11g Release 1 (11.1.1.5.0)
Part Number E20433-01
Contents
Previous
Next
|
Oracle® Fusion
Applications Customer Data Management Implementation Guide 11g Release 1 (11.1.1.5.0) Part Number E20433-01 |
Contents |
Previous |
Next |
This chapter contains the following:
Define Data Quality: Explained
Manage Matching Configurations
Manage Cleansing Configurations
Defining data quality involves defining and managing lookup choices and configurations used in data matching, cleansing, and matching index synchronization.
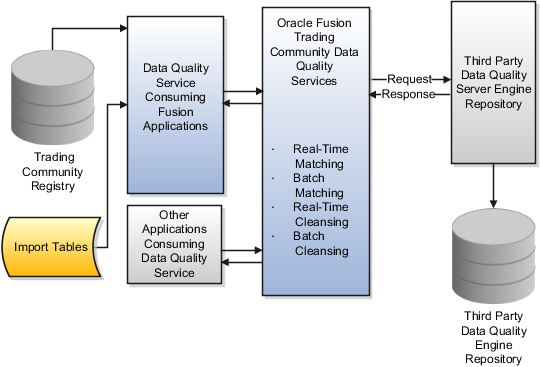
The Oracle Fusion Trading Community Data Quality services are designed to cater to all Oracle Fusion applications that use the trading community registry.
This figure illustrates the data quality management architecture. The data quality services receive matching or cleansing requests, such as duplicate prevention or address validation, from a variety of consuming applications, such as Oracle Fusion Sales and Oracle Fusion Trading Community Hub, and then internally invoke the appropriate third party services based either on a default configuration or a specific configuration passed to the services.
Review and define lookup values that provide choices for data matching and cleansing, such as address fields, quality error messages, and match tolerances.
Perform the configurations required to enable data quality processes such as data quality matching and cleansing operations.
You can enable data quality processes such as matching and address cleansing for real-time or batch matching and cleansing, and as part of the data import process.
Real-time matching can prevent individual entry of duplicate trading community entities, such as organization, person, or location, into the trading community registry. Batch matching leads to identification of duplicates entries in the trading community registry.
As part of defining and managing data quality configurations, you search, review, and edit seeded matching and cleansing configurations for real-time and batch matching and cleansing of trading community entities.
Define, review, and update the data quality server configurations to integrate with the embedded data quality engine.
Next, associate the server name with the matching and cleansing configurations to perform duplicate prevention, batch duplicate identification, and real-time and batch data cleansing.
Review and update matching index synchronization options, to synchronize Oracle Fusion Trading Community Hub registry data with the data quality engine repository, such as system and identity tables. View the latest synchronization results, evaluate errors, and reset for continued processing after resolving error conditions.
Server configurations are predefined configurations for third-party data quality servers.
You can search, review, and edit server configurations. Although you can edit the configuration name, server address, server port, and values of some of the configuration parameters, you cannot add or delete a server configuration parameter.
There are four predefined server configurations:
Real-Time and Batch Basic Match Server
Real-Time Cleanse Server
Batch Cleanse Server
Advanced Batch Match Server
Used for basic real-time duplicate prevention and batch data matching and duplicate identification. This configuration requires you to synchronize the Oracle Fusion Trading Community Hub registry data with the third party data quality engine repository periodically to ensure appropriate matching indexes are updated continuously.
Used for real-time data cleansing operations that happen at touch point applications, such as Oracle Fusion Sales and Oracle Fusion Customer Center, and so do not need synchronization.
Used for batch cleansing operations during which records in a batch are sent to the data quality server for cleansing one at a time, and the data quality engine returns the cleansed record to the registry likewise, one at a time, thus completing the loop.
Used for advanced batch matching that is done to find duplicates amongst a group of records before uploading them to the Oracle Fusion Trading Community Hub registry. For example, an acquiring company may do an advanced batch match of the legacy data of the acquired company before uploading the data to the registry. In such a case, data is uploaded to the repository of the data quality engine directly for duplication identification and after the duplication identification processing it is imported to the Oracle Fusion Trading Community Hub registry.
Matching configurations are predefined configurations used for real-time and batch matching of party entities with the intention of preventing and identifying duplicate entries in the trading community registry.
Real-time and batch matching are available for the following trading community entities:
Organization
Person
Location
There are six predefined matching configurations, three each for real-time and batch matching. The following are the predefined real-time matching configurations:
Real Time Location Duplicate Prevention
Real Time Organization Duplicate Prevention
Real Time Person Duplicate Prevention
The following are the predefined batch matching configurations:
Batch Location Basic Duplicate Identification
Batch Organization Basic Duplicate Identification
Batch Person Basic Duplicate Identification
You can search, review, and edit these seeded matching configurations. While you cannot add or delete a configuration parameter, you can change configuration name and update the parameter values to suite your requirements.
These configurations include both Oracle Fusion Trading Community Hub parameters and the parameters of the embedded data quality engine. While some of the parameters, such as MatchTolerance, are single valued, others, such as Manage Search Definition, are multi-valued.
Real-time matching prevents individual entry of duplicate trading community entities, such as organization, person, or location, through calling touch point applications, such as Oracle Fusion Sales and Oracle Fusion Customer Center into the trading community registry.
Real-time matching finds all possible duplicate records that may exist in the registry for an entered record, and assigns a match score to each potential duplicate identified. Based on the match score returned by the service and the threshold settings in the configuration, the calling application can provide the option to either select an existing duplicate record or continue to create a new record.
Batch matching leads to the identification of duplicate entries in the trading community registry, between trading community registry and sets of data, such as import batches, or within sets of data to resolve them by merging or linking.
While real-time matching provides duplicate prevention for only one record and returns potential matches for the record being entered, the batch matching service takes a set of records of the same type, such as person, organizations, or locations and identifies all possible matches within these sets of records. The duplicate data is presented in sets of possible matches with 'a score associated with each individual record in the set.
Real-time duplicate prevention enables you to prevent the individual entry of duplicate trading community entities, such as organization, person, or location, in the trading community registry through Oracle Fusion Trading Community Data Quality matching services consuming applications, such as Oracle Fusion Customer Center.
Real-time duplicate prevention comprises the following components:
Real-Time Matching Service
Data quality service consuming applications
Matching configurations
Server configurations
This figure shows the real-time duplicate prevention components in action.
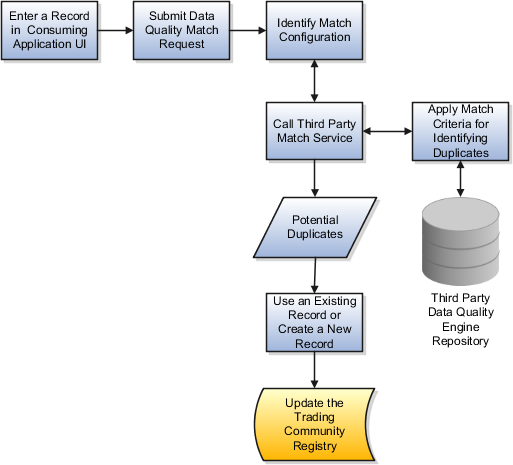
During the data entry process, the Real-Time Matching Service finds all possible duplicate records that may exist in the trading community registry for an entered record, and assigns a match score to each potential duplicate identified.
Real-time duplicate prevention finds use in data quality service consuming applications such as Oracle Fusion Receivables and Oracle Fusion Customer Center. When users try to enter a new person, organization, or location record through their UI into the Oracle Fusion trading community registry, the service finds all possible duplicate records that may exist in the registry for an entered record, and assigns a match score to each potential duplicate identified. Based on the match score returned by the service and the threshold settings in the configuration, the calling application can provide the option to either select an existing duplicate record or continue to create a new record.
Matching configurations are predefined configurations used for real-time and batch matching of party entities with a view to preventing and identifying duplicate entries in the trading community registry. Oracle Fusion Trading Community Data Quality has three predefined real-time matching configurations:
Real Time Location Duplicate Prevention
Real Time Organization Duplicate Prevention
Real Time Person Duplicate Prevention
You can search, review, and edit these seeded matching configurations. While you cannot add or delete a configuration parameter, you can change configuration name and update the parameter values to suite your requirements.
Real-time duplicate prevention makes use of the Real-Time and Batch Basic Match Server.
Matching server configurations provide the address and port of the third party server to which the match request should be sent for processing. Server configurations show all the parameters that can be set at either the matching configuration level or the server configuration level and provide the ability to modify the values of the server configuration level parameters. The parameters that are set at the server level are applicable to all the matching configurations.
Batch duplicate identification enables you to identify duplicate entries in the trading community registry, between trading community registry and sets of data, such as import batches, or within sets of data to resolve them by merging or linking.
Batch duplicate identification comprises the following components:
Batch Matching Service
Data quality service consuming applications
Matching configurations
Server configurations
This figure shows the batch duplicate identification components in action.

The Batch Matching Service is used for identification of potential duplicates for trading community entities such as persons, organizations, and locations.
The batch duplicate identification capability finds use in master data management applications such as Oracle Fusion Trading Community Hub, and other data quality service consuming applications that import data in batches. The capability takes a set of records of the same type, such as persons, organizations, or locations and identifies all possible matches within these sets of records. The duplicate data is presented in sets of possible matches with a score associated with each individual record in the set. These sets of potential duplicates can then be resolved by merging or linking.
Matching configurations are predefined configurations used for batch and real-time matching of party entities with a view to identifying and preventing duplicate entries in the trading community registry. Oracle Fusion Trading Community Data Quality has three predefined batch matching configurations:
Batch Location Basic Duplicate Identification
Batch Organization Basic Duplicate Identification
Batch Person Basic Duplicate Identification
You can search, review, and edit these seeded matching configurations. While you cannot add or delete a configuration parameter, you can change configuration name and update the parameter values to suite your requirements.
Batch duplicate prevention makes use of the Real-Time and Batch Basic Match Server.
Matching server configurations provide the address and port of the third party server to which the match request should be sent for processing. Server configurations show all the parameters that can be set at either the matching configuration level or the server configuration level and provide the ability to modify the values of the server configuration level parameters. The parameters that are set at the server level are applicable to all the matching configurations.
Matching configuration parameters are system-level parameters that control aspects of the Oracle Fusion Trading Community Data Quality matching services. The Oracle Fusion Trading Community Data Quality matching services read values from the ZCQ_CONFIG_PARAM_VALUES and ZCQ_SO_PARAM_VALUES tables.
Matching configurations are predefined configurations that include parameters from both Oracle Fusion applications and the integrated third-party data quality engine. Although you cannot add or delete a configuration parameter, you can change configuration name and update the parameter values to suite your requirements. The text describes only the generic Oracle Fusion Trading Community Data Quality parameters and their values. For third-party data quality engine specific parameters and their values, see relevant third-party documentation.
Real Time Location, Organization, and Person Duplicate Prevention Parameters
The following Oracle Fusion Trading Community Data Quality parameters control matching operations for preventing individual entry of duplicate trading community entities, such as location, organization, and person through calling touch point applications, such as Oracle Fusion Sales and Oracle Fusion Customer Center into the trading community registry.
MaxNumReturn
Parameter Value: 1 or more. Default Value: 10
Parameter Description: Controls the maximum number of matched records returned by the data quality real-time matching service.
ScoreThreshold
Parameter Value: Between 0 and 100. Default Value: 90
Parameter Description: Determines the score above which the matched records are returned by the matching service. Records equal to or greater than the score are considered as matches and the records with scores less than the threshold are rejected.
Batch Location, Organization, and Person Basic Duplicate Identification Parameters
The following Oracle Fusion Trading Community Data Quality parameters control matching operations for identification of duplicate entries in the trading community registry, between trading community registry and sets of data, such as import batches, or within sets of data to resolve them by merging or linking.
MatchMode
Parameter Value: Optimized or Exhaustive Default Value: Optimized
Parameter Description: Determines how the records in the batch are matched during batch matching process. Select Exhaustive to include in the batch match process even the records already showing up in previously matched groups. Select Optimized to skip such records.
NumChildJobs
Parameter Value: 1 or more. Default Value: 2
Parameter Description: Determines the number of child requests spawned for a batch matching request. The child requests are useful when there is a need to process data in parallel.
ScoreThreshold
Parameter Description: As described earlier.
Cleansing configurations are predefined configurations used for real-time and batch cleansing of the location entity.
There are two predefined cleansing configurations, one each for real-time and batch matching:
Real Time Data Quality Location Cleanse
Batch Data Quality Location Cleanse
You can search, review, and edit these seeded matching configurations. Although you cannot add or delete a configuration parameter, you can change configuration name and update the parameter values to suite your requirements.
These configurations include parameters from both Oracle Fusion applications and the integrated address cleansing engine. While some of the parameters are single valued others are multi-valued.
Real-time cleansing endows Oracle Fusion applications with an online, interactive service to cleanse, standardize, and validate addresses during the data entry process either through a UI or any other service creating address data into the Oracle Fusion Trading Community Hub registry.
Batch cleansing enables you to perform address cleansing, standardization, and validation for a subset or entirety of the location records in the registry, or as part of a data import process. It also enables you to ensure data accuracy of the Oracle Fusion Trading Community Hub registry. The need to cleanse the registry data arises owing to data decay over time and the need to resolve inherited issues from consolidated data in the registry. For example, postal codes and city boundaries change over time and require regular address cleansing to ensure that the addresses in the registry are correct, validated, and standardized at all times. Besides, historic incoming address data may have originated from multiple sources with each source system following different data storage formats and norms and the addresses might not have been cleansed during the import or consolidation process.
Real-time cleansing provides consuming applications an online, interactive service to cleanse, standardize, and validate addresses during the data entry process.
Real-time address cleansing comprises the following components:
Real-Time Cleansing Service
Data quality service consuming applications
Cleansing configurations
Server configurations
This figure shows the real-time address cleansing components in action.
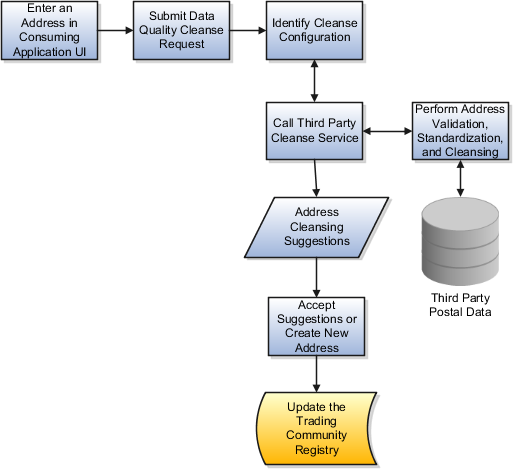
The Real-Time Cleansing Service perform validation, standardization, and cleansing of addresses during data entry into the trading community registry.
Real-time address cleansing finds use in data quality service consuming applications such as Oracle Sales and Oracle Fusion Customer Center. When a user tries to enter a new address record through the UI of these applications or through any other service creating address data into the Oracle Fusion trading community registry, the service validates the entered address data against country-specific postal service list, such as United States Postal Service. If there are any issues with the entered address data, the service returns a list of possibilities from which the consuming application user can select an appropriate one or continue to create a new address record.
Cleansing configurations are predefined configurations used for real-time and batch cleansing of the location entity.
Oracle Fusion Trading Community Data Quality has a predefined real-time cleansing configuration named Real Time Data Quality Location Cleanse. The real-time address cleansing service uses this cleansing configuration to derive the default country to be used to perform validation when address parsing fails to find a valid country within the address.
You can review and edit this predefined cleansing configuration. While you cannot add or delete a configuration parameter, you can change the configuration name and update the parameter values to suite your requirements.
Real-time cleansing makes use of the Real-Time Cleanse Server configuration.
Cleansing server configurations provide the address and port of the third party data quality server to which the cleanse request should be sent for processing. There are no server configurations level parameters for cleansing.
Batch cleansing enables you to perform address cleansing, standardization, and validation for a subset or entirety of the location records in the Oracle Fusion Trading Community Hub registry, or as part of a data import process.
Batch address cleansing comprises the following components:
Batch Cleansing Service
Data quality service consuming applications
Cleansing configurations
Server configurations
This figure shows the batch address cleansing components in action.
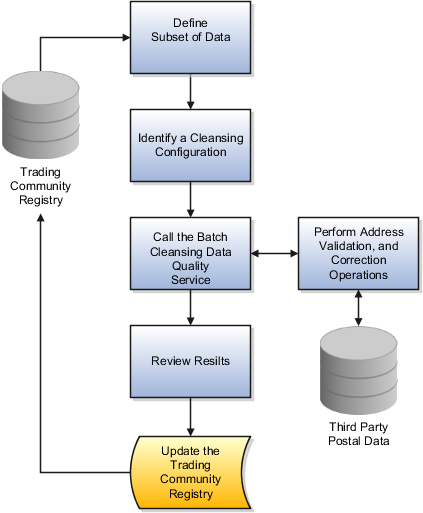
The Batch Cleansing Service performs validation, standardization, and cleansing of addresses to ensure data accuracy during the import of addresses in batches, to reduce decay and obsolescence of existing address data in the trading community registry , and to resolve inherited issues from consolidated data in the registry.
Batch address cleansing finds use in master data management applications such as Oracle Fusion Trading Community Hub, and other data quality service consuming applications that import data in batches. Unlike real-time cleansing that validates addresses one by one and runs in suggest cleansing mode, batch cleansing allows for validation and correction of multiple addresses through a single call.
Cleansing configurations are predefined configurations used for batch and real-time cleansing of the location entity.
Oracle Fusion Trading Community Data Quality has a predefined batch cleansing configuration named Batch Data Quality Location Cleanse. The batch address cleansing service uses this cleansing configuration to derive the default country to be used to perform validation when address parsing fails to find a valid country within the address.
You can review and edit this predefined cleansing configuration. While you cannot add or delete a configuration parameter, you can change the configuration name and update the parameter values to suite your requirements.
Batch address cleansing makes use of the Batch Data Quality Location Cleanse server configuration.
Cleansing server configurations provide the address and port of the third party data quality server to which the cleanse request should be sent for processing. There are no server configurations level parameters for cleansing.
Cleansing configuration parameters are system-level parameters that control aspects of the Oracle Fusion Trading Community Data Quality cleansing services. The Oracle Fusion Trading Community Data Quality cleansing services read values from the ZCQ_CONFIG_PARAM_VALUES and ZCQ_SO_PARAM_VALUES tables.
Cleansing configurations are predefined configurations that include parameters from both Oracle Fusion applications and the integrated third-party data quality engine. Although you cannot add or delete a configuration parameter, you can change configuration name and update the parameter values to suite your requirements. The text describes only the generic Oracle Fusion Trading Community Data Quality parameters and their values. For third-party data quality engine specific parameters and their values, see relevant third-party documentation.
Real Time Data Quality Location Cleanse Parameters
The following parameters control real-time data cleansing operations that happen at touch point applications, such as Oracle Fusion Sales and Oracle Fusion Customer Center.
RuntimeMapping
TRUE or FALSE TRUE
Determines if the real-time cleansing service should use the attribute mapping defined between Oracle Fusion Trading Community Data Quality attributes and the third-party data quality engine. If the value is set to FALSE, the data quality real-time service will pass through attributes as they are between Oracle Fusion Trading Community Data Quality and the third party cleansing engine.
Batch Data Quality Location Cleanse Parameters
The following parameters control address cleansing, standardization, and validation operations for a subset or entirety of the location records in the registry, or as part of a data import process.
AMCommitRate
1 or more 100
Controls the transaction batch size for the address cleansing process which in turn determines how often the cleansing results are committed. Set this value based on available system resources for optimum performance. If the value is too low, the data is committed often, which may cause slow performance. In contrast setting it to too high a value may require higher memory for processing.
NumChildJobs
1 or more 2
Determines the number of child requests spawned for a batch matching request. The child requests are useful when there is a need to process data in parallel.
Real-time duplicate prevention during data entry and batch duplicate identification of trading community entities in the Oracle Fusion Trading Community Hub registry and during the data import process require both initial indexing and index synchronization of the integrated third party data quality engine repository with the registry.
Periodic index synchronization of the third party data quality engine repository with the Oracle Fusion Trading Community Hub registry lets you account for the continual updates made to the registry.
Some of the entities that need to be synchronized to the matching engine repository are organization, person, and location. The synchronization should be done when these entities are created or updated.
However, no data synchronization is required for advanced batch match configuration and real-time and batch cleanse operations because of the following reasons:
Advanced configuration is used only for batch matching such as finding duplicates within a set of interface tables records before running a bulk import process to load the records in the registry.
Data synchronization is not needed for real-time address cleansing functions as the address is checked against the country specific postal address files and not against the existing address in the registry. Note that the postal reference files need to be updated periodically.
During the batch cleanse operation, records in a batch are sent to the data quality server for cleansing one at a time and the data quality engine returns the cleansed record to the registry likewise, one at a time, thus completing the loop.
This example demonstrates the index synchronization of the integrated third party data quality engine repository with the trading community registry. Index synchronization facilitates accounting for the changes made to the registry as part of creating new and updating existing organization, person, and location records since initial indexing. This example focuses on the index synchronization of person party records for the third-party data quality engine Informatica Identity Resolution (IIR).
Index synchronization for the Informatica Identity Resolution data quality engine involves the following tasks:
Scheduling the synchronization process: Schedule this task to run periodically to account for the continual updates to the Oracle Fusion Trading Community Hub registry. While running the synchronization process you can select the entities for which you want to synchronize updates and specify the date and time from which to synchronize the updates. A synchronization request performs index synchronization from the last synchronized date and time until the date and time it is submitted.
Starting Informatica Identity Resolution (IIR) Update Synchronizer: Administrators and integrators typically perform this task. Once started the synchronizer can be left running, for the life cycle of the Informatica Identity Resolution server, unless there is a need to bring it down as part of a maintenance window. However, whenever there is a loss of connectivity with the database Update Synchronizer stops functioning and needs to be manually restarted.
Note
Initial indexing and index synchronization are required only for performing matching operations aimed real-time duplicate prevention and batch duplicate identification. Real-time and batch cleanse operations do not require initial indexing and Index synchronization.
|
Field |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Country |
US |
|
Last Synchronized Time |
Select Date and Time: 3/23/11 9:30:15 AM |
cd <PROV.TOP>/InformaticaIR/bin
setfusionEnv.sh
./idsconc -a
Matching configurations are used for real-time and batch matching of party entities with a view to preventing and identifying duplicate entries in the trading community registry. The matching configuration includes the parameters that can be set at the matching configuration level and can be modified depending on matching strategy, data, and result requirements. Use the matching configuration to view or change the values of the matching configuration level parameters.
Matching server configurations provide the address and port of the third party server to which the match request should be sent for processing. Server configurations show all the parameters that can be set at either the matching configuration level or the server configuration level along with the parameter type (third party data quality engine or Oracle Fusion Trading Community Data Quality) and the cardinality of the parameter. The parameters that are set at the server level are applicable to all the matching configurations. Use the server configuration to view or change the values of the server configuration level parameters.
Cleansing configurations are used for real-time and batch cleansing of addresses during data entry and on a periodical basis to cleanse, standardize, and validate existing addresses to ensure data accuracy. The cleansing configuration includes the parameters that can be set at the cleansing configuration level and can be modified depending on cleansing strategy, data, and result requirements.
Cleansing server configurations provide the address and port of the third party data quality server to which the cleanse request should be sent for processing. There are no server configurations level parameters for cleansing.
Real-time duplicate prevention involves identification of all possible duplicate records that may exist in the trading community registry for an entered record. This enables prevention of individual entry of duplicate trading community entities, such as organization, person, or location, through calling touch point applications, such as Oracle Fusion Sales and Oracle Fusion Customer Center in the registry.
Duplicate identification of trading community entities is achieved by batch matching. The objective is to identify potential duplicate entities already existing in the trading community registry, and then resolve the duplicates by merging or linking.
The objective of basic duplicate identification is to resolve the duplicate entities in the Oracle Fusion Trading Community Hub registry by merging or linking.
Advanced duplicate identification is mainly done to find duplicates in a group of records before uploading them to the Oracle Fusion Trading Community Hub registry. For example, an acquiring company may do an advanced duplicate identification of the legacy data of the acquired company before uploading the data to the registry.
Real-time address cleansing is an online, interactive service to cleanse, standardize, and validate addresses during the data entry process.
Batch address cleansing enables you to cleanse, standardize, and validate addresses that are either existing in the Oracle Fusion Trading Community Hub registry or are being imported into it.