| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Autonomy Search Integration Sample Guide for Oracle WebLogic Portal 10g Release 3 (10.3.2) Part Number E15073-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Autonomy Search Integration Sample Guide for Oracle WebLogic Portal 10g Release 3 (10.3.2) Part Number E15073-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter includes the following sections:
The tasks in this guide are organized according to the portal life cycle. For more information about the portal life cycle, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Overview for Oracle WebLogic Portal. The portal life cycle contains four phases: architecture, development, staging, and production.
Figure 1-1 shows how search fits into the portal life cycle.
Figure 1-1 How Search Fits into the Four Phases of the Life Cycle
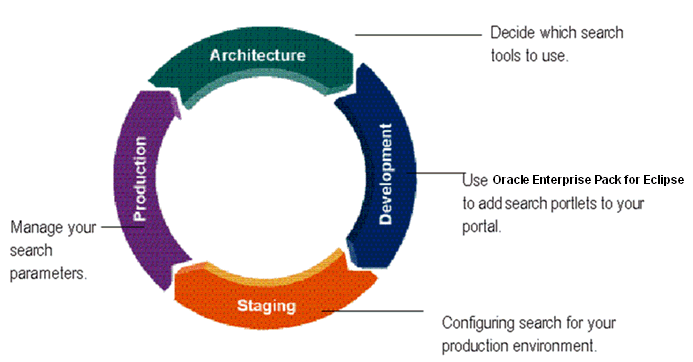
During the architecture phase, you determine what enterprise content you want to make available for your portal and who within your portal environment will be able to search this information.
The following chapter describes tasks within the architecture phase:
During the development phase, you add search portlets to your portal, use the APIs to retrieve content, and optionally, write portlets to surface search features for your portal users.
The following chapter describes tasks within the development phase:
The staging phase is when you prepare your production environment. During this phase, you reconfigure your search configuration to match your deployment configuration and enable tools to configure search when running in a production environment.
The following chapter describes tasks within the staging phase:
Optional search features provided by Autonomy include the following:
Natural language queries can be input to the IDOL Server and will be processed based on the words contained in the queries.
Basic XML Search - basic features to index and search XML documents Natural Language Support.
Relevance Ranking. Each retrieval operation produces a relevancy score which can be used in the search results interface
Document Similarity Search – "More Like This" feature using keyword similarity between documents.
Proximity Controls. Basic Boolean, proximity, and field searches are provided.
Table 1-1 lists the components of Autonomy search tools and what each provides.
Table 1-1 Autonomy Search Components Optionally Used with Oracle WebLogic Portal
| Autonomy Component | What It Does: |
|---|---|
|
Autonomy IDOL Server |
The Intelligent Data Operating Layer (IDOL) server is responsible for indexing content as well as processing content queries made from your portal. For more information about the Autonomy IDOL Server, see the Autonomy IDOL Server documentation. |
|
Autonomy DiSH |
The Distributed Service Handler – DiSH, provides the crucial maintenance, administration, control and monitoring functionality of the Intelligent Data Operating Layer (IDOL). DiSH delivers a unified way to communicate with all Autonomy services from a centralized location. DiSH can be managed with the Autonomy Service Dashboard. For more information about the Autonomy DiSH, see the Autonomy DiSH documentation. |
|
Autonomy Service Dashboard |
The Autonomy Service Dashboard is a standalone front-end web application that communicates with one or more Autonomy Distributed Service Handler (DiSH) modules that provide the back-end process for monitoring and controlling all the Autonomy child services, such as fetches. For more information about the Autonomy Service Dashboard, see the Autonomy DiSH documentation. |
|
Autonomy HTTP Fetch |
HTTP Fetch allows documents from internet or intranet sites to be aggregated from remote servers and indexed into Autonomy IDOL server. For more information about the HTTPFetch, see the Autonomy HTTP Fetch documentation. |
|
Autonomy ODBC Fetch |
ODBC Fetch is an Autonomy connector that automatically retrieves data that is stored in ODBC data sources, imports it into IDX file format and indexes it into Autonomy IDOL server. For more information about the ODBC Fetch, see the Autonomy ODBC Fetch documentation. |
|
Autonomy File System Fetch |
File System Fetch analyzes file systems on local or network machines (including Novell, NT, UNIX file systems and Samba-mounted servers) for new documents to aggregate into the Autonomy IDOL server. It keeps the IDOL server's view of the file system in sync so that files deleted are automatically removed from IDOL server, and modifications to files are reflected automatically. Note: If a file name contains any Japanese characters using Shift JIS encoding, Autonomy will not index them. This means that if a file with Shift JIS characters in the file name are placed in a directory to be indexed by the File System Fetch utility, it will not be indexed by Autonomy and not be returned within the search results provided by the Enterprise Search portlet. Therefore, you must rename any files that contain Shift JIS characters to a name without any Shift JIS characters. For more information about the File System Fetch, see the Autonomy File System Fetch documentation. |
|
Autonomy Portlets |
Autonomy portlets are designed to integrate search functionality with your portal. For more information about the Autonomy portlets, see Section 3.1.4, "Installing Autonomy Portlets". For additional documentation on the Autonomy portlets, see the Autonomy Portlets for WebLogic Guide or the Autonomy Portlets User Guide, published by Autonomy Corporation. Contact WebLogic Portal Customer Support to obtain a copy of these guides. |
The number of CPUs that you need for a production instance varies with the number and type of documents you are exposing, as well as the way they are exposed (for example, automated searching, user driven, and so on).
A single instance of one CPU can potentially support tens of thousands of users and millions of documents.
When you deploy your portal and install Autonomy within your portal environment, you will need to install the operating system-specific version of Autonomy on your server on which you run the Autonomy services. For more information about installing and deploying the Autonomy services, see Chapter 7, "Staging Autonomy Search Functionality."
Note:
Autonomy binary executable files are named with a.exe extension (Windows style) for all operating systems.Additionally, note the following:
If you upgraded to Oracle WebLogic Portal 10.3.2, during development mode Autonomy services are automatically started for the operating system of the host computer. This allows developers to use Autonomy during portal development.
If you performed a clean installation of Oracle WebLogic Portal and installed Autonomy separately, you must modify your Oracle WebLogic Server start script to start the Autonomy search engine for Autonomy services to automatically start the operating system of the host computer. For details on modifying the Oracle WebLogic Server start script to start the Autonomy search engine, see Chapter 4, "Modifying the Oracle WebLogic Server Start Script to Start the Autonomy Search Engine."
When configuring Autonomy search for your portal application, please note Autonomy's system requirements, see the Autonomy documentation.
To disable search indexing:
Start your portal domain.
Start the Oracle WebLogic Portal Administration Console.
Select Content > Content Management from the navigation menu at the top of the console.
Select Manage | Repositories.
In the resource tree, click the repository for which you want to disable search indexing.
In the Summary tab, click Advanced to view the Edit Advanced Properties for Repository dialog.
In the Edit Advanced Properties for Repository dialog, clear the Search Enabled/Search Indexing Enabled check boxes.
When finished making changes, click Save.