| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide 11g Release 1 (11.1.1) E10105-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide 11g Release 1 (11.1.1) E10105-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
Deployment is the process of packaging application files as an archive file and transferring them to a target application server. This chapter describes how to deploy applications, such as Java EE or SOA applications, to Oracle Fusion Middleware.
It contains the following topics:
Deploying, Undeploying, and Redeploying Java EE Applications
Deploying, Undeploying, and Redeploying Oracle ADF Applications
Deploying, Undeploying, and Redeploying SOA Composite Applications
Deploying, Undeploying, and Redeploying WebCenter Applications
Changing MDS Configuration Attributes for Deployed Applications
Oracle WebLogic Server provides a Java EE-compliant infrastructure for deploying, undeploying, and redeploying Java EE-compliant applications and modules.
You can deploy the following into Oracle WebLogic Server:
A complete Java EE application packaged as an Enterprise Archive (EAR) file.
Standalone modules packaged as Java Archive files (JARs) containing Web Services, Enterprise JavaBeans (EJBs), application clients (CARs), or resource adapters (RARs).
An ADF application. Oracle Application Development Framework (Oracle ADF) is an end-to-end application framework that builds on Java Platform, Enterprise Edition (Java EE) standards and open-source technologies to simplify and accelerate implementing service-oriented applications.
An Oracle SOA Suite composite application. A SOA composite application is a single unit of deployment that greatly simplifies the management and lifecycle of SOA applications.
An Oracle WebCenter application. WebCenter applications differ from traditional Java EE applications in that they support run-time customization, including the application's pages, the portlets contained within these pages, and document libraries.
A Metadata Archive (MAR) is a compressed archive of selected metadata, such as the application-level deployment profile, for an application. A MAR is used to deploy metadata content to the metadata service (MDS) repository. The following application types use a MAR as a container for content that is deployed to the MDS repository: ADF applications, SOA composite applications, and Oracle WebCenter applications.
You can use Fusion Middleware Control, Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console, Oracle JDeveloper, or the command line to deploy, undeploy, or redeploy an application. Which method you use depends on the type of application, as described in Table 8-1.
Table 8-1 Tools to Deploy Applications
| Type of Application | Tools to Use |
|---|---|
|
Pure Java EE application |
Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Fusion Middleware Control: Deployment Wizard Oracle JDeveloper WLST command line |
|
ADF application |
Fusion Middleware Control: Deployment Wizard Oracle JDeveloper WLST command line |
|
SOA Composite application |
Fusion Middleware Control: SOA Composite Deployment Wizard Oracle JDeveloper WLST command line |
|
WebCenter application |
Fusion Middleware Control: Deployment Wizard Oracle JDeveloper WLST command line |
If your application uses an MDS Repository, you must register the repository with the Oracle WebLogic Server domain before you deploy your application. Applications such as custom Java EE applications developed by your organization and some Oracle Fusion Middleware component applications, such as Oracle B2B, and Oracle Web Services Manager, use an MDS Repository. For information about the MDS Repository and registering the repository, see Section 11.3.
|
Note: If your application contains an application-level credential store, and you are moving the application from a test to a production environment, you must reassociate the credential store, as described in "Reassociating the Domain Policy Store" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Security Guide. |
A data source is a Java object that application components use to obtain connections to a relational database. Specific connection information, such as URL or user name and password, are set on a data source object as properties and do not need to be explicitly defined in an application's code. This abstraction allows applications to be built in a portable manner, because the application is not tied to a specific back-end database. The database can change without affecting the application code.
Applications use the Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI) API to access a data source object. The application uses a JNDI name that is bound to the data source object. The JNDI name is logical and can be mapped to any data source object. Like data source properties, using JNDI provides a level of abstraction, since the underlying data source object can change without any changes required in the application code. The end result is the details of accessing a database are transparent to the application.
|
See Also: Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuring and Managing JDBC for Oracle WebLogic Server for more information about data sources |
When you configure certain Oracle Fusion Middleware components, such as Oracle SOA Suite or Oracle WebCenter, using the Oracle WebLogic Server Configuration Wizard, you specify the data source connection information. If the components use the MDS Repository, the Configuration Wizard prepends "mds-" to the data source name to indicate that the data source is a system data source used by MDS Repository.
|
See Also: Oracle Fusion Middleware Creating Domains Using the Configuration Wizard for information about specifying data sources with the Configuration Wizard |
To create an MDS data source, you should use Fusion Middleware Control or WLST to set the correct attributes for the data source. The MDS data source is displayed in the navigation pane in Fusion Middleware Control and in the domain structure in the Administration Console. If your application uses an MDS Repository, you must register the repository with the Oracle WebLogic Server domain before you deploy your application. For information about the MDS Repository and registering the repository, see Section 11.3.
|
Note: When you create the data source, you must use the MDS schema created by the Repository Creation Utility (RCU), not other schemas. |
Although it is not recommended, you can also use the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console to create a MDS data source. If you do, note the following:
You must prefix the data source name with "mds-" if you intend it to be used with MDS Repository.
You must target the data source to the Administration Server and to all Managed Servers to which you are deploying applications that need the data source.
You must turn off global transactions.
If you are using RAC or Oracle Fusion Middleware Cold Failover Cluster, you must configure multi data sources. To do so, you must use the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console. Note that if you create a multi data source and you add an existing MDS data source to it, the data source you added is no longer considered a valid MDS repository. The repository is not displayed in Fusion Middleware Control or Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console. For example, the MDS repository is not listed in the Fusion Middleware Control navigation pane and is not displayed as a choice for a target metadata repository when you deploy an application.
|
See Also: Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuring and Managing JDBC for Oracle WebLogic Server for more information about configuring multi data sources |
You can use Fusion Middleware Control, Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console, Oracle JDeveloper, or the command line to deploy, undeploy, or redeploy a Java EE application. The following topics describe using Fusion Middleware Control and the command line to accomplish these tasks.:
|
See Also: Oracle Fusion Middleware Deploying Applications to Oracle WebLogic Server for information about deploying using Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console and for more information about using the WLST command line |
You can deploy an application to a WebLogic Managed Server or a cluster. This section describes how to deploy an application to a Managed Server.
To deploy a Java EE application to a Managed Server using Fusion Middleware Control:
From the navigation pane, expand the farm, then WebLogic Domain, and then the domain.
Select the server in which you want to deploy the application.
The server home page is displayed.
From the WebLogic Server menu, choose Application Deployment, then Deploy.
The Deployment Wizard, Select Archive page is displayed, as shown in the following figure:

In the Archive or Exploded Directory section, you can select one of the following:
Archive is on the machine where this browser is running. Enter the location of the archive or click Browse to find the archive file.
Archive or exploded directory is on the server where Enterprise Manager is running. Enter the location of the archive or click Browse to find the archive file.
In the Deployment Plan section, you can select one of the following:
Create a new deployment plan when deployment configuration is done.
Deployment plan is on the machine where this web browser is running. If you select this option, enter the path to the plan.
Deployment plan is on the server where Enterprise Manager is running. If you select this option, enter the path to the plan.
Click Next.
The Select Target page is displayed.
Select the target to which you want to deploy the application. The Administration Server, Managed Servers, and clusters are listed. You can select a cluster, one or more Managed Server in the cluster, or a Managed Server that is not in a cluster. Although the Administration Server is shown in the list of targets, you should not deploy an application to it. The Administration Server is intended only for administrative applications such as the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
Click Next.
The Application Attributes page is displayed.
In the Application Attributes section, for Application Name, enter the application name.
In the Context Root of Web Modules section, if the web module does not have the context root configured in the application.xml file, you can specify the context root for your application. The context root is the URI for the web module. Each web module or EJB module that contains web services may have a context root.
In the Distribution section, you can select one of the following:
Distribute and start application (servicing all requests)
Distribute and start application in admin mode (servicing only admin requests)
Distribute only
Click Next.
The Deployment Wizard, Deployment Settings page is displayed.
On this page, you can perform common tasks before deploying your application or you can edit the deployment plan or save it to a disk. Depending on the type of application, you can:
Configure Web modules: Click Go to Task in the Configure Web Modules row. The Configure Web Modules page is displayed. Click Configure General Properties to view and edit the general configuration for the Web Module or Map Resource References to map the resource references.
For example, you can change the session invalidation interval or the maximum age of session cookies.
Configure application security. Click Go to Task in the Configure Application Security row. Depending on what type of security is used, different pages are displayed.
If the application contains jazn-data.xml or cwallet.sso, the Configure Application Security page displays the following sections:
If it contains jazn-data.xml, the page displays the Application Policy Migration section.
If it contains cwallet.sso, the page displays the Application Credential Migration section.
If it contains both, the page displays both sections.
For information about these settings, see "Deploying JavaEE and ADF Applications with Oracle Enterprise Manager" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Security Guide.
If the application contains neither of these files, the Configure Application Security page displays the following options:
DD Only: Use only roles and policies that are defined in the deployment descriptors.
Custom Roles: Use roles that are defined in the Administration Console; use policies that are defined in the deployment descriptor.
Custom Roles and Policies: Use only roles and policies that are defined in the Administration Console.
Advanced: Use a custom model that you have configured on the realm's configuration page.
Configure EJB modules: Click Go to Task in the Configure EJB modules row. The Configure EJB Modules page is displayed. Click Configure EJB Properties to view and edit the general configuration for the EJBs or Map Resource References to map the resource preferences.
For example, you can configure the maximum number of beans in the free pool or the network access point.
Expand Deployment Plan.
You can edit and save the deployment plan, if you choose. If you edit the deployment plan and change descriptor values, those changes are saved to the deployment plan. In addition, the following configurations are saved to the deployment plan:
Application attributes
Web module configuration
EJB configuration
Application attributes related to MDS are stored in the file adf-config.xml. Application security attributes are stored in weblogic-application.xml.
Fusion Middleware Control updates the relevant files and repackages the .ear file.
Click Deploy.
Fusion Middleware Control displays processing messages.
When the deployment is completed, click Close.
To deploy an application to multiple servers at the same time, navigate to the domain. Then, from the WebLogic Domain menu, select Application Deployment, then Deploy. The deployment wizard displays a page where you can select the servers.
You can deploy an application using the WLST command line. To deploy a Java EE application when WLST is connected to the Administration Server, you use the WLST command deploy, using the following format:
deploy(app_name,path, [targets] [stageMode], [planPath], [options])
You must invoke the deploy command on the computer that hosts the Administration Server.
For example, to deploy the application mainWebApp:
deploy("myApp","/scratch/applications/wlserver_10.3/samples/server/examples/build/mainWebApp")
You can also deploy the application using the weblogic.deployer, as shown in the following example:
java weblogic.Deployer -adminurl http://localhost:7001 -user weblogic -password weblogic -deploy -name myApp c:\localfiles\mainWebApp -plan c:\localfiles\productionEnvPlan.xml
|
See Also:
|
You can undeploy an application from a Managed Server or a cluster. This section describes how to undeploy an application from a Managed Server.
To undeploy a Java EE application from a Managed Server using Fusion Middleware Control:
From the navigation pane, expand Application Deployments.
Select the application to undeploy.
The application home page is displayed.
From the Application Deployment menu, choose Application Deployment, then Undeploy.
The confirmation page is displayed.
Click Undeploy.
Processing messages are displayed.
When the operation completes, click Close.
Alternatively, you can navigate to the domain, Managed Server, or cluster. Then, from the target's menu, choose Application Deployment, then Undeploy. In the Select Application page, select the application you want to undeploy.
You can undeploy an application using the WLST command line. To undeploy a Java EE application when WLST is connected to the Administration Server, you use the WLST command undeploy, using the following format:
undeploy(app_name,path, [targets] [options])
You must invoke the undeploy command on the computer that hosts the Administration Server.
For example, to undeploy the application businessApp from all target servers and specify that WLST wait 60,000 ms for the process to complete:
wls:/mydomain/serverConfig> undeploy('businessApp', timeout=60000)
You can redeploy an application that has been undeployed from a WebLogic Managed Server or a cluster. This section describes how to redeploy an application to a Managed Server.
To redeploy a Java EE application to a Managed Server using Fusion Middleware Control:
From the navigation pane, expand the farm, then Application Deployments.
Select the application.
The application home page is displayed.
From the Application Deployment menu, choose Application Deployment, and then Redeploy.
The Select Application page is displayed.
Click Next.
In the Archive or Exploded Directory section, you can select one of the following:
Archive is on the machine where this browser is running. Then, enter the location of the archive or click Browse to find the archive file.
Archive or exploded directory is on the server where Enterprise Manager is running. Then, enter the location of the archive or click Browse to find the archive file.
In the Deployment Plan section, you can select one of the following:
Create a new deployment plan when deployment configuration is done.
Deployment plan is on the machine where this web browser is running. If you select this option, enter the path to the plan.
Deployment plan is on the server where Enterprise Manager is running. If you select this option, enter the path to the plan.
Click Next.
The Application Attributes page is displayed.
Click Next.
The Deployment Wizard, Deployment Settings page is displayed.
On this page, you can perform common tasks before deploying your application or you can edit the deployment plan or save it to a disk. Depending on the type of application, you can:
Configure Web modules
Configure application security
Configure EJB modules
Expand Deployment Plan.
You can edit and save the deployment plan, if you choose. If you edit the deployment plan and change descriptor values, those changes are saved to the deployment plan. In addition, the following configurations are saved to the deployment plan:
Application attributes
Web module configuration
EJB configuration
Application attributes related to MDS are stored in the file adf-config.xml. Application security attributes are stored in weblogic-application.xml.
Fusion Middleware Control updates the relevant files and repackages the .ear file.
Click Redeploy.
Processing messages are displayed.
When the operation completes, click Close.
You can redeploy an application using the WLST command line. To redeploy a Java EE application when WLST is connected to the Administration Server, you use the WLST command redeploy, using the following format:
redeploy(app_name,planpath, [options])
You must invoke the redeploy command on the computer that hosts the Administration Server.
For example, to redeploy the application businessApp from all target servers:
redeploy('businessApp')
The Oracle Application Development Framework (Oracle ADF) is an end-to-end application framework that builds on Java Platform, Enterprise Edition (Java EE) standards and open-source technologies to simplify and accelerate implementing service-oriented applications.
You can use Fusion Middleware Control, Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console, Oracle JDeveloper, or the command line to deploy, undeploy, or redeploy an Oracle ADF application. The following topics describe using Fusion Middleware Control, the Administration Console, and the command line to accomplish these tasks:
|
See Also: Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework for information on developing ADF applications and for deploying them using Oracle JDeveloper |
You can deploy an application to a WebLogic Managed Server or a cluster. This section describes how to deploy an application to a Managed Server. This example assumes that you have created an .ear file containing the ADF application.
To deploy an Oracle ADF application using Fusion Middleware Control:
From the navigation pane, expand the farm, then WebLogic Domain, and then the domain.
Select the server in which you want to deploy the application.
The server home page is displayed.
From the WebLogic Server menu, choose Application Deployment, then Deploy.
The Deployment Wizard, Select Archive page is displayed.
In the Archive or Exploded Directory section, you can select one of the following:
Archive is on the machine where this browser is running. Then, enter the location of the archive or click Browse to find the archive file.
Archive or exploded directory is on the server where Enterprise Manager is running. Then, enter the location of the archive or click Browse to find the archive file.
In the Deployment Plan section, you can select one of the following:
Create a new deployment plan when deployment configuration is done.
Deployment plan is on the machine where this web browser is running. If you select this option, enter the path to the plan.
Deployment plan is on the server where Enterprise Manager is running. If you select this option, enter the path to the plan.
Click Next.
The Select Target page is displayed.
Select the target to which you want to deploy the application.
Click Next.
The Application Attributes page is displayed, as shown in the following figure:
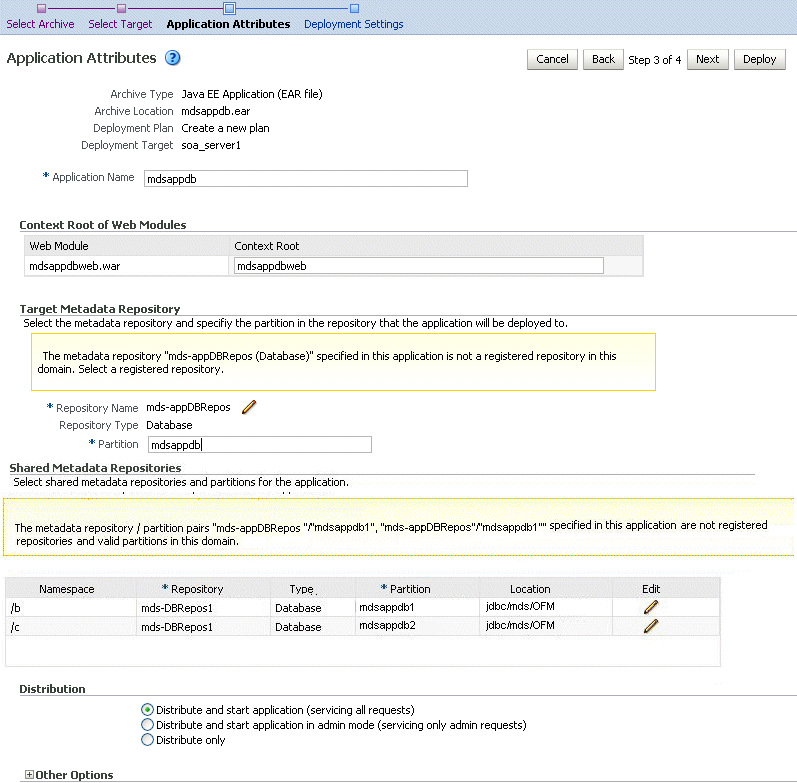
In the Application Attributes section, for Application Name, enter the application name.
In the Context Root of Web Modules section, if the web module does not have the context root configured in the application.xml file, you can specify the context root for your application. The context root is the URI for the web module. Each web module or EJB module that contains web services may have a context root.
The Target Metadata Repository section allows you to choose the repository and partition for this application. If the partition name is not specified in the adf-config.xml file, the application name plus the version is used as the default partition name. This ensures that the partition used is unique in the domain so that the metadata for different applications will not be accidentally imported into the same repository partition and overwrite each other. Typically, each application's metadata is deployed to its own partition.
To change the repository, click the icon next to the Repository Name. In the Metadata Repositories dialog box, select the repository and click OK.
To change the partition, enter the partition name in Partition Name. Oracle recommends that you create a new partition for each application. If you enter a name of a partition that does not exist, the partition is created.
The adf-config.xml file in the .ear file is updated with the new information.
If the partition or repository specified in the application is not valid in the domain, Fusion Middleware Control displays a message.
If the application's adf-config.xml file archive contains MDS configuration for an MDS shared repository, the Shared Metadata Repository section is displayed. It allows you to choose the repository and partition for this application. If the partition or repository specified in the application is not valid in the domain, Fusion Middleware Control displays a message.
If you change the repository or partition, the adf-config.xml file in the .ear file is updated with the new information.
In the Distribution section, you can select one of the following:
Distribute and start application (servicing all requests)
Distribute and start application in admin mode (servicing only admin requests)
Distribute only
Click Next.
The Deployment Wizard, Deployment Settings page is displayed.
On this page, you can perform common tasks before deploying your application or you can edit the deployment plan or save it to a disk. Depending on the type of application, you can:
Configure Web modules: Click Go to Task in the Configure Web Modules row. The Configure Web Modules page is displayed. Click Configure General Properties to view and edit the general configuration for the Web Module or Map Resource References to map the resource references.
For example, you can change the session invalidation interval or the maximum age of session cookies.
Configure application security. Click Go to Task in the Configure Application Security row. Depending on what type of security is used, different pages are displayed.
If the application contains jazn-data.xml or cwallet.sso, the Configure Application Security page displays the following sections:
If it contains jazn-data.xml, the page displays the Application Policy Migration section.
If it contains cwallet.sso, the page displays the Application Credential Migration section.
If it contains both, the page displays both sections.
For information about the settings in this page, see "Deploying JavaEE and ADF Applications with Oracle Enterprise Manager" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Security Guide
If the application contains neither of these files, the Configure Application Security page displays the following options:
DD Only: Use only roles and policies that are defined in the deployment descriptors.
Custom Roles: Use roles that are defined in the Administration Console; use policies that are defined in the deployment descriptor.
Custom Roles and Policies: Use only roles and policies that are defined in the Administration Console.
Advanced: Use a custom model that you have configured on the realm's configuration page.
Configure EJB modules: Click Go to Task in the Configure EJB modules row. The Configure EJB Modules page is displayed. Click Configure EJB Properties to view and edit the general configuration for the EJBs or Map Resource References to map the resource preferences.
For example, you can configure the maximum number of beans in the free pool or the network access point.
Configure ADF Connections. To modify the ADF connections, click Go to Task in the Configure ADF Connections row. The Configure ADF Connections page is displayed, showing the current connection information. To modify a connection type, click the Edit icon for a particular row. For example, you can modify the connection information for an external application. For more information about ADF connections, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
Expand Deployment Plan.
You can edit and save the deployment plan, if you choose.
Click Deploy.
Fusion Middleware Control displays processing messages.
When the deployment is completed, click Close.
To deploy an application to multiple servers at the same time, navigate to the domain. Then, from the WebLogic Domain menu, select Application Deployment, then Deploy. The deployment wizard displays a page where you can select the servers.
You can deploy an ADF application using the WLST command line or the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
Take the following steps:
If your application uses an MDS repository, you must configure the application archive (.ear) file before you deploy your application. You must provide the repository information for the deploy target repository and any shared metadata repositories using the WLST getMDSArchiveConfig command. The repository specified must already be registered with the domain before deploying the application. The following example show how to use this command to get the MDSArchiveConfig and call the setAppMetadataRepository method to set the deploy target repository. Otherwise, your application will fail to start.
wls:/offline> archive = getMDSArchiveConfig(fromLocation='/tmp/App1.ear')
wls:/offline> archive.setAppMetadataRepository(repository='AppRepos1',
partition='partition1', type='DB', jndi='mds-jndi1')
The operation places the changes in the MDS configuration portion of the adf-config.xml file in the archive file.
Save the changes to the original .ear file, using the following command:
wls:/offline> archive.save()
Deploy the application.
To deploy an application when WLST is connected to the Administration Server, you use the WLST command deploy, using the following format:
deploy(app_name,path, [targets] [stageMode], [planPath], [options])
You must invoke the deploy command on the computer that hosts the Administration Server.
For example, to deploy the application myApp:
deploy("myApp","/scratch/applications/myApp", targets='myserver', timeout=120000))
|
See Also:
|
To deploy the application using the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console:
If you have not already done so, in the Change Center of the Administration Console, click Lock & Edit.
In the left pane of the Administration Console, select Deployments.
In the right pane, click Install.
|
See Also: The Help in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console. |
To undeploy an Oracle ADF application using Fusion Middleware Control:
From the navigation pane, expand Application Deployments, then the application to undeploy.
The application home page is displayed.
From the Application Deployment menu, choose Application Deployment, then Undeploy.
The confirmation page is displayed.
Click Undeploy.
Processing messages are displayed.
When the operation completes, click Close.
Alternatively, you can navigate to the domain, Managed Server, or cluster. Then, from the target's menu, choose Application Deployment, then Undeploy. In the Select Application page, select the application you want to undeploy.
Note that when you undeploy an application, documents stored in the MDS partition are not deleted.
When you redeploy an application, if the application contains a Metadata Archive (MAR), the contents of the MAR is imported to the application's metadata repository only if the MAR is changed. If the MAR is unchanged from previous deployment of the application, it is ignored.
To redeploy an Oracle ADF application using Fusion Middleware Control:
From the navigation pane, expand the farm, then Application Deployments.
Select the application.
The application home page is displayed.
From the Application Deployment menu, choose Application Deployment, and then Redeploy.
The Select Application page is displayed.
Click Next.
The Select Archive page is displayed.
In the Archive or Exploded Directory section, you can select one of the following:
Archive is on the machine where this browser is running. Then, enter the location of the archive or click Browse to find the archive file.
Archive or exploded directory is on the server where Enterprise Manager is running. Then, enter the location of the archive or click Browse to find the archive file.
In the Deployment Plan section, you can select one of the following:
Create a new deployment plan when deployment configuration is done.
Deployment plan is on the machine where this web browser is running. If you select this option, enter the path to the plan.
Deployment plan is on the server where Enterprise Manager is running. If you select this option, enter the path to the plan.
Click Next.
The Application Attributes page is displayed.
In the Application Attributes section, for Application Name, enter the application name.
In the Context Root of Web Modules section, if the web module does not have the context root configured in the application.xml file, you can specify the context root for your application. The context root is the URI for the web module. Each web module or EJB module that contains web services may have a context root.
The Target Metadata Repository section is displayed. It allows you to choose the repository and partition for this application:
To change the repository, click the icon next to the Repository Name. In the Metadata Repositories dialog box, select the repository and click OK.
To change the partition, enter the partition name in Partition Name. Oracle recommends that you create a new partition for each application. If you enter a name of a partition that does not exist, the partition is created.
If the application's adf-config.xml file archive contains MDS configuration for an MDS shared repository, the Shared Metadata Repository section is displayed. It allows you to choose the repository and partition for this application.
Click Next.
The Deployment Settings page is displayed.
On this page, you can perform common tasks before deploying your application or you can edit the deployment plan or save it to a disk. You can:
Configure Web modules
Configure application security
Expand Deployment Plan.
You can edit and save the deployment plan, if you choose.
Click Deploy.
Fusion Middleware Control displays processing messages.
When the deployment is completed, click Close.
In the Confirmation page, click Redeploy.
SOA composite applications consist of the following:
Service components such as Oracle Mediator for routing, BPEL processes for orchestration, human tasks for workflow approvals, business rules for designing business decisions, and complex event processing (CEP) for queries of event streams
Binding components (services and references) for connecting SOA composite applications to external services, applications, and technologies
These components are assembled together into a SOA composite application. This application is a single unit of deployment that greatly simplifies the management and lifecycle of SOA applications.
You can use Fusion Middleware Control, Oracle JDeveloper, or the command line to deploy, undeploy, or redeploy a SOA application. The following topics describe using Fusion Middleware Control to accomplish these tasks:
|
See Also: Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite |
When you deploy a SOA composite application, the deployment extracts and activates the composite application in the SOA Infrastructure.
You can deploy SOA composite applications from Fusion Middleware Control with the Deploy SOA Composite wizard:
From the navigation pane, expand the farm, then SOA, and then select soa-infra.
The SOA Infrastructure home page is displayed.
From the SOA Infrastructure menu, choose SOA Deployment, then Deploy.
The Deployment Wizard, Select Archive page is displayed, as shown in the following figure:
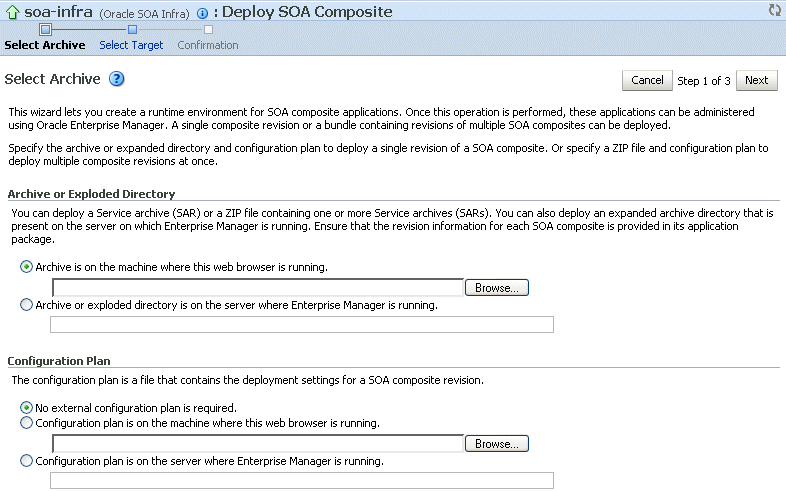
In the Archive or Exploded Directory section, specify the archive of the SOA composite application to deploy. The archive contains the project files of the application to be deployed (for example, HelloWorld_rev1.0.jar for a single archive or OrderBooking_rev1.0.zip for multiple archives).
In the Configuration Plan section, optionally specify the configuration plan to include with the archive. The configuration plan enables you to define the URL and property values to use in different environments. During the process deployment, the configuration plan is used to search the SOA project for values that must be replaced to adapt the project to the next target environment.
Click Next.
The Select Target page appears.
Select the WebLogic Server or cluster to which to deploy the SOA composite application archive. You can deploy to multiple servers and clusters.
Click Next.
The Confirmation page appears.
Review your selections.
Select whether or not to deploy the SOA composite application as the default revision. The default revision is instantiated when a new request comes in.
Click Deploy.
Processing messages are displayed.
When deployment has completed, click Close.
|
See Also: Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite for complete information about deploying SOA Composite applications |
You can undeploy SOA composite applications from Fusion Middleware Control:
From the navigation pane, expand the farm, then SOA, and then select soa-infra.
The SOA Infrastructure home page is displayed.
From the SOA Infrastructure menu, choose SOA Deployment, then Undeploy.
The Confirmation page is displayed.
Review your selections.
If you are satisfied, click Undeploy.
Processing messages are displayed.
When undeployment has completed, click Close.
|
See Also: Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite for complete information about deploying SOA Composite applications |
You can redeploy SOA composite applications from Fusion Middleware Control with the Redeploy SOA Composite wizard:
From the navigation pane, expand the farm, then SOA, and then select soa-infra.
The SOA Infrastructure home page is displayed.
From the SOA Infrastructure menu, choose SOA Deployment, then Redeploy.
The Select Archive page appears.
In the Archive or Exploded Directory section, select the location of the SOA composite application revision you want to redeploy.
In the Configuration Plan section, optionally specify the configuration plan to include with the archive.
Click Next.
The Confirmation page appears.
Select whether or not to redeploy the SOA composite application as the default revision.
Click Redeploy.
Processing messages are displayed.
When redeployment has completed, click Close.
|
See Also: Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite for complete information about deploying SOA Composite applications |
WebCenter applications differ from traditional Java EE applications in that they support run-time customization, such as the application's pages, the portlets contained within these pages, and the document libraries. Customizations are stored as follows:
WebCenter application customizations are stored in Oracle Metadata Services (MDS), which is installed in a database.
Portlet producer customizations (or preferences) are usually stored in a database preference store.
You can use Fusion Middleware Control, Oracle JDeveloper, or the command line to deploy, undeploy, or redeploy a WebCenter application. The following topics describe using Fusion Middleware Control to accomplish these tasks:
|
See Also: Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle WebCenter |
To deploy your application to a Managed Server that resides outside JDeveloper, you must first create application deployment plans. In Oracle JDeveloper, first create a project-level deployment profile and then an application-level deployment profile. The project-level deployment profile is packaged as a Web Application Archive (WAR) file. The application-level deployment profile is packaged as a Metadata Archive (MAR). A MAR is a compressed archive of selected metadata. A single MAR can contain metadata content of multiple projects. MAR files are used to deploy metadata content to the MDS repository. For information about creating deployment plans with Oracle JDeveloper, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle WebCenter.
To deploy an Oracle WebCenter application to a Managed Server using Fusion Middleware Control:
From the navigation pane, expand the farm, then WebLogic Domain, and then the domain.
Select the server in which you want to deploy the application.
The server home page is displayed.
From the WebLogic Server menu, select Application Deployment, then Deploy.
The Deployment Wizard, Select Archive page is displayed.
In the Archive or Exploded Directory section, you can select one of the following:
Archive is on the machine where this browser is running. Then, enter the location of the archive or click Browse to find the archive file.
Archive or exploded directory is on the server where Enterprise Manager is running. Then, enter the location of the archive or click Browse to find the archive file.
In the Deployment Plan section, you can select one of the following:
Create a new deployment plan when deployment configuration is done.
Deployment plan is on the machine where this web browser is running. If you select this option, enter the path to the plan.
Deployment plan is on the server where Enterprise Manager is running. If you select this option, enter the path to the plan.
Click Next.
The Select Target page is displayed.
Select the target to which you want to deploy the application.
Click Next.
The Application Attributes page is displayed.
In the Application Attributes section, for Application Name, enter the application name.
In the Context Root of Web Modules section, specify the context root for your application if you have not specified it in application.xml. The context root is the URI for the web module. Each web module or EJB module that contains web services may have a context root.
The Target Metadata Repository section allows you to choose the repository and partition for this application. If the partition or repository specified in the application is not valid in the domain, Fusion Middleware Control displays a message.
To change the repository, click the icon next to the Repository Name. In the Metadata Repositories dialog box, select the repository and click OK.
To change the partition, enter the partition name in Partition Name. Oracle recommends that you create a new partition for each application. If you enter a name of a partition that does not exist, the partition is created.
Each application must have a unique partition in the repository.
Click Next.
The Deployment Wizard, Deployment Settings page is displayed.
On this page, you can perform common tasks before deploying your application or you can edit the deployment plan or save it to a disk. Depending on the type of application, you can:
Configure Web modules: Click Go to Task in the Configure Web Modules row. The Configure Web Modules page is displayed. Click Configure General Properties to view and edit the general configuration for the Web Module or Map Resource References to map the resource references.
For example, you can change the session invalidation interval or the maximum age of session cookies.
Configure application security. Click Go to Task in the Configure Application Security row. Depending on what type of security is used, different pages are displayed.
If the application contains jazn-data.xml or cwallet.sso, the Configure Application Security page displays the following sections:
If it contains jazn-data.xml, the page displays the Application Policy Migration section.
If it contains cwallet.sso, the page displays the Application Credential Migration section.
If it contains both, the page displays both sections.
For information about the settings in this page, see "Deploying JavaEE and ADF Applications with Oracle Enterprise Manager" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Security Guide.
If the application contains neither of these files, the Configure Application Security page displays the following options:
DD Only: Use only roles and policies that are defined in the deployment descriptors.
Custom Roles: Use roles that are defined in the Administration Console; use policies that are defined in the deployment descriptor.
Custom Roles and Policies: Use only roles and policies that are defined in the Administration Console.
Advanced: Use a custom model that you have configured on the realm's configuration page.
Configure EJB modules: Click Go to Task in the Configure EJB modules row. The Configure EJB Modules page is displayed. Click Configure EJB Properties to view and edit the general configuration for the EJBs or Map Resource References to map the resource references.
For example, you can configure the maximum number of beans in the free pool or the network access point.
Configure ADF Connections. To modify the ADF connections, click Go to Task in the Configure ADF Connections row. The Configure ADF Connections page is displayed, showing the current connection information. To modify a connection type, click the Edit icon for a particular row.
For more information about setting these attributes, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle WebCenter.
Expand Deployment Plan.
You can edit and save the deployment plan, if you choose.
Click Deploy.
Fusion Middleware Control displays processing messages.
When the deployment is completed, click Close.
To undeploy a WebCenter Application:
From the navigation pane, expand Application Deployments, then the application to undeploy.
The application home page is displayed.
From the Application Deployment menu, select Application Deployment, then Undeploy.
The confirmation page is displayed.
Click Undeploy.
Processing messages are displayed.
When the operation completes, click Close.
Alternatively, you can navigate to the domain, Managed Server, or cluster. Then, from the target's menu, choose Application Deployment, then Undeploy. In the Select Application page, select the application you want to undeploy.
To redeploy a WebCenter Application:
From the navigation pane, expand the farm, then WebLogic Domain, and then the domain.
Select the server in which you want to deploy the application.
The server home page is displayed.
From the WebLogic Server menu, select Application Deployment, then Redeploy.
The Select Application page is displayed. You can only redeploy applications that are versioned. If the application is not versioned, you must undeploy, then redeploy.
Select the application to redeploy.
Click Next.
The Select Archive page is displayed.
In the Archive or Exploded Directory section, you can select one of the following:
Archive is on the machine where this browser is running. Then, enter the location of the archive or click Browse to find the archive file.
Archive or exploded directory is on the server where Enterprise Manager is running. Then, enter the location of the archive or click Browse to find the archive file.
In the Deployment Plan section, you can select one of the following:
Create a new deployment plan when deployment configuration is done
Deployment plan is on the machine where this web browser is running. If you select this option, enter the path to the plan.
Deployment plan is on the server where Enterprise Manager is running. If you select this option, enter the path to the plan.
Click Next.
The Application Attributes page is displayed.
In the Application Attributes section, for Application Name, enter the application name.
In the Context Root of Web Modules section, specify the context root for your application if you have not specified it in application.xml. The context root is the URI for the web module. Each web module or EJB module that contains web services may have a context root.
In the Target Metadata Repository section, select the MDS repository and for Partition Name, enter a partition name. If the partition or repository specified in the application is not valid in the domain, Fusion Middleware Control displays a message.
Click Next.
The Deployment Settings page is displayed.
On this page, you can perform common tasks before deploying your application or you can edit the deployment plan or save it to a disk. You can:
Configure Web modules
Configure application security
Expand Deployment Plan.
You can edit and save the deployment plan, if you choose.
Click Redeploy.
Fusion Middleware Control displays processing messages.
When the deployment is completed, click Close.
If your application uses an MDS repository, you can modify configuration attributes after the application is deployed. To view or modify the attributes, you can use the System MBean Browser or WLST.
|
Note: Changes to this configuration are persisted in MDS as customizations. Because these are persisted as customizations:
|
Take the following steps:
Navigate to the application's home page by expanding the farm, then Application Deployments. Then, select an application.
The application's home page is displayed.
From the Application Deployment menu, choose System MBean Browser.
The System MBean Browser page is displayed.
Expand Application Defined MBeans, then oracle.adf.share.config, then Server: name, then Application: name, then ADFConfig, then ADFConfig, and ADFConfig.
Select MDSAppConfig.
The Application Defined MBeans page is displayed, as shown in the following figure:
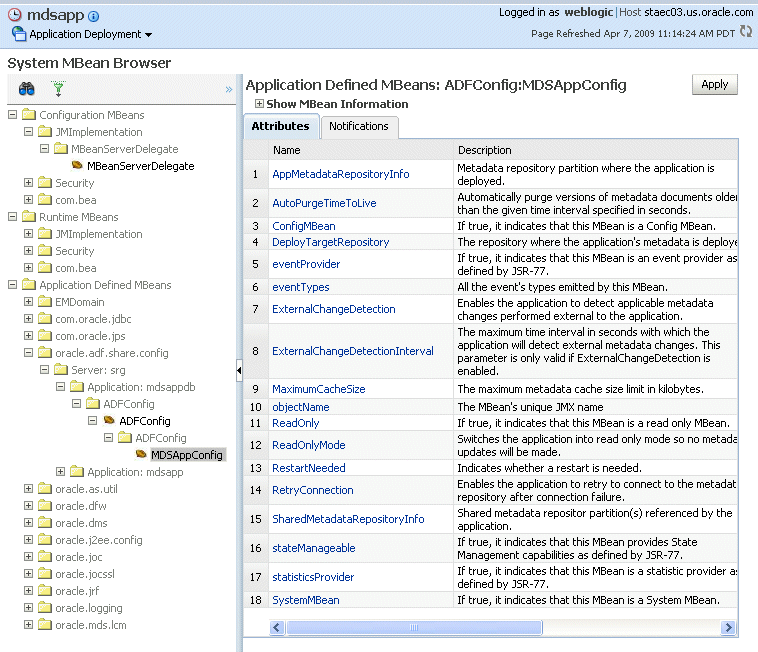
You can view the description and values for the attributes.
Table 8-2 describes the configuration attributes that are specific to MDS. Note that other attributes, such as ConfigMBean appear in browser, but these are generic attributes for all MBeans.
Table 8-2 MDS Configuration Attributes for Deployed Applications
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
AppMetadataRepositoryInfo |
Read only. Describes the metadata repository partition where the application is deployed. |
|
AutoPurgeTimeToLive |
Automatically purge versions of metadata documents older than the given time interval, specified in seconds. Any unlabeled versions older than this time interval are automatically purged on any subsequent update from this application. If the value is not set, versions are not automatically purged. |
|
DeployTargetRepository |
The name of the target repository configured for the application. |
|
ExternalChangeDetection |
Specifies that the MDS repository is polled to determine if any applicable metadata changes have been performed external to the application. If changes are detected, notifications are sent. This attribute is applicable only to database-based repositories. The default is true. |
|
ExternalChangeDetectionInterval |
The maximum time interval, in seconds, to poll the MDS repository to determine if there are external metadata changes. This attribute is only valid if ExternalChangeDetection is enabled. The default is 30 seconds. |
|
MaximumCacheSize |
The maximum metadata cache size limit, in kilobytes. If the value is 0, caching is disabled. If no value is specified, there is no cache limit. In this case, cached data is stored indefinitely. |
|
ReadOnlyMode |
Changes the application to read-only mode, so that no updates can be made to the application's repository partition, including configuration and application metadata. |
|
RetryConnection |
Enables the application to retry the connection to the metadata repository after connection failure. |
|
SharedMetadataRepositoryInfo |
Read only. Specifies the MDS repository partition used by the application. Note that an application can use more than one shared metadata repository. |
To view or modify an attribute, select the attribute.
The attribute page is displayed.
If the attribute is not read-only, you can change the values. For example, for AutoPurgeTimeToLive, you can change the interval, by entering a new value in Value.
Click Apply.
Navigate up to ADFConfig (the parent of MDSAppConfig) and select it.
In the Operations tab, click Save.
Click Invoke.
You can change the MDS configuration using WLST. The following example shows a WLST script that reads and then sets the ReadOnlyMode attribute:
"""
Getting ReadOnlyMode Attribute from MBean
"""
connect('username','password','hostname:port')
application = 'application_name'
attribute = 'ReadOnlyMode'
beanName = 'oracle.adf.share.config:ApplicationName='+ application +',name=MDSAppConfig,type=ADFConfig,Application='+ application +',ADFConfig=ADFConfig,*'
beanObjectName = ObjectName(beanName)
beans = mbs.queryMBeans(beanObjectName, None)
bean = beans.iterator().next().getObjectName()
custom()
value = mbs.getAttribute(bean, attribute)
print value
"""
Setting ReadOnlyMode Attribute from MBean
"""
attr = Attribute(attribute, Boolean(0))
mbs.setAttribute(bean,attr)
value = mbs.getAttribute(bean, attribute)
print value
"""
Saving the Changes. This is required to persist the changes.
"""
adfConfigName = 'oracle.adf.share.config:ApplicationName='+ application + ',name=ADFConfig,type=ADFConfig,Application='+ application + ',*'
adfConfigObjectName = ObjectName(adfConfigName)
adfConfigMBeans = mbs.queryMBeans(adfConfigObjectName, None)
adfConfigMBean = adfConfigMBeans.iterator().next().getObjectName()
mbs.invoke(adfConfigMBean, 'save', None, None)