| Oracle® Identity Manager Connector Guide for SAP User Management Release 9.1.2 E11212-06 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
| Oracle® Identity Manager Connector Guide for SAP User Management Release 9.1.2 E11212-06 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
This chapter is divided into the following sections:
|
Note: These sections provide both conceptual and procedural information about configuring the connector. It is recommended that you read the conceptual information before you perform the procedures. |
Section 3.2, "Scheduled Task for Lookup Field Synchronization"
Section 3.7, "Provisioning Operations Performed in an SoD-Enabled Environment"
Section 3.8, "Switching Between SAP R/3 and SAP CUA Target Systems"
Section 3.10, "Enabling and Disabling the Compliant User Provisioning Feature"
Full reconciliation involves reconciling all existing user records from the target system into Oracle Identity Manager. After you deploy the connector, you must first perform full reconciliation. In addition, you can switch from incremental reconciliation to full reconciliation whenever you want to ensure that all target system records are reconciled in Oracle Identity Manager.
To perform a full reconciliation run, set the Last Execution Timestamp attribute of the SAP User Management User Recon and SAP User Management Delete Recon scheduled tasks to 0. At the end of the reconciliation run, this attribute is automatically set to the time stamp at which the run started. From the next run onward, only records created or modified after this time stamp value are considered for reconciliation.
The SAP User Management Lookup Recon scheduled task is used for lookup field synchronization. Table 3-1 describes the attributes of this scheduled task. The procedure to configure scheduled tasks is described later in the guide.
Table 3-1 Attributes of the SAP User Management Lookup Recon Scheduled Task
Apply the following guidelines while configuring reconciliation:
On SAP CUA, an account that is directly created on the target system must be assigned a master system before changes to that account can be detected and brought to Oracle Identity Manager during reconciliation.
On a Microsoft Windows platform, if you encounter the org.quartz.SchedulerException exception during a reconciliation run, then download and install the Microsoft Visual C++ 2005 SP1 Redistributable Package from the Microsoft Web site.
As mentioned earlier in this guide, reconciliation involves duplicating in Oracle Identity Manager the creation of and modifications to user accounts on the target system. This section discusses the following topics related to configuring reconciliation:
The Last Execution Timestamp attribute of the scheduled task stores the time stamp at which a reconciliation run begins. During a reconciliation run, the scheduled task fetches only target system records that are added or modified after the time stamp stored in the parameter for reconciliation. This is incremental reconciliation. If you set the parameter to 0, then full reconciliation is performed. In full reconciliation, all existing target system records are fetched into Oracle Identity Manager for reconciliation.
As mentioned earlier in this chapter, you can switch from incremental to full reconciliation at any time.
By default, all target system records that are added or modified after the last reconciliation run are reconciled during the current incremental reconciliation run. For full reconciliation, all target system records are fetched into Oracle Identity Manager.
You can configure limited reconciliation to specify the subset of target system records that must be fetched into Oracle Identity Manager.
You configure limited reconciliation by specifying a query condition as the value of the Custom Query attribute of the SAP User Management User Recon scheduled task.
You must use the following format to specify a value for the Custom Query attribute:
RESOURCE_OBJECT_FIELD_NAME=VALUE
For example, suppose you specify the following as the value of the Custom Query attribute:
Last Name=Doe
With this query condition, only records for users whose last name is Doe are considered for reconciliation.
You can add multiple query conditions by using the ampersand (&) as the AND operator and the vertical bar (|) as the OR operator. For example, the following query condition is used to limit reconciliation to records of those users whose first name is John and last name is Doe:
First Name=John & Last Name=Doe
|
Note: This feature cannot be applied to the Locked/Unlocked status attribute of the target system. |
To configure limited reconciliation:
Ensure that the attribute that you want to use in the query exists in the Lookup.SAP.UM.ReconAttrMap lookup definition.
If there is no entry in this lookup definition for the attribute that you want to use, then create an entry. See Section 4.2, "Adding New Attributes for Reconciliation" for more information.
Create the query condition. Apply the following guidelines to create the query condition:
Use only the equal sign (=), ampersand (&), and vertical bar (|) in the query condition. If any other special character is included, then it is treated as part of the attribute value that you specify.
Add a space before and after ampersands and vertical bars used in the query condition. For example:
First Name=John & Last Name=Doe
This is to help the system distinguish between ampersands and vertical bars used in the query and the same characters included as part of attribute values specified in the query condition.
You must not include unnecessary blank spaces between operators and values in the query condition.
A query condition with spaces separating values and operators would yield different results as compared to a query condition that does not contain spaces between values and operators. For example, the output of the following query conditions is not the same:
First Name=John & Last Name=Doe
First Name= John & Last Name= Doe
In the second query condition, the reconciliation engine would look for first name and last name values that contain a space at the start.
Ensure that attribute names that you use in the query condition are in the same case (uppercase and lowercase) as the case of values in the Lookup.SAP.UM.ReconAttrMap lookup definition. For example, the following query condition would fail:
fiRst Name = John
While configuring the SAP User Management User Recon scheduled task, specify the query condition as the value of the Custom Query attribute. The procedure is described later in this chapter.
You must specify values for the attributes of the following scheduled tasks:
|
Note: Attribute values are predefined in the connector XML file that you import. Specify values only for the attributes that you want to change. |
You use the SAP User Management User Recon scheduled task to reconcile user data from the target system. Table 3-2 describes the attributes of this scheduled task.
Table 3-2 Attributes of the SAP User Management User Recon Scheduled Task
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
This attribute holds the name of the lookup definition that stores attribute mappings for reconciliation. Value: |
|
|
Enter the number of records that must be included in each batch fetched from the target system during a reconciliation run. This attribute is used to implement batched reconciliation. Default value: |
|
|
This attribute holds the name of the lookup definition that stores child attribute mappings for reconciliation. Value: |
|
|
Custom Query |
Enter the query that you want the connector to apply during reconciliation. See Section 3.4.2, "Limited Reconciliation" for more information. |
|
IT Resource |
Enter the name of the IT resource for the target system installation from which you want to reconcile user records. Default value: |
|
Last Execution Timestamp |
This attribute holds the time stamp at which the last reconciliation run started. For the next reconciliation run, only target system records that have been added or modified after this time stamp are considered for reconciliation. For consecutive reconciliation runs, the connector automatically enters a value for this attribute. However, you can use this attribute to switch from incremental reconciliation to full reconciliation. See Section 3.4.1, "Full Reconciliation vs. Incremental Reconciliation" for more information. Default value: |
|
Resource Object |
This attribute holds the name of the resource object. Default value: |
|
SAP System Time Zone |
Enter the abbreviation for the time zone of the target system host computer. The value that you enter must be one of the time zones supported by the java.util.TimeZone class. Note: The connector does not validate the value that you enter. In addition, no error is thrown during reconciliation if the value entered is not a valid time zone. Sample value: |
|
Schedule Task Name |
This attribute holds the name of the scheduled task. Value: |
You use the SAP User Management Delete Recon scheduled task to reconcile deleted users from the target system. Table 3-3 describes the attributes of this scheduled task.
Table 3-3 Attributes of the SAP User Management Delete Recon Scheduled Task
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Enter the number of records that must be included in each batch fetched from the target system during a reconciliation run. This attribute is used to implement batched reconciliation. Default value: |
|
|
Disable User |
Enter Default value: |
|
IT Resource |
Enter the name of the IT resource for the target system installation from which you want to reconcile user records. Default value: |
|
Last Execution Timestamp |
This attribute holds the time stamp at which the last reconciliation run started. For the next reconciliation run, only target system records that have been added or modified after the recorded time stamp are considered for reconciliation. For consecutive reconciliation runs, the connector automatically enters a value for this attribute. However, you can use this attribute to switch from incremental reconciliation to full reconciliation. See Section 3.4.1, "Full Reconciliation vs. Incremental Reconciliation" for more information. Default value: |
|
Resource Object |
This attribute holds the name of the resource object. Default value: |
|
SAP System Time Zone |
Enter the abbreviation for the time zone of the target system host computer. The value that you enter must be one of the time zones supported by the java.util.TimeZone class. Note: The connector does not validate the value that you enter. In addition, no error is thrown during reconciliation if the value entered is not a valid time zone. Sample value: |
|
Schedule Task Name |
This attribute holds the name of the scheduled task. Default value: |
You use the SAP CUP Status Update Recon scheduled task to fetch the status of provisioning requests sent to SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning. For a particular user, only the status of the latest request is brought to Oracle Identity Manager. This request is the one currently stored on the process form. Table 3-4 describes the attributes of this scheduled task.
Table 3-4 Attributes of the SAP CUP Status Update Recon Scheduled Task
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
This attribute holds the name of the lookup definition that holds constant values used by the connector during reconciliation and provisioning. Default value: |
|
|
IT Resource |
Enter the name of the IT resource for the SAP GRC installation from which you want to fetch request status data. Default value: |
|
Resource Object |
This attribute holds the name of the resource object. Default value: |
|
Schedule Task Name |
This attribute holds the name of the scheduled task. Default value: |
|
Note: Configure this scheduled task only if you enable the Compliant User Provisioning feature. |
You use the SAP CUP Delete Recon scheduled task to revoke accounts (resources) of users in Oracle Identity Manager for whom the Create User provisioning requests are rejected by SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning.
When you perform a Create User provisioning operation, the account is allocated to the OIM User even before SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning clears the provisioning request and creates an account on the target system. For a particular user, if account creation on the target system fails, then the account provisioned in Oracle Identity Manager is an invalid account. You use the SAP CUP Delete Recon scheduled task to identify and delete such accounts.
Table 3-5 Attributes of the SAP CUP Delete Recon Scheduled Task
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
This attribute holds the name of the lookup definition that stores configuration values used by the connector during reconciliation and provisioning. You can set values for some of the entries in this lookup definition. Default value: |
|
|
This attribute holds the name of the lookup definition that holds constant values used by the connector during reconciliation and provisioning. Default value: |
|
|
IT Resource |
Enter the name of the IT resource for the target system installation from which you want to reconcile user records. Default value: |
|
Resource Object |
This attribute holds the name of the resource object. Default value: |
|
Schedule Task Name |
This attribute holds the name of the scheduled task. Default value: |
This section describes the procedure to configure scheduled tasks. You can apply this procedure to configure the scheduled tasks for lookup field synchronization and reconciliation.
Table 3-6 lists the scheduled tasks that you must configure.
Table 3-6 Scheduled Tasks for Lookup Field Synchronization and Reconciliation
| Scheduled Task | Description |
|---|---|
|
SAP User Management Lookup Recon |
This scheduled task is used for lookup field synchronization. Section 3.2, "Scheduled Task for Lookup Field Synchronization" describes this scheduled task. |
|
SAP User Management User Recon |
This scheduled task is used for user record reconciliation. Section 3.4.3.1, "SAP User Management User Recon" describes this scheduled task. |
|
SAP User Management Delete Recon |
This scheduled task is used for reconciliation of deleted user records. Section 3.4.3.2, "SAP User Management Delete Recon" describes this scheduled task. |
|
This scheduled task is used to fetch the status of provisioning requests sent to SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning. Section 3.4.3.3, "SAP CUP Status Update Recon" describes this scheduled task. Note: This scheduled task is created only if you configure the Compliant User Provisioning feature. |
|
|
This scheduled task is used to revoke accounts (resources) of users in Oracle Identity Manager for whom the Create User provisioning requests are rejected by SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning. Section 3.4.3.4, "SAP CUP Delete Recon" describes this scheduled task. Note: This scheduled task is created only if you configure the Compliant User Provisioning feature. |
To configure a scheduled task:
Log in to the Administrative and User Console.
Expand Resource Management.
Click Manage Scheduled Task.
On the Scheduled Task Management page, enter the name of the scheduled task as the search criteria and then click Search.
In the search results table, click the edit icon in the Edit column for the scheduled task.
On the Edit Scheduled Task Details page, you can modify the following details of the scheduled task by clicking Edit:
Status: Specify whether or not you want to leave the task in the enabled state. In the enabled state, the task is ready for use.
Max Retries: Enter an integer value in this field. This number represents the number of times Oracle Identity Manager must attempt to complete the task before assigning the ERROR status to the task. The default value is 1.
Next Start: Use the date editor to specify the date when you want the task to run. After you select a date value in the date editor, you can modify the time value that is automatically displayed in the Next Start field.
Frequency: Specify the frequency at which you want the task to run.
After modifying the values for the scheduled task details listed in the previous step, click Continue.
Specify values for the attributes of the scheduled task. To do so, select each attribute from the Attribute list, specify a value in the field provided, and then click Update.
|
Note: Attribute values are predefined in the connector XML file that you import. Specify values only for the attributes that you want to change. |
The attributes of the scheduled task that you select for modification are displayed on this page.
Click Save Changes to commit all the changes to the database.
|
Note: If you want to stop a scheduled task while it is running, then use the Stop Execution feature of the Design Console. See "The Task Scheduler Form" in Oracle Identity Manager Design Console Guide for information about this feature. |
Apply the following guidelines while performing provisioning operations in any of the supported deployment configurations:
Through provisioning, if you want to create and disable an account at the same time, then you can set the value of the Valid Through attribute to a date in the past. For example, while creating an account on 31-Jul, you can set the Valid Through date to 30-Jul. With this value, the resource provisioned to the OIM User is in the Disabled state immediately after the account is created.
However, on the target system, if you set the Valid Through attribute to a date in the past while creating an account, then the target system automatically sets Valid Through to the current date. The outcome of this Create User provisioning operation is as follows:
The value of the Valid Through attribute on Oracle Identity Manager and the target system do not match.
On the target system, the user can log in all through the current day. The user cannot log in from the next day onward.
You can lock the user on the target system so that the user is not able to log in the day the account is created.
Remember that if password or system assignment fails during a Create User provisioning operation, then the user is not created.
When you try to provision a multivalued attribute, such as a role or profile, if the attribute has already been set for the user on the target system, then the status of the process task is set to Completed in Oracle Identity Manager. If required, you can configure the task so that it shows the status Rejected in this situation. See Oracle Identity Manager Design Console Guide for information about configuring process tasks.
When you perform the Lock User or Unlock User provisioning operation, remember that the connector makes the required change on the target system without checking whether the account is currently in the Locked or Unlocked state. This is because the target system does not provide a method to check the current state of the account.
The target system does not accept non-English letters in the E-mail Address field. Therefore, during provisioning operations, you must enter only English language letters in the E-mail Address field on the process form.
The process form provides lookup definitions for both the target system IT resource and the Compliant User Provisioning IT resource (SAP GRC IT Resource). If you configure the Compliant User Provisioning feature, then you must select IT resources in both lookup definitions. In the Basic User Management mode, you need not select an IT resource for Compliant User Provisioning.
On a Microsoft Windows platform, if you encounter the java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError exception during a provisioning operation, then download and install the Microsoft Visual C++ 2005 SP1 Redistributable Package from the Microsoft Web site.
Apply the following guidelines while performing provisioning operations after configuring the Compliant User Provisioning feature of the connector:
During a Create User operation performed when the Compliant User Provisioning is configured, first submit process form data. Submit child form data after the user is created on the target system. This is because when Compliant User Provisioning is enabled, the connector supports modification of either process form fields or child form fields in a single Modify User operation.
The following fields on the process form are mandatory attributes on SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning:
|
Note: When the Compliant User Provisioning feature is configured, you must enter values for these fields even though some of them are not marked as mandatory fields on the Administrative and User Console. |
CUP Requestor ID
CUP Requestor First Name
CUP Requestor Last Name
CUP Requestor Email
GRC IT Resource
User ID
First Name
Last Name
E Mail
The Valid From and Valid Through attributes are not mandatory attributes.
As mentioned earlier in this guide, SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning does not process passwords. Therefore, any value entered in the Password field is ignored during Create User provisioning operations. After a Create User operation is performed, the user for whom the account is created on the target system must apply one of the following approaches to set the password:
To use the Oracle Identity Manager password as the target system password, change the password through Oracle Identity Manager.
Directly log in to the target system, and change the password.
You perform an Enable User operation by setting the Valid From field to a future date. Similarly, you perform a Disable User operation by setting the Valid Through field to the current date. Both operations are treated as Modify User operations.
When you delete a user (account) on the Administrative and User Console (process form), a Delete User request is created.
When you select the Lock User check box on the process from, a Lock User request is created.
When you deselect the Lock User check box on the process from, an Unlock User request is created.
The Enable User and Disable User operations are implemented through the Valid From and Valid Through fields on the process form.
In a Modify User operation, you can specify values for attributes that are mapped with SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning and attributes that are directly updated on the target system. A request is created SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning only for attributes whose mappings are present in these lookup definitions. If you specify values for attributes that are not present in these lookup definitions, then the connector sends them to directly the target system.
SAP GRC Compliant User Provisioning does not process passwords. Therefore, any value entered in the Password field is ignored during Create User provisioning operations. During a Modify User provisioning operation, the password is sent directly to the target system.
Provisioning a resource for an OIM User involves using Oracle Identity Manager to create a target system account for the user. The following are types of provisioning operations:
Request-based provisioning of entitlements
|
See Also: Oracle Identity Manager Connector Concepts for information about the types of provisioning |
This section discusses the following topics:
Section 3.7.1, "Overview of the Provisioning Process in an SoD-Enabled Environment"
Section 3.7.3, "Direct Provisioning in an SoD-Enabled Environment"
Section 3.7.4, "Request-Based Provisioning in an SoD-Enabled Environment"
The following is the sequence of steps that take places during a provisioning operation performed in an SoD-enabled environment:
The provisioning operation triggers the appropriate adapter.
The user runs the scheduled task (either ResubmitUninitiatedProvisioningSODCheck or Resubmit Uninitiated Approval SOD Checks).
The scheduled task passes the entitlement data to the Web service of SAP GRC.
After SAP GRC runs the SoD validation process on the entitlement data, the response from the process is returned to Oracle Identity Manager.
The status of the process task that received the response depends on the response itself. If the entitlement data clears the SoD validation process, then the adapter carries provisioning data to the corresponding BAPI on the target system and the status of the process task changes to Completed. This translates into the entitlement being granted to the user. If the SoD validation process returns the failure response, then status of the process task changes to Canceled.
Apply the following guidelines while performing provisioning operations:
When you assign a role to a user through provisioning, you set values for the following attributes:
Role System Name
Role Name
Start Date
End Date
However, when you update a role assignment, you can specify values only for the Start Date and End Date attributes. You cannot set new values for the Role System Name and Role Name attributes. This also applies to new child forms that you add.
You can only assign profiles. You cannot update an assigned profile.
To provision a resource by using the direct provisioning approach:
Log in to the Administrative and User Console.
From the Users menu, select Manage if you want to provision a target system account to an existing OIM User.
If you select Create, on the Create User page, enter values for the OIM User fields and then click Create User. The following screenshot shows the Create User page.
If you select Manage, then search for the OIM User and select the link for the user from the list of users displayed in the search results.
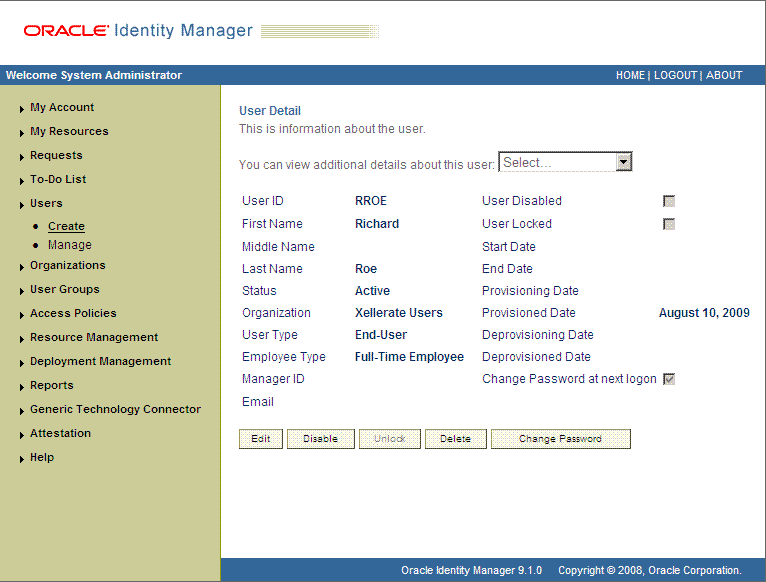
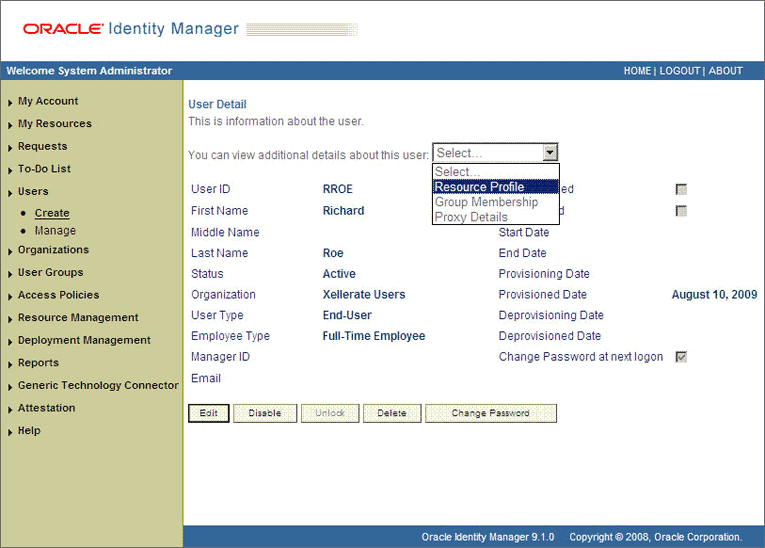
On the User Detail page, select Resource Profile from the list at the top of the page. The following screenshot shows the User Detail page.
On the Resource Profile page, click Provision New Resource. The following screenshot shows the Resource Profile page.
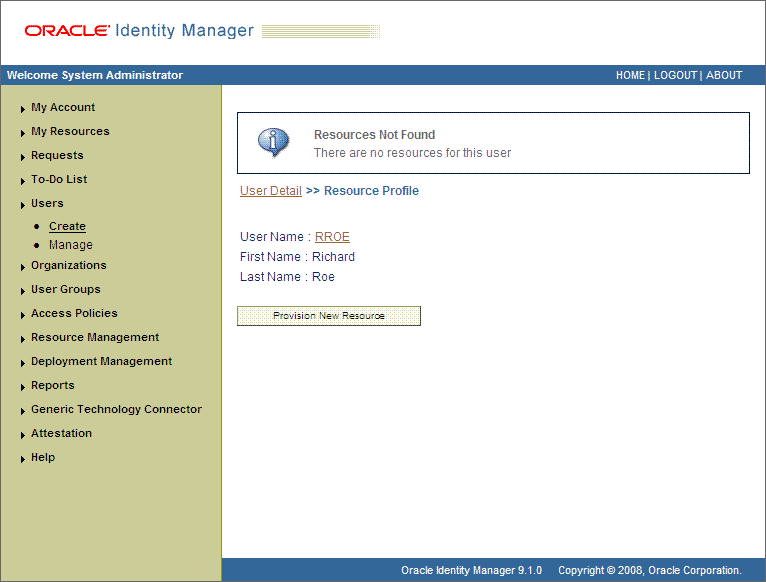
On the Step 1: Select a Resource page, select SAP UM Resource Object from the list and then click Continue. The following screenshot shows the Step 1: Select a Resource page.
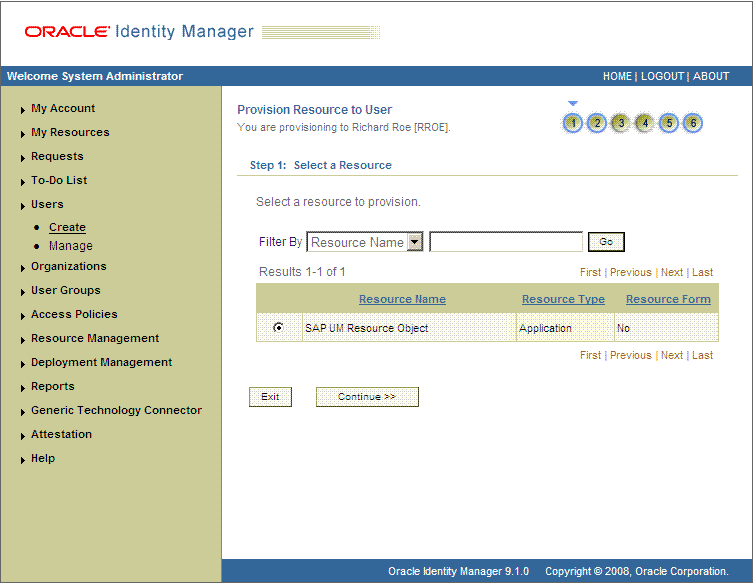
On the Step 2: Verify Resource Selection page, click Continue. The following screenshot shows the Step 2: Verify Resource Selection page.
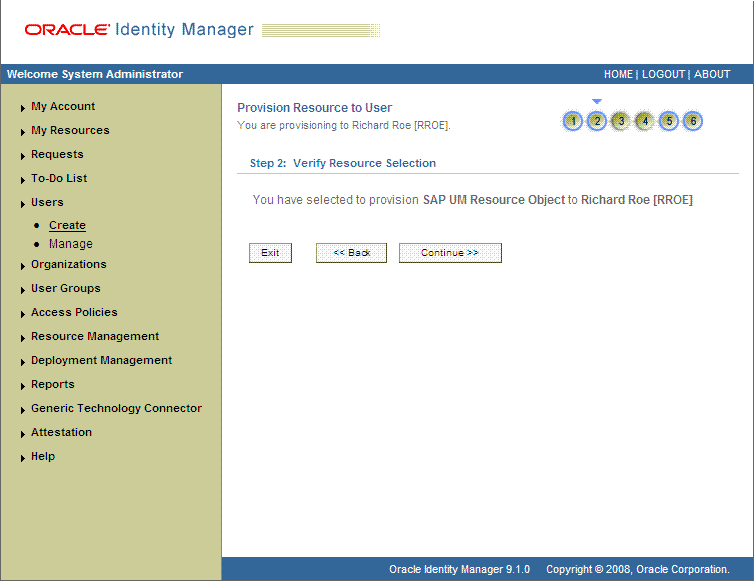
On the Step 5: Provide Process Data page for process data, enter the details of the account that you want to create on the target system and then click Continue. The following screenshot shows the user details added.
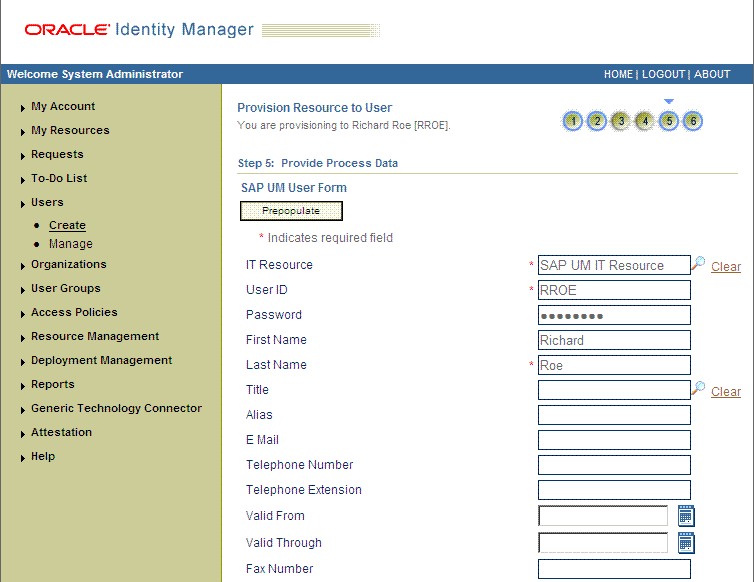
On the Step 5: Provide Process Data page for profile data, search for and select profiles for the user on the target system and then click Continue. The following screenshot shows this page.
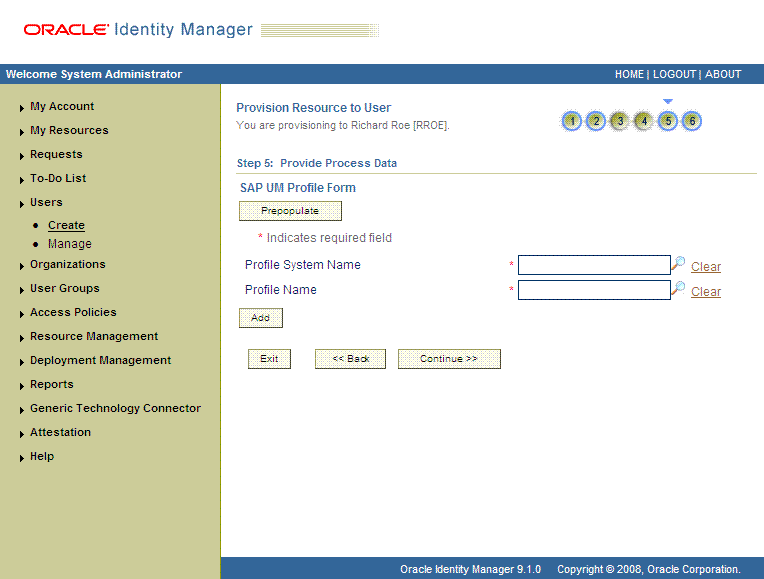
On the Step 5: Provide Process Data page for role data, search for and select roles for the user on the target system and then click Continue. The following screenshot shows this page.
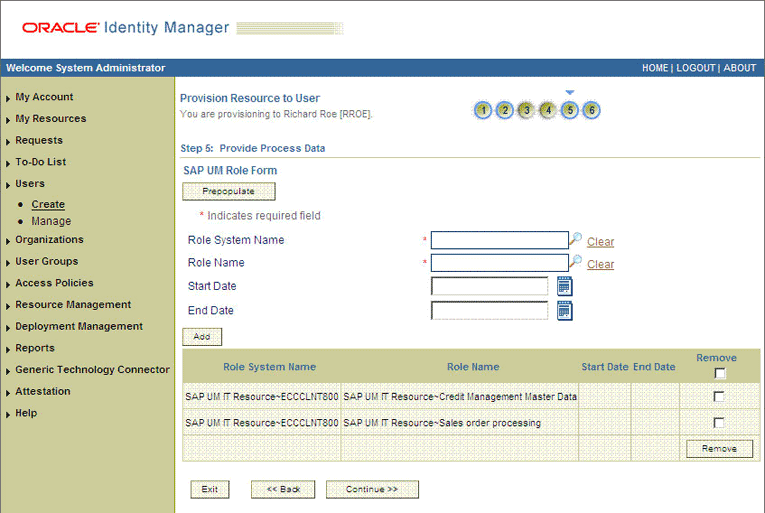
On the Step 6: Verify Process Data page, verify the data that you have provided and then click Continue. The following screenshot shows Step 6: Verify Process Data page.
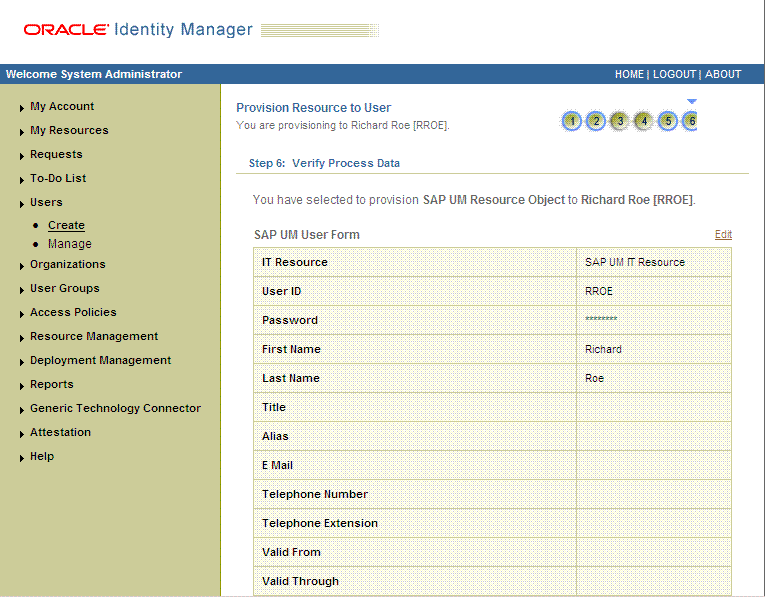
The "Provisioning has been initiated" message is displayed. Click Back to User Resource Profile. The Resource Profile page shows that the resource has been provisioned to the user.
The following screenshot shows this page:
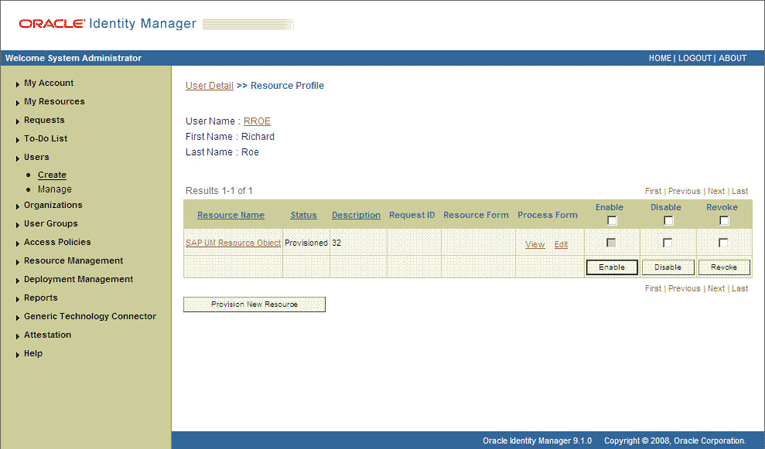
If you click the View link in the Process Form column, then the process form is displayed. The following screenshot shows this page:
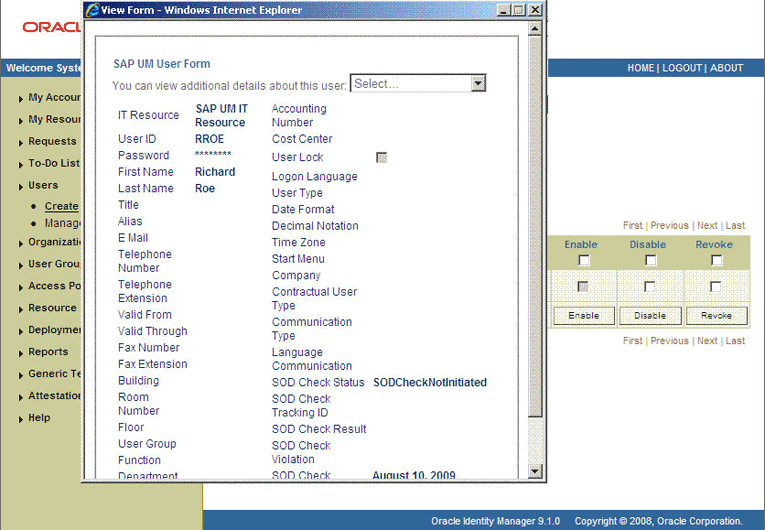
In this screenshot, the SOD Check Status field shows SODCheckNotInitiated. The value in this field can be SoDCheckNotInitiated, SoDCheckResultPending, or SoDCheckCompleted.
If you click the resource, then the Resource Provisioning Details page is displayed. The following screenshot shows this page:
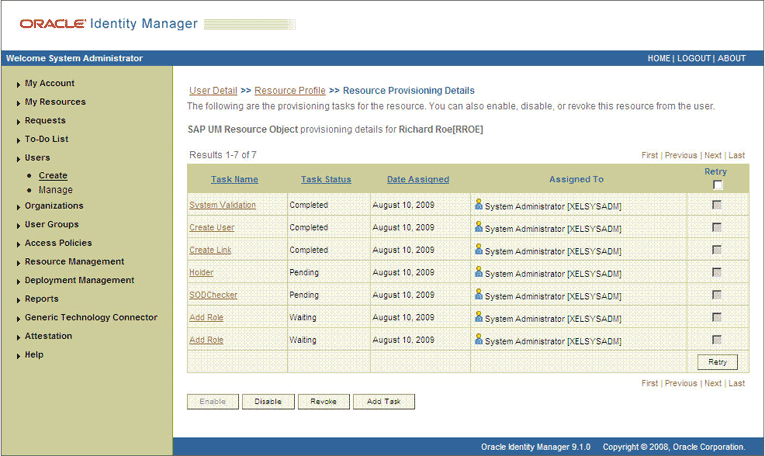
This page shows the details of the process tasks that were run. The Holder and SODChecker tasks are in the Pending state. These tasks will change state after the status of the SoD check is returned from the SoD engine. The Add User Role tasks correspond to the two roles selected for assignment to this user.
The SODCheckNotInitiated status in the SOD Check Status field indicates that SoD validation has not started. To start SoD validation, you must run the ResubmitUninitiatedProvisioningSODChecks scheduled task.
The following screenshot shows the ResubmitUninitiatedProvisioningSODChecks scheduled task in the Design Console:
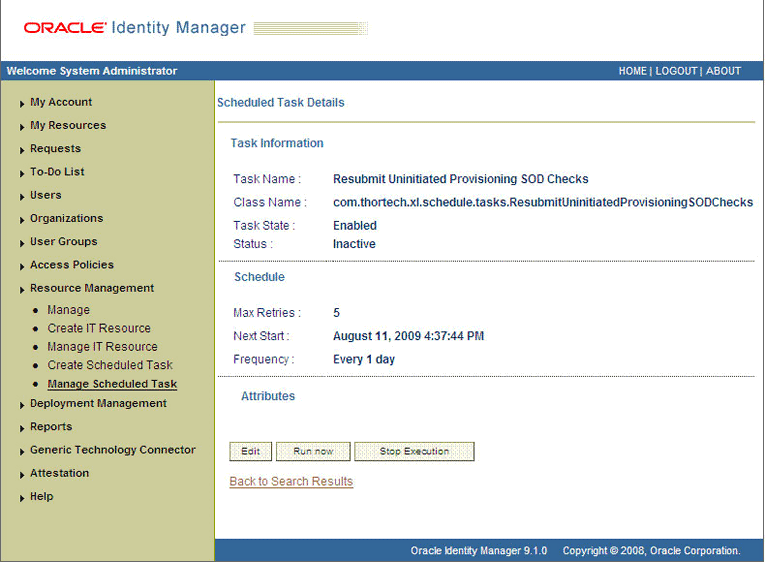
After the ResubmitUninitiatedProvisioningSODChecks scheduled task is run, the results of the SoD validation process are brought to Oracle Identity Manager. If you click the View link in the Process Form column, then the process form is displayed. The following screenshot shows this page:
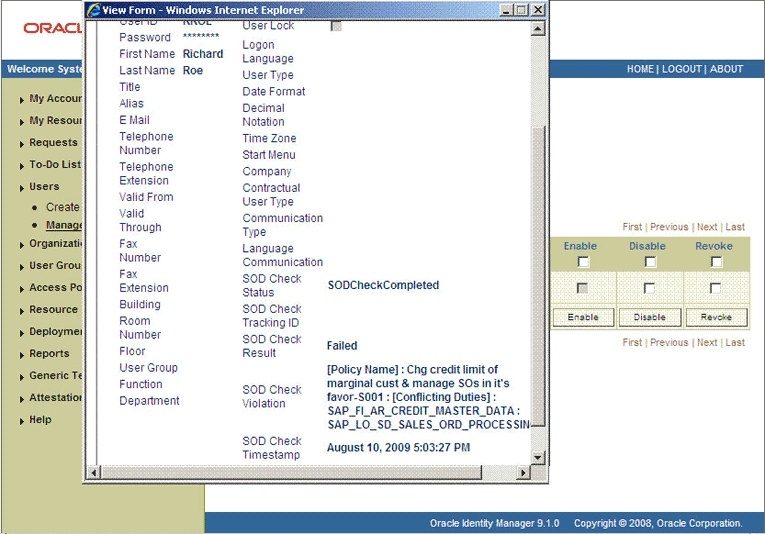
In this screenshot, the SOD Check Status field shows SoDCheckCompleted. Because a violation by the SoD engine in this particular example, the SoD Check Violation field shows the details of the violation.
In addition, the Resource Provisioning Details page shows the status of the SODChecker and Holder tasks as Completed.
The following screenshot shows this page:
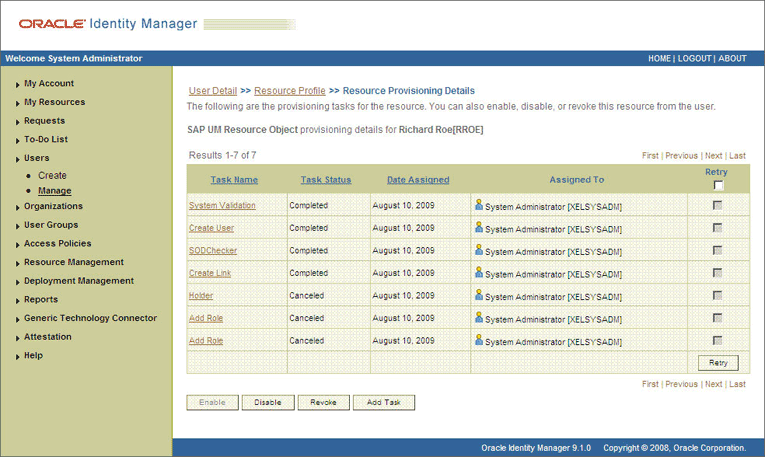
In this screenshot, the status of the Add User Role tasks is Canceled because the request failed the SoD validation process.
As the administrator assigning a resource to a user, you can either end the process when a violation is detected or modify the assignment data and then resend it. To modify the assignment data, first click the Edit link in the Process Form column on the Resource Profile page.
In the Edit Form window that is displayed, you can modify the role and profile data that you had selected earlier.
|
Note: To modify a set of entitlements In the Edit Form window, you must first remove all entitlements and then add the ones that you want to use. |
In the following screenshot, one of the roles selected earlier is marked for removal:
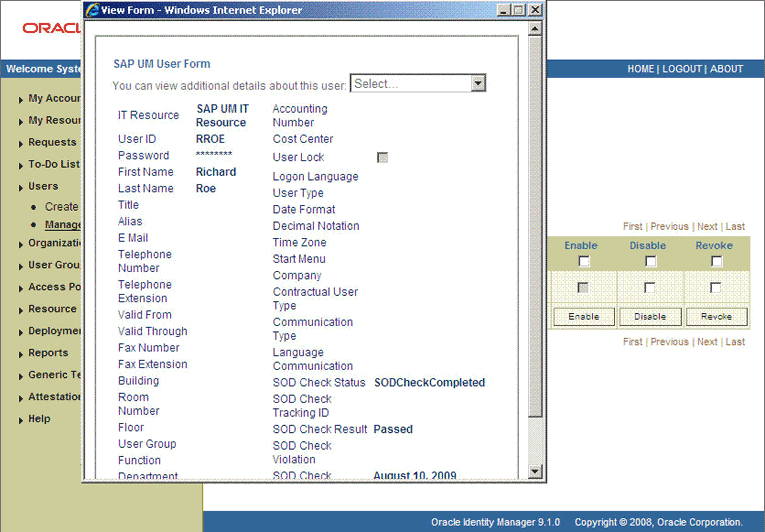
Rerun the ResubmitUninitiatedProvisioningSODChecks scheduled task to initiate the SoD validation process.
After the ResubmitUninitiatedProvisioningSODChecks scheduled task is run, the results of the SoD validation process are brought to Oracle Identity Manager. If you click the View link in the Process Form column, then the process form is displayed. The following screenshot shows this page:
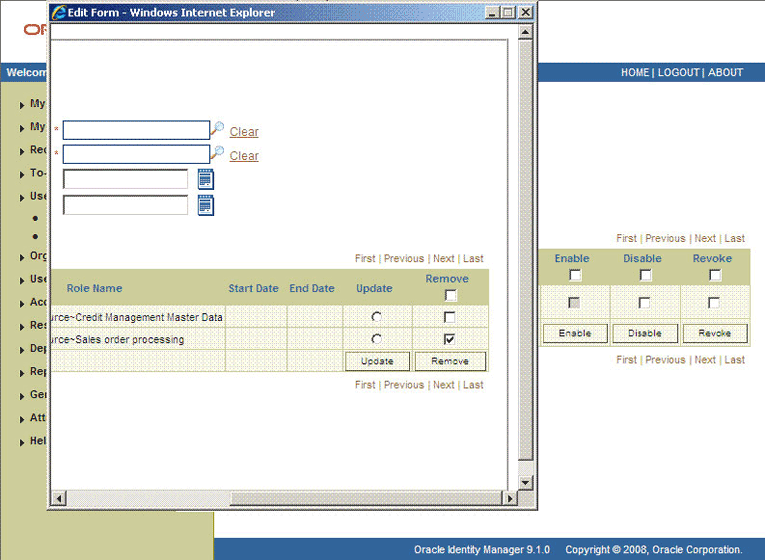
In this screenshot, the SOD Check Status field shows SoDCheckCompleted. Because no violation was detected by the SoD engine, the SoD Check Violation field shows Passed.
In addition, the Resource Provisioning Details page shows the status of the SODChecker and Holder tasks as Completed.
The following screenshot shows this page:

On the Resource Provisioning Details page, the state of the Add User Role task is Completed.
The request-based provisioning operation involves both end users and approvers. Typically, these approvers are in the management chain of the requesters. The request-based provisioning process described in this section covers steps to be performed by both entities.
In the example used in this section, the end user creates a request for two roles on the target system. The request clears the SoD validation process and is approved by the approver.
End-User's Role in Request-Based Provisioning
The following are types of request-based provisioning:
Request-based provisioning of accounts: OIM Users are created but not provisioned target system resources when they are created. Instead, the users themselves raise requests for provisioning accounts.
Request-based provisioning of entitlements: OIM Users who have been provisioned target system resources (either through direct or request-based provisioning) raise requests for provisioning entitlements.
The following steps are performed by the end user in a request-based provisioning operation:
|
Note: The procedure is almost the same for request-based provisioning of both accounts and entitlements. Differences have been called out in the following sequence of steps. |
Log in to the Administrative and User Console.
Expand My Resources, and then click Request New Resources.
On the Step 1: Provide resources page, use the Add button to select one of the following:
SAP UM Resource Object, if you want to create a request for a target system account
SAP UM Roles or SAP UM Profiles, if you want to create a request for an entitlement on the target system
The following screenshot shows the SAP UM Roles entitlement selected:
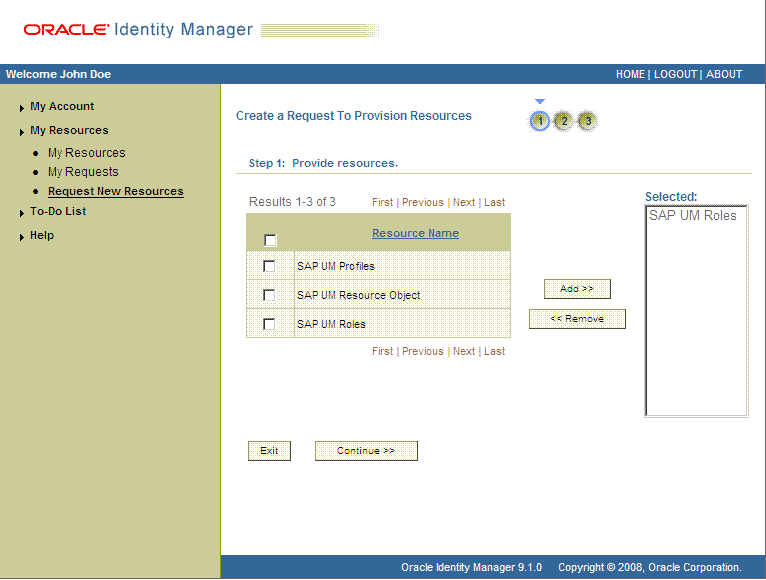
On the Step 2: Provide resource data page, click Continue.
The following screenshot shows this page:
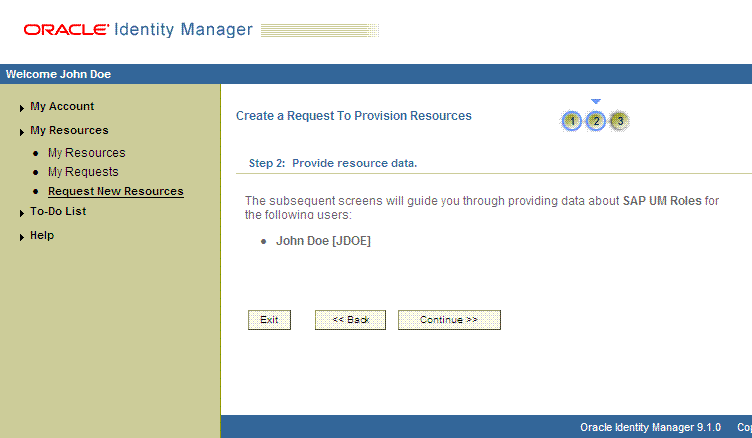
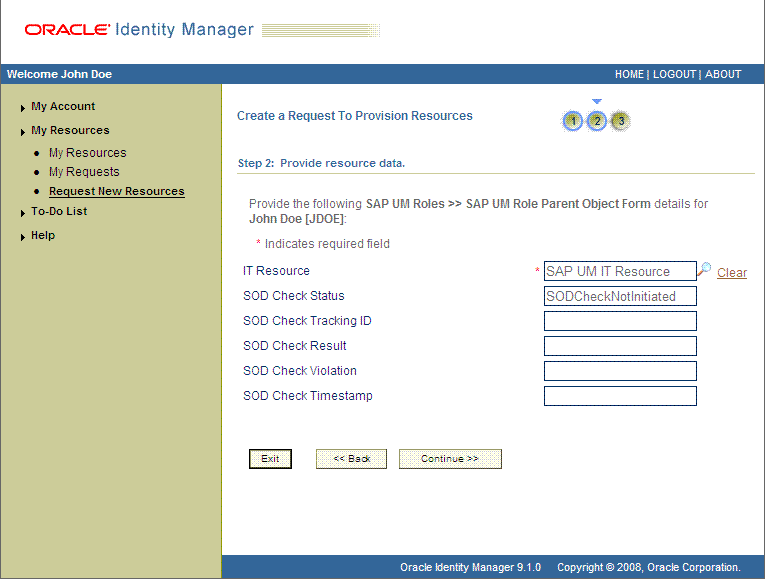
On the second Step 2: Provide resource data page, select the IT resource corresponding to the target system installation on which you want the selected entitlement.
The following screenshot shows this page:
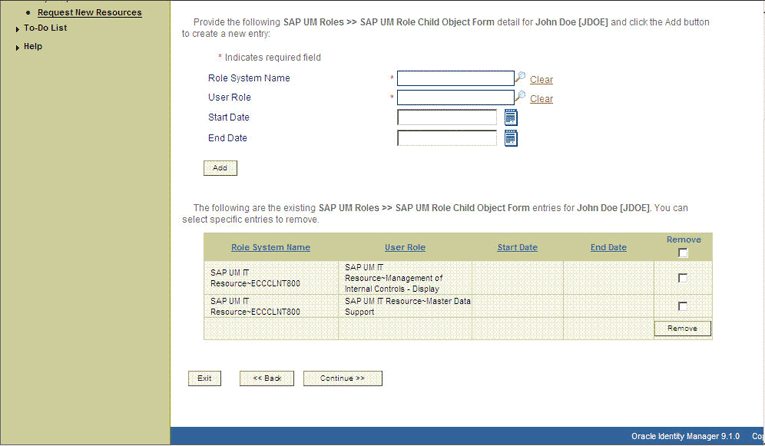
On the third Step 2: Provide resource data page, select the entitlements that you want to request.
The following screenshot shows two roles selected on this page:
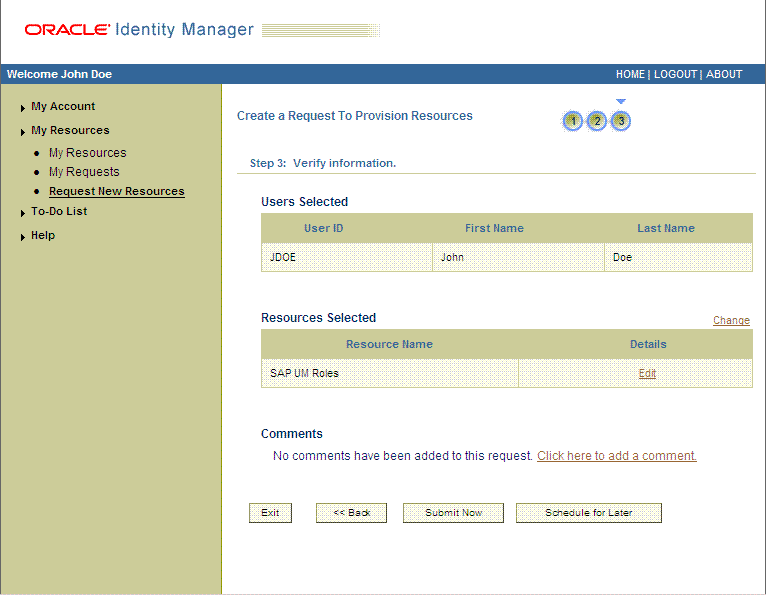
On the Step 3: Verify information page, review the information that you have provided and then submit the request.
The following screenshot shows this page:
If you click Submit Now, then the Request Submitted page shows the request ID.
The following screenshot shows this page:
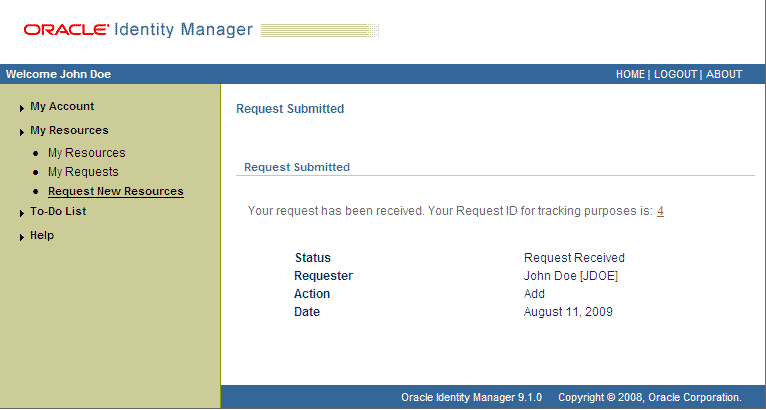
If you click the request ID, then the Request Details page is displayed.
The following screenshot shows this page:
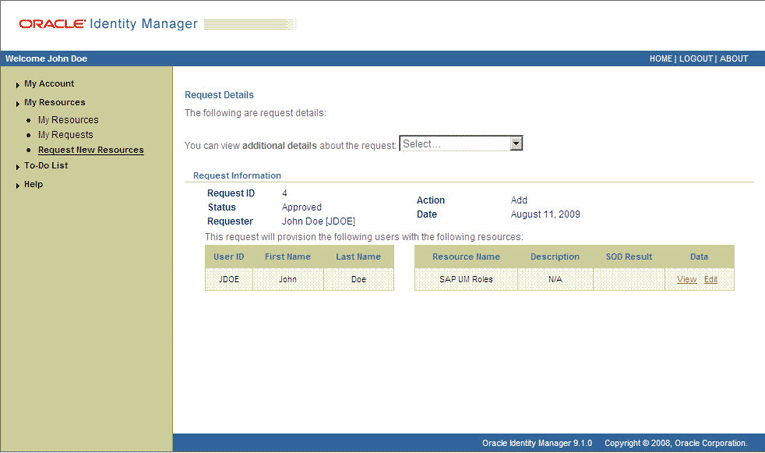
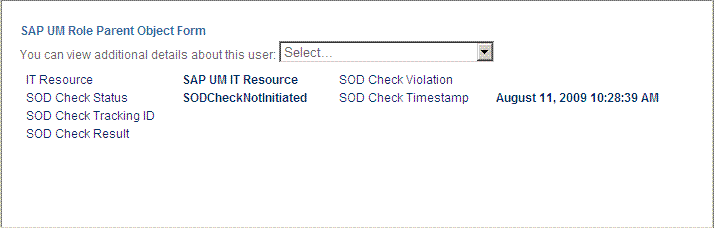
On the page displayed when you click View, the SOD Status field shows SODCheckNotInitiated. The value in this field can be SoDCheckNotInitiated, SoDCheckResultPending, or SoDCheckCompleted.
The following screenshot shows this page:
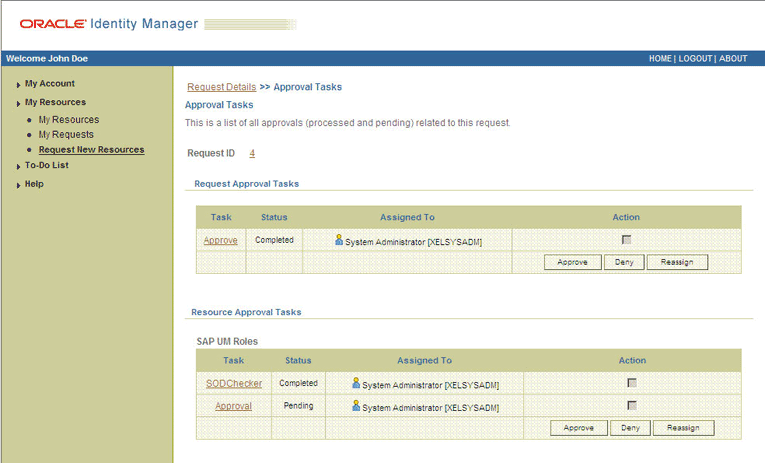
To view details of the approval, select Approval Tasks from the list at the top of the page. The Approval Tasks page is displayed. The following screenshot shows this page:
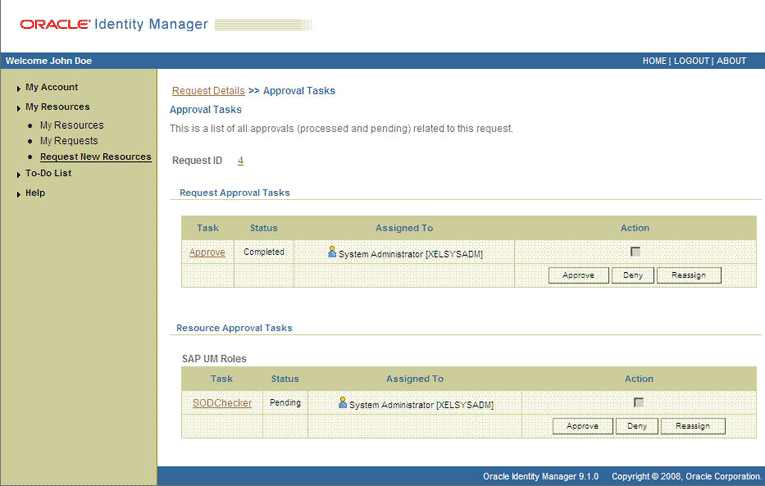
On this page, the status of the SODChecker task is Pending.
To initiate SoD validation of pending entitlement requests, an administrator must run the Resubmit Uninitiated Approval SOD Checks scheduled task. The following screenshots shows this scheduled task in the Design Console:
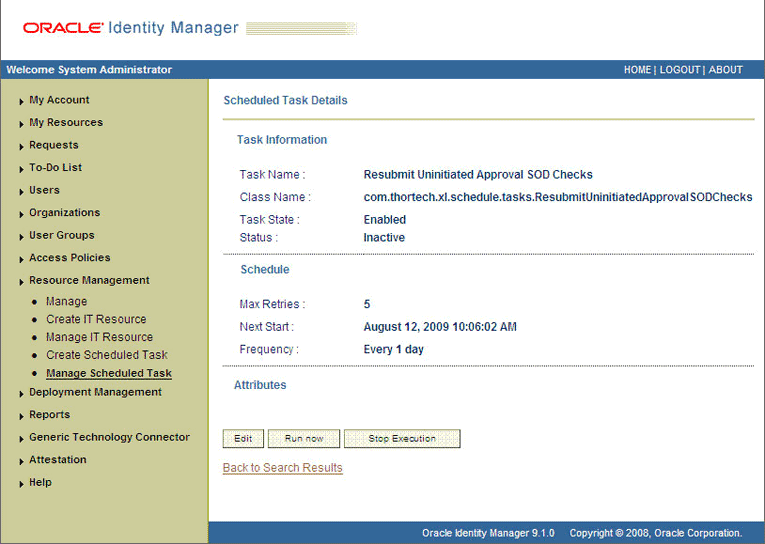
After the Resubmit Uninitiated Approval SOD Checks scheduled task is run, on the Approvals Task page, the status of the SODChecker task is Completed and the Approval task status is Pending. This page also shows details of the administrator who must now approve the request.
The following screenshot shows the Approvals Task page after the request passes the SoD validation process.
Approver's Role in Request-Based Provisioning
This section discusses the role of the approver in a request-based provisioning operation.
The approver to whom the request is assigned can use the Pending Approvals feature to view details of the request.
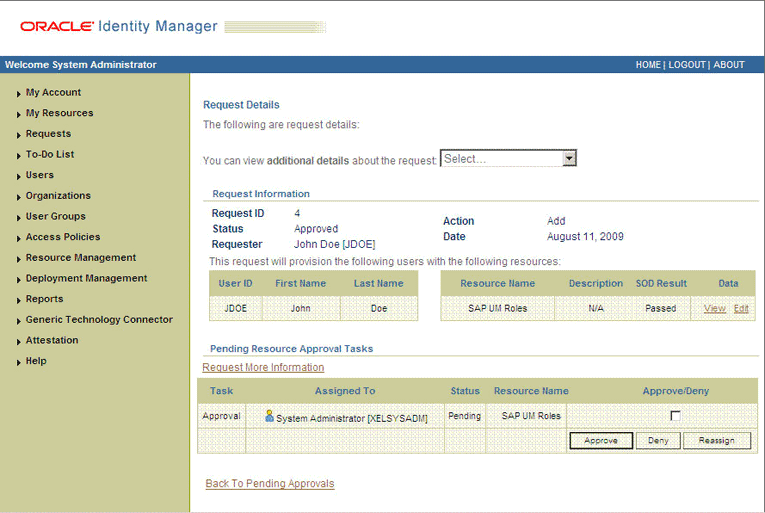
In addition, the approver can click the View link to view details of the SoD validation process.
The approver can decide whether to approve or deny the request, regardless of whether the SoD engine accepted or rejected the request. The approver can also modify entitlements in the request.
The following are steps that the approver can perform:
As the approver, to edit and approve a request, click the Edit link.
In the Edit Form window, select the entitlement request data that you want to modify from the list at the top of the window and then make the required change. In the following screenshot, one of the roles that the requester had included in the request has been removed:
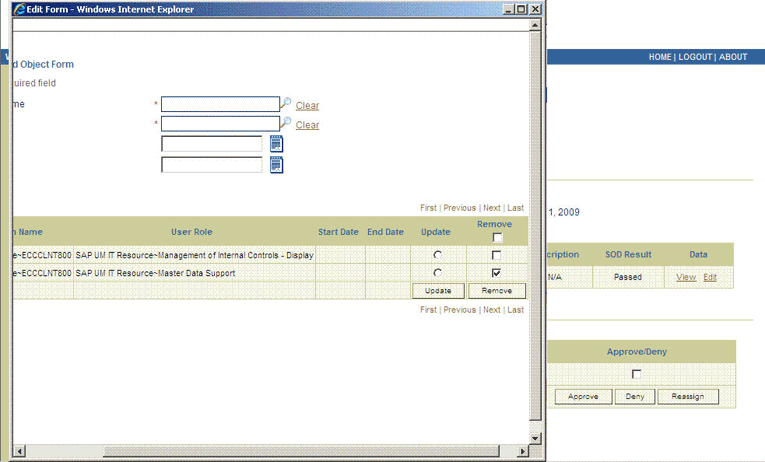
Close the Edit Form window, select the check box for the task that you want to approve, and then click Approve.
On the Confirmation page, click Confirm.
The following screenshot shows this page:
On the Request Details page, the SOD Status column shows SODCheckCompleted.
If you search for and open the requester's profile, the entitlements granted to the user are shown in the Provisioned state. This is shown in the following screenshot:
To switch target systems for reconciliation:
If you are switching to SAP CUA, then set the value of the Is CUA Enabled entry to yes in the Lookup.SAP.UM.Configuration lookup definition. If you are switching to SAP R/3, then set the value to no.
See Section 2.3.2, "Setting Up the Configuration Lookup Definition in Oracle Identity Manager" for more information.
In the SAP User Management User Recon and SAP User Management Delete Recon scheduled tasks, set values for the following attributes:
IT Resource: Enter the name of the required IT resource.
Last Execution Timestamp: Enter 0 as the value of this attribute. Alternatively, if you have saved the time stamp value from the previous reconciliation run on the same target system, then you can enter that value in the Time Stamp attribute. See Section 3.4.3, "Reconciliation Scheduled Tasks" for information about the scheduled task.
To switch target systems for provisioning:
If you are switching to SAP CUA, then set the value of the Is CUA Enabled entry to yes in the Lookup.SAP.UM.Configuration lookup definition. If you are switching to SAP R/3, then set the value to no.
If you have configured the target system for SoD, then set the Is CUA Enabled entry in the Lookup.SAP.UM.SoDConfiguration lookup definition to yes or no depending on the target system that you want to use.
In the SAP User Management Lookup Recon scheduled task, set values for the following attributes:
Run the SAP User Management Lookup Recon scheduled task.
Start the provisioning operation on the Administrative and User Console by selecting the required IT resource.
See the "Segregation of Duties (SoD) in Oracle Identity Manager" chapter in Oracle Identity Manager Tools Reference for Release 9.1.0.2 for information about enabling and disabling the SoD feature in Oracle Identity Manager.
To enable or disable the Compliant User Provisioning feature of the connector:
Set one of the following values for the CUP request mode entry in the Lookup.SAP.UM.Configuration lookup definition:
Enter yes as the value of this entry to enable the Compliant User Provisioning feature.
Enter no to disable this feature.
If you are enabling Compliant User Provisioning, set yes as the value of the Password Disabled entry in the Lookup.SAP.UM.Configuration lookup definition.
See Section 2.3.2.3, "Setting Values in the Lookup.SAP.UM.Configuration Lookup Definition" for information about setting values in this lookup definition.