 Table Conversion Programs
Table Conversion Programs
This chapter discusses:
Table conversion programs.
Realtime events.
Adapter services.
Interface flows.
Integration flows.
Integration points.
Batch loads.
Incremental synchronizations.
See Also
The Interactive Services Repository:
http://www.oracle.com/applications/peoplesoft/dev_integration_portals/isr/index.html
 Table Conversion Programs
Table Conversion Programs
A table conversion is a batch process that lets you manipulate data in tables at a high speed.
Many of the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne application integrations with PeopleSoft Enterprise applications use table conversions to export data from JD Edwards EnterpriseOne tables for initial batch loads of data from the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system to the PeopleSoft Enterprise system. These table conversions select data from JD Edwards EnterpriseOne tables based on data selection and processing options, and write the selected data to a flat file. The table conversions place the flat files in a folder called Export in the \B9\package name\ directory in which the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system was installed.
Note. The name of the subdirectory under the B9 directory is determined during installation and might not correspond to the name of the package that was installed.
You can copy or move the flat files from the Export directory to a different location before running the integration flows for the initial load of data. However, you must specify the location of the flat files in the integration options.
Note. If you are running the Integration Server on a UNIX server, the flat files generated by the table conversion programs must
be stored on the same server as the Integration Server to enable the integration flows to locate the files. The location of
the files must be a relative path of the path specified in the integration options using the UNIX file separator (/).
Some firewalls and network settings can interfere with the retrieval of the flat files from the designated network folder
if on a different domain. If this problem occurs, copy the flat files to a share drive on the same network domain as the Integration
Server.
You run table conversion programs from the Batch Versions program (P98305) in much the same way you run other batch programs.
See JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Tools 8.96 Development Tools: Tables and Business Views, "Converting Tables," Running Table Conversions.
For all of the table conversion programs used in these integrations, you may want to select the Clear Output Tables option. If this option is selected when you run any a table conversion program, any existing flat file in the target location is overwritten. If this option is not selected, data produced by subsequent running of the table conversion is appended to any existing flat file in the target location.
 Realtime Events
Realtime Events
A realtime event (RTE) is notification to an external system that a business transaction has occurred in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system. External systems subscribe to the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system to receive notification when a specific transaction occurs.
Many of the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne application integrations with PeopleSoft Enterprise applications use RTEs to export data from JD Edwards EnterpriseOne tables for the incremental synchronization of data that has already been transferred during the initial batch loads. Some integrations also use RTEs for passing transactional data from the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system to the PeopleSoft Enterprise system.
For these integrations, the Integration Server subscribes to the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system to receive the RTE notifications. The Integration Server then transforms the data and passes it to the PeopleSoft Enterprise system.
 Adapter Services
Adapter Services
Adapter services perform a specific operation on a resource. Adapter services exist within the context of an adapter and run on the WSG Integration Server
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne application integrations with PeopleSoft Enterprise applications use adapter services during the transfer of data out of the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system for incremental synchronizations of data and for the transfer of transactional data. The adapter service retrieves the RTE data and creates a published interface document (PID), which contains the data as it is transferred to an integration flow, and which is retrieved by an integration flow. Adapter services are also used for transactional and query processing to expose business functions and database tables in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system.
See Also
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Tools Web Services Gateway 8.96 Adapter Programmer's Guide
 Interface Flows
Interface Flows
Interface flows run on the WSG Integration Server and are used to transfer data to the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system.
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne application integrations with PeopleSoft Enterprise applications use interface flows during the transfer of data from the PeopleSoft Enterprise system to the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system for some incremental synchronizations of data and for the transfer of transactional data.
Interface flows use PIDs to transfer data between the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system and integration flows. For the transfer of data into the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system, PIDs are generated by an integration flow and contain the data as it is transferred to an interface flow.
 Integration Flows
Integration Flows
Integration flows describe the interaction between integration tasks and tie the integration logic together. Integration flows run on the WSG Integration Server.
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne application integrations with PeopleSoft Enterprise applications use integration flow for all point-to-point integrations, including initial batch loads of data, incremental synchronizations of data, and the transfer of transactional data. The mapping and transformation of data between the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system and the PeopleSoft Enterprise system is performed by the integration flows.
During the transfer of data from the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system to the PeopleSoft Enterprise system, the integration flows retrieve either the flat files created by the table conversions (for batch loads) or the PIDs created by adapter services (for incremental synchronizations and transactions). The flows then transform the data, and create XML messages, which are received in the PeopleSoft Enterprise system by integration points (IPs).
During the transfer of data from the PeopleSoft Enterprise system to the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system, the integration flows receive XML messages from PeopleSoft Enterprise IPs, transform the data, and create PIDs, which are passed to the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system by interface flows.
 Integration Points
Integration Points
PeopleSoft Enterprise integration points are web service connections that enable PeopleSoft Enterprise applications to work with third-party systems or software and with other PeopleSoft applications.
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne application integrations with PeopleSoft Enterprise applications use integration points to send data out of the PeopleSoft Enterprise system and to receive data in the PeopleSoft Enterprise system. During the transfer of data from the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system to the PeopleSoft Enterprise system, integration flows create XML messages, which are received in the PeopleSoft Enterprise system by integration points. During the transfer of data from the PeopleSoft Enterprise system to the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system, integration points send messages that contain data from the PeopleSoft Enterprise system. The integration flows receive these messages.
 Batch Loads
Batch Loads
Batch loads are used to load master data from one system to another and done as a prerequisite to processing integrated transactions. For most of the integrations between JD Edwards EnterpriseOne applications and PeopleSoft Enterprise applications, master data is loaded from the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system to the PeopleSoft Enterprise system.
This diagram illustrates the processes of loading master data from JD Edwards EnterpriseOne applications to the PeopleSoft Enterprise system by means of batch loads:
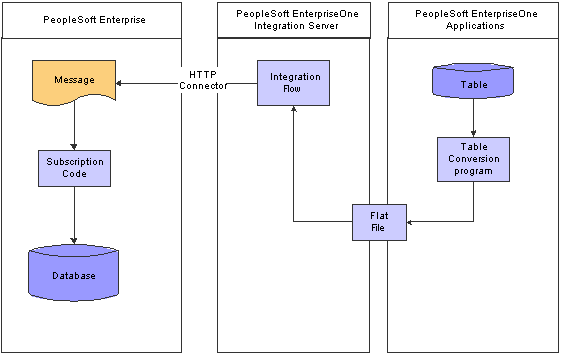
Batch Loads diagram
To perform an initial data load:
Run a table conversion program in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system, which extracts data from the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne database and writes it to a flat file.
Run a batch integration in the Integration Server, which retrieves the flat file, transforms it, and creates one or more messages that are then retrieved by an IP, which writes the data to the PeopleSoft Enterprise database.
The Integration Server Dispatcher picks up the XML message and sends it to the PeopleSoft Enterprise system using HTTP.
(Optional). Run any additional required batch programs in the PeopleSoft Enterprise system to complete the data load process, such as the item loader or Bill of Materials (BOM) loader.
Note. If you are processing a large number of records, you should consider subdividing the records by using data selection and running the table conversion and batch integration multiple times to improve performance.
 Incremental Synchronizations
Incremental Synchronizations
Incremental synchronizations are used to keep master data that is stored in both the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system and the PeopleSoft Enterprise system in sync after the initial batch load of master data. For most of the integrations between JD Edwards EnterpriseOne applications and PeopleSoft Enterprise applications, incremental synchronizations transfer data from the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system to the PeopleSoft Enterprise system.
This diagram illustrates the incremental synchronization of master data from JD Edwards EnterpriseOne applications to the PeopleSoft Enterprise system:
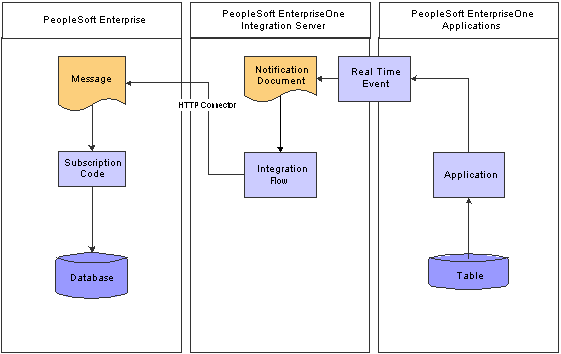
Incremental Synchronizations diagram
The incremental sync integration points run automatically. They are triggered by a Realtime Event (RTE) from JD Edwards EnterpriseOne applications. The RTE from the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system is triggered when an add, change, or delete action is performed on one or more tables by a Master Business Function (MBF), an interactive application, a Universal Batch Engine (UBE) or through another function. The RTE triggers an adapter service, which publishes a PID. An integration flow receives the PID, and transforms the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne message to a JD Edwards EnterpriseOne XML message. The XML message is retrieved by an integration point, which writes the data to the PeopleSoft Enterprise database.