| Oracle® Real User Experience Insight Installation Guide Release 4.5.2 for Linux x86-64 Part Number E14989-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Real User Experience Insight Installation Guide Release 4.5.2 for Linux x86-64 Part Number E14989-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter describes the procedure for preparing the server system(s) for RUEI, and installing the RUEI software. This is performed by a system administrator. Post-installation configuration of the RUEI system is described in Chapter 3.
Note:
Throughout this guide is is assumed that you are logged on asroot, unless indicated otherwise.Before you start
Before starting the installing procedure described in the following sections, ensure you have the following information to hand:
The IP address of the RUEI system.
The root password.
The process of preparing the server system, and installing the RUEI software, has the following phases:
Install the Linux operating system. This is described in Section 2.2, "Installing the Linux Operating System".
Install and configure the Oracle database. This is described in Section 2.3, "Installing and Configuring the Oracle Database".
Configure the Apache Web server. This is described in Section 2.4, "Installing the Apache Web Server and PHP".
Install the RUEI software. This is described in Section 2.5, "Installing the RUEI Software".
Important:
The installation procedure described in the following sections assumes that each system is dedicated to RUEI. Indeed, it is strongly recommended that RUEI is only installed on dedicated systems.Obtaining the RUEI Software
The RUEI software is available from the Oracle E-Delivery Web site (http://edelivery.oracle.com). Select the following media pack criteria:
Product pack: Oracle Enterprise Manager.
Platform: Linux Intel (64-bit).
Select the required media pack from the displayed list and download.
Upgrading to Release 4.5.2
The procedure for upgrading an existing RUEI 4.5.0 or 4.5.1 installation to release 4.5.2 is fully explained in Section 2.6, "Upgrading from RUEI 4.5.x to 4.5.2". For information on upgrading to RUEI 4.5.2 from a release prior to 4.5.0, please contact Customer Support.
The procedure for installing Oracle Enterprise Linux 5.x is fully described in the product documentation. This section presents a summary of that procedure, and assumes a sound knowledge of Linux administration.
Although the installation procedure described in this section is based on Oracle Enterprise 5.x, the procedure for installing RedHat Enterprise Linux 5.x is virtually identical. For information on vendor-specific variations, consult the appropriate documentation.
Obtaining the Linux Operating System
The Oracle Enterprise Linux 5.x software is available from the Oracle E-Delivery Web site (http://edelivery.oracle.com/linux).
Download the appropriate ISO image. This should be Oracle or RedHat Enterprise Linux 5.x for the x86 64-bit architecture.
Unzip each of the files.
Burn the ISO files to CD. The operating system consists of sixFoot 1 CDs. Note that this requires the use of a CD-burning utility (such as UltraISO or Magic ISO Maker).
Note:
According to your corporate policy, the installation procedure may use a different procedure to that described in the following sections.Note:
After installing Linux on the first node, repeat the Linux installation on the next required system(s).Ensure that server system is able to boot from CD. Insert Oracle Enterprise Linux CD #1 into the first server, and power on.
When the Oracle Enterprise Linux boot screen appears, press Enter to start the installation process.
When asked to test the CD media, select Skip. After a short interval, the installer goes into GUI mode. (The media test is not necessary because the CD burning software would have informed you of any errors on the media).
At the Welcome to Oracle Enterprise Linux screen, click Next.
Select the appropriate options from the Language and Keyboard settings screens.
If the installer detects a previous version of Enterprise Linux, you are prompted to "Install Enterprise Linux" or "Upgrade an existing installation". Select "Install Enterprise Linux", and click Next.
Important:
Oracle recommends that you install the Linux operating system with the default software packages (RPMs), and that you do not customize the RPMs during installation. This installation includes most required packages, and helps you limit manual checks of package dependencies.When prompted, select the default Remove Linux partitions on selected drives and create default layout option, and check the option Review and modify partitioning layout. When prompted to confirm your selection, select Yes. Click Next to continue.
Note:
A check box allows you to encrypt the entire system. If selected, for security reasons, a password is required during booting the system.When prompted to confirm the removal of all partitions, click Yes.
Review and modify (if necessary) the automatically selected disk partitions.
For most automatic layouts, the installer assigns 100 MB for /boot, 2 GB for swap, and the remainder is assigned to the root (/) partition. The specified swap space is not enough for a working RUEI installation. See Table 2-1 and Table 2-2 for required disk space and swap space requirements.
The installer creates a disk configuration using the Logical Volume Manager (LVM). For example, it will partition the first hard drive (/dev/sda in the described configuration) into two partitions: one for the /boot partition (/dev/sda1), and the remainder of the disk dedicated to a LVM named VolGroup00 (/dev/sda2). The LVM Volume Group (VolGroup00) is then partitioned into two LVM partitions: one for the root file system (/), and another for swap. If you have selected a non-standard layout, ensure that the system meets the required disk space specifications shown in Table 2-1. Ensure enough swap space is allocated for Oracle Enterprise Linux. Its required swap space is shown in Table 2-2.
Table 2-1 Required Disk Space Specifications
| Partition | Minimum Required Disk Space (GB) |
|---|---|
/u01/app/Foot 1 |
300 |
/home/moniforce/ |
100 |
Footnote 1 This is the example location of the database used throughout this guide.
| Available RAM | Swap Space Required |
|---|---|
|
Up to 8192 MB |
Equal to the size of RAM |
|
More than 8192 MB |
0.75 times the size of RAM |
Important:
The Reporter server requires high performance data storage. RAID-0 or RAID-5 (or equivalent) storage configurations with high performance disks are strongly recommended.Note:
The requirements shown in Table 2-1 and Table 2-2 can vary depending upon the composition and volume of monitored data. For more information, please contact Customer Support.Accept the GRUB boot loader, as well as all default values, and click Next.
Ensure that a static IP address is assigned to the interface used to access the RUEI Web interface. In addition, the assigned IP address should be configured in the /etc/hosts file. If necessary, ensure that all Reporter and Collector systems are correctly defined in the DNS system.
Ensure that the network interface(s) used for network packet monitoring are administratively up, but without an IP address.
Important:
Make the network interface up status permanent (after a reboot) by setting the ONBOOT parameter of the capturing interfaces to yes in the interface configuration files. The network interfaces configuration can be found in/etc/sysconfig/networking/devices/ifcfg-ethX (where X represents the necessary network interface). Alternatively, use the graphical utility system-config-network to set the appropriate interfaces to "activate device when computer starts".Select the appropriate time zone for your environment, and click Next.
Specify a root password, and click Next.
At the additional tasks dialog box shown in Figure 2-1, check the Web server check box, leave the Customize later radio button checked, and click Next.
At the About to install screen, click Continue to start the installation.
Depending on the packages you have selected to install, you will be prompted to insert additional CDs. At the prompt screen, click Next to begin installation of Enterprise Linux.
Upon successful installation, remove the CD, and click Reboot.
Important:
It is strongly recommended that you use the settings described above, and do not perform a "minimal" installation of Oracle Enterprise Linux. This can lead to a wide range of problems, further described in Section A.8, "Missing Packages and Fonts Error Messages".When the system boots for the first time, a post-installation wizard appears, and allows you to finalize the operating system configuration settings. Click Forward.
At the User license agreement screen, read the license terms. You cannot proceed until you have accepted the license terms. Then click Forward.
Use the screen shown in Figure 2-2 to allow only secure WWW (HTTPs) and SSH traffic. Be aware that, by default, SSH traffic is enabled, but secure WWW (HTTPS) traffic is not. Note that, when prompted with a warning about not setting the firewall, click Yes.
Use the screen shown in Figure 2-3 to disable Security Enhanced Linux (SELinux). Click Forward. Note that you are prompted with a warning that changing the SELinux setting requires rebooting the system so that the entire system can be relabeled. Click Yes.
Important:
Security Enhanced Linux (SELinux) must be disabled for correct operation of RUEI.Accept the default setting on the Kdump screen (disabled), and click Forward.
Adjust the date and time settings using the screen shown in Figure 2-4. The use of NTP is strongly recommended, and is required in a split-server deployment. Click OK.
Create any additional required (non-Oracle) operating system user accounts. Note that during the installation of the RUEI software, the moniforce user account is created. The creation of the oracle user is described in a later section. Do not create either user account at this point.
If prompted, confirm the detection of a sound card.
On the Additional CDs screen, click Finish.
Because the SELinux option has been changed (to disabled), you are prompted to reboot the system. Click OK.
After reboot, use the root user account, and the password you specified during installation to logon.
Text Mode Installation (Optional):
When using the text mode installation, by default:Firewall: HTTPS (TCP 443) is blocked.
Security: SE Linux is enabled.
Allow HTTPS traffic (TCP 443) and disable SElinux using the system-config-securitylevel utility.
Kickstart installation (tip):
In addition to the base installation, two additional packages are required:web-server and gnome-desktop. You can include these package names in the %package section of your kickstart configuration file.Because the NTP daemon is a critical component of RUEI, it is recommended that you verify that it is activated in at least run level 5 during boot. Use the following commands:
/sbin/chkconfig --list | grep ntp ntpd 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off chkconfig ntpd on /sbin/chkconfig --list | grep ntp ntpd 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off /etc/init.d/ntpd start Starting ntpd: [ OK ]
Note that if the NTP daemon is not already running, you can start it with the command
/etc/init.d/ntpd restart
The following sample output show when the NTP daemon is synchronized (indicated by an "*").
ntpq -pn
remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter
==============================================================================
*194.171.167.130 .PPS. 1 u 994 1024 377 6.429 0.041 0.093
+80.85.129.25 130.235.20.3 3 u 725 1024 377 4.435 0.673 0.129
+82.94.235.106 135.81.191.59 2 u 678 1024 377 1.709 1.774 0.020
127.127.1.0 .LOCL. 10 l 8 64 377 0.000 0.000 0.001
This section describes the procedure for installing the Oracle database and its required components.
Download Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1.0.6.0) Standard Edition, Standard Edition One, and Enterprise for Linux x86-64 Edition from the Oracle database home page (http://www.oracle.com/technology/software/products/database/index.html).
The procedure for installing the Oracle database is fully described in the product documentation. This section presents a summary of that procedure.
In addition, it is recommended that you download and review the information in the Oracle Database 11g for Linux x86-64 Quick Installation Guide (available at http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/B28359_01/install.111/b32285/toc.htm).
The following (or later versions of) Oracle Enterprise Linux 5.x and RedHat Enterprise Linux 5.x should be installed before installing the 11g database.
binutils-2.17.50.0.6compat-libstdc++-33-3.2.3compat-libstdc++-33-3.2.3 (32 bit)elfutils-libelf-0.125elfutils-libelf-devel-0.125gcc-4.1.1gcc-c++-4.1.1glibc-2.5-12glibc-2.5-12 (32 bit)glibc-common-2.5glibc-devel-2.5glibc-devel-2.5-12 (32 bit)libaio-0.3.106libaio-0.3.106 (32 bit)libaio-devel-0.3.106libgcc-4.1.1libgcc-4.1.1 (32 bit)libstdc++-4.1.1libstdc++-4.1.1 (32 bit)libstdc++-devel 4.1.1make-3.81sysstat-7.0.0
Memory Usage
The Oracle database's maximum memory usage is set by the MEMORY_TARGET parameter. By default, this is set to 40% of the available server RAM. For example, in a system with 16 GB RAM, it is set to approximately 6.4 GB.
Note that if extra RAM is added to the server system to increase performance, it is not made available to the Oracle database until the MEMORY_TARGET parameter is manually increased.
Information about automatic memory management is available at http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/B28359_01/server.111/b28310/memory003.htm#ADMIN11200.
Insert the Oracle or RedHat Enterprise Linux 5.x CD #1, and issue the following commands:
cd /media/cdrom/Serverrpm -Uhv kernel-headers-2.6.18-92.el5.x86_64.rpmcd /eject
Insert the Oracle or RedHat Enterprise Linux 5.x CD #2Foot 2 , and issue the following commands:
cd /media/cdrom/Serverrpm -Uhv elfutils-libelf-devel-0.125-3.el5.x86_64.rpm \ elfutils-libelf-devel-static-0.125-3.el5.x86_64.rpmrpm -Uhv glibc-devel-2.5-* glibc-headers-2.5-24.x86_64.rpmrpm -Uhv gcc-4.1.2-42.el5.x86_64.rpm gcc-c++-4.1.2-42.el5.x86_64.rpm \ libstdc++-devel-4.1.2-42.el5.x86_64.rpm libgomp-4.1.2-42.el5.x86_64.rpmcd /
Insert the Oracle or RedHat Enterprise Linux 5.x CD #3, and issue the following commands:
cd /media/cdrom/Serverrpm -Uhv libaio-devel-0.3.106-3.2.x86_64.rpm cd /eject
Insert the Oracle or RedHat Enterprise Linux 5.x CD #4Footref 2, and issue the following commands:
cd /media/cdrom/Serverrpm -Uhv sysstat-7.0.2-1.el5.x86_64.rpm cd /eject
Required Components and Using a Yum Repository (Optional)
As an alternative to manual installation, you can use a Yum repository to install the required RPMs. This requires a working Yum repository. For information on Yum repositories, see http://linux.duke.edu/projects/yum/. Install the necessary Oracle packages using the following commands:
yum -y install gccyum -y install gcc-c++yum -y install compat-libstdc++-33yum -y install libstdc++-develyum -y install elfutils-libelf-develyum -y install glibc-devel yum -y install libaio-devel yum -y install sendmail-cf yum -y install sysstat
Install the necessary RUEI packages using the following commands:
yum -y install perl-URIyum -y install net-snmpyum -y install sendmail-cfyum -y install httpdyum -y install phpyum -y install php-gdyum -y install php-pearyum -y install php-mbstringyum -y install bitstream-vera-fontsyum -y install librsvg2yum -y install xorg-x11-xinit
Create two groups (dba and oinstall) with the following commands:
/usr/sbin/groupadd dba/usr/sbin/groupadd oinstall
Create the oracle user, and specify oinstall as the primary group and dba as the secondary group, with the following command:
/usr/sbin/useradd -g oinstall -G dba oracle
Set the oracle user password with the following command:
passwd oracle
Modify the /etc/sysctl.conf file to satisfy the Oracle installer's requirements by adding the following lines:
kernel.sem = 250 32000 100 128net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65000net.core.rmem_default = 4194304net.core.rmem_max = 4194304net.core.wmem_default = 262144net.core.wmem_max = 262144fs.file-max = 6553600
Make these changes effective immediately with the following command:
sysctl -p
To improve the performance of the software, you must increase the shell limits for the oracle user. Add the following lines to the /etc/security/limits.conf file:
oracle soft nproc 2047oracle hard nproc 16384oracle soft nofile 1024oracle hard nofile 65536
If not already present, add the following lines to the /etc/pam.d/login file:
session required /lib64/security/pam_limits.sosession required pam_limits.so
Depending on the oracle user's default shell, you need to make changes to it. For the Bourne, Bash, or Korn shell, add the following lines to the bottom of the /etc/profile file:
if [ $USER = "oracle" ]; then if [ $SHELL = "/bin/ksh" ]; then ulimit -p 16384 ulimit -n 65536 else ulimit -u 16384 -n 65536 fifi
For information about other shells, you should refer to the Oracle Database 11g Release 1 for Linux x86-64 Quick Installation Guide (at http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/B28359_01/install.111/b32285/toc.htm).
Throughout this guide it is assumed that the directory /u01/app is the root of the Oracle installation. This is specified in the ORACLE_BASE environment variable.
Enter the following command to display information about all mounted file systems:
df -k
This command displays information about all the file systems mounted on the system, including:
The physical device name
The total amount, used amount, and available amount of disk space
The mount point directory for that file system
Create the necessary subdirectories in the mount point directory that you identified and set the appropriate owner, group, and permissions for them using commands similar to the following:
mkdir -p /u01/appchown -R oracle:oinstall /u01/appchmod -R 775 /u01/app
Logon to the system as the oracle user and add or edit the umask setting in the ~/.bash_profile file to the following:
umask 022
Make the setting active for the current shell by issuing the following command:
. ./.bash_profile
Set the ORACLE_BASE environment variable to define the location of the root of the Oracle directory tree:
export ORACLE_BASE=/u01/app/oracle
Unzip the Oracle database installation zip file. This creates the directory database. Then, run the graphical installer (note this will not run under user root). Ensure that your X Window environment is properly set up. In addition, when logging on remotely with SSH, ensure X forwarding is enabled. Use the following commands:
cd <location of the zip file>unzip linux_11gR1_database.zip./database/runInstaller
Use the installation wizard, and specify the values shown in Figure 2-5.
Note that the Create Starter Database check box should be unchecked.
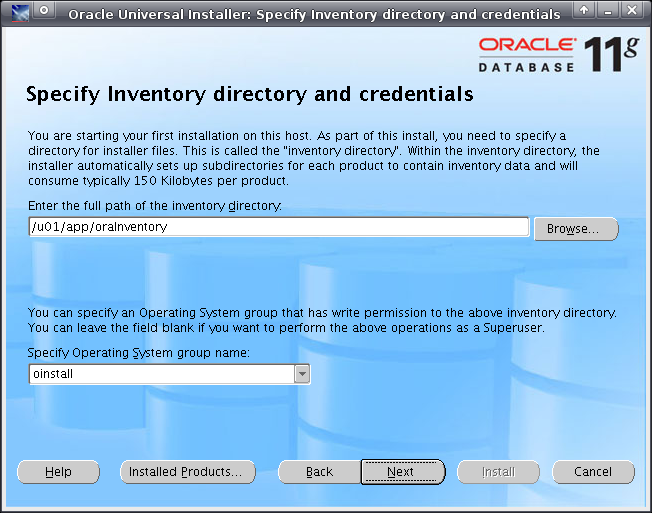
When ready, click Next. Specify the values shown in Figure 2-6. When ready, click Next.
Figure 2-6 Specify Inventory Directory and Credentials
Important:
Any warnings or errors reported during database installation (especially any missing prerequisties) must be resolved before proceeding. See Section 2.3.1, "Installing the Required Packages" and Appendix A, "Troubleshooting" for information about required components.If all dependencies are met, you can click Next.
When installation is almost complete, you are prompted to run two scripts, orainstRoot.sh and root.sh, as root. This is shown in Figure 2-7.
Run the two scripts indicated in Figure 2-7. They should be run in a terminal window as root. You will receive output similar to the following:
/u01/app/oraInventory/orainstRoot.sh Changing permissions of /u01/app/oraInventory to 770. Changing groupname of /u01/app/oraInventory to oinstall. The execution of the script is complete Finished product-specific root actions.
The second script generates the following output:
/u01/app/oraInventory/orainstRoot.sh
Changing permissions of /u01/app/oraInventory to 770.
Changing groupname of /u01/app/oraInventory to oinstall.
The execution of the script is complete
/u01/app/oracle/product/11.1.0/db_1/root.sh
Running Oracle 11g root.sh script...
The following environment variables are set as:
ORACLE_OWNER= oracle
ORACLE_HOME= /u01/app/oracle/product/11.1.0/db_1
Enter the full pathname of the local bin directory: [/usr/local/bin]:
Copying dbhome to /usr/local/bin ...
Copying oraenv to /usr/local/bin ...
Copying coraenv to /usr/local/bin ...
Creating /etc/oratab file...
Entries will be added to the /etc/oratab file as needed by
Database Configuration Assistant when a database is created
Finished running generic part of root.sh script.
Now product-specific root actions will be performed.
Finished product-specific root actions.
On completion of each script, return the dialog shown in Figure 2-7, and click OK. In the main installer screen, verify that the message "The installation of Oracle database 11g was successful" appears. Click Exit, and confirm by clicking Yes.
Create an /etc/init.d/oracledb script file (as root) to start and stop the Oracle database. It should contain the following:
#!/bin/bash## /etc/init.d/oracledb## chkconfig: 2345 95 10# description: Run-level Startup script for the Oracle Listener and # Instances. It relies on the information in /etc/oratabexport ORACLE_BASE=/u01/app/oracleexport ORACLE_HOME=/u01/app/oracle/product/11.1.0/db_1export ORACLE_OWNR=oracleexport PATH=$PATH:$ORACLE_HOME/binif [ ! -f $ORACLE_HOME/bin/dbstart -o ! -d $ORACLE_HOME ]then echo "Oracle startup: cannot start" exit 1ficase "$1" in start) # Oracle listener and instance startup echo -n "Starting Oracle: " su $ORACLE_OWNR -c "$ORACLE_HOME/bin/lsnrctl start" su $ORACLE_OWNR -c "$ORACLE_HOME/bin/dbstart $ORACLE_HOME" touch /var/lock/oracle echo "OK" ;; stop) # Oracle listener and instance shutdown echo -n "Shutdown Oracle: " su $ORACLE_OWNR -c "$ORACLE_HOME/bin/lsnrctl stop" su $ORACLE_OWNR -c "$ORACLE_HOME/bin/dbshut $ORACLE_HOME" rm -f /var/lock/oracle echo "OK" ;; reload|restart) $0 stop $0 start ;; *) echo "Usage: `basename $0` start|stop|restart|reload" exit 1esacexit 0
A copy of this initialization script is available in the RUEI installation zip file (in /root/RUEI/45). Note that you will need to modify the settings for the ORACLE_BASE and ORACLE_HOME environment variables shown above if you selected a different installation directory for the Oracle database.
Make the script file executable and use it to start the Oracle database with the following commands:
chmod +x /etc/init.d/oracledb/sbin/chkconfig --add oracledbservice oracledb start
This section describes the installation and configuration of the Apache Web server, and the components that use it.
Ensure that the Web server starts automatically by issuing the following command:
/sbin/chkconfig httpd on
Edit the /etc/sysconfig/httpd file to include the following lines:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/instantclient/libexport TNS_ADMIN=/home/moniforce
Add or edit the following settings in the /etc/php.ini file:
session.gc_maxlifetime = 14400 memory_limit = 96M upload_max_filesize = 128M post_max_size = 128M
Explicitly set the required time zone in the [Date] section. For example:
[Date] ; Defines the default timezone used by the date functions date.timezone = "Europe/Amsterdam"
Important:
The time zone specified here determines the time displayed in the Reporter interface. Therefore, ensure that the time zone is set according to your local needs. The time zone specified here must to be the same as the time zone specified in the operating system. If the time zone was correctly set during Linux installation, you can obtain the time zone information from theZONE variable in /etc/sysconfig/clock. A complete list of available time zones can be found at http://us3.php.net/manual/en/timezones.php.Insert CD #3 and mount it. For example, mount /dev/hdc /mnt/cdrom. Then issue the following commands:
cd /media/cdrom/Server rpm -Uhv php-mbstring-5.1.6-*
The GD module is required for changing the company logo in the RUEI dashboard. Install the RPM from CD #3 using the following commands:
cd /media/cdrom/Server rpm -Uhv php-gd-5.1.6-*
In order to install Microsoft Excel export support in RUEI, you will need to install the PEAR package manager.
Prepare the PEAR environment by setting the following environment variables:
export ORACLE_HOME=/u01/app/oracle/product/11.1.0/db_1export PATH=$PATH:/u01/app/product/11.1.0/db_1/bin
Install the RPM from CD #4 using the following commands:
cd /media/cdrom/Server rpm -Uhv php-pear-1.4.9-*.rpm
Download the PEAR::Spreadsheet_Excel_Writer package from http://pear.php.net/package/Spreadsheet_Excel_Writer, and the PEAR::OLE package from http://pear.php.net/package/OLE. Note that Spreadsheet Excel Writer version 0.9.1 and OLE version 0.6 are required.
Install the modules by issuing the following commands as the root user:
pear install OLE-0.6.0.tgz install ok: channel://pear.php.net/OLE-0.6.0 pear install Spreadsheet_Excel_Writer-0.9.1.tgz install ok: channel://pear.php.net/Spreadsheet_Excel_Writer-0.9.1
Note that any warnings received during installation of the above modules can be safely ignored as long as the last report line reads "install OK".
Verify that the modules are installed correctly (directories /usr/share/pear/Spreadsheet and /usr/share/pear/OLE should be present).
Copy the downloaded RUEI zip file to /root directory on the server, and unzip it. Use the following commands:
cd /root
unzip package_name.zip
The following directories are created which contain the software needed to complete the RUEI installation:
/root/RUEI/45
/root/RUEI/ZendOptimizer
/root/RUEI/IC
/root/RUEI/PHP
Install the Oracle database Instant Client and SQLplus extension with the following commands as the root user:
cd /root/RUEI/ICrpm -Uhv oracle-instantclient-basic-11.1.0.*.rpmrpm -Uhv oracle-instantclient-sqlplus-11.1.0.*.rpm
Create symlinks for the Oracle database Instant Client using the following commands:
mkdir -p /usr/local/instantclientln -sv /usr/lib/oracle/11.1.0.1/client64/lib /usr/local/instantclientln -sv /usr/lib/oracle/11.1.0.1/client64/bin /usr/local/instantclient
Install the php-oci8 module (this is part of the RUEI distribution set) using the following commands:
cd /root/RUEI/PHP rpm -Uhv php-oci8-5.1.6-*
Go to the directory containing the Zend Optimizer code, unpack the tar file, and run the Zend optimizer code installer. Read the user license agreement. You cannot proceed until you have accepted the license agreement. Accept all default settings, and allow the installer to restart the Apache Web server. Issue the following commands:
cd /root/RUEI/ZendOptimizertar zxvf ZendOptimizer-3.3.3-linux-glibc23-x86_64.tar.gzcd ZendOptimizer-3.3.3-linux-glibc23-x86_64./install
Add the following lines to the /home/oracle/.bash_profile for the environment variable for the RUEI installer:
ORAENV_ASK=NO . oraenv
Run the prepare_uxinsight_db.sh script as root. It is located in the /root/RUEI/45 directory. You are prompted to set ORACLE_HOME. In this guide, this is assumed to be /u01/app/oracle/product/11.1.0/db_1. Make the script executable and run it using the following commands:
chmod +x prepare_uxinsight_db.sh ./prepare_uxinsight_db.sh
Note:
Theprepare_uxinsight_db.sh script can be run with the --clean option to remove the current database and install a new one. Note that the ux-core RPM also needs to be re-installed with the --force option when this option has been used.Password credentials for connecting to the database are stored in an Oracle wallet. The script will prompt you for the RUEI database user password and the password used to protect the wallet. Once the wallet password is stored in a secure location, the RUEI application can login to the database automatically. The default location of the wallet files are cwallet.sso and ewallet.p12 in the /home/moniforce directory.
Add the following lines to the /etc/profile file to make the Oracle database known to RUEI:
ORACLE_SID=uxexport ORACLE_SID
Go to the directory which holds the RUEI software, and install the RUEI RPM packages with the following commands:
cd /root/RUEI/45rpm -Uhv ux-*
Restart the Apache Web server using the following command:
service httpd restart
If installation of the above RPMs fail, change to the moniforce user and obtain an SQL*Plus prompt with the following commands:
su - moniforce sqlplus /@uxinsight
You should receive the SQL*Plus command line without being prompted for a password. This indicates that the Oracle wallet authentication was successful. Do not proceed further with the installation and configuration procedure until this step is successfully performed. If you encounter problems, please refer to Appendix A, "Troubleshooting".
Change to the moniforce user and set the RUEI Administration password to enable logging on to the RUEI interface with the following commands:
su - moniforce set-admin-password
You are prompted to enter and confirm the password.
Note:
When defining the Administrator password, bear the following in mind:The password must have at least eight characters, and contain at least one non-alphanumeric character (such as $, @, &, and !).
The password must be changed within seven days.
The password is case sensitive.
If necessary, reset the database quota with the following commands:
su - moniforce set-tablespace-quota
By default, the maximum size of the RUEI database (ux) is set is to 200 GB. If additional disk space is available, you can increase the maximum size limit. When this limit is reached, the oldest data is removed to make room for the most recent data.
Make the monitoring network interface up status permanent (after a reboot) by setting the ONBOOT parameter of the capturing interfaces to yes in the interface configuration files. The network interfaces configuration can be found in /etc/sysconfig/networking/devices/ifcfg-ethX (where X represents the necessary network interface). Alternatively, use the graphical utility system-config-network to set the appropriate interfaces to "activate device when computer starts".
RUEI assumes a working local MTA for sending PDF reports and E-mail alerts. By default, Enterprise Linux uses the Sendmail MTA. By default, Sendmail will deliver the E-mail directly to the destination MTA. If this behavior is not according to your needs or policies, sending mail via a SmartHost (relay) might be an alternative. To configure a SmartHost in Sendmail, do the following:
Install the sendmail-cf RPM package from CD #2 by mounting the CD. For example, mount /dev/cdrom /media/cdrom.
Issue the following commands:
cd /media/cdrom/Server rpm -Uhv sendmail-cf-8.13.8-2.el5.x86_64.rpm
Find the line which contains the Smart Host setting in /etc/mail/sendmail.mc. Modify the SMART_HOST setting to your needs. For example:
define('SMART_HOST', 'my.example')dnl
Generate the new configuration into a new sendmail.cf by executing the following command:
make -C /etc/mail
Restart sendmail. For example:
/etc/init.d/sendmail restart
For SNMP trap support, additional RPMs need to be installed from disk #2. Use the following command:
rpm -Uhv lm_sensors-2.10.0-*
From disk #4, use the following command:
rpm -Uhv net-snmp-utils-5.3.1-* net-snmp-5.3.1-*
You can download the RUEI MIB definition file through the Reporter interface. This definition file can be added to the SNMP manager. The procedure for downloading the MIB file is described in the Oracle Real User Experience Insight User Guide.
To have the browser automatically redirected to the correct RUEI path, create the file /var/www/html/index.html with the following content:
<head>
<meta http-equiv="REFRESH" content="0;URL=/ruei/">
</head>
A password-less SSH connection must be setup between the Moniforce user from the Reporter system to each Collector system. Do the following:
Logon to the Reporter server as root. Issue the following commands:
su - moniforcessh-keygen -P ""
Press Enter to accept the defaults.
Logon as root on each of the Collector systems. Issue the following commands:
su - moniforcecd ~/.sshssh root@Reporter cat /home/moniforce/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> authorized_keys
(you will need to specify the Reporter system root password)
chmod 600 authorized_keys
Check that it is now possible to execute a remote command (as moniforce user) on the Reporter system without using a password. For example:
Logon as root on the Reporter server.
Logon as moniforce user: su - moniforce.
Execute a remote pwd command: ssh Collector pwd.
Enter yes to the question "Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?".
The command should return /home/moniforce.
The above steps must be performed for each Collector!
Note:
If the connection between the Reporter and the Collector(s) has not been correctly configured, you will receive an authorization error when you try to register the remote Collector.On completion of the Initial Setup Wizard (described in Section 3.1, "Performing Initial RUEI Configuration"), you can verify you installation by selecting System > Maintenance > Environment check. This is fully described in the Oracle Real User Experience Insight User Guide.
If you are upgrading an existing RUEI 4.5.0 or 4.5.1 installation to release 4.5.2, you should follow the procedure described in this section. Note that the upgrade procedure takes approximately 45 minutes. During that time, network traffic will continue to be monitored However, there is a short interruption during the installation of the RPM packages, and a temporary loss of current session-related information. In addition, a backlog in processing may occur.
Upgrading a Reporter System
Do the following:
Logon onto the Reporter system as root, unzip the RUEI software file, and change to the directory containing the application files using the following commands:
unzip Vxxxx.zip
cd RUEI/45
Stop all RUEI processing by logging onto the RUEI Reporter system using the following commands:
su - moniforce project -stop wg exit
Run the ruei-upgrade-4.5.x-4.5.2.sh script as root. This script performs all prerequisite actions necessary for the upgrade. Use the following command:
chmod +x ruei-upgrade-4.5.x-4.5.2.sh ./ruei-upgrade-4.5.x-4.5.2.sh
Install the RUEI RPM packages with the following command:
rpm -Uhv ux-*
Turn on data processing by issuing the following commands:
su - moniforce project -start wg
At this point, processing of the backlog commences. The time required to do this depends on the system load, and the size of the backlog.
Note:
After upgrading, you should use the Reporter interface to review the defined SSL keys, and reactivate any that have deactivated during the upgrade procedure. This only applies to SSL keys with an activation passphase. This is fully explained in the Oracle Real User Experience Insight User Guide.Upgrading Collector-Only systems
Do the following:
Logon onto the Collector system as root, unzip the RUEI software file, and change to the directory containing the application files using the following commands:
unzip Vxxxx.zip
cd RUEI/45
Install the RUEI RPM packages with the following command:
rpm -Uhv ux-*
Footnote Legend
Footnote 1: This guide assumes an Oracle Enterprise Linux 5.2 installation (which has six CDs). Oracle Enterprise 5.0 and 5.1 has five CDs.