8 Server Migration
In this enterprise topology, you must configure server migration for the WLS_SOA1 and WLS_SOA2 managed servers. The WLS_SOA1 managed server is configured to restart on SOAHOST2 should a failure occur. The WLS_SOA2 managed server is configured to restart on SOAHOST1 should a failure occur. For this configuration, the WLS_SOA1 and WLS_SOA2 servers listen on specific floating IPs that are failed over by WLS Server Migration. Configuring server migration for the WLS_SOAn managed servers consists of the following steps:
-
Step 1: Setting Up a User and Tablespace for the Server Migration Leasing Table
-
Step 2: Creating a Multi-Data Source Using the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console
-
Step 5: Setting Environment and Superuser Privileges for the wlsifconfig.sh Script
-
Step 7: Testing the Server Migration
8.1 Setting Up a User and Tablespace for the Server Migration Leasing Table
The first step is to set up a user and tablespace for the server migration leasing table:
-
Create a tablespace called
leasing. For example, log on to SQL*Plus as the sysdba user and run the following command:SQL> create tablespace leasing logging datafile 'DB_HOME/oradata/orcl/leasing.dbf' size 32m autoextend on next 32m maxsize 2048m extent management local;
-
Create a user named
leasingand assign to it the leasing tablespace.SQL> create user leasing identified by welcome1; SQL> grant create table to leasing; SQL> grant create session to leasing; SQL> alter user leasing default tablespace leasing; SQL> alter user leasing quota unlimited on LEASING;
-
Create the leasing table using the
leasing.ddlscript.-
Copy the
leasing.ddlfile located in either theWL_HOME/server/db/oracle/817or theWL_HOME/server/db/oracle/920directory to your database node. -
Connect to the database as the
leasinguser. -
Run the
leasing.ddlscript in SQL*Plus.SQL> @copy_location/leasing.ddl;
-
8.2 Creating a Multi-Data Source Using the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console
The second step is to create a multi-data source for the leasing table from the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console:
You create a data source to each of the RAC database instances during the process of setting up the multi-data source, both for these data sources and the global leasing multi-data source. When you create a data source:
-
Make sure that this is a non-xa data source
-
The names of the multi-data sources are in the format of <MultiDS>-rac0, <MultiDS>-rac1, and so on
-
Use Oracle's Driver (Thin) Version 9.0.1, 9.2.0, 10, 11
-
Use Supports Global Transactions, One-Phase Commit, and specify a service name for your database
-
Target these data sources to the SOA cluster
-
Make sure the datasources' connection pool initial capacity is set to 0. To do this, select Services, JDBC, and then Datasources. In the Datasources screen, click the Datasource Name, then click the Connection Pool tab, and enter 0 in the Initial capacity field.
To create a multi-data source, complete these steps:
-
From Domain Structure window in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console, expand the Services node, then expand the JDBC node.
-
Click Multi Data Sources. The Summary of JDBC Multi Data Source page appears.
-
Click Lock and Edit.
-
Click New.
The Create a New JDBC Multi Data Source page appears.
-
Enter leasing as the Name
-
Enter jdbc/leasing as the JNDI name.
-
Select Failover as algorithm (default).
-
Click Next.
-
Select SOA_Cluster as the target.
-
Click Next.
-
Select non-XA driver (the default).
-
Click Next.
-
Click Create New Data Source.
-
Enter leasing-rac0 as name. Enter jdbc/leasing-rac0 as JNDI name. Enter oracle as the database type. For the driver type, enter Oracle Driver (Thin) for RAC server-Instance connection Version 10,11.
Note:
When creating the multi-datasources for the leasing table, enter names in the format of <MultiDS>-rac0, <MultiDS>-rac1, and so on. -
Click Next.
-
Deselect Supports Global Transactions.
-
Click Next.
-
Enter the service name, database name, host port, and password for your leasing schema.
-
Click Next.
-
Click Test Configuration and verify the connection works.
-
Click Next.
-
Target the data source to SOA_Cluster.
-
Select the data source and add it to the right screen.
-
Click Create a New Data Source for the second instance of your RAC database, target it to SOA_Cluster, repeating the steps for the second instance of your RAC database.
-
Add the second data source to your multi-data source.
-
Click Activate Changes.
8.3 Enabling Host Name Verification Certificates between SOAHOST1 and SOAHOST2 and the Administration Server
The third step is to create the appropriate certificates for host name verification between the Node Manager and the Administration Server. This procedure is described in Section 7.2, "Enabling Host Name Verification Certificates for Node Manager in SOAHOST1" and Section 7.4, "Enabling Host Name Verification Certificates for the Node Manager in SOAHOST2."
8.4 Editing the Node Manager's Properties File
The fourth step is to edit the Node Manager's properties file. This needs to be done for the node managers in both nodes where server migration is being configured:
Interface=eth0
NetMask=255.255.255.0
UseMACBroadcast=true
-
InterfaceThis property specifies the interface name for the floating IP (for example, eth0).
Note:
Do not specify the sub interface, such aseth0:1oreth0:2. This interface is to be used without the:0, or:1. The Node Manager's scripts traverse the different:Xenabled IPs to determine which to add or remove. For example, the valid values in Linux environments areeth0,eth1, or,eth2,eth3,ethn, depending on the number of interfaces configured. -
NetMaskThis property specifies the net mask for the interface for the floating IP. The net mask should the same as the net mask on the interface; 255.255.255.0 is used as an example in this document.
-
UseMACBroadcastThis property specifies whether or not to use a node's MAC address when sending ARP packets, that is, whether or not to use the -b flag in the
arpingcommand.
Verify in Node Manager's output (shell where Node Manager is started) that these properties are being used, or problems may arise during migration. You should see something like this in the Node Manager's output:
... StateCheckInterval=500 Interface=eth0 NetMask=255.255.255.0 ...
Note:
The steps below are not required if the server properties (start properties) have been properly set and the Node Manager can start the servers remotely.-
Set the following property in the
nodemanager.propertiesfile.-
StartScriptEnabledSet this property to
true. This is required for the shiphome to enable the Node Manager to start the managed servers.
-
-
Start the Node Manager on Node 1 and Node 2 by running the
startNodeManager.shscript located in theWL_HOME/server/bindirectory.
Note:
When running Node Manager from a shared storage installation, multiple nodes are started using the samenodemanager.properties file. However, each node may require different NetMask or Interface properties. In this case, specify individual parameters on a per-node basis using environment variables. For example, to use a different interface (eth3) in SOAHOSTn, use the Interface environment variable as follows: SOAHOSTn> export JAVA_OPTIONS=-DInterface=eth3 and start Node Manager after the variable has been set in the shell.8.5 Setting Environment and Superuser Privileges for the wlsifconfig.sh Script
The fifth step is to set environment and superuser privileges for the wlsifconfig.sh script:
-
Ensure that your PATH environment variable includes these files:
-
Grant sudo configuration for the
wlsifconfig.sh script.-
Configure sudo to work without a password prompt.
-
For security reasons, sudo should be restricted to the subset of commands required to run the
wlsifconfig.shscript. For example, to set the environment and superuser privileges for thewlsifconfig.shscript, complete these steps:-
Grant sudo privilege to the WebLogic user ('oracle') with no password restriction, and grant execute privilege on the /sbin/ifconfig and /sbin/arping binaries.
-
Make sure the script is executable by the WebLogic user ('oracle'). The following is an example of an entry inside /etc/sudoers granting sudo execution privilege for
oracleand also overifconfigandarping:oracle ALL=NOPASSWD: /sbin/ifconfig,/sbin/arping
-
Note:
Ask the system administrator for the sudo and system rights as appropriate to this step. -
8.6 Configuring Server Migration Targets
The sixth step is to configure server migration targets. Configuring Cluster Migration sets the DataSourceForAutomaticMigration property to true. Follow the steps below to configure cluster migration in a migration in a cluster:
-
Log into the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console (
http://<host>:<adminPort>/console. Typically,adminPortis 7001 by default). -
In the Domain Structure window, expand Environment and select Clusters. The Summary of Clusters page appears.
-
Click the cluster for which you want to configure migration (SOA_Cluster) in the Name column of the table.
-
Click the Migration tab.
-
Click Lock and Edit.
-
In the Available field, select the machine to which to allow migration and click the right arrow. In this case, select SOAHOST1 and SOAHOST2.
-
Select the data source to be used for automatic migration. In this case select the leasing data source.
-
Click Save.
-
Click Activate Changes.
-
Set the Candidate Machines for Server Migration. You must perform this task for all of the managed servers as follows:
-
In Domain Structure window of the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console, expand Environment and select Servers.
-
Select the server for which you want to configure migration.
-
Click the Migration tab.
-
In the Available field, located in the Migration Configuration section, select the machines to which to allow migration and click the right arrow. For WLS_SOA1, select SOAHOST2. For WLS_SOA2, select SOAHOST1.
-
Select Automatic Server Migration Enabled. This enables the Node Manager to start a failed server on the target node automatically.
-
Click Save.
-
Click Activate Changes.
-
Restart the Administration Server and the servers for which server migration has been configured.
Tip:
Click Customize this table in the Summary of Servers page, move Current Machine from the Available Window to the Chosen window to view the machine on which the server is running. This will be different from the configuration if the server gets migrated automatically. -
8.7 Testing the Server Migration
The seventh and final step is to test the server migration. To verify that Server Migration is working properly, follow these steps:
From Node 1:
-
Stop the WLS_SOA1 managed server.
To do this, run this command:
SOAHOST1> kill -9 <pid>
pid specifies the process ID of the managed server. You can identify the pid in the node by running this command:
SOAHOST1> ps -ef | grep WLS_SOA1 -
Watch the Node Manager console: you should see a message indicating that WLS_SOA1's floating IP has been disabled.
-
Wait for the Node Manager to try a second restart of WLS_SOA1. Node Manager waits for a fence period of 30 seconds before trying this restart.
-
Once Node Manager restarts the server, stop it again. Now Node Manager should log a message indicating that the server will not be restarted again locally.
From Node2:
-
Watch the local Node Manager console. After 30 seconds since the last try to restart WLS_SOA1on Node 1, Node Manager on Node 2 should prompt that the floating IP for WLS_SOA1 is being brought up and that the server is being restarted in this node.
-
Access the soa-infra console in the same IP.
Verification From the Administration Console
Migration can also be verified in the Administration Console:
-
Log into the Administration Console.
-
Click on Domain on the left console.
-
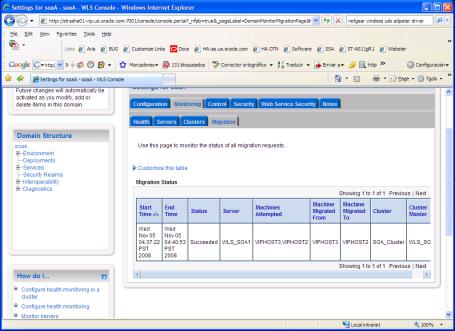
Click the Monitoring tab and then the Migration subtab.
The Migration Status table provides information on the status of the migration.
Figure 8-1 Migration Status Screen in the Administration Console
Description of "Figure 8-1 Migration Status Screen in the Administration Console"