 Prerequisites
PrerequisitesThis chapter lists prerequisites, provides overviews of asset information flow and accounting entry setup, and discusses how to create accounting entries.
 Prerequisites
PrerequisitesBefore you initiate any processing, you should review your application options. Ensure that you have:
Defined business unit and book accounting entry options.
Established the accounting entry template IDs to be used for PeopleSoft Asset Management processing.
Established the accounting entry templates to be used for PeopleSoft Asset Management processing.
Determined the depreciation open and close status for periods.
 Understanding Asset Information Flow
Understanding Asset Information Flow
Each financial transaction that is entered into PeopleSoft Asset Management can be used to generate balanced accounting entries. These entries in turn can be summarized and written to a journal, which can then be rolled up and posted to the general ledger system.
Balanced accounting entries are generated from financial transactions and are the basis for creating journals that are posted to the general ledger. The primary sources of accounting entries within PeopleSoft Asset Management include:
Accounting entries that are created from financial transactions such as asset additions, adjustments, allocations or retirements.
Accounting entries that are created from depreciation close for a particular accounting period.
Accounting entries that are created from lease payments.
Others include processing transactions to adjust for inflation and accounting entries that are created from an active integration with other PeopleSoft products such as Billing, Purchasing, and Payables.
Each time financial asset information is entered or adjusted, PeopleSoft Asset Management creates an open transaction. This transaction remains open until accounting entries are created or depreciation is calculated for the transaction. The process for accounting entry creation generates accounting entries for all financial transactions that are not related to depreciation. The Depreciation Close process (AM_DPCLOSE) generates accounting entries for depreciation in a particular accounting period.
To create accounting entries:
Enter asset transactions.
Based on the context of the transaction that you enter, the system creates an open transaction with a transaction type such as Add, Transfer, Adjust, Retire, and so forth. These open transactions form a list of accounting entry or depreciation tasks to be processed.
Calculate depreciation for open transactions.
Create asset transaction accounting entries by running the Accounting Entry Creation process (AM_AMAEDIST), which applies the appropriate accounting entry templates to the open transactions that were created in step 1.
Selection of an accounting entry template is determined by the accounting entry template ID, category, cost type, transaction type, and transaction code of the asset transaction. You can run this process at any interval. You should run the process more than once a month to prevent the process from being slowed at period close time. Use Process Scheduler to schedule and automatically initiate these processes.
At the end of each accounting period, create depreciation accounting entries by running the Depreciation Close process; the process applies the depreciation (DPR) and prior depreciation period (PDP) accounting entry templates to the asset depreciation table.
Run this process only once for each accounting period, and only after all of the transaction activity for the period has been completed.
Reverse accounting entries by running the Depreciation Close process with the option Reverse Posted Entries selected.
This option reverses only those journal entries that have been created and posted to the general ledger, and creates reversal entries.
This diagram shows the processes for creating accounting entries:
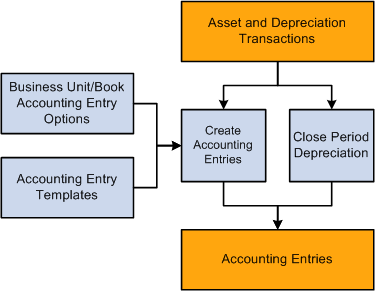
Processes for creating accounting entries
See Setting Up Accounting Entry and Financial Processing for PeopleSoft Asset Management.
See Establishing Asset Processing.
 Understanding Accounting Entry Setup
Understanding Accounting Entry Setup
This section discusses:
Business unit and book accounting entry options.
Accounting entry templates.
Depreciation close status.

 Business Unit and Book Accounting Entry Options
Business Unit and Book Accounting Entry OptionsBusiness unit and book accounting entry options are defined in the Establish Business Units component, and they control which business unit book is used to create accounting entries. Select one book for each business unit to create accounting entries.
Note. When processing accounting entries, you should understand the relationship between PeopleSoft Asset Management business units and PeopleSoft General Ledger business units. If you are using different business units for the applications because you use multiple ledgers, you must be sure to specify the ledger. The ledger is required when you are searching on the Asset Journals page. Failing to enter the value generates an error, and the journal lines for business units that are different do not appear, even though the PeopleSoft Asset Management entries are generated and posted to the journal tables.
See Establishing PeopleSoft Asset Management Business Units.

 Accounting Entry Templates
Accounting Entry Templates
The accounting entry template is the central table that the system uses to create accounting entries, which are the basis for general ledger journals. The accounting entry template defines accounting entry types based on asset category, cost type, transaction type, transaction code, and accounting entry template ID. For each accounting entry type, you specify:
The accounts to use during accounting entry.
The journal template to use for recording actual transactions.
The budget journal template to use to record budget transactions.
When you add an accounting entry template in PeopleSoft Asset Management, the system populates it with standard accounting entry types (distribution types), based on the asset category, cost type, and action that is specified for all supported features that require accounting types.
If impairment and revaluation options are enabled at the installation level, you can specify within the cost type definition if you want to enable a given cost type for impairment or revaluation processing. If enabled, the system displays the appropriate impairment and revaluation related accounts at the Accounting Entry Template level.
Use the features within the Accounting Entry Template ID component to define accounting entry template IDs that include or exclude the appropriate accounting entry (distribution) types for each type of transaction. The accounting entry template IDs can be associated with business unit-level features such as the Book Code feature, the Derogatory Depreciation feature, the Like Kind Exchange feature, and the Revaluation feature.
Accounting entry types are delivered with the PeopleSoft system, and each asset event has an associated set of accounting entry types. For each combination of category, cost type, transaction code, and accounting entry template ID, you must set up an accounting entry template for the following transaction types:
|
Transaction Type |
Description |
|
ADD |
Additions. |
|
ADJ |
Adjustments. |
|
TRF |
Transfers. |
|
RCT |
Recategorizations. |
|
DPR |
Depreciation expense. |
|
PDP |
Prior period depreciation. |
|
RET |
Retirements (also used for processing reinstatements). |
|
LPY |
Lease payments. |
|
INF |
Inflation adjustment. |
Note. If you enter a transaction into the system with a combination of category, cost type, transaction code, and accounting entry template ID for which no accounting entry template exists, the accounting entry process will fail the next time it is run.
DPR and PDP transaction types are used only on an accounting entry template with a blank transaction code.
Accounting Entry Types (Distribution Types)
Asset Management creates accounting entries by using standard accounting entry types (distribution types), based on the asset category, cost type, and action that is specified for all supported features that require accounting entry types. The following tables list the accounting distribution types that are associated with each accounting entry feature.
Following are the distribution types for the ADD (addition) transaction type (if there is no 'X' for a distribution type (blank), that type is not applicable for the listed feature):
|
Type |
Description |
Basic |
Expensed Asset |
Lease |
Derogatory |
Like Kind Exchange |
Revaluation |
|
AD |
Accumulated Depreciation |
X |
X |
||||
|
AP |
Contra Asset |
X |
X |
X |
|||
|
DD |
Accumulated Derogatory Depreciation |
X |
|||||
|
DE |
Depreciation Expense |
X |
X |
||||
|
DR |
Derogatory Depreciation Reversal |
X |
|||||
|
DX |
Derogatory Depreciation Expense |
X |
|||||
|
EX |
Expense |
X |
|||||
|
FA |
Fixed Asset |
X |
X |
||||
|
IV |
Investment Property |
X |
X |
||||
|
IX |
Investment Property Accumulated Depreciation Adjustment |
X |
X |
||||
|
LO |
Lease Obligation |
X |
|||||
|
TI |
Trade In |
X |
X |
||||
|
UR |
Unrecognized Gain/Loss |
X |
X |
||||
|
RL |
Recognized Loss |
X |
X |
||||
|
PR |
Provision for Revaluation |
X |
Following are the distribution types for the ADJ (adjustment) transaction type:
|
Type |
Description |
Basic |
Expensed Asset |
Lease |
Derogatory |
Like Kind Exchange |
Revaluation |
|
AD |
Accumulated Depreciation |
X |
X |
||||
|
AP |
Contra Asset |
X |
X |
X |
|||
|
DD |
Accumulated Derogatory Depreciation |
X |
|||||
|
DE |
Depreciation Expense |
X |
X |
||||
|
DR |
Derogatory Depreciation Reversal |
X |
|||||
|
DX |
Derogatory Depreciation Expense |
X |
|||||
|
EX |
Expense |
X |
|||||
|
FA |
Fixed Asset |
X |
X |
||||
|
IV |
Investment Property |
X |
X |
||||
|
LO |
Lease Obligation |
X |
|||||
|
PG |
Investment Property Gain |
X |
X |
||||
|
PL |
Investment Property Loss |
X |
X |
||||
|
PR |
Provision for Revaluation |
X |
|||||
|
RD |
Reversal of Depreciation |
X |
|||||
|
IM |
Impairment Loss |
X |
X |
||||
|
IN |
Impairment Contra |
X |
Here are the distribution types for the TRF (transfer) transaction type:
|
Type |
Description |
Basic |
Lease |
Derogatory |
Like Kind Exchange |
Revaluation |
|
AD |
Accumulated Depreciation |
X |
X |
|||
|
DD |
Accumulated Derogatory Depreciation |
X |
||||
|
DR |
Derogatory Depreciation Reversal |
X |
||||
|
DX |
Derogatory Depreciation Expense |
X |
||||
|
FA |
Fixed Asset |
X |
X |
|||
|
IV |
Investment Property |
X |
X |
|||
|
PR |
Provision for Revaluation |
X |
||||
|
RC |
Provision for Revaluation Contra |
X |
Here are the distribution types for the RCT (recategorize) transaction type:
|
Type |
Description |
Basic |
Lease |
Derogatory |
Like Kind Exchange |
Revaluation |
|
AD |
Accumulated Depreciation |
X |
X |
|||
|
DD |
Accumulated Derogatory Depreciation |
X |
||||
|
DR |
Derogatory Depreciation Reversal |
X |
||||
|
DX |
Derogatory Depreciation Expense |
X |
||||
|
FA |
Fixed Asset |
X |
X |
|||
|
IV |
Investment Property |
X |
X |
|||
|
PR |
Provision for Revaluation |
X |
||||
|
RC |
Provision for Revaluation Contra |
X |
Here are the distribution types for the RET (retire) transaction type:
|
Type |
Description |
Basic |
Lease |
Derogatory |
Like Kind Exchange |
Revaluation |
|
AD |
Accumulated Depreciation |
X |
||||
|
AP |
Contra Asset |
X |
||||
|
BI |
Proceeds to Billing Account |
X (If Billing is installed) |
||||
|
CA |
Proceeds |
X |
||||
|
DD |
Accumulated Derogatory Depreciation |
X |
||||
|
DR |
Derogatory Depreciation Reversal |
X |
||||
|
DX |
Derogatory Depreciation Expense |
X |
||||
|
FA |
Fixed Asset |
X |
||||
|
GA |
Gain |
X |
||||
|
GL |
Loss |
X |
||||
|
IV |
Investment Property |
X |
||||
|
LG |
Lease Guarantee Contra |
X |
||||
|
LO |
Lease Obligation |
X |
||||
|
LU |
Lease Guarantee Obligation |
X |
||||
|
MA |
Mortgage - Others |
X |
||||
|
ML |
Mortgage - Comp |
X |
||||
|
NV |
Net Book Value |
X |
||||
|
PR |
Provision for Revaluation |
X |
||||
|
RC |
Provision for Revaluation Contra |
X |
||||
|
RD |
Reversal of Depreciation |
X |
||||
|
RG |
Recognized Gain |
X |
||||
|
RM |
Removal Contra |
X |
||||
|
SL |
Sales of Fixed Asset |
X |
||||
|
TI |
Trade In |
X |
||||
|
UG |
Unrealized Gain |
X |
||||
|
UL |
Unrealized Loss |
X |
Here are the distribution type for the DPR (depreciation) transaction type:
|
Type |
Description |
Basic |
Lease |
Derogatory |
Like Kind Exchange |
Revaluation |
|
AD |
Accumulated Depreciation |
X |
X |
|||
|
DD |
Accumulated Derogatory Depreciation |
X |
||||
|
DE |
Depreciation Expense |
X |
X |
|||
|
DR |
Derogatory Depreciation Reversal |
X |
||||
|
DX |
Derogatory Depreciation Expense |
X |
||||
|
RC |
Provision for Revaluation Contra |
X |
||||
|
RD |
Reversal of Depreciation |
X |
Here are the distribution types for the PDP (prior period depreciation) transaction type:
|
Type |
Description |
Basic |
Lease |
Derogatory |
Like Kind Exchange |
Revaluation |
|
AD |
Accumulated Depreciation |
X |
||||
|
DD |
Accumulated Derogatory Depreciation |
X |
||||
|
DE |
Depreciation Expense |
X |
||||
|
DR |
Derogatory Depreciation Reversal |
X |
||||
|
DX |
Derogatory Depreciation Expense |
X |
||||
|
RC |
Provision for Revaluation Contra |
X |
||||
|
RD |
Reversal of Depreciation |
X |
Here are the distribution types for the LPY (lease payment) transaction type:
|
Type |
Description |
Basic |
Lease |
Derogatory |
Like Kind Exchange |
Revaluation |
|
LC |
Lease Interest Contra |
X |
||||
|
LI |
Lease Interest |
X |
||||
|
LO |
Lease Obligation |
X |
||||
|
LP |
Lease Obligation contra |
X |
Here are the distribution types for the INF (inflation) transaction type:
|
Type |
Description |
Basic |
Lease |
Derogatory |
Like Kind Exchange |
Revaluation |
|
IA |
Inflation Accum Depr |
X |
||||
|
IB |
Inflation Accum Depr |
X |
||||
|
IC |
Inflation Cost Adjustment |
X |
||||
|
ID |
Inflation Cost Adjustment |
X |
||||
|
IG |
Inflation Gain |
X |
||||
|
IL |
Inflation Loss |
X |
||||
|
IP |
Inflation Period Depr |
X |
||||
|
IQ |
Inflation Period Depr |
X |
||||
|
IY |
Inflation YTD Depr |
X |
||||
|
IZ |
Inflation YTD Depr |
X |
See Defining Accounting Entries.
See Creating PeopleSoft Asset Management Business Units.

 Depreciation Close Status
Depreciation Close Status
You can run the Depreciation Close process only in an open period. You use the Business Unit/Book Definition page to determine which accounting periods have been closed. Select Depreciation Closed List to display all closed periods.
Note. Open and close accounting periods are maintained in General Ledger and migrated with the financial subsystems. Each subsystem application can either use the periods that are created in General Ledger or update the open and close periods at the application business unit level.
See Defining and Updating Open Periods and Adjustment Periods.
 Creating Accounting Entries
Creating Accounting Entries
This section provides an overview of the Depreciation Close process, lists common elements, and discusses how to:
Request accounting entry creation.
Run the Depreciation Close process.
Close accounting periods.

 Understanding the Depreciation Close Process
Understanding the Depreciation Close Process
The Depreciation Close process generates period depreciation accounting entries for all depreciable assets in a particular accounting period, including lease payments and offset accounts for the period. Run this process only for an accounting period that has not yet been closed. You can reverse or rerun this process if errors are detected in the results. The flexible run parameters allow processing to close the period, reversing the output of the last posting run, or reversal with reprocessing of the close entries.
Open and close accounting periods are maintained in General Ledger and migrated to the financial subsystems. Each subsystem application can either use the periods that are created in General Ledger or update the open and close periods at the application business unit level.
When you run the Depreciation Close process, you have two options: Rerun Depreciation Close and Reverse Posted Entries. The following examples demonstrate how these options affect processing.
Example of the Rerun Depreciation Close Option
With Rerun Depreciation Close enabled and the journal entries not yet created, the Depreciation Close process creates a new accounting entry, as shown in this table, and deletes the existing one (if any). If the journal entries have already been created, depreciation close will neither delete nor generate entries. No actions occur.
|
DISTRIBUTION_TYPE |
DTTM_STAMP |
AMOUNT |
GL_DISTRIB_STATUS |
REVERSE_STATUS |
REVERSE_DTTM_STAMP |
Journal ID |
Journal Dttm Stamp |
|
AD |
2009-09-05 14:25:20 |
–110.00 |
N |
|
NULL |
|
NULL |
|
DE |
2009-09-05 14:25:20 |
110.00 |
N |
|
NULL |
|
NULL |
When the journal entries have been posted, the system updates the general ledger distribution status to D (done).
This table shows the results after the PeopleSoft General Ledger run:
|
DISTRIBUTION_TYPE |
DTTM_STAMP |
AMOUNT |
GL_DISTRIB_STATUS |
REVERSE_STATUS |
REVERSE_DTTM_STAMP |
Journal ID |
Journal Dttm Stamp |
|
AD |
2009-09-05 14:25:20 |
–110.00 |
D |
|
NULL |
XX |
Journal Dttmstamp |
|
DE |
2009-09-05 14:25:20 |
110.00 |
D |
|
NULL |
XX |
Journal Dttmstamp |
Example of the Reverse Posted Entries Option
When the Reverse Posted Entries option is selected and the journal entries have been created, the original entry is reversed with new rows inserted showing the reversed amounts. The new entries display the statuses R for reversal and X for reversed entries.
This table shows the original entry:
|
DISTRIBUTION_TYPE |
DTTM_STAMP |
AMOUNT |
GL_DISTRIB_STATUS |
REVERSE_STATUS |
REVERSE_DTTM_STAMP |
Journal ID |
Journal Dttm Stamp |
|
AD |
2009-09-05 14:25:20 |
–110.00 |
D |
X |
NULL |
XX |
Journal Dttmstamp |
|
DE |
2009-09-05 14:25:20 |
110.00 |
D |
X |
NULL |
XX |
Journal Dttmstamp |
This table shows the reversed entry:
|
DISTRIBUTION_TYPE |
DTTM_STAMP |
AMOUNT |
GL_DISTRIB_STATUS |
REVERSE_STATUS |
REVERSE_DTTM_STAMP |
Journal ID |
Journal Dttm Stamp |
|
AD |
2009-09-12 17:37:25 |
110.00 |
N |
R |
2003-09-05 14:25:20 |
|
|
|
DE |
2009-09-12 17:37:25 |
–110.00 |
N |
R |
2003-09-05 14:25:20 |
|
|
Example of Both the Rerun Depreciation Close and Reverse Posted Entries Options
When the Reverse Posted Entries and the Rerun Depreciation Close options are both selected, and the journal entries have been created, then the original entry is reversed as shown in the previous example, and a new accounting entry is created.
This table shows the original entry:
|
DISTRIBUTION_TYPE |
DTTM_STAMP |
AMOUNT |
GL_DISTRIB_STATUS |
REVERSE_STATUS |
REVERSE_DTTM_STAMP |
Journal ID |
Journal Dttm Stamp |
|
AD |
2009-09-05 14:25:20 |
–110.00 |
D |
X |
NULL |
XX |
Journal Dttmstamp |
|
DE |
2009-09-05 14:25:20 |
110.00 |
D |
X |
NULL |
XX |
Journal Dttmstamp |
This table shows the reversed entry:
|
DISTRIBUTION_TYPE |
DTTM_STAMP |
AMOUNT |
GL_DISTRIB_STATUS |
REVERSE_STATUS |
REVERSE_DTTM_STAMP |
Journal ID |
Journal Dttm Stamp |
|
AD |
2009-09-12 17:37:25 |
110.00 |
N |
R |
2003-09-05 14:25:20 |
|
|
|
DE |
2009-09-12 17:37:25 |
–110.00 |
N |
R |
2003-09-05 14:25:20 |
|
|
This table shows the results of the rerun with the new entry:
|
DISTRIBUTION_TYPE |
DTTM_STAMP |
AMOUNT |
GL_DISTRIB_STATUS |
REVERSE_STATUS |
REVERSE_DTTM_STAMP |
Journal ID |
Journal Dttm Stamp |
|
AD |
2009-09-12 17:37:25 |
–140.00 |
N |
|
NULL |
|
NULL |
|
DE |
2009-09-12 17:37:25 |
140.00 |
N |
|
NULL |
|
NULL |

 Common Elements Used in This Section
Common Elements Used in This Section
|
Request ID |
Displays the number of process requests that you have submitted. |
|
Unit |
Enter the business unit for which transactions are processed. |
|
Book Name |
Enter the book for which transactions are processed. |
|
Currency |
Displays the currency in which the transactions are processed, based on the base currency for the selected book or business unit. |

 Pages Used to Create Accounting Entries
Pages Used to Create Accounting Entries|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
Create Accounting Entries |
AM_AMAEDIST_RQST |
Asset Management, Accounting Entries, Create Accounting Entries, Create Accounting Entries |
Set up and initiate a request or set of requests for accounting entry creation. |
|
Run Depreciation Close Process |
DEPR_CLOSE_RQST |
Asset Management, Accounting Entries, Close Depreciation, Run Depreciation Close Process |
Enter and initiate a depreciation close request or requests. |
|
Close Accounting Period |
DEPR_CLOS_PD |
Asset Management, Accounting Entries, Close Accounting Period, Close Accounting Period |
Close accounting periods to ensure that you do not make any new transactions in the period. |
|
Review Financial Entries - List |
ASSET_DIST_LIST |
Asset Management, Accounting Entries, Review Financial Entries, List |
Review accounting financial entries in summary list. Note. In the case where there are multiple "Future-dated" EFFDT, only the MAXIMUM effective-dated row will be displayed in the prompt for ACCOUNT in the Review Financial Entries component. |
|
Review Financial Entries - Detail |
ASSET_DIST_DETAIL |
Asset Management, Accounting Entries, Review Financial Entries, Detail |
Review accounting financial entries in detail. Note. In the case where there are multiple "Future-dated" EFFDT, only the MAXIMUM effective-dated row will be displayed in the prompt for ACCOUNT in the Review Financial Entries component. |
|
Review Operating Leases - List |
ASSET_NF_DIST_LN |
Asset Management, Accounting Entries, Review Operating Leases, List |
Review operating lease entries in summary list. |
|
Review Operating Leases - Detail |
LEASE_DIST_DETAIL |
Asset Management, Accounting Entries, Review Operating Leases, Detail |
Review operating lease entries in summary list. |
|
Review Asset Journals |
AM_GL_DRILL |
Asset Management, Accounting Entries, Review Asset Journals |
Review asset journal information. |
|
Calculate Inflation - Request |
DEPR_INF_RQST |
Asset Management, Accounting Entries, Calculate Inflation, Request |
Run a process to calculate inflation for assets. |
|
Review Expense Entries - List |
ASSET_NF_LIST |
Asset Management, Accounting Entries, Review Expense Entries, List |
Review the expense entries (nonfinancial assets) that were created by running the Clearing Reconciliation process. |
|
Review Expense Entries - Details |
ASSET_NF_DET |
Asset Management, Accounting Entries, Review Expense Entries, Details |
Review the expense entry details (nonfinancial assets) that were created by running the Clearing Reconciliation process. |
|
Clearing Reconciliation |
AM_CLEREC_RQST |
Asset Management, Accounting Entries, Clearing Reconciliation, Clearing Reconciliation |
Run the process to reconcile the clearing account that is created by trackable assets from feeder systems against the expense account. |

 Requesting Accounting Entry Creation
Requesting Accounting Entry Creation
Access the Create Accounting Entries page (Asset Management, Accounting Entries, Create Accounting Entries).
|
Cost Summarize |
Select to create cost summary while creating accounting entries. |
|
From Asset ID and To Asset ID |
Enter the transaction range to process. |
Note. The system calls the Inter/IntraUnit central processor to create balanced accounting entries.
See Using Interunit and Intraunit Accounting and ChartField Inheritance.

 Running the Depreciation Close Process
Running the Depreciation Close Process
Access the Run Depreciation Close Process page (Asset Management, Accounting Entries, Close Depreciation).
|
Fiscal Year and Period |
Enter the appropriate fiscal year and open periods to be closed. |
|
Rerun Depreciation Close |
Select to delete all existing accounting entries that haven't been generated as journal entries for depreciation expense and lease obligations for the specified business unit, book, fiscal year, and period. The system generates new entries. To generate new journal entries and to reverse a journal entry, run a request with both Rerun Depreciation Close and Reverse Posted Entries options selected. To rerun depreciation close for budgeted depreciation, run a request with both Rerun Depreciation Close and Create Budgeted Depreciation options selected. |
|
Reverse Posted Entries |
Select to reverse only those accounting entries that have been created and posted to the general ledger, including all existing accounting entries for depreciation expense and lease payments for the specified business unit, book, fiscal year, and period. The process creates reversal entries and marks the old entries with a status of Reversed. If journal entries have not been created, the entries marked Reversed are not used by the Journal Generator process. To reverse entries that are created and post them again, use Reverse Posted Entries in tandem with Rerun Depreciation Close. When you do this, the original journal entry is reversed and a new entry is created. When an entry has not been posted to the general ledger, use the rerun option. Reverse Posted Entries does not reverse unposted entries. |
|
Create budgeted Depreciation |
Displays the resulting accounting entries as budgeted depreciation and lease payments. These entries are posted to the budget ledger that is specified in the Business Unit Book options page when you run the Journal Generator process. |
|
Process a range of assets |
Select to process a specific range of assets for a business unit, book, fiscal year, and period. Use this option to split up a large volume of assets for a particular business unit and book. Because the program AM_DPCLOSE commits its work after each request, selecting this option accelerates the process. You can also use this selection with the parallel option to take advantage of servers that have parallel processors. This speeds up processing for large volumes of data. For example, to increase throughput when creating depreciation accounting entries for 1,000,000 assets, you can enter 10 requests to process 100,000 assets each. Select Process in Parallel, and assign a processing sequence number to each process request. Processing sequence numbers must be unique. Use care when specifying From asset ID and To asset ID processing parameters, as these parameters are inclusive. Overlapping can occur, and no edit is available to verify that you have set up inclusive asset ranges. For example, suppose that request 1 is processed from asset ID 0001 and to asset ID 0005. If request 2 is processed from asset ID 0005 and to asset ID 9999, asset 0005 is processed twice. You can use Query to verify ranges by counting the number of assets in total and number of assets per range. |
Note. If you use the interface between PeopleSoft Asset Management and PeopleSoft Billing, accounting entries are created by these integrated transactions. How the entries are created is described in more detail in the PeopleSoft Billing documentation.
See Pages Used to Define Accounting Entry for PeopleSoft Asset Management.
See Integrating PeopleSoft Asset Management with Other Products.
See Understanding Asset Management Business and Cash Generating Units.
See Making General Ledger Journal Entries.
See Integrating with PeopleSoft Asset Management.

 Closing Accounting Periods
Closing Accounting Periods
Access the Close Accounting Period page (Asset Management, Accounting Entries, Close Accounting Period, Close Accounting Period).
Enter the year and period to be closed, and save the page. When a period has been closed, you cannot create additional depreciation-related accounting entries for that period.
See Managing Interim and Year End Closing.

 Running the Clearing Reconciliation Process
Running the Clearing Reconciliation Process
Access the Clearing Reconciliation page (Asset Management, Accounting Entries, Clearing Reconciliation, Clearing Reconciliation).
PeopleSoft Asset Management provides an optional Capitalization Threshold feature that, once enabled, can automatically determine capitalization status of an asset, by profile, based on its cost or quantity according to limits that you define. The system classifies assets as capital, noncapital, or expense. The Clearing Reconciliation process (AM_CLEREC) provides a way to reconcile accounting entries for expensed assets.
See Setting Up Capitalization Thresholds.
When assets came from other sources, a debit is usually recorded to a fixed asset account and a clearing account is credited that was previously debited in the source system. When an asset is deemed trackable because of the specified threshold, the asset ID is generated but no accounting activities take place. This reconciliation process provides a way to balance out the clearing account that was debited in the source system and debit the expense account instead. This is not applicable to expensed (trackable) assets that are entered directly in Asset Management with no clearing account.
Enter the parameters and run the process. The system searches noncapital assets for the specified parameters in the acquisition detail. For each noncapital row that matches the system source, the following entry is generated in the DIST_LN table:
|
Debit |
Credit |
Distribution Type |
|
Expense Account |
EX |
|
|
Clearing Account |
AP |