33 Getting Started with Binding Components
This chapter provides a high-level overview of supported binding component types and technologies that you can integrate in a SOA composite application. This chapter also provides references to documentation that more fully describes these technologies.
This chapter includes the following sections:
33.1 Introduction to Binding Components
Binding components establish the connection between a SOA composite application and the external world. There are two types of binding components:
-
Services
Provide the outside world with an entry point to the SOA composite application. The WSDL file of the service advertises its capabilities to external applications. These capabilities are used for contacting the SOA composite application components. The binding connectivity of the service describes the protocols that can communicate with the service, for example, SOAP/HTTP or a JCA adapter.
-
References
Enable messages to be sent from the SOA composite application to external services in the outside world.
Figure 33-1 shows a SOA composite application in which a service (Service1) in the Exposed Services swimlane provides the entry point to the composite and a reference (WriteFile) in the External References swimlane enables messages to be sent to an external service in the outside world.
Figure 33-1 Service and Reference Binding Components
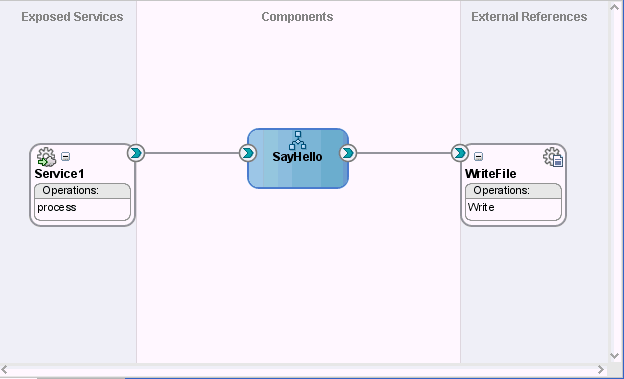
Description of "Figure 33-1 Service and Reference Binding Components"
Binding components enable you to integrate the following types of technologies with SOA composite applications:
-
Web services
-
JCA adapters
-
Oracle Business Activity Monitoring (BAM)
-
Oracle B2B
-
ADF-BC services
-
EJB services
-
Direct binding services
These technologies are described in the following sections.
33.1.1 Web Services
This service enables you to integrate with a standards-based web service using SOAP over HTTP. Web services are described in the WSDL file.
Dragging a web service into a swimlane of the SOA Composite Editor invokes the Create Web Service dialog for specifying configuration properties.
For more information, see Section 2.3.2, "How to Add a WSDL for a Web Service."
33.1.2 JCA Adapters
JCA adapters enable you to integrate services and references with the following technologies:
-
Databases
-
File systems
-
FTP servers
-
Message systems such as Advanced Queueing (AQ) and Java Messaging Systems (JMS)
-
IBM WebSphere MQ
-
Oracle E-Business Suite
-
TCP/IP sockets
-
Third-party adapters (SAP, PeopleSoft, and others)
Dragging a JCA adapter into a swimlane of the SOA Composite Editor invokes the Adapter Configuration Wizard for specifying configuration properties.
33.1.2.1 AQ Adapter
The AQ adapter enables you to interact with a single consumer or multiconsumer queue.
Oracle Streams AQ provides a flexible mechanism for bidirectional, asynchronous communication between participating applications. Advanced queues are an Oracle database feature, and are therefore scalable and reliable. Multiple queues can also service a single application, partitioning messages in a variety of ways and providing another level of scalability through load balancing.
For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Technology Adapters.
33.1.2.2 Database Adapter
The database adapter enables a BPEL process to communicate with Oracle databases or third-party databases through JDBC.
For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Technology Adapters.
33.1.2.3 File Adapter
The file adapter enables a BPEL process or Oracle Mediator to exchange (read and write) files on local file systems. The file contents can be in both XML and non-XML data formats.
For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Technology Adapters.
33.1.2.4 FTP Adapter
The FTP adapter enables a BPEL process or Oracle Mediator to exchange (read and write) files on remote file systems through use of the file transfer protocol (FTP). The file contents can be in both XML and non-XML data formats.
For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Technology Adapters.
33.1.2.5 JMS Adapter
The JMS adapter enables an Oracle BPEL process or Oracle Mediator to interact with a Java Messaging System (JMS).
The JMS architecture uses one client interface to many messaging servers. The JMS model has two messaging domains, point-to-point and publish-subscribe. In the point-to-point domain, messages are exchanged through a queue and each message is delivered to only one receiver. In the publish-subscribe model, messages are sent to a topic and can be read by many subscribed clients.
For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Technology Adapters.
33.1.2.6 MQ Adapter
The MQ adapter provides message exchange capabilities between BPEL processes and Oracle Mediator and the WebSphere MQ queuing systems.
Messaging and Queuing Series (MQ Series) is a set of products and standards developed by IBM. MQ Series provides a queuing infrastructure that provides guaranteed message delivery, security, and priority-based messaging.
For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Technology Adapters.
33.1.2.7 Oracle Applications Adapter
The Oracle applications adapter provides connectivity to Oracle Applications. The adapter supports all modules of Oracle Applications in Release 12 and Release 11i, including selecting custom integration interface types based on the version of Oracle E-Business Suite.
For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Adapter for Oracle Applications User's Guide.
33.1.2.8 Socket Adapter
The socket adapter enables you to create a client or a server socket, and establish a connection. This adapter enables you to model standard or nonstandard protocols for communication over TCP/IP sockets. The transported data can be text or binary in format.
For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Technology Adapters.
33.1.2.9 Third Party Adapter
The third party adapter enables you to integrate third-party adapters such as PeopleSoft, SAP, and others into a SOA composite application. These third-party adapters produce artifacts (WSDLs and JCA files) that can configure a JCA adapter.
For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Technology Adapters.
33.1.3 Oracle BAM
The Oracle BAM adapter enables you to integrate Java EE applications with Oracle BAM Server to send data.
Dragging an Oracle BAM adapter into a swimlane of the SOA Composite Editor invokes the Adapter Configuration Wizard for specifying configuration properties.
For more information, see Part X, "Using Oracle Business Activity Monitoring" and Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle Business Activity Monitoring.
33.1.4 Oracle B2B
The Oracle B2B service enables you to browse B2B metadata in the MDS repository and select document definitions.
Oracle B2B is an e-commerce gateway that enables the secure and reliable exchange of transactions between an organization and its external trading partners. Oracle B2B and Oracle SOA Suite are designed for e-commerce business processes that require process orchestration, error mitigation, and data translation and transformation within an infrastructure that addresses the issues of security, compliance, visibility, and management.
Dragging Oracle B2B into a swimlane of the SOA Composite Editor invokes the B2B Configuration Wizard for specifying configuration properties.
For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle B2B.
33.1.5 ADF-BC Services
The ADF-BC service enables you to integrate Oracle Application Development Framework (ADF) applications using service data objects (SDOs) with SOA composite applications.
Dragging an ADF-BC Service into a swimlane of the SOA Composite Editor invokes the Create ADF-BC Service dialog for specifying configuration properties.
For more information about ADF, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework, Oracle Fusion Middleware Web User Interface Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework, and Section 6.2, "Delegating XML Data Operations to Data Provider Services."
33.1.6 EJB Services
The EJB service enables Enterprise JavaBeans and SOA composite applications to interact by passing service data object (SDO) parameters.
SDOs enable you to modify business data regardless of how it is physically accessed. Knowledge is not required about how to access a particular back-end data source to use SDO in a SOA composite application. Consequently, you can use static or dynamic programming styles and obtain connected and disconnected access.
Enterprise JavaBeans are server-side domain objects that fit into a standard component-based architecture for building enterprise applications with Java. These objects become distributed, transactional, and secure components.
Dragging an EJB service into a swimlane of the SOA Composite Editor invokes the Create EJB Service dialog for specifying configuration properties.
For more information, see Chapter 34, "Using Service Data Objects and Enterprise JavaBeans."
33.1.7 Direct Binding Services
The direct binding service uses the Direct Binding API to invoke a SOA composite application and exchange messages over a remote method invocation (RMI). This option supports the propagation of both identities and transactions across JVMs and uses the T3 optimized path. Both synchronous and asynchronous invocation patterns are supported.
Dragging a direct binding service into the Exposed Services swimlane of the SOA Composite Editor invokes the Create Direct Binding Service dialog for specifying configuration properties.
Note:
This service is supported only in the inbound direction (Exposed Services swimlane) for this release (that is, invocation of a SOA composite application).For more information, see Chapter 46, "Using the Direct Binding Invocation API."
For information about the Direct Binding API, visit the following URL:
33.2 Introduction to Integrating a Binding Component in a SOA Composite Application
You integrate a binding component with a SOA composite application by dragging it from the Component Palette.
33.2.1 How to Integrate a Binding Component in a SOA Composite Application
-
From the Service Adapters section of the Component Palette, drag a binding component to the appropriate swimlane. The swimlane in which to drag the component is based on the action you want to perform.
-
If you want to provide the outside world with an entry point to the SOA composite application, drag the binding component to the Exposed Services swimlane.
-
If you want to enable messages to be sent from the SOA composite application to external services in the outside world, drag the binding component to the External References swimlane.
Figure 33-2 shows a web service being dragged into the composite. This action invokes a dialog for specifying various configuration properties.
-
Figure 33-2 Integration of a Web Service Binding Component into a Composite
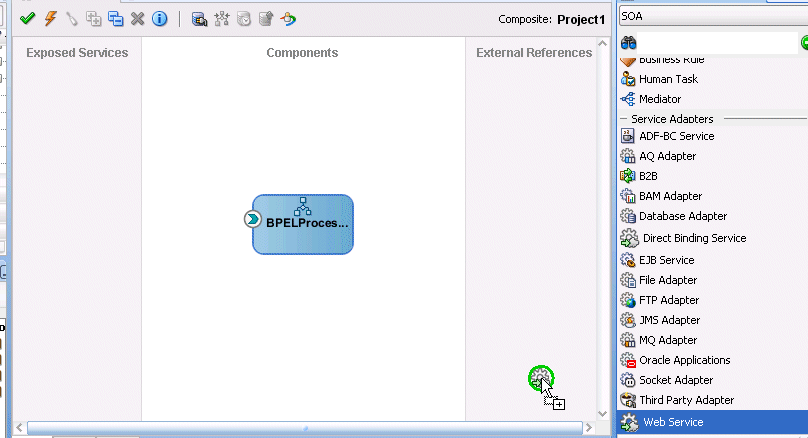
Description of "Figure 33-2 Integration of a Web Service Binding Component into a Composite"
For more information on adding binding components, see Section 2.3, "Adding Service Binding Components" and Section 2.4, "Adding Reference Binding Components."