33 Setting Up Your System to Work with SPED Accounting
This chapter contains the following topics:
-
Section 33.2, "Adding and Maintaining Register Requirements for SPED Bookkeeping Types"
-
Section 33.5, "Adding Inscription Information to Address Book Records"
33.1 Setting Up UDC Values for SPED Accounting
Before you enter additional information for SPED accounting or generate records to report, set up these UDC tables.
33.1.1 Inscription Type (76B/AI)
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system provides hard-coded values for this UDC table. You assign an inscription type to address book records. The system uses the inscription type when it generates data for the registration number and signatories for the SPED accounting electronic file.
Values are:
| Codes | Description |
|---|---|
| 10 | Commercial Registration |
| 20 | Worker Register Number |
| 30 | Accountant Inscription Number |
| 99 | Other Inscriptions |
33.1.2 P/L Closing Journal Doc Types (76B/CJ)
Set up values in this UDC table to define batch types for profit and loss closing statements. When you run the Block I - Accounting Journal program (R76B965), the system looks for the batch type in the first JE (journal entry) document type of the batch. If the document type is listed in this UDC table, the system uses a value of E (P/L closing journal) for field 5 of the I200 register of block I. If the JE document type is not in this UDC table, the system writes a value of N (standard journal) to field 5.
33.1.3 Company Relation Code (76B/CR)
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system provides hard-coded values for this UDC table. You assign a company relation code to a company when you complete subsidiary or participant information for the company in its address book record. Examples of values are:
| Codes | Description |
|---|---|
| 4 | Controladora |
| 5 | Controlada |
| 6 | Subsidiária integral |
33.1.4 Decentralized Bookkeeping Entity (76B/DB)
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system provides hard-coded values for this UDC table. You assign a decentralized bookkeeping code to companies when you set up legal companies in the Legal Company Constants program (P76B010). The system uses the code in the decentralized bookkeeping field in register 0020 of block 0 for the electronic file for SPED accounting.
Values are:
| Codes | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | Legal entity |
| 1 | Establishment |
33.1.5 Inscriptions Responsible (76B/ER)
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system provides hard-coded values for this UDC table. You assign a responsible entity when you set up inscription information for address book records. The system writes information about the responsible entity to block 0.
Example are:
| Codes | Description |
|---|---|
| 01 | Banco Central |
| 03 | Comissão de Valores Mobiliário (CVM) |
| BA | Secretaria de Fazenda do Bahia |
33.1.6 Table of federation units (76B/FU) (Release 9.1 Update)
This UDC is used to validate that the municipal code entered in the COD_MUN field (Field 09) of register 0000 is compatible with the code of the Federation Unit.
33.1.7 Account/Group type code (76B/GA)
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system provides hard-coded values for this UDC table. You assign a code from this UDC table when you set up GL accounts with information that is required for SPED accounting reporting. Values are:
| Codes | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Assets |
| 2 | Liabilities |
| 3 | Equity |
| 4 | Profit and Loss |
| 5 | Compensations |
| 9 | Others |
33.1.8 Chart of Accounts Responsible (76B/RA)
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system provides hard-coded values for this UDC table. You assign a value from this UDC table when you set up the cross-references between your chart of accounts and the legal chart of accounts. The codes indicate the agency responsible for the legal chart of accounts.
The system uses this code in register I051 of block I.
Examples of valid values are:
| Codes | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | PJ in general |
| 3 | Financial Companies |
| 5 | Exempt companies in general |
| 10 | Secretaria da Receita Federal |
| 20 | Banco Central do Brasil |
33.1.9 Signatory Qualification Codes (76B/SG)
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system provides hard-coded values for this UDC table. You assign a value from this UDC code when you set up signatories for legal companies. The system uses this code in register J930 of block J.
Examples of values are:
| Codes | Description |
|---|---|
| 205 | Administrador |
| 220 | Administrador Judicial -Pessoa Física |
| 309 | Procurador |
| 999 | Outros |
33.1.10 Co Special situation Indicator (76B/SI)
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system provides hard-coded values for this UDC table. You assign a value from this UDC code when you set up information for legal companies. These codes indicate is a special situation, such as a merger or closure, exists for the company. The system uses this code in register 0000 of block 0.
Values are:
| Codes | Description |
|---|---|
| (blank) | No special situation |
| 0 | Opening |
| 1 | Handover |
| 2 | Fusion |
| 3 | Incorporation |
| 4 | Extinction |
33.1.11 SPED Bookkeeping Types (76B/SL)
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system provides hard-coded values for this UDC table. You assign a value from this UDC code when you set up book types for legal companies. The system uses this code to identify the type of bookkeeping files that you submit. The reporting requirements differ based on the book type. The system writes this value to the I010 register of book I, and uses the value to determine the data to write to other registers and books.
Values are:
| Codes | Description |
|---|---|
| A | Auxiliary daily book with resumed bookkeeping |
| B | Daily balance books and balance sheet |
| G | Daily books |
| R | Daily books with resumed bookkeeping |
| Z | Auxiliary Major Book |
33.1.12 Legal Representative of Company (76B/SN) (Release 9.1 Update)
The values for this UDC is not hard-coded. The values S and N help to identify the signatory code as legal representative or non-legal representative for a company.
| Codes | Description |
|---|---|
| S | Represents the legal representative for the company |
| N | Represents the non-legal representative for the company |
33.1.13 Company Size Indicator (76B/CA) (Release 9.1 Update)
The system provides hard coded values for this UDC. You can specify whether the company is considered as a small size company or not when working with legal company constants.
Values are:
| Codes | Description |
|---|---|
| Blank | Size not informed |
| 0 | Small company |
| 1 | Large company |
33.1.14 Purpose of Bookkeeping (76B/BP) (Release 9.1 Update)
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system provides hard-coded values for this UDC table. You specify details about the NIRE situation.
These values are hard-coded for Brazilian localization:
| Codes | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | Original |
| 1 | Substitute with NIRE |
| 2 | Substitute without NIRE |
| 3 | Substitute with exchange NIRE |
33.1.15 Company Initial Situation Indicator (76B/BN) (Release 9.1 Update)
The system provides hard coded values for this UDC. You can specify what kind of special situation was the company in at the beginning of the period.
Values are:
| Codes | Description |
|---|---|
| (blank) | Indicator not informed |
| 0 | Normal |
| 1 | Opening |
| 2 | Resulting fission, fusion, etc. (Remainder from scission, merger, etc.) |
| 3 | Beginning of compulsory of ECD |
33.1.16 EDC Type (76B/ED) (Release 9.1 Update)
The system provides hard coded values for this UDC. You use this UDC table to specify the Digital Accounting Bookkeeping Type for the company according to the following values:
| Codes | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | ECD of Company not participant...: The company does not have ostensible partners. |
| 1 | ECD of Company participant in...: The company has one or more ostensible partners. |
| 2 | ECD of SCP (Sociedade en comta da partic.) |
The system writes information about the company to the ECD Type - Tag File F76B010 (F76B010T) and includes this information in the block 0 when you work with SPED Accounting reports.
33.1.17 Sub-Account Nature Code (76B/NC) (Release 9.1 Update)
The system provides hard coded values for this UDC. You use this UDC table to classify sub-accounts when you set up related accounts for SPED Accounting reports according to the list of codes pre-defined by the fiscal authorities.
Examples of valid values are:
| Codes | Description 01 | Description 02 |
|---|---|---|
| 02 | TBU | Direct Subsidiary Abroad |
| 10 | Goodwill | |
| 71 | AVJ | Accrued depreciation |
| 77 | AVP | Accrued amortization |
33.2 Adding and Maintaining Register Requirements for SPED Bookkeeping Types
This section provides an overview of adding and maintaining mandatory registers, lists the forms used to maintain register requirements, and discusses how to:
-
Add records to define required registers.
-
Set processing options for Initial Setup - UBEs by Block and Required Registers (R76B932).
33.2.1 Understanding How to Add and Maintain Register Requirements for SPED Bookkeeping Types
The tax authority determines which registers in each block must be included in the SPED accounting files for each book type. The mandatory registers vary based on the type of book that you submit. For example, register I012 (Daily Auxiliary Books) is mandatory when you generate book type B (Daily Balance books and Balance sheet), but is not mandatory when you generate book type G (Daily books).
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system provides the Initial Setup - UBEs by Block and Required Registers program to enable you to populate the SPED Records Rules table (F76B930) with data that defines which registers are required for each book type. After you run the Initial Setup - UBEs by Block and Required Registers program to populate the F76B930 table, you can use the Required Registers program (P76B930) to modify the records, if necessary.
|
Note: In most cases, you will run the Initial Setup - UBEs by Block and Required Registers program once only, and then use the Required Registers program to modify records, if necessary. If the initial run of the Initial Setup - UBEs by Block and Required Registers program does not finish or if the records in the F76B930 table become corrupted, you can run the Initial Setup - UBEs by Block and Required Registers program again with the processing options set to update existing records. The system will replace the existing records with the initial data that is provided in the software. |
The Initial Setup - UBEs by Block and Required Registers program also sets up your system with the definition of each SPED book and the associations between the SPED books and the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne programs that you run to generate the registers and records for the books. The system stores the associations in the Ato Cotepe Header Blocks Template (F76B0730) and Ato Cotepe Detail Blocks Template (F76B0731) tables.
See Block and Report Sequencing for more information.
33.2.2 Forms Used to Maintain Register Requirements
| Form Name | Form ID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work with SPED Records Rules | W76B930A | SPED Setup (G76B0925), Required Registers | Review and select existing records. |
| SPED Records Rules | W76B930B | Select a record on the Work with SPED Records Rules form and then click Select.
Click Add on the Work with SPED Records Rules form. |
Modify an existing record or add a new record. |
33.2.3 Adding Records to Define Required Registers
Generally, you run this program only when you initially set up your system to process SPED accounting records.
Select SPED Setup (G76B0925), Initial Setup - UBEs by Block and Required Registers.
33.2.4 Setting Processing Options for Initial Setup - UBEs by Block and Required Registers (R76B932)
Processing options enable you to specify default processing values.
33.2.4.1 General
- Update SPED Record Rules
-
Specify whether to delete existing records and repopulate the SPED Records Rules table (F76B930) with the initial setup data provided in the software. Values are:
Y: Yes
N: No
- Update Electronic Reporting Header/Details Blocks Setup
-
Specify whether to delete existing records and repopulate the Electronic Reporting Header table (F76B0730) and Electronic Reporting Detail table (F76B0731). Values are:
Y: Yes
N: No
33.2.5 Setting Processing Options for Block I - General Information (R76B954) (Release 9.1 Update)
Processing options enable you to specify default processing values.
33.2.5.1 SPED Version
- SPED Contable Version
-
Layout version code. The system retrieves the version code from the processing options of batch version program R76B954. Enter the SPED Contable layout version code.
Enter 1.00 for calendar years previous to 2013.
Enter 2.00 from calendar year 2013 to year 2015.
Enter 3.00 from calendar year 2015 on.
33.3 Setting Up GL Accounts for SPED Accounting
This section provides an overview of the setup for general ledger (GL) accounts for SPED accounting; an overview of parent/child relationships and account group codes; an overview of related accounts; and discusses how to:
-
Import the referential chart of accounts.
-
Manually add records for the referential chart of accounts.
-
Import associations between GL accounts and referential accounts.
-
Manually add an association between a GL account and a referential account.
-
Import group type codes for accounts.
-
Globally update group type codes for accounts.
-
Manually add an association between a GL main account and its related sub-accounts.
33.3.1 Understanding Setup for GL Accounts for SPED Accounting
You must associate your GL accounts with a government recognized chart of accounts. Depending on your business, you might associate you GL accounts to the chart of accounts from the Secretaria da Receita Federal or the Banco Central do Brasil.
To set up your GL accounts with associations between your GL accounts and the government chart of accounts (referential accounts):
-
Import or manually add the referential accounts.
You use the Referential Chart of Accounts program (P76B920) to import, manually add, or modify records for the referential chart of accounts. The system saves the referential chart of accounts to the Referential Chart of Account table (F76B920).
-
Import or manually add associations between your GL accounts and the referential accounts.
You use the Ref Accounts by Account program (P76B926) to import, manually add, or modify the associations. The system calls the Ref Accounts by Account program from the Brazil Account Information program (P76B925). The system saves the data for the associations to the Ref Accounts by Accounts - BR table (F76B926) and Brazilian Account Information table (F76B925).
-
Import or use a global update function to group your accounts by type.
You use the Brazil Account Information program to assign values from the Account/Group type code (76B/GA) UDC table to your GL accounts. The system saves the account group information to the Brazilian Account Information table (F76B925). The system uses the group type codes to determine which accounts are used for assets, liabilities, and so on.
-
(Release 9.1 Update) Manually add associations between main accounts and related sub-accounts (Contas Correlatas).
You can use the Related Accounts Revisions form in the Brazil Account Information program (P76B925) to manually add or modify associations between a main account and related sub-accounts. You can only associate existing accounts in your GL chart of accounts that are posting accounts.
You must assign a unique account group ID code to every group formed by a main account and its related accounts. You must also identify each related account according to the list of nature codes that the fiscal authority provides listed in the Sub-Account Nature Code UDC table (76B/NC).
The system saves the data for the associations to the Related Accounts - 7AB - BRA table (F76B927) and includes the accounts that you set up as related accounts in the register I053 when you work with Accounting SPED reports.
33.3.1.1 Importing the Government Referential Chart of Accounts
Instead of entering each record separately, you can import the government chart of accounts from a spreadsheet. You must set up the spreadsheet with columns for each of the fields on the Multiple Add Referential Chart Accounts form in the order in which the fields appear on the form. The fields are:
-
Chart of Account Responsible
When you save the imported data, the system validates the value in this field against the values in the Chart of accounts Responsible (76B/RA) UDC table, so the values for this field must exist in the 76B/RA UDC table. The hard-coded values in the UDC table are 10(Secretaria da Receita Federal) and 20(Banco Central do Brasil).
-
Referential Account
-
Referential Account Description
33.3.1.2 Importing Associations Between Your GL Accounts and Referential Accounts
Instead of manually associating each GL account to a referential account, you can import the associations from a spreadsheet. You must set up the spreadsheet with columns for each of the fields on the Multiple Add Referential Accounts by Account form in the order in which the fields appear on the form. The fields are:
-
Business Unit
-
Object Account
-
Subsidiary
-
Chart of Account Responsible
The system validates the value for this field against the values in the Chart of accounts Responsible (76B/RA) UDC table when you import the values, so the value in your spreadsheet must exist in the UDC table.
-
Referential Account
33.3.1.3 Assigning Group Types to GL Accounts
You assign a group type code to group your GL accounts for reporting. You set up group type codes in the Account/Group type code (76B/GA) UDC table, and then assign the codes to accounts in the Brazilian Account Information program. You can import records with the relationship between GL accounts and group type codes, or you can use a group update function to select GL accounts that exist in the F0901 table and then assign a group type code to all of the selected records.
If you import the values, you must set up the spreadsheet that you use with the fields as they are listed on the Multiple Add Brazilian Account Information from. The fields are:
-
Business Unit
-
Object Account
-
Subsidiary
-
Account/Group Type Code
The system validates the value in this field against the 76B/GA UDC table, so the values in the spreadsheet must exist in the 76B/GA UDC table.
-
Account ID
The system will populate the Account ID field; you do not need to provide a value.
33.3.1.4 Deleting Records
You can delete the referential accounts only when you have not associated the account with a GL account.
|
Note: When a GL account is no longer used, you must set up the account as inactive by specifying that the account is inactive (code I) in the Review and Revise Accounts program (P0901) instead of deleting the account or giving the account a posting code of N (nonposting).You do not delete the account because an account might be listed in the I050 register but not show any transactions posted against it in other registers. Registers that appear in register I050 are based on the selected chart of account, not on the transactions. You do not assign an inactive account the nonposting code because the posting code of N is used by the SPED accounting software to determine the accounts to include. See Understanding Parent/Child Relationships and Account Group Codes |
You can delete the association between a referential account and a GL account by selecting the record on the Work with Referential Accounts by Account form and then selecting Delete selected rec. from the Form menu.
You can delete the group type code for accounts by selecting the accounts on the Work with Brazilian Account Information form and selecting Clear Account Code from the Form menu.
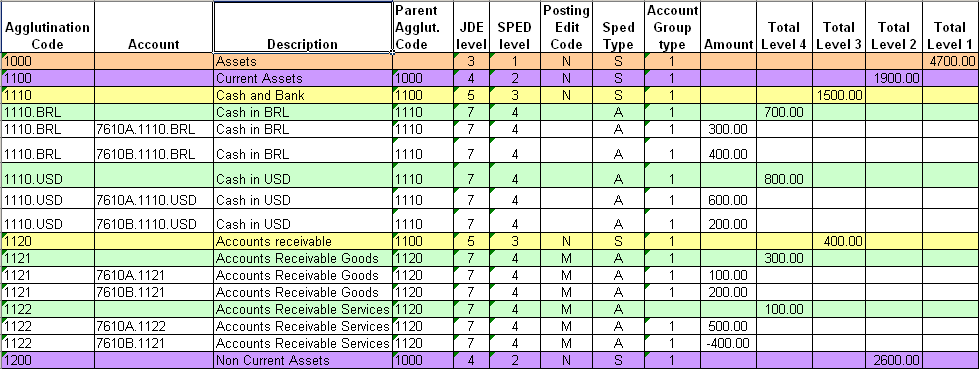
33.3.2 Understanding Parent/Child Relationships and Account Group Codes
When you set up GL accounts in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system, you can assign a level of detail for the accounts. You use the levels to specify a parent/child relationship between accounts. The system enables you to skip numerical levels between a parent account and child account. For example, you might set up an account at a level 4 that is the child of an account at a level 2.
The files that you submit for SPED accounting must show the parent/child relationships between accounts. However, the relationships can contain no gaps in the levels between a parent and child account. For example, an account at a level 4 cannot be a child of a level 2 parent account. Instead, an account at a level 4 must have a parent account at a level 3.
For SPED accounting, the relationships between the parent and child accounts are referred to as the agglutination level. To report on your accounts, you generate data that includes the accounts, the agglutination level, and an agglutination code. When you run the Block J - Opening Balance Sheet and Income Statement program (R76B985), the system assigns to the accounts an agglutination level that is based on the level of detail that you set up for your accounts. The system logic assigns the agglutination levels with no gaps, as required by the SPED reporting requirements.
When you set up accounts for reporting, you associate an account group type code to the accounts that you report. You must assign an account group type code to every account to include in the reports. The system uses the highest level account that is assigned a group code as the parent for all other accounts in the group, and uses the OBJ.SUB of the parent account as the agglutination code.
|
Note: The first level of each account group must be unique. For example, only one account that is assigned an account group code of 01 (assets) can be a first level, or parent, account.If you have more than one account at the top level in your chart of accounts and assign them the same account group code, the system does not accurately report your data. For example, if you have two accounts that are at a detail level of 1 in your chart of accounts, and you assign both of those accounts the same account group code, your data is not accurately reported. |
The system uses the posting edit code to determine which child accounts to include in the totals for each account group type. The system uses the posting edit code of N to determine which accounts to include (summarize). Accounts that have a posting edit code other than N are considered to be analytical accounts and are not included in the SPED reporting.
|
Important: If you use a posting edit code of N to prevent transactions from posting to an account, you must change the code before you process accounts for SPED reporting or the account will be included for reporting. |
This chart shows an example of how the system determines the accounts to include for SPED accounting. The accounts in the non-colored fields appear in block I. The accounts in the colored fields appear in block J.
33.3.3 Forms Used to Set Up GL and Referential Accounts
| Form Name | Form ID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work with Referential Chart of Accounts | W76B920A | General Accounting System Setup (G76B0941), Referential Chart of account | Review and select existing records. |
| Referential Chart Accounts Revisions | W76B920B | Select a record on the Work with Referential Chart of Accounts form and click Select. | Modify the description of the referential account. |
| Multiple Referential Chart of Accounts | W76B920C | Click Add on the Work with Referential Chart of Accounts form. | Manually add a record. |
| Multiple Add Referential Chart Accounts - Import Assistant | n/a | On the Multiple Referential Chart of Accounts, select Import Grid Data from the Tools menu. | Complete information about the referential chart of accounts to import from a spreadsheet. |
| Work with Brazilian Account Information | W76B925A | General Accounting System Setup (G76B0941), Brazilian Account Information | Review and select existing GL accounts. |
| Work with Referential Accounts by Account | W76B926A | On the Work with Brazilian Account Information form, select Referential Accounts from the Form menu. | Review and select existing records for associations between GL accounts and referential accounts. |
| Multiple Add Referential Accounts by Account | W76B926C | Click Add on the Work with Referential Accounts by Account form. | Associate a single GL account to a referential account. |
| Multiple Add Referential Accounts by Account - Import Assistant | n/a | On the Multiple Add Referential Accounts by Account form, select Import Grid Data from the Tools menu. | Complete information about the associations between GL accounts and the referential chart of accounts to import from a spreadsheet. |
| Multiple Add Brazilian Account Information | W76B925C | Click Add on the Work with Brazilian Account Information form. | Add the group type code for a single account. |
| Multiple Add Brazilian Account Information - Import Assistant | n/a | On the Multiple Add Brazilian Account Information from, select Import Grid Data from the Tools menu. | Complete information about the Brazilian account information to import from a spreadsheet. |
| Brazilian Account Information Revisions | W76B925E | On the Work with Brazilian Account Information form, select a record and click Select. | Add or modify the group type code for a single, existing account record. |
| Referential Accounts by Account Revisions | W76B926B | On the Work with Referential Accounts by Account form, select a record and then click Select. | Modify the relationship between a referential account and a GL account by modifying the referential account number, the responsible entity, or the GL account ID. |
| Related Accounts Revisions | W76B925B | Select a record on the Work with Brazilian Account Information form, and select Rel. Accts. Revisions from the Row menu. | Add or modify the relationship between a main account and one or several related accounts, and assign an Account Group ID to the relations. |
| Review Related Accounts | W76B925F | On the Work with Referential Accounts by Account form, select the Form menu Rel. Accts. Review. | Review existing related accounts records. You can browse by main account, related account, group ID or related account nature code. |
33.3.4 Importing the Referential Chart of Accounts
Access the Multiple Add Referential Chart Accounts - Import Assistant form.
-
Click Import from Excel in the Define Import File area.
-
Use the Browse button to navigate to the spreadsheet to import.
-
In the Define Cell Range area, specify the rows and columns to import.
-
In the Define Import Location in Grid area, specify the target location to import the data. Options are:
-
Insert: The system imports the data column A, row 0 of the grid.
-
Paste: The system imports the data to the location that you specify in the Col and Row fields that appear when you select this option. Use this option to add additional records.
The data that you specified appears in the grid.
-
-
Do one of the following:
-
Click Continue to add the data to the F76B920 table.
The system returns you to the Multiple Add Referential Chart Accounts form. When you click OK on the Multiple Add Referential Chart Accounts form, the system saves the data to the F76B920 table if no errors exist, or it displays an error message if one or more records do not pass the validation.
-
Click Reset to delete the records from the grid.
-
33.3.5 Manually Adding Records for the Referential Chart of Accounts
Access the Setup Multiple Referential Chart of Accounts form.
- Chart of Account Responsible
-
Enter a value from the Chart of accounts Responsible (76B/RA) UDC table to specify the government agency that provides the chart of accounts.
- Referential Account
-
Enter the account ID from the government chart of accounts.
- Description
-
Enter the description of the account.
33.3.6 Importing the Associations Between GL and Referential Accounts
Access the Multiple Add Referential Accounts by Account - Import Assistant form.
-
Click Import from Excel in the Define Import File area.
-
Use the Browse button to navigate to the spreadsheet to import.
-
In the Define Cell Range area, specify the rows and columns to import.
-
In the Define Import Location in Grid area, specify the target location to import the data. Options are:
-
Insert: The system imports the data column A, row 0 of the grid.
-
Paste: The system imports the data to the location that you specify in the Col and Row fields that appear when you select this option. Use this option to add additional records.
The data that you specified appears in the grid.
-
-
Do one of the following:
-
Click Continue to add the data to the F76B926 table.
The system returns you to the Multiple Add Referential Accounts by Account form. When you click OK on the Multiple Add Referential Accounts by Account form, the system saves the data to the F76B926 table if no errors exist, or it displays an error message if one or more records do not pass the validation.
-
Click Reset to delete the records from the grid.
-
33.3.7 Manually Adding an Association Between a GL and Referential Account
Access the Multiple Add Referential Accounts by Account form.
- Business Unit
-
Enter the business unit for the GL account.
- Object Account
-
Enter the object portion of the GL account number.
- Subsidiary
-
Enter the subsidiary portion of the GL account number.
- Chart of Account Responsible
-
Enter a value from the 76B/GA UDC table to specify the government entity responsible for the referential chart of accounts.
- Referential Account
-
Enter the referential account number to associate with your GL account. You obtain the number from the government chart of accounts.
33.3.8 Importing Group Type Codes for Accounts
Access the Multiple Add Brazilian Account Information - Import Assistant form.
-
Click Import from Excel in the Define Import File area.
-
Use the Browse button to navigate to the spreadsheet to import.
-
In the Define Cell Range area, specify the rows and columns to import.
-
In the Define Import Location in Grid area, specify the target location to import the data. Options are:
-
Insert: The system imports the data column A, row 0 of the grid.
-
Paste: The system imports the data to the location that you specify in the Col and Row fields that appear when you select this option. Use this option to add additional records.
The data that you specified appears in the grid.
-
-
Do one of the following:
-
Click Continue to add the data to the F76B925 table.
The system returns you to the Multiple Add Brazilian Account Information form. When you click OK on the Multiple Add Brazilian Account Information form, the system save the data to the F76B925 table if no errors exist, or it displays an error message if one or more records do not pass the validation.
-
Click Reset to delete the records from the grid.
-
33.3.9 Globally Update Group Type Codes for Accounts
Access the Work with Brazilian Account Information form.
-
Select the records to which to add or update the group type code.
You can use the fields in the QBE (query by example) line to filter records. To select all of the records that appear on the Work with Brazilian Account Information form, click the check box next to the Company field. Or, you can individually select the lines to update.
-
Select Global Update from the Form menu.
-
Select Update Account Group/Type.
-
In the Account/Group Type Code field, enter a value from the 76B/GA UDC table to specify the group type code to assign to the selected records.
-
Click OK to update the selected records in the F76B925 table.
33.3.10 Manually Adding an Association Between a Main Account and a Related Account (Release 9.1 Update)
Access the Related Accounts Revisions form.
- Account Group ID
-
Enter a code to identify the group formed by the main account and its related sub-accounts.
- Business Unit
-
Enter the business unit for the GL account.
- Object Account
-
Enter the object portion of the GL account number.
- Subsidiary
-
Enter the subsidiary portion of the GL account number.
- Nature Account Related Code
-
Enter a value from the Sub-Account Nature Code UDC table (76B/NC) that identifies the nature of the related account.
33.4 Defining the Books for SPED Accounting
This section provides an overview of SPED book type definitions and discusses how to define the books for SPED accounting.
33.4.1 Understanding SPED Book Type Definitions
You must submit the SPED accounting electronic files for specific types of GL accounts. For example, you must report information about balance sheet accounts, asset accounts, and transaction accounts.
You use the Book Type Definition program (P76B935) to set up information about the SPED books that you must report. You specify the purpose of the book, the order in which it appears in the file, the book type, and other related information. You also specify the ledger type from which the system reads the transaction information for the SPED book.
Most companies need to set up and report only book type G (daily books). You must set up other book types if some of the data that you must report resides in another software system, or if you generate some of the data files from another system for any other reason. When you generate data from more than one source, you must:
-
Set up additional book types:
-
R (Daily Book with resumed bookkeeping)
-
A (Auxiliary daily book with resumed bookkeeping)
-
B (Daily Balance books and balance sheet)
-
S (SCP Book)
-
Z (Auxiliary major book)
If you set up a book type R, you must also set up a book type A or Z. If you set up a book type B, you must also set up a book type Z.
You can only set up a book type S if the company is an SCP company (if the ECD Type for the company is set to 2). For all other companies, you can set any book type except book type S.
-
-
Associate the auxiliary book to the main book.
Associate auxiliary book A with main book R. Associate auxiliary book Z with main book B.
-
Associate GL accounts to books A and Z. You do not associate GL accounts to book types G, R, or Z.
The system stores the data that you enter in these tables.
-
SPED Book Type Definition (F76B935)
This table stores information about the main SPED books.
-
SPED Book Type Relation (F76B936)
This table stores the auxiliary book information.
-
SPED Book Ledger Types (F76B937)
This table stores the ledger type that you associate with the book type. The system selects transactional information for blocks I and J according the period, company, participant/subsidiary companies and the ledger type corresponding to the book for the job that you run.
You use the data that you set up for SPED books when you set up jobs to generate the electronic files for SPED accounting reporting. You use the SPED Job Administrator program (P76B940) to set up and run a job for each book that you set up in the Book Type Definition program.
33.4.2 Forms Used to Define the Books for SPED Accounting
| Form Name | Form ID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Working with SPED Book Definition | W76B935A | SPED Setup (G76B0925), Book Type Definition | Review and select existing records. |
| SPED Book Definition Revisions | W76B935B | Click Add on the Working with SPED Book Definition form. | Define the books for SPED accounting. |
| SPED Book Ledger Type | W76B935E | Select a record on the Working with SPED Book Definition form and then select Ledger Types from the Row menu. | Associate the book with a ledger type. You must complete this task. The system uses this ledger type to select records from the Account Master (F0901) or Account Balance (F0902) table when you generate the SPED accounting files. |
| Auxiliary Book Definition | W76B935C | On the Working with SPED Book Definition form, select a record for SPED booking type R or B, and then select Auxiliary Book from the Row menu. | Associate an auxiliary book with the main SPED book record. |
| Bookkeeping Addl Info
(Release 9.1 Update) |
W76B935G | On the Working with SPED Book Definition form, select a record for Bookkeeping Purpose type 1, 2 or 3, and then select Additional Info from the Row menu. | Specify additional details when the NIRE inscription number has changed: The situation of the company at the beginning of the period, the substitute inscription number and the substitution hash code. |
33.4.3 Defining SPED Accounting Books
Access the SPED Book Definition Revisions form.
You must complete all of the fields on this form.
- Sped Book Order Number
-
Enter a number for the book. You use the book number when you set up the jobs to extract data for reporting. The order in which you set up the books is not critical; the system and the electronic file use the number for a reference only.
- Sped Book Purpose
-
Enter the purpose of the book in this free-form text field. The text that you enter appears in the electronic file.
- Account Number
-
Enter the GL account from which the system will obtain transaction data for the SPED book types A or Z.
You do not associate a GL account number to book types G, R, or B.
- Sped Bookkeeping Type
-
Enter a value from the SPED Bookkeeping Types (76B/SL) UDC table to specify the SPED book type. Values are:
A: Auxiliary daily book with resumed bookkeeping
B: Daily Balance books and Balance sheet
G: Daily books
R: Daily Book with resumed bookkeeping
S: SCP Book
Z: Auxiliary Major Book
- Bookkeeping Type Book Assoc.
-
Specify whether the data for the SPED book will be included in the submission file. Values are:
Blank or 0: Digital (include in the file)
1: Other (not included in the file)
- Bookkeeping External Type
-
Specify whether the SPED book information is generated by a system other than JD Edwards EnterpriseOne. Values are:
N: Generated by the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system.
Y: Generated by a different system.
- Bookkeeping Purpose (Release 9.1 Update)
-
Specify the bookkeeping purpose using a code from UDC 76B/BP. Values are:
-
0: Original.
-
1: Substitute with NIRE
-
2: Substitute without NIRE
-
3: Substitute with NIRE exchange.
-
33.4.3.1 Adding Additional Bookkeeping Information (Release 9.1 Update)
Access the Bookkeeping Additional Information form.
Figure 33-2 Bookkeeping Additional Information
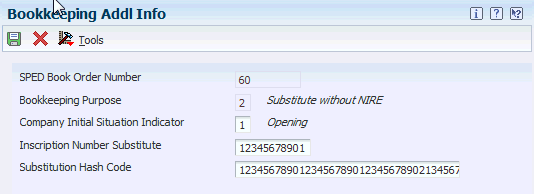
Description of ''Figure 33-2 Bookkeeping Additional Information''
- Company Initial Situation Indicator
-
Select a code from UDC 76B/BN to specify the special situation of the company at the beginning of the period, according to published SPED tables. Values are:
-
Blank: Indicator not informed.
-
0: Normal (Starting the first day of the year).
-
1: Opening
-
2: Resulting fission, fusion, etc. (Remainder from scission or merger, etc.)
-
3: Beginning of compulsory of ECD (Beginning of the requirement to use ECD).
-
- Inscription Number Substitute
-
Enter the 11-character substitute inscription number.
- Substitution Hash Code
-
Enter the substitution hash code. The code format is a sequence of up to 40 characters containing numbers and uppercase letters "A" through "F".
33.5 Adding Inscription Information to Address Book Records
This section provides an overview of inscription information and discusses how to add inscription information to an address book record.
33.5.1 Understanding Inscription Information
You use the Address Book Additional Information program (P01012BR) to add registration or inscription information to address book records. Registration or inscription information includes the type of registration or inscription, the number, issuer, and date. The system saves the inscription information to the Address Book Inscription table (F76B140). The system writes inscription information to registers 0007, 0150, and J930.
33.5.2 Forms Used to Add Inscription Information to Address Book Records
| Form Name | Form ID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work with Addresses | W01012B | Address Book - Brazil (G76B01), Address Book Revisions | Review and select existing records. |
| Address Book Revisions | W01012A | Click Add on the Work With Addresses form, or select a record and click Select. | Add or revise an address book record. |
| Address Book Additional Information - Brazil | W01012BRA | Select Regional Info from the Form menu on the Address Book Revision form.
Select a record and then select Regional Info from the Row menu on the Work with Addresses form. |
Add tax information specific to Brazil for address book records. |
| Additional Address Book Registrations | W01012BRB | Select Address Book Inscn from the Form menu on the Address Book Additional Information - Brazil form. | Add or modify inscription information. |
33.5.3 Adding Inscription Information to an Address Book Record
Access the Additional Address Book Registration form.
- Address Number Inscription Type
-
Enter a value from the Inscription Type (76B/AI) UDC table to specify the type of registration or inscription number to associate with the address book record. Values are:
10: Commercial Registration
20: Worker Register Number
30: Accountant Inscription Number
99: Other inscriptions
- Address Number Responsible Entity
-
Enter a value from the Inscriptions responsible (76B/ER) UDC table to specify the code that identifies the issuer of the inscription number. You complete the Address Number Responsible Entity field only if you select 30 as the value for the Address Number Inscription Type field.
- Address Number Inscription Nbr (address number inscription number)
-
Enter the inscription number to associate with the address book number. The inscription number might be assigned to a company or individual by a government entity, professional association, or other regulatory entity.
- Issue Date
-
Enter the date that the inscription number was issued.
33.6 Setting Up Legal Company Constants
This section provides an overview of legal company constants and discusses how to:
-
Set up legal company information.
-
Add company subsidiary information.
-
Add decentralized bookkeeping information to a legal company.
-
Add signatory information to a legal company.
33.6.1 Understanding Legal Company Constants
A legal company is the company for which you report the accounting data. You use the Legal Company Constants program (P76B010) to associate data about decentralized bookkeeping, subsidiaries, and signatories for the reporting company. The system uses the data that you enter to populate fields in the files that you submit for SPED accounting.
The system writes the data that you enter to these tables:
-
Legal Company Constants (F76B010)
-
Legal Company - Subsidiaries (F76B015)
-
Decentralized Accounting Bookkeeping (F76B020)
-
Signatories (F76B025)
-
ECD Type - Tag File F76B010 (F76B010T)
-
SCP Identification and Name (F76B045)
33.6.2 Forms Used to Set Up Legal Company Constants
| Form Name | Form ID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work with Legal Company Constants | W76B010A | General Accounting System Setup (G76B0941), Legal Company Constants | Review and select existing records. |
| Legal Company Constants Revision | W76B010B | Click Add on the Work with Legal Company Constants form. | Associate information about the company situation, such as the creation or conversion date and whether the company operated under special conditions, such as a merger. |
| Subsidiaries / Participants | W76B010C | Select a record on the Work with Legal Company Constants form and then select Subsidiaries / Partici from the Row menu. | Associate another company to the legal company and specify the relationship between the companies. |
| Decentralized Bookkeeping | W76B010D | Select a record on the Work with Legal Company Constants form and then select Decentralized Bookkeeping from the Row menu. | Specify the address book number and the code of the company or accountant if some or all accounting activities occur outside of the legal company. You complete this information only when the legal company uses decentralized bookkeeping. |
| Signatories | W76B010E | Select a record on the Work with Legal Company Constants form and then select Signatories from the Row menu. | Enter the address number and code for the title or responsibility of the signatory. |
| SCP Identification and Name | W76B010G | Select a record on the Work with Legal Company Constants form and then select SCP Identification from the Row menu.
Note: The form only displays if the ECD type selected for the company is not set to 0. |
Enter the name and SCP identification code of the ostensible partners for the company. The system saves this information to the SCP Identification and Name table (F76B045), and incudes it in the register 0035. |
33.6.3 Setting Up Legal Company Information
Access the Legal Company Constants Revision form.
- Legal Company
-
Enter a value from the Company Constants table (F0010) to specify the company for which you set up the SPED accounting required information.
- CO Special Indicator (company special indicator)
-
Enter a value that exists in the Co Special situation Indicator (76B/SI) UDC table to specify if the company experienced a special event, such as a merger or a change in legal status, during the reporting year. Values are:
Blank: No special situation
0: Opening
1: Handover
2: Fusion (merger)
3: Incorporation
4: Extinction
- DesCent Bookkeep (decentralized bookkeeping)
-
Enter a code to specify if the company uses decentralized bookkeeping. Decentralized bookkeeping occurs when some or all of the accounting activities take place with a company or accountant outside of the legal company.
Values are:
0 or N: No
1 or Y: Yes
- CO Creation Date (company creation date)
-
Enter the date that the company started.
- CO Conv Date (company conversion date)
-
Enter the date that the company converted its legal status from a simple association to a company association.
- Company Size Indicator (Release 9.1 Update)
-
Enter a code from UDC table 76B/CA to specify the company size. Values are:
Blank: Size not informed
0: Small company
1: Large company
- ECD Type (Release 9.1 Update)
-
Enter a code from the ECD Type UDC (76B/NC) to specify the Digital Accounting Bookkeeping Type for the company according to the following values:
0 - ECD of Company not participant...: The company does not have ostensible partners.
1 - ECD of Company participant in...: The company has one or more ostensible partners.
2 - ECD of SCP (Sociedade en comta da partic.): The company is a SCP. If you set the ECD Type to 1, the system generates the Register 0035 to report the ostensible partners.
If you set the ECD type to 2, the report displays the SCP code of the company in the field 19 of the register 0000
33.6.4 Adding Company Subsidiary Information
Access the Subsidiaries / Participants form.
- Company
-
Enter the company that is the subsidiary of the legal company.
- Participant Flag
-
Specify whether the subsidiary is part of a group of companies. Values are:
1 or Y: Yes.
0 or N: No
A value for the participant code is written to the 0150 and 0180 registers.
- CO Relation Code (company relation code)
-
Enter a value from the Company Relation Code (76B/CR) UDC table to specify the type of relationship between the subsidiary and the legal company. You must complete this field if you entered Y or 1 in the Participant Flag field.
A value for the participant code is written to the 0150 and 0180 registers.
- CO Relation From Date
-
Enter the date that the relationship between the subsidiary and the legal company began.
- CO Relation To Date
-
Enter the date that the relationship between the subsidiary or participant and the legal company ended. If the relationship extends beyond the fiscal year, enter the last day of the reporting period. For example, you might enter December 31, 2008.
- Contributor Address Number
-
Enter the address number for a participant other than a subsidiary who contributed to the accounting data.
33.6.5 Adding Decentralized Bookkeeping Information to a Legal Company
Access the Decentralized Bookkeeping form.
- Address Number
-
Enter the address book number of the entity who contributed some or all of the accounting data.
- Decentralized Indicator
-
Enter a value from the Decentralized Bookkeeping Entity (76B/DB) UDC table to specify the type of entity. Values are:
0: Legal entity
1: Establishment
33.6.6 Adding Signatory and Auditors Information to a Legal Company
Access the Signatories form.
|
Note: You might set up numerous signatories for a legal company. |
- Address Number
-
Enter the address book number of the person who is authorized to sign the SPED accounting electronic file.
- Signatory Code
-
Enter a value from the Signatory qualification Codes (76B/SG) UDC table to specify the title of the person who is signing the SPED accounting electronic file.
If the record you enter is for an auditor, the system generates register J935 where it includes all the records entered for auditors.
33.6.7 Adding SCP Identification Information (Release 9.1 Update)
Access the SCP Identification form.
|
Note: You can set up numerous ostensible partners for a legal company. |
- SCP Identification
-
Enter the 14-digit SCP number code that identifies the ostensible partner.
- SCP Name
-
Enter the name of the ostensible partner as it should be displayed in the SPED Accounting file.
33.7 Specifying Blocks, Versions, and Sequencing
This section provides an overview of blocks, versions, and sequencing and discusses how to:
-
Set processing options for Block Setup (P76B0730).
-
Set processing options for Block I - Open Chart of Accounts and Cost Center (R76B955).
-
Set processing options for Block I - Balances / PL Account Balances (R76B960).
-
Specify block information.
33.7.1 Understanding Blocks, Versions, and Sequencing
You use the Block Setup program to set up the batch programs (UBEs) and versions to run for each block. You set up versions of the programs provided by Oracle, and can also set up versions of the custom programs that you create to generate blocks or populate registers for data that does not reside in JD Edwards EnterpriseOne tables.
When you set up the blocks, you must specify the UBE and versions to run for each block, as well as the sequence number in which the system runs the batch programs.
You can access the UBEs for SPED accounting from the SPED Setup menu (G76B0925) to set up versions with data selection. However, you must run the programs from the SPED Job Administrator program (P76B940).
See Extracting and Reviewing Data for SPED Accounting
The Block Setup program saves data to these tables:
-
Ato Cotepe Header Blocks Template (F76B0730)
-
Ato Cotepe Detail Blocks Template (F76B0731)
33.7.1.1 Block and Report Sequencing
You must run some UBEs in a specific sequence. For example, you must run the UBE for block 0 prior to running UBEs for any other blocks, so you must set the sequence number for the UBE for block 0 at a lower sequence number than for other UBEs. Similarly, you must run the UBE for block 9 after you run the UBEs for all other blocks, including any custom programs that you need to run.
|
Note: If you ran the Initial Setup - UBEs by Block and Required Registers program to populate the SPED Records Rules table (F76B930), the program also populated the Ato Cotepe Detail Blocks Template table (F76B0731) with the program IDs, versions, and sequence. You only modify this information if you have customer programs to add.See Adding and Maintaining Register Requirements for SPED Bookkeeping Types |
This table shows how the Initial Setup - UBEs by Block and Required Registers program populates the F76B731 table for SPED accounting (Ato Cotepe Version is SD).
| Block | Program ID | Version | Block Sequence | Report Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Block 0 | R76B952 | ZJDE0001 | 1 | 1 |
| Block I | R76B954 | ZJDE0001 | 2 | 1 |
| Block I | R76B955 | ZJDE0001 | 2 | 2 |
| Block I | R76B960 | ZJDE0001 | 2 | 3 |
| Block I | R76B965 | ZJDE0001 | 2 | 4 |
| Block I | R76B970 | ZJDE0001 | 2 | 5 |
| Block I | R76B960 | ZJDE0002 | 2 | 6 |
| Block I | R76B950 | ZJDE0001 | 2 | 7 |
| Block J | R76B985 | ZJDE0001 | 3 | 1 |
| Block J | R76B990 | ZJDE0001 | 3 | 1 |
| Block 9 | R76B995 | ZJDE0001 | 4 | 1 |
|
Important: If you use custom programs to report data, add the custom programs in the appropriate order. You must sequence the programs so that the program for block 0 runs first and the program for block 9 is the last program to run. |
33.7.2 Forms Used to Specify Block Information
| Form Name | Form ID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work With Electronic Reporting Blocks Template | W76B0730A | SPED Setup (G76B0925), Block Setup | Review and select existing records. |
| Electronic Reporting Blocks Template Revision | W76B0730B | Click Add on the Work With Electronic Reporting Blocks Template. | Set up or modify the block sequence and requirement for a version of the program for the block. |
33.7.3 Setting Processing Options for Block Setup (P76B0730)
Processing options enable you to specify default processing values.
33.7.3.1 General
- Electronic Reporting Version
-
Enter a value that exists in the Version of Ato Cotepe (76B/VC) UDC table to specify the version to use. For SPED accounting, enter SD (Accounting - SPED).
33.7.4 Setting Processing Options for Block I - Open Chart of Accounts and Cost Center (R76B955)
Processing options enable you to specify default processing values.
33.7.4.1 Process
- Agglutination Level
-
Specify the level of detail for the accounts that you report. Values are 1–7, with 1 being the level with the least detail and 7 being the level with the most detail.
33.7.5 Setting Processing Options for Block I - Balances / PL Account Balances (R76B960)
Processing options enable you to specify default processing values.
33.7.5.1 General
- 1. Registers to generate:
-
Specify the register to generate. Values are:
Blank: Periodic Balances (Registers I150/I155). The system filters records by ledger type and generates accumulated positive and negative amounts for the accounts processed.
1: PL accounts Balances (Registers I350/I355). The system generates records for the PL account balances.
33.7.6 Specifying Block Information
Access the Electronic Reporting Blocks Template Revision form.
- Electronic Reporting Version
-
Enter a value that exists in the Version of Ato Cotepe (76B/VC) UDC table to specify the version to run. For SPED accounting, enter SD (Accounting - SPED).
- Electronic Reporting Block
-
Enter the block number or letter of the block that you set up.
- Description
-
Enter a description of the block.
- Block Sequence
-
Enter the sequence number of the block. You must run the programs for block 0 before running the programs for any other block, and must run the program for block 9 after running the programs for all other blocks.
- Required Y/N
-
Select to indicate that the block is required.
- Report Sequence
-
Note:
This field is not used for SPED accounting.Enter the sequence number of the report.
Some blocks are populated by more than one program. Use this field to specify the order in which the system runs the programs for blocks populated by multiple programs. If only one program exists for the block, enter 1.
- Program ID
-
Enter the program ID of the report that you run to populate the block.
- Version
-
Enter the version of the report that you specify in the Program ID field.