 Understanding How to Compensate Employees in Global Payroll for Time
Reported Through Time and Labor
Understanding How to Compensate Employees in Global Payroll for Time
Reported Through Time and Labor
This chapter provides an overview of how to compensate employees in Global Payroll for time reported through Time and Labor and discusses how to:
Configure Global Payroll to work with Time and Labor.
Run a payroll with Time and Labor data.
Update the payable status of payable time entries.
Share work schedules with Time and Labor.
 Understanding How to Compensate Employees in Global Payroll for Time
Reported Through Time and Labor
Understanding How to Compensate Employees in Global Payroll for Time
Reported Through Time and Labor
This section discusses:
Tasks performed by Global Payroll after integration.
How Time and Labor creates payable time.
What happens when you start a pay run.
Planning considerations.

 Tasks Performed by Global Payroll After Integration
Tasks Performed by Global Payroll After IntegrationTime and Labor tracks the time that payees work and generates payable time that can be processed by payroll systems such as Global Payroll. If your organization uses Time and Labor with Global Payroll, you can process payable time during your pay runs, transmit cost data back to Time and Labor after a pay run, and share employee schedules.
Once you configure your systems to work together, Global Payroll:
Makes approved absence data available to Time and Labor so that it can be evaluated by the rules process that Time and Labor uses to create payable time for cost evaluation.
Loads payable time into Global Payroll when you start the Calculate phase of a pay run.
Treats payable time as generated positive input, meaning that all rules that apply to generated positive input also apply to payable time.
Processes payable time for the current period or an offsetting period.
Sends cost data back to Time and Labor after a pay run is complete so that the data can be distributed across payable time entries and sent to PeopleSoft Projects and other applications.
Note. When using Time and Labor with Global Payroll, you can enter absence events in Global Payroll using the Absence Event page, Time and Labor Self Service time sheet in the Absence Event section, or Absence Self Service pages. Absence events populate the Absence Event Definition table (GP_ABS_EVENT) that is used during the Absence Take process and the Time Administration process in Time and Labor.
See Also
Integrating Time and Labor with Global Payroll
Entering and Approving Self Service Absence Requests

 How Time and Labor Creates Payable Time
How Time and Labor Creates Payable Time
Each incident of time that is reported in Time and Labor is associated with a time reporting code (TRC) that identifies its type (for example, regular or meeting), units, currency, and other attributes. You can also assign task codes to each time entry, enabling your organization to track time at a finer level of detail—by product, location, and other categories. In addition, you can track the accounting information that flows between Time and Labor and Global Payroll. Integrating Time and Labor with Global Payroll requires that you map earning, deduction, and absence take elements to TRCs. You might also need to map supporting elements or variable task codes, and chartfields.
Time that is reported in Time and Labor must be converted to payable time before it can be sent to a payroll system for processing. The payable time must also have a payable status to indicate that it is ready for processing. The Time Administration process in Time and Labor creates payable time that's ready for payroll processing by applying a set of user-defined rules to time entries based on their TRCs. It can apply rules for overtime, holiday pay, guaranteed hours, consecutive days, and other situations.

 What Happens When You Start a Pay Run
What Happens When You Start a Pay Run
During the Calculate phase of a pay run, Global Payroll retrieves payable time that's ready for processing from Time and Labor. The first time that the Calculate phase runs, Global Payroll processes all payees that are identified in the current calendars. During subsequent runs, Global Payroll creates an iterative trigger and a retroactive trigger for each instance of payable time that has changed and reprocesses only the payees that are in error or have iterative triggers. Payable time is retrieved each time the payroll is run.
After a pay run is finalized, you start an update process that updates the payable time entries in Time and Labor. This process also invokes the Labor Distribution and Labor Dilution processes in Time and Labor, if you have elected to use those features. If you are not using labor distribution, Global Payroll sets the status of payable time entries to CL (closed).
The following flowchart illustrates the interactions between Global Payroll and Time and Labor:
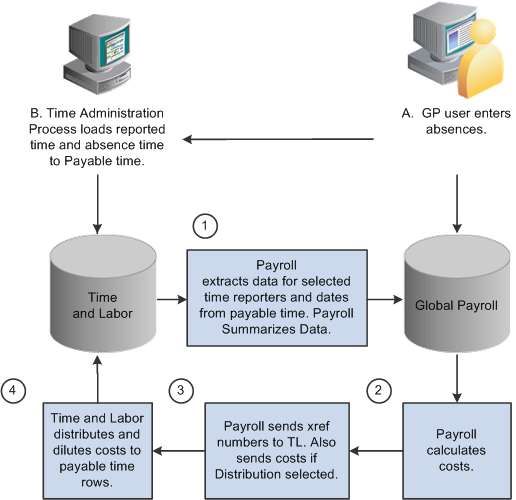
Integration between Global Payroll and Time and Labor
Note. Absence data that is sent to Time and Labor is not used to compensate payees for absences. Global Payroll calculates payee compensation for absences, and when the labor distribution feature is used, sends the resultant amounts back to Time and Labor after a pay run is finalized.

 Planning Considerations
Planning Considerations
Both Global Payroll and Time and Labor are rules-based systems that are capable of carrying out some of the same types of rules. Before integrating the two products, think carefully about which rules you want each system to apply. In general:
Define rules that calculate payable time, including overtime, shift differentials, and other special situations, in Time and Labor.
Define rules that calculate pay in Global Payroll.
Time reporting codes (TRCs) are mapped to Global Payroll earnings and deductions that add to or subtract from gross and net pay accumulators. You should decide on a strategy for mapping earning elements to TRCs. For example, you might map a TRC to an earning element that does not accumulate to gross pay. This enables you to use a separate rule to calculate the costs that are associated with a TRC but do not contribute to gross pay, such as an employer-paid health insurance premium. You might use the same approach for salaried employees, where the hours that are reported by Time and Labor are not used in the payroll calculation, but are used for costing.
To summarize:
Define one earning element that accumulates to gross.
This is the earning element that the payroll process uses to calculate a payee's payslip. Do not map this element to a TRC.
Define a second earning element that does not contribute to gross pay.
This earning element is used for costing purposes only and, in addition to the payee's salary, can include overhead costs or any costs that you want to add. Map this element to a TRC so that accurate cost data is returned to Time and Labor and made available to the cost accounting, planning, or budgeting application.
Note. For hourly workers and in other situations where you do want the second earning elements to add to gross pay, you can map a TRC to a second earning element that accumulates to gross pay.
Note. Make sure that any earnings to which you map TRCs are set up to receive positive input. This is because Global Payroll brings in Time and Labor information as generated positive input.
Note. If you change the status of an element that's mapped to a TRC to Inactive, update the TRC mapping in Time and Labor.
 Configuring Global Payroll to Work with Time and Labor
Configuring Global Payroll to Work with Time and Labor
.
This section discusses how to:
Map chartfields to variables.
Map TRCs to run types.
Create triggers for payable time.
Map tasks to supporting elements.
See Also
PeopleSoft Enterprise Time and Labor 9.1 PeopleBook

 Pages Used to Configure Global Payroll to Work with Time and Labor
Pages Used to Configure Global Payroll to Work with Time and Labor|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
GP_CHART_ELEM |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Integration, Chartfield Code Map, Chartfield Code Map |
Map chartfields that are defined in Time and Labor to chartfield variables that are defined in Global Payroll. |
|
|
Run Types |
GP_RUN_TYPE |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Framework, Processing, Run Types, Run Types |
Define a run type to identify a payroll run and associate Time and Labor TRCs and Variable Compensation earnings. |
|
Trigger Definition |
GP_TRGR_SETUP |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Triggers, Trigger Definitions, Trigger Definitions |
Define trigger types, record levels and associated fields and link to event IDs. |
|
GP_TL_TASK_ELEM |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Integration, Task Code Map, Task Code Map |
Map task codes that are defined in Time and Labor to supporting elements that are defined in Global Payroll. |

 Mapping Chartfields to Variables
Mapping Chartfields to Variables
Access the Chartfield Code Map page (Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Integration, Chartfield Code Map, Chartfield Code Map).
Global Payroll delivers variables to represent each of the Time and Labor chartfields:
GP GL PRODUCT
GP GL PROJECT
GP GL DEPT
GP GL FUND
GP GL PROGRAM
GP GL CLASS
GP GL AFFILIATE
GP GL ALT_ACCOUNT
GP GL BUDGET_REF
GP GL CHARTFIELD1
GP GL CHARTFIELD2
GP GL CHARTFIELD3
GP GL AFF_INTRA1
GP GL AFF_INTRA2
This page enables you to map the PeopleSoft standard configuration chartfields to these delivered chartfield variables. This mapping enables Global Payroll to receive chartfield information for payable time. You can create a separate mapping scheme for each country in which your organization operates.
Note. The system can send a maximum of eight mapped chartfields to PeopleSoft Enterprise General Ledger. Therefore, we recommend that you add no more than eight chartfields to each mapping scheme.
|
Chartfield Code |
Enter the Time and Labor chartfield to map to a variable. |
|
Element Entry Type |
Select the type of element to which the chartfield is mapped. Values are: Variable: User-created variable. For example, you may decide to rename GP GL CHARTFIELD1 so that the name matches the information contained in the field. SystemElem (system element): PeopleSoft standard configuration chartfields. |
|
Element Name |
Select the name of the variable to which you are mapping the chartfield. |
|
SetID Field Code and Supporting Element |
Displays the set ID fields associated with the variable or system element. |
Mapping Tasks and Bundling Payable Time
Mapping task codes to elements specifies the criteria by which Global Payroll bundles payable time that is received from Time and Labor. As payable time is loaded into the Positive Input tables, Global Payroll consolidates or bundles rows of similar data, assigning each bundle a cross-reference number that it later returns to Time and Labor. To be bundled, entries must:
Fall within the same slice and segment.
Share the same currency and rate (when this information is provided).
Share the same task value.
This rule applies only to tasks that are mapped to supporting elements.
Note. Global Payroll populates the Rate As Of Date system element that is associated with a set of bundled entries with the end date of the Time and Labor period, segment, or slice. (If there's no segmentation, the Time and Labor period end date is used. If segmentation exists, the segment or slice end date is used.) The system element retrieves the effective-dated definition of the rate code.
Defining Chartfield Value Overrides at the Payee Level
After you map the PeopleSoft standard configuration chartfields from Time and Labor to Global Payroll variables or system elements, the system knows what chartfields are associated with these earning or deductions. Global Payroll uses these SOVRs to store the payee-level chartfield values that the system passes from Time and Labor to Global Payroll.

 Mapping TRCs to Run Types
Mapping TRCs to Run Types
Access the Run Types page (Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Framework, Processing, Run Types, Run Types).
In Global Payroll, a run type must be associated with each calendar. The run type identifies the type of process (payroll or absence), the process list, and the valid TRCs for the pay run. During the payroll process, the system retrieves the effective-dated definition (as of the Global Payroll period end date) for each TRC listed on the run type. It then retrieves only the payable time entries for TRCs that are included in the run type.
In Time and Labor, you map earning, deduction, and absence take elements to the corresponding TRCs.
See Also

 Creating Triggers for Payable Time
Creating Triggers for Payable Time
Access the Trigger Definition page (Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Triggers, Trigger Definitions, Trigger Definitions).
Global Payroll uses triggers to detect changes to data that result in some type of system action. You create two triggers (an iterative trigger and a retroactive trigger) that detect the changes that Time and Labor makes to the payable time entries that have been sent to Global Payroll. These changes trigger retroactive processing the next time that you run the payroll process.
Note. Before creating the retroactive trigger, define the trigger event ID on the Retro Event Definition page.
|
Record (Table) Name |
Select TL_PAYABLE_TIME. |
|
Trigger Type |
Select Retro or Iterative. |
|
Trigger Status |
Select Active. |
|
Trigger Level |
Select Record. |
|
Trigger Event ID |
Applicable to the retroactive trigger only. |
|
Trigger Effdt Type |
Applicable to the retroactive trigger only. |
See Also
Setting Up Trigger Definitions

 Mapping Tasks to Supporting Elements
Mapping Tasks to Supporting Elements
Access the Task Code Map page (Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Integration, Task Code Map, Task Code Map).
Tasks define companies, business units, products, departments, and other entities to which payees can report time.
If you don't map task entities, Global Payroll calculates costs at the earning and deduction level only and cannot supply Time and Labor with a cost breakdown by task. You can create a separate mapping scheme for each country in which your organization operates.
Task Mapping
Insert a row for each Time and Labor element that you want to load into Global Payroll. During the bundling process, Global Payroll consolidates instances of payable time that share the same values for the entities that you select. For example, if you select BUS_UNIT in the Task Field Code field, instances of payable time that share the same business unit are bundled at the start of the pay run.
|
Task Field Code |
Select the Time and Labor entity to map to a supporting element. Values are: BUS_UNIT (business unit), COMBO_CD (combination code), COMPANY, COUNTRY, DEPTID (department ID), JOBCODE, LOCATION, PRODUCT, RATE_VAL (rate value), STATE, TASK, and USERFIELD1 to 5. |
|
Element Type |
Select the type of element to which the task code is mapped. Values are: Variable and SystemElem (system element). |
|
Element Name |
If you selected DEPTID, LOCATION, or JOBCODE as the task field code and SystemElem as the element type, the name of the element that retrieves the value of the task entity appears in this field. Otherwise, select the name of the element that you are mapping the task to. You can select from system or variable elements only, depending on the value in the Element Type field. |
|
SetID Field Code and Supporting Element |
If you selected DEPTID, LOCATION, or JOBCODE as the task field code and SystemElem as the element type, the system displays the SetID field code that is associated with the element and the name of the system element that's associated with the SetID field code, respectively. |
 Running a Payroll with Time and Labor Data
Running a Payroll with Time and Labor Data
This section provides an overview of retroactive processing and discusses how to:
Prepare for a pay run.
Start a pay run.
Cancel a pay run.

 Understanding Retroactive Processing
Understanding Retroactive ProcessingPayable time that is adjusted in Time and Labor creates two rows of data: one that reverses or offsets the old value and one that contains the new value. Global Payroll ignores the original row and offset row and processes the newly created row.
Changes to Time and Labor data create a retro trigger and cause the pay period to be recalculated and corrected in either the current pay period or in a forwarding period.

 Preparing for a Pay Run
Preparing for a Pay RunTo prepare for a pay run:
Ensure that the Time and Labor Time Administration process has been run.
For each approved absence event, Time and Labor looks at the code for the absence take element, the beginning and end dates of the absence and, when applicable, partial hours for absences of less than a day. It also triggers the Schedule Resolution process in Time and Labor, which looks at the absent days for which partial hours were not reported and determines the number of hours that the time reporter was absent based on his or her default schedule.
The Time Administration process must also be run to convert reported and scheduled time to payable time.
Note. Time and Labor processes only approved absences; unapproved absences are not passed to the Time and Labor Payable Time table.
Create calendars that select Time and Labor data.
When using the Calendars - Definition page in Global Payroll to create calendars for the pay run, set up the calendars to:
Retrieve data for the period of time that you specify.
Select the time period in the Time & Labor Calendar field. You select from a prompt table that displays all calendar periods. If you leave the Time & Labor Calendar field blank, payable time is not retrieved. The Time and Labor calculation period ID can be the same as or different from the calculation period ID. For example, if your Time and Labor calculation period ID is March and the current calculation period ID is April, payees (in order to be selected) must have payable time in March and have been active for at least one day in April.
Use a run type that identifies the TRCs that you want to process.
Ensure that the Time Administration process has been run for the payees that you want to pay.
Note. In Global Payroll, you run the payroll process by pay group. In Time and Labor, you run the Time Administration process by workgroup. Before starting the pay run, be sure that the Time Administration process has been run for all payees that are included in your pay run.
See Sharing Work Schedules with Time and Labor, Linking Criteria Associated with a Calendar.

 Starting a Pay Run
Starting a Pay RunTo start a pay run with Time and Labor data:
Start the Identify phase of the Payroll process to select payees.
Global Payroll identifies payees who have payable time for TRCs that are mapped to the calendar's run type and the time period that is defined by the Time & Labor Calendar field on the Calendars - Definition page. (You can start the Identify process by itself or with the Calculate process.)
Start the Calculate phase to select payable time.
Global Payroll loads payable time for the selected payees into the Generate Positive Input table. It retrieves only the rows of payable time that have:
A TRC that is mapped to the calendar's run type.
For current period entries, a payable status of:
ES (Estimated - Ready for Payroll)
AP (Approved - Goes to Payroll)
SP (Sent to Payroll)
RP (Rejected by Payroll)
For retro periods entries, any payable status except:
NA (Needs Approval)
CL (Closed) when the Pay System field is not set to GP (Global Payroll)
IG (Ignore)
NP (No Pay)
OE (Online Estimate)
Global Payroll also updates the payable status of each entry:
SP - For all payable time entries that are loaded into Global Payroll except those with a payable status of PD (Paid - Labor Distributed) or DL (Paid - Labor Diluted).
IG - For all payable time entries that the system will not use as a result of changes by Time and Labor that created offset and new entries.
Review results and correct errors.
Review the Payee Messages page for processing errors and messages. You can view payable time entries that have gone through the Calculate phase on the Generated Positive Input - Payroll page. Look for entries with a Source value of Time&Labor. You can also see processed bundled payable time entries on the Positive Input - Payroll page.
To adjust or correct entries that originated in Time and Labor, make the changes in Time and Labor and then run the Calculate phase again. This ensures that the Time and Labor data and Global Payroll data remain in sync.

 Cancelling a Pay Run
Cancelling a Pay RunIf you cancel a pay run, Global Payroll deletes the payable data that was loaded from Time and Labor and updates the payable status for each payable time entry to RP with a reason code of Cancelled by Payroll, unless either of the following conditions exist:
The payable status is PD, DL, CL, or TP (Taken - Used by Payroll).
The payable time has also been sent to another payroll system (according to the Pay System flag associated with the entry).
 Updating the Payable Status of Payable Time Entries
Updating the Payable Status of Payable Time Entries
This section provides an overview of updating the status of payable time and discusses how to update the payable status and return cost data.

 Updating the Status of Payable Time
Updating the Status of Payable TimeLaunch the Update process from the Global Payroll Send Costs to Time and Labor page to start the update.
The Update process:
Updates the payable status for each entry that was set to SP:
CL with a reason code of Not Distributed if the entry was processed, but the Labor Distribution feature is not enabled in Time and Labor.
RP with a reason code of Not Processed if the entry was retrieved but not processed.
This status applies when payable time is not processed by Global Payroll. This can result from a user manually entered positive input for the same earning or deduction element. Manually entered positive input always takes precedence. This can also occur if the employee is not eligible for the earning or deduction or if the payee was cancelled from the payroll.
Returns the original Time and Labor sequence number for each payable time entry along with the corresponding cross-reference numbers that Global Payroll generated during the bundling process.
The cross-reference numbers tell Time and Labor which entries were bundled, making it possible to link the costs that were calculated for earning and deduction to the daily detail.
If the Labor Distribution feature in Time and Labor is enabled, sends cost data that is associated with payable time entries to Time and Labor.
If Labor Distribution is enabled but Labor Dilution is not, the labor distribution amount and diluted labor distribution amount sent by Global Payroll are the same.
If Labor Distribution and Labor Dilution are activated in Time and Labor, Global Payroll sends the Labor Distribution Amounts to Time and Labor and invokes the Labor Dilution process.
See Also
Labor Distribution and Dilution

 Page Used to Update the Payable Status of Payable Time Entries
Page Used to Update the Payable Status of Payable Time Entries|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
GP_TL_PREPARE |
Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Time and Labor/GL Costs, Send Costs to Time and Labor, Send Costs to Time and Labor |
Update the payable status of payable time entries in Time and Labor; return cost data if Labor Distribution is enabled. Before using this page, you must finalize the pay run. |

 Updating the Payable Status and Returning Cost Data
Updating the Payable Status and Returning Cost Data
Access the Send Costs to Time and Labor page (Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Time and Labor/GL Costs, Send Costs to Time and Labor, Send Costs to Time and Labor).
You can run the update process only once per pay run. If you used process streams to run the payroll, you can use the same process streams to send data back to Time and Labor. You start the run control for one stream at a time, returning to this page after each launch to invoke the next stream.
Payroll Run
|
Calendar Group |
Select the calendar group for sending data to Time and Labor. You can select finalized calendar groups only. |
|
Stream Number and Process Streams |
If the selected calendar group is defined for stream processing, the Process Streams check box is selected. Enter the stream number to process. |
|
Posting Date |
Displays the current date as the default value that the user can change to the desired posting date. If GL has been run, the field is not available for entry and it displays the GL posting date. |
Processing Options
|
Update Statistics |
This check box is for the database administrator to help with fine-tuning system performance. If selected, the system generates statistics during batch processing that provide information about how worktables are being used. |
Calendars List
|
Pay Group and Calendar ID |
The Pay Group field displays the pay group that is associated with the calendar that appears in the Calendar ID field (associated with the Calendar Group ID field). |
|
Payment Date |
Displays the calendar's payment date. |
Streams
|
Stream |
Displays the number of the stream that has been processed. |
|
EmplID From and EmplID To |
Displays the employees who were processed for this stream. |
|
Sent Time and Labor At |
Displays the time that the process stream was sent to Time and Labor. |
See Also
 Sharing Work Schedules with Time and Labor
Sharing Work Schedules with Time and Labor
Time and Labor and Global Payroll use many of the same pages and records for setting up and assigning schedules. If you're using both systems, you create and assign schedules only once. However, note that the scheduling information that is displayed varies in each application:
When you access the Assign Work Schedule page in Global Payroll, you see fields for assigning alternate work schedules.
These fields are hidden when you access the same page in Time and Labor.
When you access the Shift page in Global Payroll, you can enter data in up to four user-defined schedule configuration fields.
These are display-only fields when you access the same page in Time and Labor.
When you access the Assign Work Schedule page in Global Payroll, you can view any payee for which you have department security.
When you access these pages in Time and Labor, that application's security options determine which payees you can view.
When you access the Assign Work Schedule page in Global Payroll or Time and Labor, the schedule that you see might differ if default schedules are in use.
In Time and Labor, a payee's default schedule is based on work group; in Global Payroll, it is based on pay group. The page views differ when a payee is set up to use the default schedule and the pay group and work group have been assigned different default schedules.
See Also