 Understanding Global Payroll for Thailand Tax Calculation
Understanding Global Payroll for Thailand Tax Calculation
This chapter provides an overview of the Global Payroll for Thailand tax processes and discusses how to:
Maintain tax rate tables.
Set up irregular income tax calculations.
Process overpaid taxes.
Track tax calculation issues.
Extend tax calculations.
 Understanding Global Payroll for Thailand Tax Calculation
Understanding Global Payroll for Thailand Tax Calculation
Global Payroll for Thailand provides payroll rules and elements to support the following tax calculation features:
Weekly, semi-monthly, and monthly payroll period types for tax calculations and payroll runs.
The Withholding, Gross Up All Cycles (GUPA) and Gross Up One Cycle (GUPO) tax allocation methods are supported for each of the payroll period types.
Only one tax calculation method within a single payroll period can apply to a payee's regular earnings. However the tax allocation method for a payee's regular earnings can change for different payroll periods at the beginning of a pay period. The tax allocation method cannot be changed in the middle of a period.
A payee can have multiple tax allocation methods applied to irregular earnings within a single payroll period.
The tax allocation method can be assigned to irregular earning, such as bonus, overtime, or car allowance, through positive input or element assignment.
Termination tax. The Withholding tax allocation method is used for payees with a length of service of five or more years. For payees with a length of service less than five years, the termination earnings are treated as irregular earnings for tax calculations. For more details, please refer to the chapter on managing termination processing.
See Managing Termination.
The following tax allowances and deductions are supported for regular and irregular earnings:
Provident Fund Allowance.
Expense Allowance.
Personal Allowance.
Spouse Allowance.
Child Allowance.
Child Education Allowance.
Parent Allowance.
Personal Life Insurance Allowance.
Spouse Life Insurance Allowance.
Provident Fund.
Mutual Fund.
Long Term Equity Fund.
Social Security Fund.
Mortgage Interest Allowance.
Education Donation Allowance.
Donation.
Sport Donation.
Parent Health Insurance.
Non-taxable deductions.
Generate a tax log report to track the tax calculation process.
Tax reporting to the Thailand Revenue Department.
Normal cycle and off cycle processing.
Other supported tax functionality.
Mid-period hires or terminations.
Retroactive amount tax processing. The retroactive earnings amount, is considered irregular earnings, and the tax allocation method of the retroactive amount is the same as the basic retroactive salary element in the retroactive period. The retroactive amount can be a negative value. If the total of the retroactive amount and other irregular earnings with the same tax allocation method is a negative value, then the taxes for that allocation method are not processed.
Negative tax payment processing.
Mid-year changes to deduction allowance information is allowed. The new information will be captured during the payroll run for the next payroll period.
Element segmentation tax calculation of basic salary.

 Understanding Tax Calculation Methods
Understanding Tax Calculation Methods
When calculating personal income tax for declaration to the Revenue Department, there are two tax calculation methods to choose from: the Calculation In Advance Method (CAM) and the Accumulative Calculation Method (ACM).
CAM is the method that the Revenue Department recommends employees use. Most companies use ACM to calculate taxes, but governmental organizations still use CAM to calculate the taxes for their officers.
Global Payroll for Thailand enables organizations to choose either calculation method. Both ACM and CAM follow the same high level processing flow as shown in the following graphic:
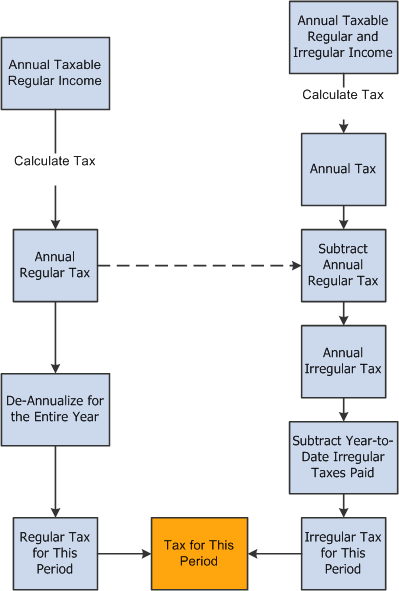
Tax calculation process
The difference between the two tax calculation methods is in the detailed processing steps, such as annualizing regular taxable incomes, and de-annualizing the total calculated tax.
Global Payroll for Thailand uses the following variables to control the tax calculation method:
TAX VR CAL CAT specifies the tax calculation category, either ACM or CAM.
TAX VR CAL NUMBER specifies the number of calculation periods the system uses to calculate income taxes when you are using CAM.
Using CAM is not accurate when calculating the tax payment for each pay period, and the payment amount must be adjusted at the end of the year. When you choose CAM for tax calculation, you must specify the number of periods that the system uses CAM to calculate income taxes. The system then uses ACM to calculate income taxes for the remainder of the year.
You can override the default values for these variables at the pay entity, pay group, and payee levels.

 Understanding Tax Calculation Types
Understanding Tax Calculation Types
PeopleSoft Enterprise Global Payroll for Thailand supports the following three tax calculation types:
Withholding Tax Income (WH).
The employer, or entity that pays the income, withholds tax at the source and identifies the condition of payment in the ITF1 and ITF1 A reports as Deduct at Source.
Gross Up One Cycle (GUPO).
The employer, or entity that pays the income, pays tax for the payee for one cycle of the tax calculation and the payee pays the tax for the remainder of the cycles. The employer, or pay entity, identifies the condition of payment in the ITF1 and ITF1 A reports as Company Paid Once.
Gross Up All Cycles (GUPA).
The employer, or entity that pays the income, pays the tax for the payee for all cycles of the tax calculation and the payee will not pay any taxes for that income. The employer, or entity that pays the income, identifies the condition of payment in the ITF1 and ITF1 A reports as Company Paid All.
Tax Calculation Types Logic
The following diagram describes the tax calculation logic of the three tax calculation types:
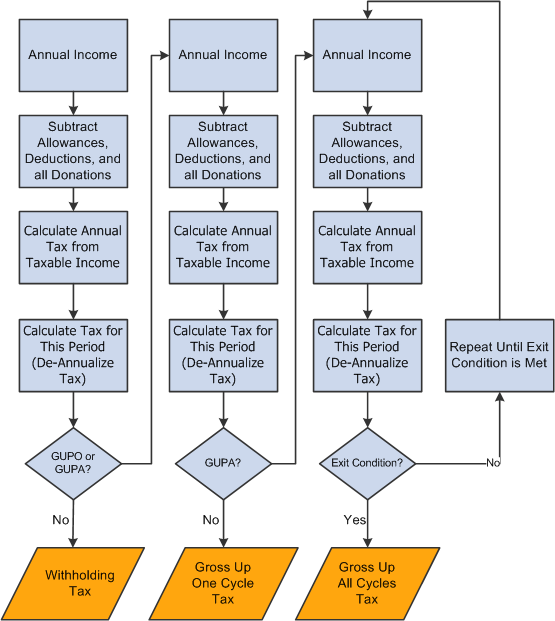
Tax calculation types logic
For each calculation type, a repeating loop function is used in the tax calculation:
If the payee's current income uses the Withholding calculation type, the system completes the loop only once.
If the payee's current income uses the Gross Up One Cycle calculation type, then the system completes the loop twice.
If the payee's current income uses the Gross Up All Cycles calculation method, then the system continues to cycle through the loop until the difference between the tax amount of the current loop and the tax amount of the previous loop is less than 0.0001.
In each tax loop, the system performs the following steps:
Calculates the annual total income based on the income for the current period and the year-to-date income.
Subtracts each tax allowance and obtains the total taxable income.
Looks up the tax rate for the total taxable income in the tax rate table.
Calculates the annual tax amount.
Calculates the tax for the current period.
Determining Tax Calculation Type
The following diagram illustrates a typical organizational structure for Global Payroll for Thailand:

Typical organization framework setup for Global Payroll for Thailand
In the previous graphic, a pay entity is the business organization that pays payees.
Pay groups combine payees with the same frequency, same pay periods and same payment dates during a payroll process. You must define at least one pay group for each typical pay frequency used in your organization.
The pay groups described in the previous graphic are not delivered in PeopleSoft Global Payroll for Thailand. The example pay groups illustrate three different income streams:
Section 40(1) income only in the Example 40(1) pay group.
A mix of Section 40(1) and Section 40(2) income in the Example 40(1) and 40(2) pay group.
Section 40(2) income only in the Example 40(2) pay group.
TAX VR CAL METHOD is the element user key that specifies the tax calculation type, Withholding, Gross Up One Cycle, or Gross Up All Cycles.
PeopleSoft Global Payroll for Thailand delivers the following eligibility groups that specify which types of regular income a payee receives:
KT401 is the eligibility group for Section 40(1) income.
KT401402 is the eligibility group for a combination of Section 40(1) and Section 40(2) income.
KT402 is the eligibility group for Section 40(2) income.
Global Payroll for Thailand delivers the following element groups:
EG-401.
Contains the SAL BAS EARN, SAL BAS PRO, and SAL RTO DELT elements for processing of Section 40(1) income.
EG-Common.
Contains all common earning and deduction elements, which are eligible to all pay groups. For example, deduction elements for tax allowance, social security contribution and provident fund contribution are eligible to all payees.
EG-Irregular.
Contains all earning elements for irregular income. This element group is eligible to all pay groups. The 'Eligibility Assignment' of all members of this element group will be set to 'By Payee'. By this means, if you want a payee gets an element processed, you have to assign this element through the payee level Earnings/Deductions Assignment page or enter positive input. This guarantees those elements that are not only eligible to the current payee, but also have been assigned through positive input or element assignment will be resolved. This can greatly improve system performance.
EG-402.
Contains the 402 ER REG, 402 ER PRO, and 402 ER RETRO elements for processing Section 40(2) income.
Each of the delivered element groups in Global Payroll for Thailand belongs to the following eligibility groups:
|
Element Group |
Eligibility 1 |
Eligibility 2 |
Eligibility 3 |
|
EG-401 |
Eligibility Group-KT401402 |
Eligibility Group-KT401 |
|
|
EG-402 |
Eligibility Group-KT401402 |
|
Eligibility Group-KT402 |
|
EG-Irregular |
Eligibility Group-KT401402 |
Eligibility Group-KT401 |
Eligibility Group-KT402 |
|
EG-Common |
Eligibility Group-KT401402 |
Eligibility Group-KT401 |
Eligibility Group-KT402 |
Determining Tax Calculation Types for Irregular Income
The tax calculation methods of irregular income are determined through positive input or element assignment while assigning values to irregular incomes.
The following diagram illustrates how to determine the tax calculation types and sequences for irregular income:
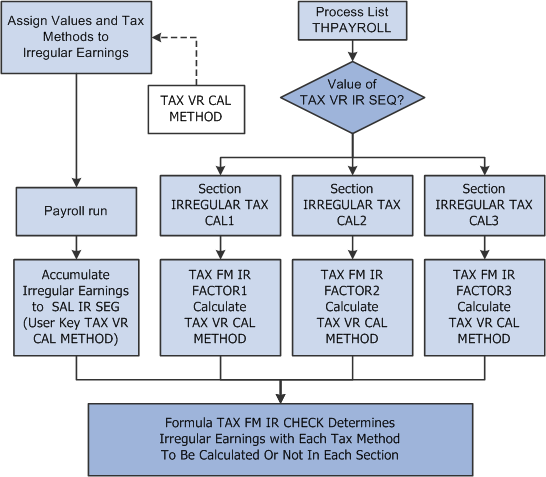
Determining the tax calculation types and sequences for irregular income
Although a single type of irregular income can use any of the three tax calculation types, Global Payroll for Thailand delivers one earnings element for each type of irregular income. Use the following steps to identify the tax calculation type for each type of irregular income:
Add the TAX VR CAL METHOD variable to each irregular income earning element as a user key.
Enter one of the tax calculation types in the TAX VR CAL METHOD variable through positive input or the Earning/Deduction Assignment page.
Use the Configuration by Element page or the Configuration by Category page to ensure that the end user assigns a value to the TAX VR CAL METHOD variable.
Add the TAX VR CAL METHOD variable as a user key for the related accumulators.
Since a payee can have all of the tax calculation types on irregular income during the same period, the pay group cannot be used to determine which tax calculation method should be used for a given irregular income. All earnings elements for irregular income use the TAX VR CAL METHOD user key to indicate which tax calculation type to use. Payroll administration needs to assign a value to this user key using supporting element overrides when entering irregular income using Positive Input or the Earning/Deduction assignment page.
See Configuring Element Overrides.

 Understanding the Overall Flow of Tax Calculations
Understanding the Overall Flow of Tax Calculations
The following graphic describes the overall flow of tax calculations in Global Payroll for Thailand:
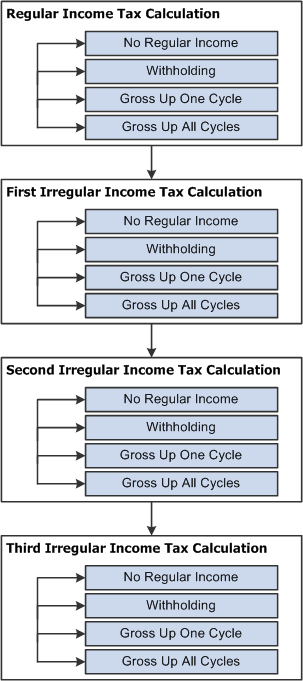
Overall Flow of Tax Calculation
The Global Payroll for Thailand process list has four sections for tax calculation:
Regular Income Tax Calculation.
This section calculates the personal income tax for regular income. Based on the current payee's type of regular income, this section chooses the tax calculation type to calculate the regular tax.
First Irregular Income Tax Calculation.
A payee can have three different types of irregular income within one payroll period: withholding, gross up all cycles and gross up one cycle. There are three separate sections to calculate different types of irregular incomes. Based on the configuration, this section can calculate withholding, gross up all cycles, and gross up one cycle irregular income taxes. If the organization specifies that this section calculates withholding tax, but the current payee does not have any withholding irregular income, then this section is skipped.
Second Irregular Income Tax Calculation.
You can specify the tax calculation type for this section.
Third Irregular Income Tax Calculation.
You can specify the tax calculation type for this section.

 Year End Processing for Tax Recalculation
Year End Processing for Tax Recalculation
Tax calculations for Thailand are not completely accurate until the end of a tax year, since the calculations are based on the projection of annual regular income. So the tax amount must be adjusted at the end of tax year. For example, tax allowance declaration data can change within a tax year, so any tax calculation before the change in declaration data is inaccurate. In addition, changes to the calculation sequence for different types of irregular income result in different tax amounts.
Principles Used in Year-End Tax Recalculation
From an entire tax year perspective, the regular income tax amount does not need to be recalculated at the end of the year. However, the irregular income tax amount must be recalculated based on the final year to date regular income, including the final year to date original regular income and the year to date tax for regular income. The total irregular tax amount paid is the same as moving the year to date withholding income, the year-to-date original gross up all cycles irregular income, and the year to date original gross up one cycle irregular income to the last period of the year.
All irregular withholding taxes should be paid by the employee. So the year to date withholding irregular income can be used for the year end tax recalculation.
All irregular gross up all cycles taxes should be paid by the employer, and a corresponding amount of gross up all cycles irregular income is added to the employee's income. For example, during the 2007 tax year, the only gross up all cycles irregular income occurs in May. The amount of this income is 50,000 THB, and the calculated tax amount is 10,000 THB. Before the recalculation at the end of the year, the year to date gross up all cycles irregular income is 50,000+10,000=60,000 THB, but the year to date original gross up all cycles irregular income of 50,000 THB should be the amount used for the year end tax recalculation.
A part of the irregular gross up one cycle tax should be paid by the employer, and a corresponding amount of relative gross up one cycle irregular income is added to the employee's income. For example, during the 2007 tax year, the only gross up one cycle irregular income occurs in June. The amount of this income is 50,000 THB, and the calculated tax amount that employer should pay is 8,000 THB. Before the year end recalculation, the year to date gross up one cycle irregular income is 50,000+8,000=58,000 THB, but the year to date original gross up one cycle irregular income of 50,000 THB should be the amount used for the year end tax recalculation.
Calculation Logic In the Last Period of One Tax Year
The irregular tax calculation process in the last period of the tax year differs from the process during other periods of the year. For example, assume that the irregular tax calculation sequence is:
Withholding.
Gross up all cycles.
Gross up one cycle.
The following diagram shows the process flow for calculating the withholding tax in the last period of the year:
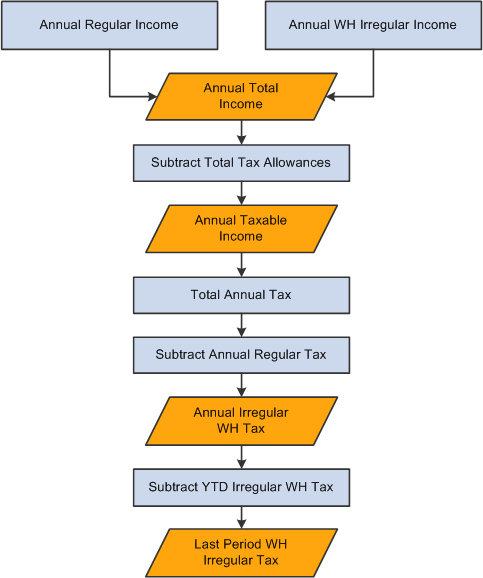
Irregular withholding tax calculation in the last period of the year
Then, the gross up all cycles irregular tax is calculated based on the withholding tax results:
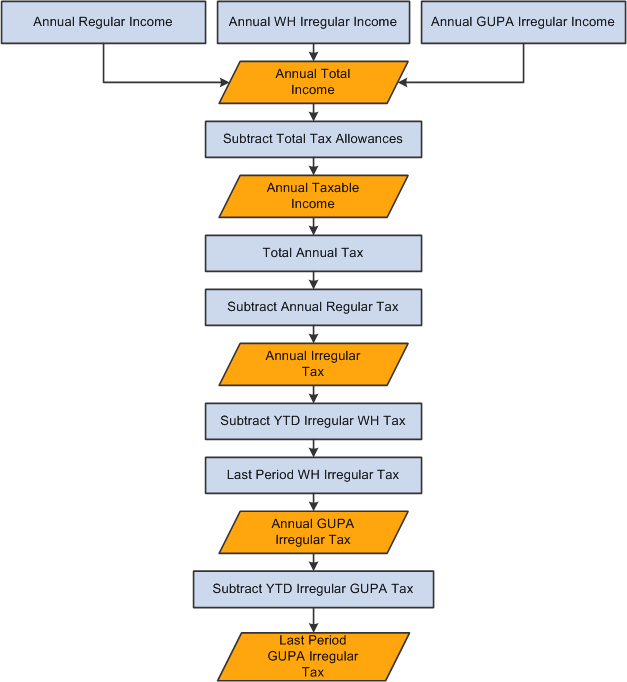
Irregular gross up all cycles tax calculation in the last period of the year
Finally, the gross up one cycle tax is calculated based on the result of the withholding and gross up all cycles tax.

 Tax Processing for Retroactive Processes
Tax Processing for Retroactive Processes
PeopleSoft Enterprise Global Payroll for Thailand supports retroactive processing of basic salary.
The amount of retroactive taxes is categorized as irregular earnings, whether the amount is positive or negative. The tax calculation type for the retroactive amount is the same as the retroactive element in the retroactive period.
If the negative retroactive tax amount plus any other irregular earnings with the same tax calculation type is negative, then the amount is not processed.

 Delivered Elements for Tax Calculation
Delivered Elements for Tax CalculationThe PeopleSoft system delivers a query that you can run to view the names of all delivered elements designed for Thailand.
See Viewing Delivered Elements.
 Maintaining Tax Rate Tables
Maintaining Tax Rate Tables
Thailand Personal Income Tax has two progressive tax rate tables: one for normal income and the second for termination income.
The following table lists the taxable income ranges and related tax rates in the Normal Income Tax Rate table:
|
Taxable Income Range |
Tax Rate |
|
0-150,000 |
0% |
|
150,001-500,000 |
10% |
|
500,001-1,000,000 |
20% |
|
1,000,001-4,000,000 |
30% |
|
4,000,001-999,999,999.99 |
37% |
The following table lists the taxable income ranges and related tax rates in the Termination Income Tax Rate table:
|
Taxable Income Range |
Tax Rate |
|
0-100,000 |
5% |
|
100,001-500,000 |
10% |
|
500,001-1,000,000 |
20% |
|
1,000,001-4,000,000 |
30% |
|
4,000,001-999,999,999.99 |
37% |
For example, assume that a person's annual taxable income is 520,000 THB. Based on the Normal Income Tax Rate table, the tax calculation would be:
150,000 * 0% for the first 150,000 THB, for a tax amount of 0 THB.
350,000 * 10% for the next 350,000 THB, for a tax amount of 35,000 THB.
20,000 * 20% for the remainder of the annual income, for a tax amount of 4,000 THB.
0 + 35,000+ 4,000 = 39,000
Add the three tax amounts together to obtain an annual tax amount of 44,000 THB.
Global Payroll for Thailand adds two columns to the tax rate tables so that the system does not need to read the tables row by row in order to calculate the final tax amount.
The following table lists the Normal Income Tax Rate table with the additional information added by Global Payroll for Thailand:
|
Taxable Income Range |
Tax Rate |
Flat Amount |
Base |
|
0-150,000 |
0% |
0 |
0 |
|
150,001-500,000 |
10% |
0 |
150,000 |
|
500,001-1,000,000 |
20% |
35,000 |
500,000 |
|
1,000,001-4,000,000 |
30% |
135,000 |
1,000,000 |
|
4,000,001-999,999,999.99 |
37% |
1,035,000 |
4,000,000 |
The following table lists the Termination Income Tax Rate table with the additional information added by Global Payroll for Thailand:
|
Taxable Income Range |
Tax Rate |
Flat Amount |
Base |
|
0-100,000 |
5% |
0 |
0 |
|
100,001-500,000 |
10% |
5,000 |
100,000 |
|
500,001-1,000,000 |
20% |
45,000 |
500,000 |
|
1,000,001-4,000,000 |
30% |
145,000 |
1,000,000 |
|
4,000,001-999,999,999.99 |
37% |
1,045,000 |
4,000,000 |
The modified tax rate tables enable the equation for tax calculation to look like this:
Tax Amount = (Annual Taxable Income - Base) * Rate + Flat Amount
So, for the previous example with an annual taxable income of 520,000 THB, the tax calculation equation would be:
(520,000 - 500,000) * 20% + 35,000 = 39,000 THB
Calculating the Flat Amount for Normal Income
The values entered in the Flat Amount column of the modified Normal Income Tax Rate table are calculated with the following formula:
Multiply the numeric value of the tax income range for the previous row with the tax rate for the previous row and add any flat rate amount from the previous row.
Calculate the individual flat rate amounts in the table as follows:
The first row is 0 THB. There is no previous row with any data.
The second row is 0 THB. This is calculated with the equation 150,000 * 0% = 0. The income range for the first row is 0 to 150,000 THB, which is a range of 150,000 THB. The tax rate for the first row is 0%.
The third row is 35,000 THB. This is calculated with the equation 0 + (35,000 * 10%) = 35,000.
0 is the flat amount from the second row.
350,000 represents the range of the second row, from 150,001 to 500,000 THB.
10% is the tax rate from the second row.
The fourth row is 135,000 THB. This is calculated with the equation 35,000 + (500,000 * 20%) = 135,000.
35,000 is the flat amount from the third row.
500,000 is the income range for the third row.
20% is the tax rate from the third row.
The fifth row is 1,035,000 THB. This is calculated with the equation 135,000 + (3000000 * 30%) = 1,035,000.
Calculating the Flat Amount for Termination Income
The values entered in the Flat Amount column of the modified Termination Income Tax Rate table are calculated in the same manner as the modified Normal Income Tax Rate table. Calculate the individual flat rate amounts in the table as follows:
The first row is 0 THB. There is no previous row with any data.
The second row is 5,000 THB. This is calculated with the equation 100,000 * 5% = 5,000.
The third row is 45,000 THB. This is calculated with the equation 5,000 + (40,000 * 10%) = 45,000.
The fourth row is 145,000 THB. This is calculated with the equation 445,000 + (500,000 * 20%) = 145,000.
The fifth row is 1,045,000 THB. This is calculated with the equation 145,000 + (3,000,000 * 30%) = 1,045,000.

 Tax Rate Brackets
Tax Rate Brackets
Global Payroll for Thailand delivers two brackets for tax rates:
TAX BR PER RATE
This is the bracket for the Normal Income Tax Rate table.
TAX BR TER RATE
This is the bracket for the Termination Income Tax Rate table.
Important! Do not modify the structure, or any property of these brackets. You should only maintain the data within the brackets if a tax rate change is introduced by the Thailand Revenue Department.

 Pages Used to Manage Brackets
Pages Used to Manage Brackets|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
GP_PIN |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Elements, Supporting Elements, Brackets, Bracket Name |
Name the element and define its basic parameters. |
|
|
GP_BRACKET1 |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Elements, Supporting Elements, Brackets, Lookup Rules |
Define the lookup rules for a bracket. |
|
|
GP_BRACKET2 |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Elements, Supporting Elements, Brackets, Search Keys/Return Columns |
Identify the search keys and the return columns for the bracket. |
|
|
GP_BRACKET3 |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Elements, Supporting Elements, Brackets, Data |
Enter lookup values. The search key values and the return column values that you selected in the Brackets - Search Keys / Return Columns page appear here. |
 Setting Up Irregular Income Tax Calculations
Setting Up Irregular Income Tax Calculations
Global Payroll for Thailand provides several formulas that enable you to determine the calculation order of the three types of irregular income: withholding, gross up one cycle, and gross up all cycles. The formulas are:
TAX FM IR FACTOR1
This formula enables you to specify which type of irregular income tax is calculated first by assigning different values to the TAX VR CAL METHOD variable. You must use specific abbreviations for each of the different types of irregular income, as follows:
WH is used to indicate the withholding irregular income tax calculation type.
GA is used to indicate gross up all cycles irregular income tax calculation type.
GO is used to indicate gross up one cycle irregular income tax calculation type.
Adding your own if-else clauses into this formula enables multiple groups of employees to use different initial tax calculation types.
TAX FM IR FACTOR2
This formula enables you to specify which type of irregular income tax calculation type is calculated second.
TAX FM IR FACTOR3
This formula enables you to specify which type of irregular income tax calculation type is calculated last.
Warning! Incorrectly configuring these three formulas can cause errors in the calculation of irregular income taxes. For example, if all three formulas contain the code:'WH' >> TAX VR CAL METHOD, then the withholding irregular tax is calculated three times, while the other types of irregular taxes are not calculated at all.
If all employees in your company use the same calculation order, these three formulas can be very simple, each formula just has one line:'WH'/'GA'/'GO' >> TAX VR CAL METHOD.
If the irregular income tax type calculation order is different for each employee, then these formulas will be very complex.
For example, assume that your organization has several pay groups that require a different order for the three tax calculation types for irregular income. The following table describes the pay groups and the required order of tax calculations for each pay group:
|
Pay Group |
First Tax Calculation Type |
Second Tax Calculation Type |
Third Tax Calculation Type |
|
Pay Group A or 'PGA' |
Gross Up All Cycles |
Gross Up One Cycle |
Withholding |
|
Pay Group B or 'PGB' |
Gross Up One Cycle |
Withholding |
Gross Up All Cycles |
|
Pay Group C or 'PGC' |
Withholding |
Gross Up All Cycles |
Gross Up One Cycle |
|
All Other Pay Groups |
Gross Up All Cycles |
Withholding |
Gross Up One Cycle |
So employees in Pay Group A use the gross up all cycles tax calculation type first, while employees in Pay Group B use the gross up one cycle type first, and employees in Pay Group C use the withholding tax calculation type first.
In order to accommodate this combination of tax calculation sequences, modify the three calculation order formulas as shown in the following table:
|
Contents of TAX FM IR FACTOR1 |
Contents of TAX FM IR FACTOR2 |
Contents of TAX FM IR FACTOR3 |
|
|
|
 Processing Overpaid Taxes
Processing Overpaid Taxes
Changes in an employee's basic salary or tax allowances may cause the employee to pay more than the actual tax amount owed to the Revenue Department. The Thailand Revenue Department only returns overpaid tax at the end of the tax year. Global Payroll for Thailand enables you to track any overpaid taxes over the course of the tax year.
You can find the tax amount the employee has actually paid to the Revenue Department in the following accumulators:
TAX RIR RP SEG/MTD/YTD
TAX RIR RP TAL SEG/MTD/YTD
You can find the tax amount the employee should pay to the Revenue Department in the following accumulators:
TAX RIR SEG/PTD/MTD/YTD
TAX IR SEG/PTD/MTD/YTD
TAX IR TAL SEG/PTD/MTD/YTD
TAX REG SEG/PTD/MTD/YTD
TAX REG TAL SEG/PTD/MTD/YTD
TAX REG EE SEG/PTD/MTD/YTD
TAX IR EE SEG/PTD/MTD/YTD
TAX REG ALL SEG/PTD/MTD/YTD
TAX IR ALL SEG/PTD/MTD/YTD
From the following deduction elements, you can find the payee's current period actual tax amount to be paid to the Revenue Department. These amounts are subtracted from the payee's net pay:
TAX WH DED
TAX GA DED
TAX GO DED
TAX DD 402WH
TAX DD 402GA
TAX DD 402GO
The following table provides a detailed explanation of the elements mentioned:
|
Element Type |
Element Name(s) |
Description |
|
Deduction |
TAX WH DED |
The total Section 40(1) income withholding tax amount to be paid to the Revenue Department, including regular and irregular Section 40(1) income. |
|
Deduction |
TAX DD 402WH |
The total Section 40(2) income withholding tax amount to be paid to the Revenue Department, including regular and irregular Section 40(2) income. |
|
Deduction |
TAX GA DED |
The total Section 40(1) gross up all cycles tax amount to be paid to the Revenue Department, including regular and irregular Section 40(1) income. |
|
Deduction |
TAX DD 402GA |
The total Section 40(2) gross up all cycles tax amount to be paid to the Revenue Department, including regular and irregular Section 40(2) income. |
|
Deduction |
TAX GO DED |
The total Section 40(1) gross up one cycle tax amount that will be paid to Revenue Department, include regular and irregular Section 40(1) income. |
|
Deduction |
TAX DD 402GO |
The total Section 40(2) gross up one cycle tax amount that will be paid to Revenue Department, include regular and irregular Section 40(2) income. |
|
Deduction |
TAX RIR RP SEG TAX RIR RP MTD TAX RIR RP YTD |
The tax amount actually paid to the Revenue Department. You can retrieve the tax amount for a specified tax type, such as the withholding tax amount or the gross up all cycles tax amount. |
|
Accumulator |
TAX RIR RP TAL SEG TAX RIR RP TAL MTD TAX RIR RP TAL YTD |
The total tax amount actually paid to the Revenue Department, including withholding, gross up all cycles, and gross up one cycle taxes. |
|
Accumulator |
TAX RIR SEG TAX RIR PTD TAX RIR MTD TAX RIR YTD |
The regular and irregular income tax amount for different tax types. |
|
Accumulator |
TAX IR SEG TAX IR PTD TAX IR MTD TAX IR YTD |
The irregular income tax amount for different tax types. |
|
Accumulator |
TAX IR TAL SEG TAX IR TAL PTD TAX IR TAL MTD TAX IR TAL YTD |
The total irregular income tax amount, including withholding, gross up all cycles, and gross up one cycle taxes. |
|
Accumulator |
TAX REG SEG TAX REG PTD TAX REG MTD TAX REG YTD |
The regular income tax amount for different tax types. |
|
Accumulator |
TAX REG TAL SEG TAX REG TAL PTD TAX REG TAL MTD TAX REG TAL YTD |
The total regular income tax amount, including withholding, gross up all cycles, and gross up one cycle taxes. |
|
Accumulator |
TAX REG EE SEG TAX REG EE PTD TAX REG EE MTD TAX REG EE YTD |
The Section 40(1) and 40(2) regular income employee tax. |
|
Accumulator |
TAX IR EE SEG TAX IR EE PTD TAX IR EE MTD TAX IR EE YTD |
The Section 40(1) and 40(2) irregular income employee tax. |
|
Accumulator |
TAX IR ALL SEG TAX IR ALL PTD TAX IR ALL MTD TAX IR ALL YTD |
The total Section 40(1) and 40(2) irregular income tax |
|
Accumulator |
TAX REG ALL SEG TAX REG ALL PTD TAX REG ALL MTD TAX REG ALL YTD |
The total Section 40(1) and 40(2) regular income tax amount, including withholding, gross up all cycles, and gross up one cycle taxes. |
 Tracking Tax Calculation Issues
Tracking Tax Calculation IssuesGlobal Payroll for Thailand provides tax log reports that you can use to track the detailed process of tax calculations for either the ACM or CAM tax calculation methods. During the payroll process, writable arrays store tax calculation related information so that you can generate tax log reports based on the information.
See Configuring Tax Log Reporting.
 Extending Tax Calculations
Extending Tax Calculations
This section discusses how to extend the tax calculation features of Global Payroll for Thailand.

 Adding New Tax Calculation Allowances
Adding New Tax Calculation AllowancesGlobal Payroll for Thailand supports all of the tax allowances allowed by the Revenue Department available at the time of release. However, you may have to enter any new tax allowances that the Thailand Revenue Department announces after the release date.
Follow these steps to enter new tax calculation allowances:
Add new fields on the Tax Allowance Declaration THA page (optional).
Global Payroll for Thailand has two pages for tax allowance declaration: GPTH_TAX_ALLOW and GPTH_SS_TAX_ALLOW. This enables you to explicitly declare tax allowances.
Modify the TAX AR ALLOWANCE array to retrieve information from the Tax Allowance Declaration Page (optional).
The TAX AR ALLOWANCE array is used to retrieve tax allowance declaration data that is used by variables during the tax allowance calculation. If you create new fields for a tax allowance, you must create the corresponding supporting elements. Then, modify the TAX AR ALLOWANCE array to map any new fields to the new supporting elements.
Create new tax allowance deduction elements.
Create one deduction element for each new tax allowance, and add this tax allowance element into the TAX ALLOWANCE section.
Specify the calculation logic of your new tax allowance that is based on the legal rule of the tax allowance. You may need use the following supporting elements:
Supporting elements that represent the declaration data on Tax Allowance Declaration page.
The total annual income variable, TAX VR TOTAL INC. Some tax allowances have limitations based on annual regular and irregular income.
The current taxable income amount variable, TAX VR TAXABLE AMT. It is equal to the difference between the TAX VR TOTAL INC variable and the total amount of tax allowances calculated before the current tax allowance.
Add the current deduction element into the TAX AC ALLOW NM accumulator.
Update the TAX VR TAXABLE AMT variable. Since this variable stores the current taxable income amount, you need to subtract the current tax allowance amount. You can create a post process formula to do this, such as the TAX FM ALL POST delivered by PeopleSoft.
Add the new tax allowance into the TAX ALLOWANCE section. Pay close attention to the sequence number, since the Thailand Revenue Department specifies the detailed calculation sequence for each tax allowance. You need to add your new tax allowance to the correct position within the TAX ALLOWANCE section.
Add the new tax allowance into the EG-COMMON element group.
Update any related tax reports to include the new tax allowance.