1 Introduction and Preinstallation Checklist
This guide uses a step-by-step approach to assist you with the installation of Oracle Fail Safe. Oracle Fail Safe consists of multiple components: Oracle Fail Safe Manager, Oracle Services for MSCS, and server components specific to Oracle Fail Safe.
Oracle Fail Safe Manager is a graphical user interface using which you configure and manage Oracle single-instance databases, Oracle Management Agent, generic services, and so on for high availability in an MSCS cluster. Oracle Services for MSCS is the main server component.
Typically, you perform the installation using Oracle Universal Installer graphical user interface. If you perform the same installation on multiple systems, you may run Oracle Universal Installer in silent mode to automate the installation process in batch files or scripts. Silent installations are described in Appendix B.
The following topics are discussed in this chapter:
1.1 Cluster Setup Prerequisites
You must perform the following configuration tasks before the installation of Oracle Fail Safe:
-
Ensure that you have a cluster hardware configuration listed on the Microsoft hardware compatibility list for Microsoft Windows clusters.
-
Check that each system has the proper Oracle Net tnsnames.ora configuration to allow the system to connect to its local database (if applicable) and the databases on the other systems.
-
If you install Oracle Services for MSCS on a subset of the nodes in the cluster, check that the Cluster Group is running on one of the nodes where you installed Oracle Fail Safe. You can view or change the location of the Cluster Group using MSCS Cluster Administrator.
-
Ensure that Microsoft Windows Event Viewer is not running while installing Oracle Services for MSCS. This is an issue only if installing on top of an existing installation (in-place upgrade).
Note:
If you attempt to install Oracle Services for MSCS while the Microsoft Windows Event Viewer is running, the installation procedure may return an error indicating that it cannot copy thefsus.dllfile (fsja.dllon Japanese systems) and asks you to retry, ignore, or cancel. You can continue the installation if you stop the Microsoft Windows Event Viewer and then click Retry in the Oracle Fail Safe installation Error window.
1.2 Software Compatibility
Refer to Oracle Fail Safe Release Notes for information on current software compatibility for different operating systems.
1.3 Recommended Order for Software Installation
Although this guide describes the Oracle Fail Safe installation in detail, other products must also be installed to implement the Oracle Fail Safe environment. Figure 1-1 shows the recommended order for installing software on a two-node cluster
Note:
(The numbers in Figure 1-1 do not correspond to the numbered steps in the subsequent list because the list contains more detailed information than the figure.Figure 1-1 Recommended Order for Installing Software on a Two-Node Cluster
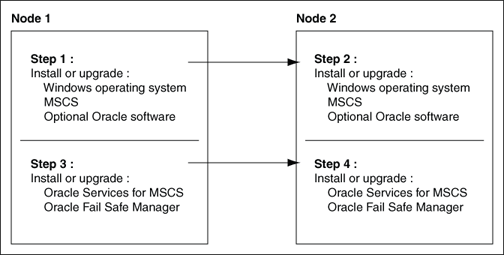
Description of "Figure 1-1 Recommended Order for Installing Software on a Two-Node Cluster"
The following list provides more detail about the installation order and other tasks to help you get started with Oracle Fail Safe:
-
On each cluster node, install:
-
Microsoft Distributed Transaction Coordinator and correctly configure for a cluster environment.
See Oracle Fail Safe Release Notes for information about the versions of Microsoft Windows that can be used with Oracle Fail Safe. The Oracle Fail Safe Web site contains more information about installing Microsoft Cluster Server.
-
On each cluster node for each Oracle product that you intend to install, create an Oracle home on a private disk (for example, the system disk). To minimize downtime during future upgrades, Oracle recommends that you use a separate Oracle home for each major component (for example, a separate Oracle home each for the database, application software, and Oracle Fail Safe). To allow applications to fail over, ensure that the Oracle homes on each cluster node have the same name. For example, name the Oracle Fail Safe home on each cluster node ofs_home, and name the database home on each cluster node dbs_home.
-
On each cluster node, install the optional Oracle software (Oracle Database and other applications) that you plan to use with Oracle Fail Safe. Place all application and database data, control, and log files on shared cluster disks so that they can fail over.
If you are installing Oracle Database software, you can create the database before or after you install Oracle Fail Safe. Create the database as you would in a noncluster environment, including the database listener. However, the database must be created on a cluster disk or disks.
-
On each cluster node, install the server component of Oracle Fail Safe, Oracle Services for MSCS. If you want, you can install the client component, Oracle Fail Safe Manager, at the same time.
See Chapter 2 for complete information about installing Oracle Fail Safe.
-
On one or more client systems, optionally, install Oracle Fail Safe Manager (for example, to set up additional management consoles).
Figure 1-2 lists the software and the files that should be installed on private disks and shared-nothing cluster disks.
Figure 1-2 Software Installed on Private, Shared-Nothing Cluster Disks
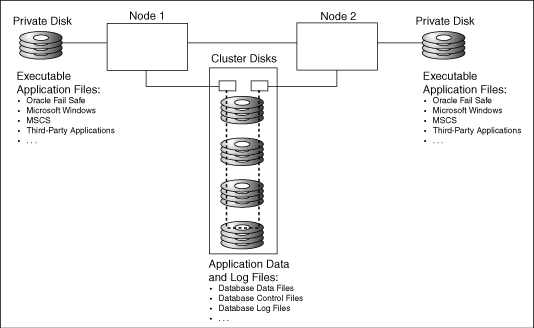
Description of "Figure 1-2 Software Installed on Private, Shared-Nothing Cluster Disks"
1.4 Adding a Node to an Existing Cluster
If you want to add a node to an existing cluster, perform the following operations:
-
Follow Microsoft's instructions to add a node to a cluster.
-
On the new node, install any desired optional Oracle software (Oracle Database and other applications) that you plan to use with Oracle Fail Safe. Install executable application files located on private disks (for example, on the system disk for each node).
-
On the new node, install Oracle Services for MSCS (which is the server component of Oracle Fail Safe). You can install Oracle Fail Safe Manager at the same time.
1.5 Adding a Sample Database
Oracle Fail Safe includes a Create Sample Database command that installs a preconfigured sample database on a cluster disk specified by the user. The sample database has limited functions and is intended only for testing purposes and for use with the online Oracle Fail Safe tutorial. The sample database should not be used for production. To create a database for production, use Database Configuration Assistant or create the database manually.
1.6 Postinstallation Procedures
After you have successfully installed Oracle Fail Safe, perform the following tasks:
-
If you installed optional Oracle software:
-
Configure application data and log files on the shared cluster disks.
-
Configure alert and trace files on either the shared cluster disks or on the private disk.
Configuring alert and trace files on private disks allows the administrator to determine the node on which problems occur, but requires that you maintain multiple sets of files. Placing parameter files on private disks is recommended only when you want the parameters to be different on each cluster node. For example, this can be useful if you want a database to use fewer resources on its failover node than on its primary node (such as when you know that another application or database on the failover node needs resources).
For information about re-creating databases on cluster disks, refer to the Import/Export documentation that is specific to your database.
-
-
Start Oracle Fail Safe Manager, connect to the cluster alias with a domain account that has Administrator privileges on each cluster node, and run the
Verify Clusteroperation when prompted.See Chapter 3 for information to help you get started with Oracle Fail Safe.
-
Refer to the Oracle Fail Safe Tutorial for step-by-step information about creating a group and adding resources to it. (To run the tutorial from the Oracle Fail Safe Manager, select Help, and then select Tutorial.)
-
Run the
fssvrcommand qualifier,/GETSECURITY, which is provided by Oracle Fail Safe on each cluster node. The/GETSECURITYqualifier displays security information about the system where the command is run.The command and its associated output should be similar to the following:
fssvr /getsecurity Looking up user account information for OracleMSCSServices. The user account must be a domain user acount with local Administrator privileges. The user account must also have the 'Log on as batch job' privilege. User account specified for OracleMSCSServices is NEDCDOMAIN\cluadmin User account specified has local Administrator privileges User account has the 'Log on as batch job' privilege Looking up user account information for Cluster Service. The user account must be a domain user account with local Administrator privileges. The user account must also have the 'Log on as batch job' privilege. User account specified for Cluster Service is NEDCDOMAIN\cluadmin User account specified has local Administrator privileges User account has the 'Log on as batch job' privilege Checking to see if DCOM is enabled. DCOM must be enabled. DCOM is enabled.