3 Configuring Web Services Manager
This chapter describes how to configure the deployed Oracle Communications Billing and Revenue Management (BRM) Web Services Manager application. Configuring Web Services Manager requires connecting the deployed application to the BRM system and configuring security, authorization, and Java logging for the deployed application.
This chapter is intended for system administrators and system integrators.
Before reading this chapter, you should have installed BRM and Web Services Manager and deployed Web Services Manager on a supported application server. You should also be familiar with the administration console of your chosen applications server and with using BRM. For installation procedures, see "Installing Web Services Manager." For deployment procedures, see "Deploying Web Services Manager." For information about BRM, see BRM Concepts.
About Connecting Web Services Manager to the BRM System
Web Services Manager connects to the BRM system through a BRM Connection Manager (CM). Figure 3-1 shows how BRM and the SOAP client communicate with the deployed application. Web Services Manager translates Portal Communication Module (PCM) communications sent from a CM in the BRM system into SOAP requests sent to the SOAP client over HTTP. Web Services Manager translates SOAP responses sent from the SOAP client over HTTP into PCM communications that are returned to the CM.
Figure 3-1 Architecture of Web Services Manager in the BRM System
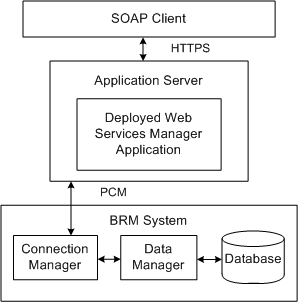
Description of ''Figure 3-1 Architecture of Web Services Manager in the BRM System''
Connecting Web Services Manager to the BRM System
Before you connect Web Services Manager to the BRM system, verify that your instance of Web Services Manager is deployed to an application server.
If you customized web services, use the custom infranetwebsvc.war or BrmWebServices.war file. Otherwise, you should use the default infranetwebsvc.war or BrmWebServices.war file. For more information about customizing web services, see "Customizing Web Services."
To connect Web Services Manager to the BRM system, do the following:
-
On your application server, copy the BRM_Home/deploy/web_services/Infranet.properties file to one of the following:
-
local_dir/WEB-INF/classes directory, where local_dir is a directory on the machine on which you installed your application server.
Note:
If you copy the Infranet.properties file to the local_dir/WEB-INF/classes directory, extract the infranetwebsvc.war file or BrmWebServices.war file to a local directory (local_dir) on the system on which your application server is installed. -
home directory on the machine on which you installed your application server.
-
-
Open the Infranet.properties file in a text editor.
-
Locate the following lines:
infranet.connection=pcp://root.0.0.0.1:password@ipAddress:port/0.0.0.1/service/admin_client 1 infranet.login.type=1
-
Do the following:
-
Replace password with the password for the BRM server.
-
Replace ipAddress with the IP address of the system on which BRM is installed.
-
Replace port with the port number used by the application server on which BRM is installed.
-
-
If SSL is enabled in connection manager (CM), locate the following lines and update the parameters if necessary:
infranet.pcp.ssl.enabled=true infranet.pcp.ssl.wallet.location=wallet_directory
where wallet_directory is the path to your client Oracle wallet. The client Oracle wallet contains the optional client SSL certificate and the private key, and it contains the Trusted CA certificate.
-
If you added custom opcodes or custom fields for Web services, add the enum values of the custom fields.
For example, if you created the custom_fld_usage_id custom field and the enum value for the custom_fld_usage_id field is 10001, add the following entry:
infranet.custom.field.10001=custom_fld_usage_id
For information about mapping enum values, see "Creating Custom Fields" in BRM Developer's Guide.
-
(Optional) To configure the connection pool parameters, modify the following entries:
infranet.connectionpool.minsize=min_connections infranet.connectionpool.maxsize=max_connections infranet.connectionpool.timeout=connection_timeout
where:
min_connections is the minimum number of connections allowed in the pool. The default number is 1.
max_connections is the maximum number of connections allowed in the pool.
connection_timeout is the connection pool timeout in milliseconds.
-
(Optional) To configure logging for Web Services Manager, modify the following entry:
webservices.log.enabled=log_value
where log_value is one of the following:
-
true enables logging. This option saves and displays the log files as standard output in the application server console.
-
false disables logging. This option saves the log files in the /domain/logs/BRMWebSvcMgr.log file. Configure the BRM_Home/deploy/web_services/lib/weblogic_ws_startup.jar file to use this option.
-
-
Save and close the file.
-
If you are working in the local_dir/WEB-INF/classes directory, regenerate the WAR file by running one of the following commands:
To regenerate the infranetwebsvc.war file:
jar -cvf infranetwebsvc.war *
To regenerate the BrmWebServices.war file:
jar -cvf BrmWebServices.war *
-
Deploy the regenerated infranetwebsvc.war or BrmWebServices.warfile on the server. See "Deploying Web Services Manager."
Changing the Instance of BRM to which Web Services Manager Connects
If you customized web services, use the custom infranetwebsvc.war or BrmWebServices.war file. Otherwise, you should use the default infranetwebsvc.waror BrmWebServices.war file. For more information about customizing web services, see "Customizing Web Services."
To change the instance of BRM to which Web Services Manager connects, do the following:
-
On your application server, copy the BRM_home/deploy/web_services/Infranet.properties file to one of the following:
-
local_dir/WEB-INF/classes directory, where local_dir is a directory on the machine on which you installed your application server.
Note:
If you copy the Infranet.properties file to the local_dir/WEB-INF/classes directory, extract the infranetwebsvc.war or BrmWebServices.war file to a local directory (local_dir) on the system on which your application server is installed. -
home directory on the machine on which you installed your application server.
-
-
Open the copied Infranet.properties file.
-
Locate the following lines:
infranet.connection=pcp://root.0.0.0.1:password@ipAddress:port/0.0.0.1/service/admin_client 1 infranet.login.type=1
-
Do the following:
-
Replace password with the password for the BRM server.
-
Replace ipAddress with the IP address of the system on which BRM is installed.
-
Replace port with the port number used by the application server on which BRM is installed.
-
-
If SSL is enabled in the Connection Manager (CM), locate the following lines and update the parameters if necessary:
infranet.pcp.ssl.enabled=true infranet.pcp.ssl.wallet.location=wallet_directory
where wallet_directory is the path to your client Oracle wallet. The client Oracle wallet contains the optional client SSL certificate and the private key, and it contains the Trusted CA certificate.
-
If you added custom opcodes or custom fields for Web services, add the enum values of the custom fields.
For example, if you created the custom_fld_usage_id custom field and the enum value for the custom_fld_usage_id field is 10001, add the following entry:
infranet.custom.field.10001=custom_fld_usage_id
For information about mapping enum values, see "Creating Custom Fields" in BRM Developer's Guide.
-
(Optional) To configure the connection pool parameters, modify the following entries:
infranet.connectionpool.minsize=min_connections infranet.connectionpool.maxsize=max_connections infranet.connectionpool.timeout=connection_timeout
where:
min_connections is the minimum number of connections allowed in the pool. The default number is 1.
max_connections is the maximum number of connections allowed in the pool.
connection_timeout is the connection pool timeout in milliseconds.
-
(Optional) To configure logging for Web Services Manager, modify the following entry:
webservices.log.enabled=log_value
where log_value is one of the following:
-
true enables logging. This option saves and displays the log files as standard output in the application server console.
-
false disables logging. This option saves the log files in the /domain/logs/BRMWebSvcMgr.log file. Configure the BRM_Home/deploy/web_services/lib/weblogic_ws_startup.jar file to use this option.
-
-
(Optional) To configure searching in BRM using the PCM_OP_SEARCH opcode, restrict the PCM_OP_SEARCH opcode to pre-defined search templates by modifying the following entry:
allowed.search.template.ids=template_id
where template_id is the template ID of the search template that you want the PCM_OP_SEARCH opcode to use for searching. Use a comma (,) to separate multiple template IDs. If you do not want to restrict the PCM_OP_SEARCH opcode to any pre-defined search templates, set template_id to None.
For a list of template IDs, connect to the BRM database and check the list of POIDS and the respective templates in the SEARCH_T table in the BRM database. For more information, see "Searching for Objects in the BRM Database" in BRM Developer's Guide.
-
If you added custom opcodes or custom fields for web services, add the enum values of the custom fields. For information about mapping enum values, see "Creating Custom Fields" in BRM Developer's Guide.
For example, if you created the custom_fld_usage_id custom field and the enum value for the custom_fld_usage_id field is 10001, add the following entry:
infranet.custom.field.10001=custom_fld_usage_id
-
Save and close the file.
-
If you are working in the local_dir/WEB-INF/classes directory, regenerate the WAR file by running one of the following commands:
To regenerate the infranetwebsvc.war file:
jar -cvf infranetwebsvc.war *
To regenerate the BrmWebServices.war file:
jar -cvf BrmWebServices.war *
-
Deploy the regenerated infranetwebsvc.war or BrmWebServices.war file on the server. See "Deploying Web Services Manager."
Configuring Security for Web Services Manager
By default, secure sockets layer (SSL) security for Web Services Manager is disabled. You can enable SSL security for Web Services Manager by configuring security parameters and enabling the SSL security feature in the application server on which Web Services Manager is deployed.
Configuring Security for Web Services Manager in WebLogic Server
Before you configure security for Web Services Manager, ensure that WebLogic Server and Web Services Manager are installed and that Web Services Manager has been deployed on a WebLogic Server domain. See "Installing Web Services Manager" and "Deploying Web Services Manager" for more information.
To configure security for Web Services Manager in WebLogic Server, do the following:
-
Configure authentication for Web Services Manager. See "Configuring Authentication for WebLogic Server."
-
Configure authorization for Web Services Manager by doing one of the following:
-
If you have deployed infranetwebsvc.war, configure role-based authentication for Apache Axis. See "Configuring Role-Based Authentication for Apache Axis in WebLogic Server."
-
If you have deployed BrmWebServices.war, configure WebLogic security policy for JAX-WS. See "Configuring WebLogic Security Policy on BRM Web Services for JAX-WS in WebLogic Server."
-
Configuring Authentication for WebLogic Server
Before you configure authentication for Web Services Manager, create a user, group, and security realm for Web Services Manager in WebLogic Server. For more information about creating users and groups, see the discussion about users, groups, and security roles in Fusion Middleware Securing Resources Using Roles and Policies for Oracle WebLogic Server. For more information about security realms, see the discussion about security realms in WebLogic Server in Fusion Middleware Securing Oracle WebLogic Server.
To configure authentication for Web Services Manager in WebLogic Server:
-
Open the local_dir/infranetwebsvc.war/WEB-INF/weblogic.xml file in a text editor, where local_dir is a directory on the WebLogic host where you copied the infranetwebsvc.war file.
-
Uncomment the following lines:
# <security-role-assignment> # <role-name>brmws</role-name> # <externally-defined/> # </security-role-assignment>
-
Save and close the file.
-
Open the local_dir/infranetwebsvc.war/WEB-INF/web.xml file in a text editor.
-
Uncomment the following lines:
# <security-constraint> # <web-resource-collection> # <web-resource-name>restricted web services</web-resource-name> # <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> # <http-method>GET</http-method> # <http-method>POST</http-method> # </web-resource-collection> # <auth-constraint> # <role-name>brmws</role-name> # </auth-constraint> # <user-data-constraint> # <transport-guarantee>CONFIDENTIAL</transport-guarantee> # </user-data-constraint> # </security-constraint> # <login-config> # <auth-method>BASIC</auth-method> # <realm-name>default</realm-name> # </login-config> # <security-role> # <role-name>brmws</role-name> # </security-role>
-
Save and close the file.
-
Log in to WebLogic Server Administration Console.
-
Expand Environment and select Servers.
The Summary of Servers page appears.
-
Select the server for which you want to enable the SSL port.
-
Click the Configuration tab.
-
Click the General subtab.
-
Select the SSL Listen Port Enabled check box.
-
In the SSL Listen Port field, enter a free port number. The default is 7002.
-
Click Save, which configures Web Services Manager with the following default port numbers:
-
HTTP connection: 7001
Web services that supports XML element payload have the default connection set to HTTP.
-
HTTPS connection: 7002
If you use a SOAP development application to generate a web service client and use port numbers other than the default port numbers, the URLs for the web services that supports XML element payload will show port numbers that do not match the port numbers you configured in WebLogic Server Administration Console. Populate the correct port numbers in the URLS for the WSDL files that are generated dynamically by your SOAP development application by doing either of the following:
-
Change the port numbers manually in your SOAP development application request.
-
Change the port numbers in the infranetwebsvc.war/WEB-INF/conf/axis2.xml file as follows:
Open the local_dir/infranetwebsvc.war/WEB-INF/conf/axis2.xml file in a text editor.
Locate the following line and change the HTTP port number:
<parameter name="port">7001</parameter>Locate the following line and change the HTTPS port number:
<parameter name="port">7002</parameter>Save and close the file.
Regenerate the infranetwebsvc.war file by running the following command:
jar -cvf infranetwebsvc.war *Deploy the regenerated infranetwebsvc.war file on WebLogic Server. See "Deploying and Launching Web Services Manager on WebLogic Server" for instructions on deploying Web Services Manager.
-
Configuring Role-Based Authentication for Apache Axis in WebLogic Server
You configure access restrictions for Web Services Manager by creating security roles and by adding conditions to the security roles.
To configure role-based authorization for Apache Axis in WebLogic Server:
-
Log in to WebLogic Server Administration Console.
-
In the Domain Structure pane, click Deployments and click the infranetwebsvc link.
-
Click the Security tab.
-
Click the Application Scope subtab.
-
Click the Roles subtab.
-
Click New.
The Create Stand-Alone Web Application Scoped Roles page appears.
-
In the Name field, enter a name for the role. For example brmws.
-
In the Provider Name list, select XACMLRoleMapper.
-
Click OK.
-
Click the link with the role name you created, for example the brmws link.
-
Click Add Conditions.
-
In the Predicate List list, select Group.
-
Click Next.
-
In the Group Argument Name field, enter the name of the desired group.
-
Click Add.
-
Click Finish.
-
Click Save.
Configuring WebLogic Security Policy on BRM Web Services for JAX-WS in WebLogic Server
You define access restrictions for web services in security policies in WebLogic Server.
To configure WebLogic Security Policy on BRM web Services for JAX-WS in WebLogic Server:
-
Log in to WebLogic Server Administration Console.
-
In the Domain Structure pane, click Deployments and click the BrmWebServices link. A list of all the web services is displayed.
-
Click any of the web service.
-
Click the Configuration tab.
-
Click the WS-Policy subtab.
-
Click the WS-Policy files associated with this web service.
-
Select WebLogic in the Configure the Policy Type for a Web Service section.
-
Add the policies from the Available Endpoint Policies for the selected service.
If you want to use the policy for HTTPS with basic authentication, add policy:policy_name-Https-BasicAuth.xml, where policy_name is name of the policy for the selected service; for example, policy:Wssp1.2-2007-Https-BasicAuth.xml.
If you want to use the policy for HTTPS without authentication, add policy:policy_name-Https.xml, where policy_name is name of the policy for the selected service; for example, policy:Wssp1.2-2007-Https.xml.
-
Click Finish.
-
Click OK in the Save Deployment Plan Assistant section.
If you have multiple deployments, then the plan.xml, which is created when you assign a policy to the service, should be saved in its respective deployment directory.
-
Click the Security tab.
-
Click the Policies subtab.
-
In the Web Service Methods list, select the web method that you want to secure.
-
Click Add Conditions.
-
In the Predicate List list, select one of the following: Roles, Users, or Groups.
-
Click Next.
-
In the User Argument Name field, add the user/group.
-
Click Add.
-
Click Finish.
-
Click Save.
If you have enabled SSL, add the following entry in the BRMWebServices.war/WEB-INF/web.xml file to enable cookie security:
<cookie-config>
<secure>true</secure>
</cookie-config>
Note:
This entry should be added in the session-config element of the BRMWebServices.war/WEB-INF/web.xml file.Configuring Security for Web Services Manager in GlassFish Server
Before you configure security for Web Services Manager, ensure that GlassFish Server and Web Services Manager are installed and that Web Services Manager has been deployed on a GlassFish Server domain. See "Installing Web Services Manager" and "Deploying Web Services Manager" for more information.
To configure security for Web Services Manager in GlassFish Server, do the following:
-
Configure authentication for Web Services Manager for Apache Axis in GlassFish Server. See "Configuring Authentication for Web Services Manager for Apache Axis in GlassFish Server."
-
Configure authentication for Web Services Manager for JAX-WS in GlassFish Server. See "Configuring Authentication for Web Services Manager for JAX-WS in GlassFish Server."
Configuring Authentication for Web Services Manager for Apache Axis in GlassFish Server
To configure authentication for Web Services Manager for Apache Axis in GlassFish Server:
-
Open the local_dir/infranetwebsvc.war/WEB-INF/web.xml file in a text editor.
-
Uncomment the following lines:
# <security-constraint> # <web-resource-collection> # <web-resource-name>restricted web services</web-resource-name> # <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> # <http-method>GET</http-method> # <http-method>POST</http-method> # </web-resource-collection> # <auth-constraint> # <role-name>brmws</role-name> # </auth-constraint> # <user-data-constraint> # <transport-guarantee>CONFIDENTIAL</transport-guarantee> # </user-data-constraint> # </security-constraint> # <login-config> # <auth-method>BASIC</auth-method> # <realm-name>default</realm-name> # </login-config> # <security-role> # <role-name>brmws</role-name> # </security-role>
-
Locate the following line and change the realm name to file:
<realm-name>file</realm-name> -
Save and close the file.
-
Open the local_dir/infranetwebsvc.war/WEB-INF/sun-web.xml file in a text editor.
-
Locate the following line and specify a name for your Web Services Manager user group:
<group-name>groupname</group-name>
where groupname is the name of your Web Services Manager user group for GlassFish Server.
-
Save and close the file.
-
Regenerate the infranetwebsvc.war file by running the following command:
jar -cvf infranetwebsvc.war *
-
Deploy the regenerated infranetwebsvc.war or BrmWebServices.war file on the server. See "Deploying and Launching Web Services Manager on GlassFish Server" for more information.
-
Log in to GlassFish Server Administration Console.
-
In the Common Tasks pane, under Configurations, select server-config.
-
Click Security and select Realms.
-
Select file.
The Edit Realm page appears.
-
Click Manage Users and add a user. See the GlassFish Server documentation for instructions about creating a user.
-
Associate the user to the group that you created in step 6. See the GlassFish Server documentation for instructions about associating a user to a group.
-
Click Save.
-
In the Common Tasks pane, under Configurations, select server-config.
-
Select Network Config.
-
Select Network Listeners.
-
Select the port that is enabled for an HTTPS connection.
Note:
By default, http-listener -1 is for an HTTP connection and http-listener-2 is for an HTTPS connection. -
Click the SSL tabbed page.
-
Select the SSL3 check box.
-
Deselect the TLS check box.
-
Enter the details about the SSL certificate and the keystore in their relevant fields.
For details about the SSL certificate and the keystore, open the local_dir/glassfish/config directory on the server on which you installed GlassFish Server.
-
Click Save.
Configuring Authentication for Web Services Manager for JAX-WS in GlassFish Server
To configure authentication for Web Services Manager for JAX-WS in GlassFish Server:
-
Open the local_dir/BrmWebServices.war/WEB-INF/web.xml file in a text editor.
-
Add the following lines:
# <security-constraint> # <web-resource-collection> # <web-resource-name>restricted web services</web-resource-name> # <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> # <http-method>GET</http-method> # <http-method>POST</http-method> # </web-resource-collection> # <auth-constraint> # <role-name>*</role-name> # </auth-constraint> # <user-data-constraint> # <transport-guarantee>CONFIDENTIAL</transport-guarantee> # </user-data-constraint> # </security-constraint> # <login-config> # <auth-method>BASIC</auth-method> # <realm-name>default</realm-name> # </login-config>
-
Locate the following line and change the realm name to file:
<realm-name>file</realm-name> -
Save and close the file.
-
Go to the local_dir/BrmWebServices.war/WEB-INF directory and create the sun-web.xml file.
-
Open the local_dir/BrmWebServices.war/WEB-INF/sun-web.xml file in a text editor.
Add the following lines:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE sun-web-app PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Application Server 9.0 Servlet 2.5//EN" "http://www.sun.com/software/appserver/dtds/sun-web-app_2_5-0.dtd"> <sun-web-app error-url=""> <security-role-mapping> <role-name>rolename</role-name> <!--Add group name as configured in the security realm 'file' --> <group-name>groupname</group-name> </security-role-mapping> </sun-web-app>
where:
rolename is the name of your Web Services Manager role for GlassFish Server.
groupname is the name of your Web Services Manager user group for GlassFish Server.
-
Save and close the file.
-
Regenerate the BrmWebServices.war file by running the following command:
To regenerate the BrmWebServices.war file:
jar -cvf BrmWebServices.war *
-
Deploy the regenerated infranetwebsvc.war or BrmWebServices.war file on the server. See "Deploying and Launching Web Services Manager on GlassFish Server" for more information.
-
Log in to GlassFish Server Administration Console.
-
In the Common Tasks pane, under Configurations, select server-config.
-
Click Security and select Realms.
-
Select file.
The Edit Realm page appears.
-
Click Manage Users and add a user. See the GlassFish Server documentation for instructions about creating a user.
-
Associate the user to the group that you created in step 6. See the GlassFish Server documentation for instructions about associating a user to a group.
-
Click Save.
-
In the Common Tasks pane, under Configurations, select server-config.
-
Select Network Config.
-
Select Network Listeners.
-
Select the port that is enabled for an HTTPS connection.
Note:
By default, http-listener -1 is for an HTTP connection and http-listener-2 is for an HTTPS connection. -
Click the SSL tabbed page.
-
Select the SSL3 check box.
-
Deselect the TLS check box.
-
Enter the details about the SSL certificate and the keystore in their relevant fields.
For details about the SSL certificate and the keystore, open the local_dir/glassfish/config directory on the server on which you installed GlassFish Server.
-
Click Save.
Configuring Security for Web Services Manager in Tomcat Server
Before you configure security for Web Services Manager, ensure that Tomcat server and Web Services Manager are installed and that Web Services Manager has been deployed on a Tomcat server domain. See "Installing Web Services Manager" and "Deploying Web Services Manager"for more information.
To configure security for Web Services Manager in Tomcat server, do the following:
-
Configure authentication for Web Services Manager for Apache Axis in Tomcat server. See "Configuring Authentication for Web Services Manager for Apache Axis in Tomcat Server."
-
Configure authentication for Web Services Manager for JAX-WS in Tomcat server. See "Configuring Authentication for Web Services Manager for JAX-WS in Tomcat Server."
-
Enable SSL in Tomcat server. See "Enabling SSL in Tomcat Server."
Configuring Authentication for Web Services Manager for Apache Axis in Tomcat Server
To configure authentication for Web Services Manager for Apache Axis in Tomcat server:
-
Open the local_dir/infranetwebsvc.war/WEB-INF/web.xml file in a text editor.
-
Uncomment the following lines:
# <security-constraint> # <web-resource-collection> # <web-resource-name>restricted web services</web-resource-name> # <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> # </web-resource-collection> # <auth-constraint> # <role-name>brmws</role-name> # </auth-constraint> # <user-data-constraint> # <transport-guarantee>CONFIDENTIAL</transport-guarantee> # </user-data-constraint> # </security-constraint> # <login-config> # <auth-method>BASIC</auth-method> # <realm-name>default</realm-name> # </login-config> # <security-role> # <role-name>brmws</role-name> # </security-role>
-
Locate the following line and specify the Web resource name as follows:
<web-resource-name>Protected Resource</web-resource-name> -
Locate the following lines and specify the realm name as follows:
<login-config> <auth-method>BASIC</auth-method> <realm-name>Apache version</realm-name> </login-config>
where version is the Tomcat server version on which you deployed Web Services Manager.
-
Save and close the file.
-
Open the local_dir/apache-tomcat-7.0.54/conf/tomcat-users.xml file in a text editor.
-
Locate the following lines and specify the login details of the user:
<role rolename="brmws"/> <user username="username" password="password" roles="brmws"/>
where:
-
username is the user name for accessing Web services.
-
password is the password for accessing Web services.
-
-
Save and close the file.
-
Open the config/server.xml file in a text editor.
-
In the <Engine> section, add the following class path:
<Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.MemoryRealm" /> -
Save and close the file.
-
Restart the Tomcat server.
Configuring Authentication for Web Services Manager for JAX-WS in Tomcat Server
To configure authentication for Web Services Manager for JAX-WS in Tomcat server:
-
Open the local_dir/BrmWebServices.war/WEB-INF/web.xml file in a text editor.
-
Add the following lines:
# <security-constraint> # <web-resource-collection> # <web-resource-name>restricted web services</web-resource-name> # <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> # <http-method>GET</http-method> # <http-method>/POST</http-method> # </web-resource-collection> # <auth-constraint> # <role-name>brmws</role-name> # </auth-constraint> # <user-data-constraint> # <transport-guarantee>CONFIDENTIAL</transport-guarantee> # </user-data-constraint> # </security-constraint> # <login-config> # <auth-method>BASIC</auth-method> # </login-config> # <security-role> # <role-name>brmws</role-name> # </security-role>
-
Save and close the file.
-
Open the local_dir/apache-tomcat-7.0.62/conf/tomcat-users.xml file in a text editor.
-
Locate the following lines and specify the login details of the user:
<role rolename="brmws"/> <user username="username" password="password" roles="brmws"/>
where:
-
username is the user name for accessing Web services.
-
password is the password for accessing Web services.
-
-
Save and close the file.
-
Open the config/server.xml file in a text editor.
-
In the <Engine> section, add the following class path:
<Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.MemoryRealm" /> -
Save and close the file.
-
Restart the Tomcat server.
Enabling SSL in Tomcat Server
To enable secure communication for Web Services Manager, enable secure sockets layer (SSL) in the Tomcat server domain on which you deploy Web Services Manager.
To enable SSL for Tomcat server:
-
Generate the keystore by running the following command:
keytool -genkey -alias mykes -keyalg RSA -keystore mykeystore
where:
-
mykes is the alias.
-
mykeystore is the name of the keystore.
-
-
Open the conf/server.xml file in a text editor.
-
Uncomment the following lines and specify the path for the keystore file:
# <Connector port="8443" protocol="org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol" # address="IPAddress" # maxThreads="150" SSLEnabled="true" scheme="https" secure="true" # clientAuth="false" sslProtocol="TLS" # keystoreFile="/glassfish/glassfish3/bin/filepath" # keystorePass="password" />
where:
-
IPAddress is the IP address of the machine on which you installed the Apache Tomcat server.
-
filepath is the keystore file path.
-
password is the password for the keystore file.
-
-
Save and close the file.
Configuring Java Logging for the Application Server
Depending on your configuration, you may wish to change the level of Java logging on the application server. To configure the Java logging level, do the following:
-
For WebLogic Server, see "Configuring Java Logging for WebLogic Server" for Web Services Manager-specific configuration. For more information, see the discussion about application logging and WebLogic logging services in Fusion Middleware Using Logging Services for Application Logging for Oracle WebLogic Server.
-
For GlassFish Server, see the discussion about configuring logging services in GlassFish Server Administration Guide.
-
For Tomcat server, see the discussion about logging in Tomcat in Tomcat User Guide.
Configuring Java Logging for WebLogic Server
To configure Java logging in WebLogic Server:
-
Specify the Java Unified Logging (JUL) mechanism. See "Specifying the Java Unified Logging (JUL) Mechanism."
-
Create a startup class. See "Creating a Startup Class."
Specifying the Java Unified Logging (JUL) Mechanism
Specifying the JUL mechanism allows Web Services Manager to use JUL in addition to the WebLogic Server Administration Console logging.
To specify the JUL mechanism:
-
Open the BRM_Home/deploy/web_services/Infranet.properties file in a text editor.
-
Uncomment the following entry:
# webservices.log.enabled = true
-
Change the value to false:
webservices.log.enabled = false
-
Save and close the file.
Creating a Startup Class
You define a startup class to enable JUL and create log files for the following Web service classes:
-
com.portal.webservices.BRMFlistToXML
-
com.portal.webservices.BRMXMLToFlist
-
com.portal.webservices.OpcodeCaller
-
com.portal.webservices.WebServicesUtilities
To create a startup class:
-
Copy the BRM_Home/deploy/web_services/weblogic_ws_startup.jar file to the server_domain/lib directory, where server_domain is the WebLogic Server domain in which Web Services Manager is deployed.
-
Log in to WebLogic Server Administration Console.
-
Click Lock and Edit.
-
In the Domain Structure pane, expand Environment and then click Startup and Shutdown classes.
The Startup and Shutdown Classes pane appears.
-
Click New.
The Configure a New Startup or Shutdown Class: Class Type pane appears.
-
Select Startup Class and click Next.
The Configure a New Startup or Shutdown Class: Startup Class Properties pane appears.
-
In the Name field, enter BRMWSLoggerStartUpClass.
-
In the Class Name field, enter com.portal.webservices.BRMWSLoggerStartUp.
-
In the Argument field, set the log level. This field sets the log level for all the classes in Web Services Manager:
-
To log problems that require attention from the system administrator, enter SEVERE. This is the default.
-
To log the most detailed trace and debug messages, enter FINEST.
-
To log highly detailed trace and debug messages, enter FINER.
-
To log trace and debug messages for performance monitoring, enter FINE.
-
-
Click Next.
The Configure a New Startup or Shutdown Class: Select Targets pane appears.
-
From the Servers list, select the server on which to deploy the class.
The Startup and Shutdown Classes pane appears.
-
Click Finish.
-
Click BRMWSLoggerStartUpClass.
The Settings for BRMWSLoggerStartUpClass pane appears.
-
Select Run Before Application Deployments and Run Before Application Activations and click Save.
-
Click Activate Changes.
-
Restart the WebLogic server, which applies changes.
-
Redeploy any existing Web Services Manager deployments. See "Deploying Web Services Manager."
By default, log files are created in the WebLogic_Home/user_projects/domains/Domain_Name/logs/BRMWebServicesMgrLogs/BRMWebServicesMgr.log file
where:
-
WebLogic_Home is the directory in which WebLogic Server is installed.
-
Domain_Name is the name of the domain you are configuring.