38 Configuring a Relational Direct Map Mapping
This chapter describes the various components that you must configure in order to use a relational direct map mapping.
This chapter includes the following sections:
For information on how to configure TopLink mappings options common to two or more mapping types, see Chapter 121, "Configuring a Mapping".
For information on how to create TopLink mappings, see Chapter 120, "Creating a Mapping".
Table 38-1 lists the configurable options for a relational direct map mapping.
38.1 Introduction to Relational Direct Map Mapping Configuration
Table 38-1 lists the configurable options for a relational direct map mapping.
Table 38-1 Configurable Options for Relational Direct Map Mapping
| Option | Oracle JDeveloper |
TopLink Workbench |
Java |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Target table (see Section 36.2, "Configuring Target Table") |
|||
|
Direct value field (see Section 38.2, "Configuring Direct Value Field") |
|||
|
Direct key field (see Section 38.3, "Configuring Direct Key Field") |
|||
|
Method or direct field access (see Section 121.6, "Configuring Method or Direct Field Accessing at the Mapping Level") |
|||
|
Read-only mapping (see Section 121.2, "Configuring Read-Only Mappings") |
|||
|
Batch reading (see Section 28.5, "Configuring Batch Reading") |
|||
|
Indirection (lazy loading) (see Section 121.3, "Configuring Indirection (Lazy Loading)") |
|||
|
Container policy (see Section 121.14, "Configuring Container Policy") |
|||
|
Mapping comments (see Section 121.8, "Configuring Mapping Comments") |
|||
|
Key converters (see Section 38.4, "Configuring Key Converters") |
|||
|
Value converters (see Section 38.5, "Configuring Value Converters") |
|||
|
Table and field references (see Section 28.7, "Configuring Table and Field References (Foreign and Target Foreign Keys)") |
Example 38-1 shows how to create a direct map mapping and add it to a descriptor using Java code.
Example 38-1 Direct Map Mapping
public void customize(ClassDescriptor descriptor) {
DirectMapMapping mapping = new DirectMapMapping();
// configure mapping
...
// add mapping to descriptor
descriptor.addMapping(mapping);
}
For more information, see the following:
For information on using JPA to configure direct map mappings, see "How to Use the @BasicMap Annotation" section of EclipseLink Developer's Guide at http://wiki.eclipse.org/Using_EclipseLink_JPA_Extensions_%28ELUG%29#How_to_Use_the_.40BasicMap_Annotation.
38.2 Configuring Direct Value Field
The direct value field in the reference table stores the primitive data value of the map value. If the value's object value and database value are different types, use a converter (see Section 38.5, "Configuring Value Converters").
38.2.1 How to Configure Direct Value Fields Using TopLink Workbench
-
Select the mapped attribute in the Navigator. Its properties appear in the Editor.
-
Click the General tab. The General tab appears.
Figure 38-1 General Tab, Direct Value Field
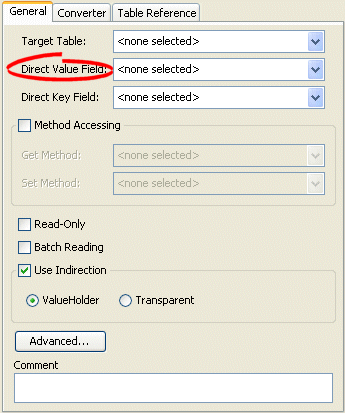
Description of "Figure 38-1 General Tab, Direct Value Field"
Use the Direct Value Field list to select the field from the Target Table table that contains the object of the direct map mapping.
38.2.2 How to Configure Direct Value Fields Using Java
Use the DirectMapMapping method setDirectFieldName to set the direct fields for your mapping.
For more information about the available methods for DirectMapMapping, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Java API Reference for Oracle TopLink.
38.3 Configuring Direct Key Field
The direct key field in the reference table stores the primitive data value of the map key. If the key's object value and database value are different types, use a converter (see Section 38.4, "Configuring Key Converters").
38.3.1 How to Configure Direct Key Field Using TopLink Workbench
To specify the direct key field in the reference table, use this procedure.
-
Select the mapped attribute in the Navigator. Its properties appear in the Editor.
-
Click the General tab. The General tab appears.
Figure 38-2 General Tab, Direct Key Field
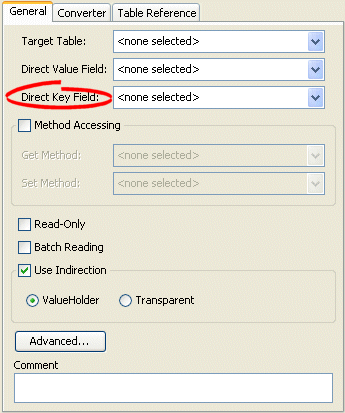
Description of "Figure 38-2 General Tab, Direct Key Field"
Use the Direct Key Field list to select the key from the Target Table table that contains the object of the direct map mapping.
38.3.2 How to Configure Direct Key Field Using Java
Use the DirectMapMapping method setDirectKeyFieldName to set the direct key field for your mapping.
For more information about the available methods for DirectMapMapping, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Java API Reference for Oracle TopLink.
38.4 Configuring Key Converters
If the key's object value and database value are different types, use a converter. TopLink supports the following key converters:
38.4.1 How to Configure Key Converters Using TopLink Workbench
Use this procedure to specify the converter for a direct map mapping key:
-
Select the mapped attribute in the Navigator. Its properties appear in the Editor.
-
Click the Converter tab. The Converter tab appears.
-
Click the Key Converter tab. The Key Converter tab appears.
Figure 38-3 Converter Tab, Key Converter Subtab
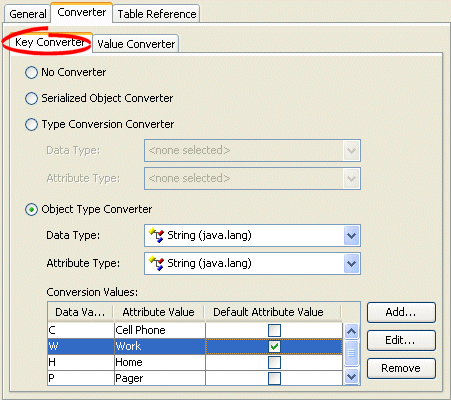
Description of "Figure 38-3 Converter Tab, Key Converter Subtab"
| Converter | Description |
|---|---|
| No Converter | Do not use a Key Converter for this mapping. |
| Serialized Object Converter | See Section 121.9, "Configuring a Serialized Object Converter". |
| Type Conversion Converter | See Section 121.10, "Configuring a Type Conversion Converter". |
| Object Type Converter | See Section 121.11, "Configuring an Object Type Converter". |
38.4.2 How to Configure Key Converters Using Java
You can configure whether or not to allow null values using the DirectMapMapping method setKeyConverter.
For more information about the available methods for DirectMapMapping, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Java API Reference for Oracle TopLink.
38.5 Configuring Value Converters
If the value's object value and database value are different types, use a converter. TopLink supports the following value converters:
38.5.1 How to Configure Value Converters Using TopLink Workbench
-
Select the mapped attribute in the Navigator. Its properties appear in the Editor.
-
Click the Converter tab. The Converter tab appears.
-
Click the Value Converter tab. The Value Converter tab appears.
Figure 38-4 Converter Tab, Value Converter Subtab
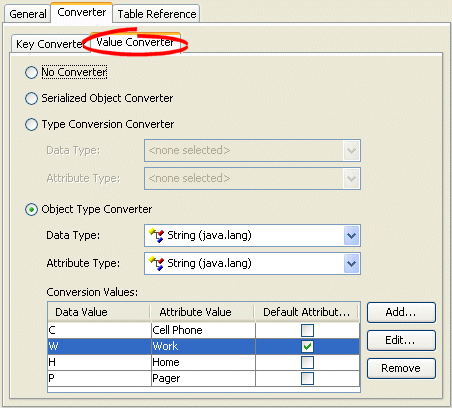
Description of "Figure 38-4 Converter Tab, Value Converter Subtab"
| Converter | Description |
|---|---|
| No Converter | Do not use a Value Converter for this mapping. |
| Serialized Object Converter | See Section 121.9, "Configuring a Serialized Object Converter". |
| Type Conversion Converter | See Section 121.10, "Configuring a Type Conversion Converter". |
| Object Type Converter | See Section 121.11, "Configuring an Object Type Converter". |