defined in the crawler plug-in.
Table and database sources have no predefined attributes. The crawler collects attributes from columns defined during source creation. You must map the columns to the search attributes.
For Siebel 7.8 sources, specify the attributes in the query while creating the source. For Oracle E-Business Suite and Siebel 8 sources, specify the attributes in the XML data feed.
For many source types, such as OracleAS Portal, e-mail, NTFS, and Microsoft Exchange sources, the crawler picks up key attributes offered by the target systems. For other sources, such as Documentum eRoom or Lotus Notes, an Attribute list parameter is in the Home - Sources - Customize User-Defined Source page. Any attributes that you define are collected by the crawler and available for search.
The list of values (LOV) for a search attribute can help you specify a search. Global search attributes can be specified on the Global Settings - Search Attributes page. For user-defined sources where LOV information is supplied through a crawler plug-in, the crawler registers the LOV definition. Use the Oracle SES Administration GUI or the crawler plug-in to specify attribute LOVs, attribute value, attribute value display name, and its translation.
When multiple sources define the LOV for a common attribute, such as title, the user sees all the possible values for the attribute. When the user restricts search within a particular source group, only LOVs provided by the corresponding sources in the source group are shown.
LOVs can be collected automatically. The following example shows Oracle SES collecting LOV values to crawl a fictitious URL.
Create a Web source with http://www.example.com as the starting URL. Do not start crawling yet.
From the Global Settings - Search Attributes page, select the Attribute for Oracle SES to collect LOVs and click Manage Lov. (For example, click Manage Lov for Author.)
Select Source-Specific for the created source, and click Apply.
Click Update Policy.
Choose Document Inspection and click Update, then click Finish.
From the Home - Schedules page, start crawling the Web source. After crawling, the LOV button in the Advanced Search page shows the collected LOVs.
There are also two system-defined search attributes, Urldepth and Infosource Path.
Urldepth measures the number of levels down from the root directory. It is derived from the URL string. In general, the depth is the number of slashes, not counting the slash immediately following the host name or a trailing slash. An adjustment of -2 is made to home pages. An adjustment of +1 is made to dynamic pages, such as the example in Table 4-3 with the question mark in the URL.
Urldepth is used internally for calculating relevance ranking, because a URL with a smaller URL depth is typically more important.
Table 4-3 lists the Urldepth of some example URLs.
Table 4-3 Depth of Example URLs
| URL | Urldepth |
|---|---|
|
http://example.com/portal/page/myo/Employee_Portal/MyCompany |
4 |
|
http://example.com/portal/page/myo/Employee_Portal/MyCompany/ |
4 |
|
http://example.com/portal/page/myo/Employee_Portal/MyCompany.htm |
4 |
|
http://example.com/finance/finhome/topstories/wall_street.html?.v=46 |
4 |
|
http://example.com/portal/page/myo/Employee_Portal/home.htm |
2 |
Infosource Path is a path representing the source of the document. This internal attribute is used in situations where documents can be browsed by their source. The Infosource Path is derived from the URL string.
For example, for this URL:
http://example.com/portal/page/myo/Employee_Portal/home.htm
The Infosource Path is:
portal/page/myo/Employee_Portal
If the document is submitted through a connector, this value can be set explicitly by using the DocumentMetadata.setSourceHierarchy API.
The first time the crawler runs, it must fetch data (Web pages, table rows, files, and so on) based on the source. It then adds the document to the Oracle SES index.
This section describes a Web source crawling process for a schedule. It is divided into these phases:
The crawling cycle involves the following steps:
Oracle spawns the crawler according to the schedule you specify with the Oracle SES Administration GUI. When crawling is initiated for the first time, the URL queue is populated with the seed URLs.
The crawler initiates multiple crawling threads.
The crawler thread removes the next URL in the queue.
The crawler thread fetches the document from the Web. The document is usually an HTML file containing text and hypertext links. When the document is not in HTML format, the crawler converts the document into HTML before caching.
The crawler thread scans the HTML file for hypertext links and inserts new links into the URL queue. Duplicate links in the document table are discarded.
The crawler caches the HTML file.
The crawler registers the URL in the URL table.
The crawler thread starts over by repeating Step 3.
Fetching a document, as described in Step 4, can be time-consuming because of network traffic or slow Web sites. For maximum throughput, multiple threads fetch pages at any given time.
When the cache is full (default maximum size is 250 MB), the indexing process begins. At this point, the document content and any searchable attributes are pushed into the index.
When the Preserve Document Cache parameter is set to false, the crawler automatically deletes the cache after indexing the documents.
Oracle SES maintains a stoplist. A stoplist is a list of words that are ignored during the indexing process. These words are known as stopwords. Stopwords are not indexed because they are deemed not useful, or even disruptive, to the performance and accuracy of indexing. The Oracle SES stoplist contains only English words, and cannot be modified.
When you run a phrase search with a stopword in the middle, the stopword is not used as a match word, but it is used as a placeholder. For example, the word "on" is a stopword. If you search for the phrase "oracle on demand", then Oracle SES matches a document titled "oracle on demand" but not a document titled "oracle demand". If you search for the phrase "oracle on on demand", then Oracle SES matches a document titled "oracle technology on demand" but not a document titled "oracle demand" or "oracle on demand".
After the initial crawl, a URL page is only crawled and indexed if it changed since the last crawl. The crawler determines whether it has changed with the HTTP If-Modified-Since header field or with the checksum of the page. URLs that no longer exist are marked and removed from the index.
To update changed documents, the crawler uses an internal checksum to compare new Web pages with cached Web pages. Changed Web pages are cached and marked for re-indexing.
Data synchronization involves the following steps:
Oracle spawns the crawler according to the schedule specified in the Oracle SES Administration GUI. The URL queue is populated with the seed URLs of the source assigned to the schedule.
The crawler initiates multiple crawling threads.
Each crawler thread removes the next URL in the queue.
Each crawler thread fetches a document from the Web. The page is usually an HTML file containing text and hypertext links. When the document is not in HTML format, the crawler converts the document into HTML before caching.
Each crawler thread calculates a checksum for the newly retrieved page and compares it with the checksum of the cached page. If the checksum is the same, then the page is discarded and the crawler goes to Step 3. Otherwise, the crawler continues to the next step.
The crawler thread scans the document for hypertext links and inserts new links into the URL queue. Links that are in the document table are discarded. Oracle SES does not follow links from filtered binary documents.
The crawler marks the URL as accepted. The URL is crawled in future maintenance crawls.
The crawler registers the URL in the document table.
If the cache is full or if the URL queue is empty, then caching stops. Otherwise, the crawler thread starts over at Step 3.
A maintenance or a forced recrawl does not move a cache from the file system to the database, or the reverse. The cache location for a source remains the same until it is migrated to a different location.
When you configure a data source, certain operations trigger an automatic forced recrawl of the data source. These operations include the following:
Deleting a document attribute from the data source
Remapping a document attribute to a different search attribute
Changing the crawler configuration "Index Dynamic Page" from No to Yes for a Web source.
These operations set the Force Recall flag, but no notice is given of this change in mode.
Monitor the crawling process in the Oracle SES Administration GUI by using a combination of the following:
Check the crawl progress and crawl status on the Home - Schedules page. (Click Refresh Status.)
Monitor your crawler statistics on the Home - Schedules - Crawler Progress Summary page and the Home - Statistics page.
Monitor the log file for the current schedule.
See Also:
"Tuning the Crawl Performance"The following crawler statistics are shown on the Home - Schedules - Crawler Progress Summary page. Some of them are also shown in the log file, under "Crawling results".
Documents to Fetch: Number of URLs in the queue waiting to be crawled. The log file uses the phrase "Documents to Process".
Documents Fetched: Number of documents retrieved by the crawler.
Document Fetch Failures: Number of documents whose contents cannot be retrieved by the crawler. This could be due to an inability to connect to the Web site, slow server response time causing time-outs, or authorization requirements. Problems encountered after successfully fetching the document are not considered here; for example, documents that are too big or duplicate documents that were ignored.
Documents Rejected: Number of URL links encountered but not considered for crawling. The rejection could be due to boundary rules, the robots exclusion rule, the mime type inclusion rule, the crawling depth limit, or the URL rewriter discard directive.
Documents Discovered: Total number of documents discovered so far. This is roughly equal to (documents to fetch) + (documents fetched) + (document fetch failures) + (documents rejected).
Documents Indexed: Number of documents that have been indexed or are pending indexing.
Documents Non-Indexable: Number of documents that cannot be indexed; for example, a file source directory or a document with robots NOINDEX metatag.
Document Conversion Failures: Number of document filtering errors. This is counted whenever a document cannot be converted to HTML format.
The log file records all crawler activity, warnings, and error messages for a particular schedule. It includes messages logged at startup, run time, and shutdown. Logging everything can create very large log files when crawling a large number of documents. However, in certain situations, it can be beneficial to configure the crawler to print detailed activity to each schedule log file.
On the Global Settings - Crawler Configuration page, you can select either to log everything or to log only summary information. You can also select the crawler log file directory and the language the crawler uses to generate the log file.
Note:
On UNIX-based systems, ensure that the directory permission is set to 700 if you change the log file directory. Only the user who installed the Oracle software should have access to this directory.A new log file is created when you restart the crawler. The location of the crawler log file can be found on the Home - Schedules - Crawler Progress Summary page. The crawler maintains the past seven versions of its log file, but only the most recent log file is shown in the Oracle SES Administration GUI. You can view the other log files in the file system.
The naming convention of the log file name is ids.MMDDhhmm.log, where ids is a system-generated ID that uniquely identifies the source, MM is the month, DD is the date, hh is the launching hour in 24-hour format, and mm is the minutes.
For example, if a schedule for a source identified as i3ds23 starts at 10:00 PM on July 8, then the log file name is i3ds23.07082200.log. Each successive schedule has a unique log file name. After a source has seven log files, the oldest log file is overwritten.
Each logging message in the log file is one line, containing the following six tab delimited columns, in order:
Timestamp
Message level
Crawler thread name
Component name. It is typically the name of the executing Java class.
Module name. It can be internal Java class method name
Message
The crawler configuration file is ORACLE_HOME/search/data/config/crawler.dat. Most crawler configuration tasks are controlled in the Oracle SES Administration GUI, but certain features (like title fallback, character set detection, and indexing the title of multimedia files) are controlled only by the crawler.dat file.
Note:
Thecrawler.dat file is not backed up with Oracle SES backup and recovery. If you edit this file, be sure to back it up manually.The Java library used to process zip files (java.util.zip) supports only UTF8 file names for zip entries. The content of non-UTF8 file names is not indexed.
To crawl zip files containing non-UTF8 file names, change the ZIPFILE_PACKAGE parameter in crawler.dat from JDK to APACHE. The Apache library org.apache.tools.zip does not read the zip content in the same order as the JDK library, so the content displayed in the user interface could look different. Zip file titles also may be different, because it uses the first file as the fallback title. Also, with the Apache library, the source default character set value is used to read the zip entry file name.
Specify the crawler logging level with the parameter Doracle.search.logLevel. The defined levels are DEBUG(2), INFO(4), WARN(6), ERROR(8), and FATAL(10). The default value is 4, which means that messages of level 4 and higher are logged. DEBUG (level=2) messages are not logged by default.
For example, the following "info" message is logged at 23:10:39330. It is from thread name crawler_2, and the message is Processing file://localhost/net/stawg02/. The component and module names are not specified.
23:10:39:330 INFO crawler_2 Processing file://localhost/net/stawg02/
The crawler uses a set of codes to indicate the crawling result of the crawled URL. Besides the standard HTTP status codes, it uses its own codes for non-HTTP related situations.
See Also:
Appendix B, "URL Crawler Status Codes"In order to scale up the indexed data size while maintaining satisfactory query response time, the indexed data can be stored in independent disks to perform disk I/O operations in parallel. The major features of this architecture are:
Oracle SES index is partitioned, so that the sub-queries are executed in parallel.
Disks perform I/O operations independent of one another. As a result, the I/O bus contention does not create a significant bottleneck on the collective I/O throughput.
Partition rules are used to control the document distribution among the partitions.
Storage areas are used to store the partitions when the partitioning option is enabled. See "Storage Areas" for more information.
There are two kinds of partition mechanisms for improving query performance, attribute-based partitioning and hash-based partitioning. Currently, Oracle SES supports only hash-based partitioning.
Hash-based partitioning uses a hash function to distribute a large set of documents into multiple partitions. A partition engine controls the partition logic at both crawl time and query time. When a large data set needs to be searched without pruning the conditions, the end user request is broken into multiple parallel sub-queries so that the I/O and CPU resources can be utilized in parallel. After the result sets of the sub-queries are returned by the independent query processors, a merged result set is returned to the end user.
Figure 4-2 shows how the mechanism works during crawl time. The documents are partitioned and stored in different storage areas. Note that the storage areas are created on separate physical disks, so that I/O operations can be performed in parallel to improve the search turn around time.
Figure 4-2 Document Partitioning at Crawl Time
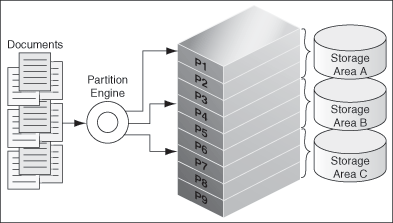
At query time, the query partition engine generates sub-queries and submits them to the storage areas, as shown in Figure 4-3.
Figure 4-3 Generation of Sub Queries at Query Time
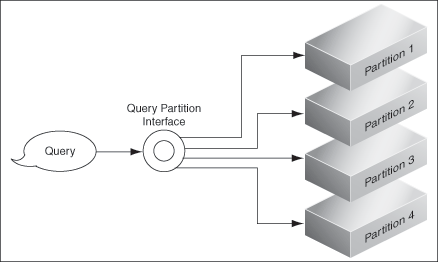
See "Parallel Querying and Index Partitioning" for more information.
Note:
In previous releases, the base path of Oracle SES was referred to asORACLE_HOME. In Oracle SES release 11g, the base path is referred to as ORACLE_BASE. This represents the Software Location that you specify at the time of installing Oracle SES.
ORACLE_HOME now refers to the path ORACLE_BASE/seshome.
For more information about ORACLE_BASE, see "Conventions".