 Understanding VAT Terminology and Principles
Understanding VAT Terminology and PrinciplesThis chapter provides an overview of VAT terminology and principles and discusses:
(FRA) Processing French VAT.
(CHN) Generating VAT on the Free Goods Journal - China report.
(ESP) Processing Spanish VAT.
(GBR) Processing VAT for the United Kingdom.
(CHE) Processing Swiss VAT.
(DEU) Processing German VAT.
(MEX) Processing VAT and the general ledger.
 Understanding VAT Terminology and Principles
Understanding VAT Terminology and PrinciplesValue-added tax (VAT) is a noncumulative tax that tax authorities impose at each stage of the production and distribution cycle. If you work with VAT, you should understand these terminology and principles:
|
Suppliers of goods and services must add VAT to their net prices. They must record output VAT for goods on the date that they issue invoices and for services on the date that they receive payment. The amount of VAT is determined by applying specific rates to the net selling prices of certain goods and services. Output VAT is also called:
|
|
|
Input VAT is the VAT paid by the purchaser of goods and services. If the purchaser is subject to output VAT, the purchaser can recover input VAT by offsetting it against output VAT. When input VAT exceeds output VAT, the purchaser can forward the VAT balance as a credit toward the tax authority for the next reporting period; or receive a cash refund, depending on the policies of the tax authority. Input VAT is also called:
|
|
|
Input VAT cannot be recovered for:
|
 (FRA) Processing French VAT
(FRA) Processing French VATThis section provides an overview and discusses how to process French VAT.
In France, the taxpayer is liable for collected VAT and deductible VAT. Collected VAT is included on sales. Deductible VAT is included in the purchase of goods, equipment, and services. Collected VAT can be offset against any deductible VAT. Businesses can also postpone the declaration of VAT in certain circumstances.
Certain services are subject to a special fiscal regime that allows you to declare the VAT when payment is made, as opposed to when the voucher is recorded. Postponing the declaration of VAT payable as long as possible can be advantageous for a business. This regime is also valid for accounts receivable transactions when VAT is recognized at the time of receipt, instead of at the time of invoicing.
Under the VAT Deductible on Payment regime, when you buy something, you pay VAT to the supplier. You then deduct that amount from the VAT which you have collected from client sales and pay the difference to the fiscal authority.
Under the VAT Collectable on Receipt regime, when you sell something, you collect VAT, which you then owe to the fiscal authority.
Each month of VAT returns must be completed on a special form (CA3) and filed with the local tax office between the 15th and 24th day of the following month.
You must pay any collected VAT that exceeds the over-deductible VAT of the business at the time of filing.
To be exempt from VAT, the business must work within these guidelines:
Goods must be physically moved to another EU-member country.
Customers must have VAT identification codes.
Invoices must display applicable VAT numbers.
Goods cannot be of a special category, such as vehicles.

 Completing the VAT Return Form
Completing the VAT Return FormIn France, the taxpayer is liable for collected VAT and deductible VAT. You must report VAT to the tax authorities. VAT returns must be completed monthly on a special form, and filed with the local tax office between the 15th and 24th day of the following month.
You can use localized software to run French VAT reports. The reports provide the information that you need to complete official tax declaration forms and reconcile the VAT accounts. You can use information from VAT reports to differentiate between transactions that are subject to the ordinary VAT regime, and transactions that are subject to the VAT Collected on Receipts and VAT Payable on Payments regimes.

 VAT on Receipts and Payments
VAT on Receipts and PaymentsThe French VAT for Receipts/Payments program (R74F100) allows you to produce VAT reports for multiple companies and provides correct and complete information required for the CA3 forms for VAT declared on receipts and payments. VAT is only reported when the voucher or invoice is paid.
You can print this report in either summary or detail format. The summary format prints:
Tax rate/area code and description.
Item VAT code.
Total taxable amount to be reported.
Total VAT to be reported.
The detail format includes all the information in the summary format, in addition to:
Final or proof mode.
Tax rule flag.
Address number.
Tax explanation code.
Document type and number.
Pay item.
Service/tax date.
Tax, taxable, and gross amounts.
VAT adjustments from discounts and write-offs.
Receipt/payment amount.
VAT and taxable amount.
You can reprint the report as needed, regardless of whether it has been run in final mode. A reprint in detail format in final mode prints only those records that have not yet been printed and updates the Final Mode Flag for those records.
Use data selection and processing options for report setup.

 Setting Processing Options for VAT for Receipts/Payments (R74F100)
Setting Processing Options for VAT for Receipts/Payments (R74F100)
Processing options enable you to specify the default processing for programs and reports.
Process
These processing options specify how to process the report.
|
Running Mode |
Specify whether to run in proof or final mode. Proof mode does not update tables. Values are: Blank: Proof mode. 1: Final mode. |
|
Sequence |
Specify the sequence in which the report should display transactions. Values are: Blank (Default): Sort transactions first by company, then by tax rate/area. The report displays transactions for the tax rate/areas within a company with a subtotal by tax rate/area then a total for the company. 1: Sort transactions first by tax rate/area, then by company. The report displays transactions for the various companies with the same tax rate/area with a subtotal by company and then a total for tax rate/area. A grand total for the report is displayed only if the currency code is the same for all subtotal fields. |
|
Print Detail |
Specify whether to display detailed transactions for VAT tax. Values are: Blank (Default): Display summary of transactions and the totals for tax rate/area for all companies. 1: Display detail and summary of transactions. The detail includes the VAT tax at the transaction pay item level. Subtotals are displayed based on how sequence is set up in the processing options. The summary displays the totals by tax rate/areas for all companies. |
|
Beginning Process Date and Ending Process Date |
Specify the beginning date or the ending date for processing this report. The system uses the GL Date only if it is greater than or equal to the date specified in this processing option. If this processing option is left blank, the system date is used. |
Receipts
These processing options are for Receipts.
|
Process Receipts |
Specify whether to process VAT from receipts. Values are: Blank (Default): Process receipts. 1: Do not process receipts. |
|
System Code |
Specify the system code for VAT on Receipts. If this processing option is left blank, the system uses system code 74. |
|
Record Type |
Specify the record type for VAT on Receipts. If this processing option is left blank, the system uses record type TX. |
Payments
These processing options are for Payments.
|
Process Payments |
Specify whether to process VAT from payments. Values are: Blank (Default): Process payments. 1: Do not process payments. |
|
System Code |
Specify the system code for VAT on Payments. If this processing option is left blank, the system uses system code 74. |
|
Record Type |
Specify the record type for VAT on Payments. If this processing option is left blank, the system uses record type TX. |
Currency
These processing options enable you to use as if currency.
|
As If Currency Code |
Specify the currency code for as if currency reporting. This option allows for amounts to display in a currency other than the currency they are stored in. They system converts and prints them in the as if currency. If this processing option is left blank, the system prints the amounts in the database currency. This processing option is for display purposes only. The amounts are recorded to the tables in their base currency. |
|
Exchange Rate Date |
Specify the date to use for currency conversion from the database currency into the as if currency. If this processing option is left blank, the system date is used. |
 (CHN) Generating VAT on Free Goods Journal - China Report
(CHN) Generating VAT on Free Goods Journal - China ReportThis section provides an overview of the VAT on Free Goods Journal - China report and discusses how to:
Run the VAT on Free Goods Journal - China report.
Set processing options for VAT on Free Goods Journal - China.

 Understanding the VAT on Free Goods Journal - China Report
Understanding the VAT on Free Goods Journal - China ReportThe VAT on Free Goods Journal Creation program (R75C4203) calculates and reports liable VAT on free goods from sales orders, and creates corresponding journal entries.
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Sales Order Management system allows users to store sales information in the F4211 table or purge those detail records. When you purge table F4211, the system moves the records to the F42119 table. The VAT on Free Goods Journal report can calculate VAT on free goods by using either table F4211 or table F42119.
Note. Journal entries are only created when you run the VAT on Free Goods Journal Creation report in final mode. The system uses the tax Automatic Accounting Instruction (AAI) (RTxxxx) to determine the credit account. The system uses the distribution AAI 4290 to determine the debit account. You can override these accounts by entering specific accounts in the processing options.

 Running the VAT on Free Goods Journal - China Report
Running the VAT on Free Goods Journal - China Report
Select VAT on Free Goods - China (G75C031), VAT on Free Goods Journal Creation.

 Setting Processing Options for VAT on Free Goods Journal - China (R75C4203)
Setting Processing Options for VAT on Free Goods Journal - China (R75C4203)Processing options enable you to specify the default processing for programs and reports.
Defaults
Use these processing options to set up defaults.
|
1. GL Date |
Specify the GL date. |
|
2. Specific Date as GL Date |
Specify which date the system uses as the GL date. Values are: 1: Use sales invoice date as GL date. 2: Use actual shipment date as GL date. 3: Use GL date created by sales update process as GL date. 4: Use system date as GL date. |
|
3. Document Type |
Specify the journal entry document type. You must enter values that have been set up in user-defined code list (00/DT). If you leave this processing option blank, the default value is JE. |
Process
Use these processing options to specify how the system processes VAT on Free Goods.
|
1. Mode |
Specify whether to run the report in proof or final mode. If you select proof mode, the system creates only the report (R75C4203). If you select final mode, the system creates the report (R75C4203) and also writes records to the F75C4203 table. Values are: Blank: Proof mode 1: Final mode |
|
2. Summarize by Company |
Specify whether the system summarizes the journal entries by company. Values are: 1: Summarizes. Blank: Does not summarize. |
|
3. Override Credit Account to |
Specify the credit account. If you leave this processing option blank, the system retrieves the credit account from the RT or RTyyyy tax AAI. |
|
4. Override Debit Account to |
Specify the debit account. If you leave this processing option blank, the system retrieves the debit account from DMAAI 4290. |
Versions
Specify the version that the system uses for the Journal Entry Master Business Function processing options (P0900049).
|
1. GL Master Business Function processing options (P0900049) |
Specify which version is used for the GL Master Business Function processing options (P0900049). If you leave this processing option blank, the system uses the default version (ZJDE0001). |
 (ESP) Processing Spanish VAT
(ESP) Processing Spanish VATThis section provides an overview of Spanish VAT.
If you work with Spanish VAT, you should understand these terminology and principles:
VAT returns for each month must be completed on a special form and filed with the local tax office on the 20th of the month.
You must pay any excess output VAT over input VAT at the time of filing.
To be exempt from VAT, the business must work within these guidelines:
Goods must be physically moved to another EU-member country.
Customers must have VAT identification codes.
Invoices must display applicable VAT numbers.
Goods cannot be of a special category, such as vehicles.
See Also
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Tax Processing Reports: Selected Reports
 (GBR) Processing VAT for the United Kingdom
(GBR) Processing VAT for the United KingdomThis section provides an overview United Kingdom VAT.
If you work with VAT in the United Kingdom, you should understand these terminology and principles:
If tax is payable, businesses must submit quarterly VAT returns to HM Customs and Excise.
You must pay any excess output VAT over input VAT at the time of filing.
Certain types of supplies are exempt from VAT. Businesses can obtain a list of these types of supplies from the local tax office.
 (CHE) Processing Swiss VAT
(CHE) Processing Swiss VATThis section provides an overview Swiss VAT.
Value-added tax (VAT) is a noncumulative tax that is imposed at each stage of the production and distribution cycle. The ordinance requiring VAT in Switzerland became effective in January 1995.
Businesses in Switzerland are required to submit an official quarterly tax declaration, along with the payment for taxes due, within 60 days of the end of each quarter. In addition to this tax declaration, businesses are required to submit reports that list transactions involving VAT.
See Also
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Tax Processing Reports: Selected Reports
 (DEU) Processing German VAT
(DEU) Processing German VATThis section provides an overview German VAT.
If you work with VAT in Germany, you should understand these terminology and principles:
VAT returns must be completed for each month by the tenth day of the following month and filed with the local tax office.
You must pay any excess output VAT over input VAT at the time of filing.
In Germany, these transactions are nontaxable:
Transactions within the same entity.
Transactions for the transfer of business.
Transactions for subsidies, penalty payments, and compensation.
 (MEX) Processing VAT and the General Ledger
(MEX) Processing VAT and the General LedgerThis section provides graphical overviews of VAT processing and the general ledger and discusses how to review Mexican VAT transactions.

 Understanding VAT Processing and the General Ledger
Understanding VAT Processing and the General Ledger
This diagram illustrates the effect of the Mexican VAT process for vouchers on the general ledger:
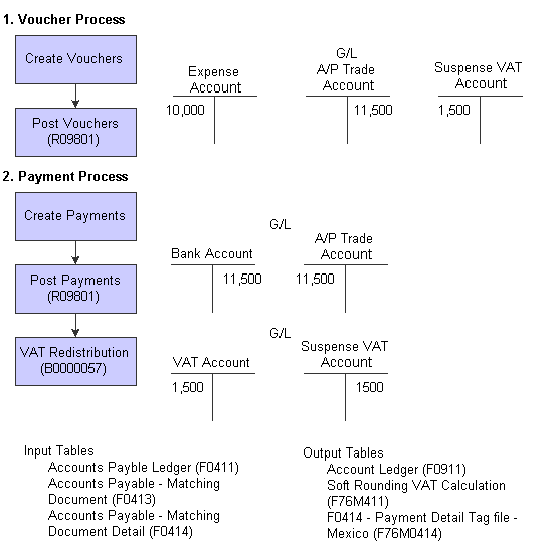
Mexican VAT Process – Vouchers
This diagram illustrates the effect of the Mexican VAT process for prepayments on the general ledger:
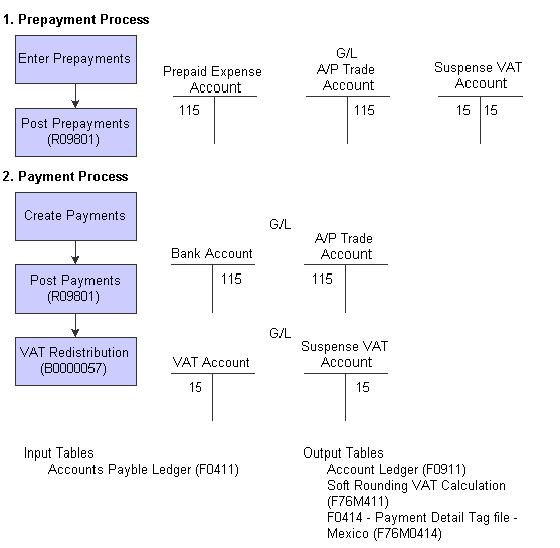
Mexican VAT – Prepayment
This diagram illustrates the effect of the Mexican VAT process for invoices on the General Ledger:
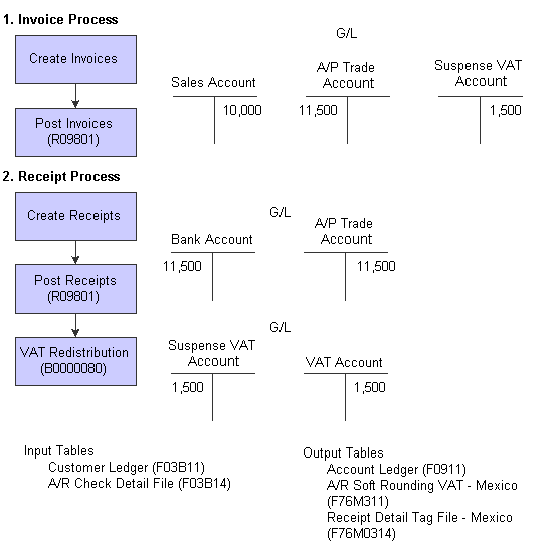
Mexican VAT – Invoices

 Reviewing Mexican VAT Transactions
Reviewing Mexican VAT Transactions
You can inquire on the reclassification journal entries in the Account Ledger Inquiry program (P09200).
For JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Payable, you can inquire using the supplier invoice number or purchase order number in addition to the payment or prepayment number.
For JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable, you can inquire using the invoice number within wildcard characters (for example, *12345*) in the Explanation field of the QBE line.
In some cases, the Mexican VAT process might be unable to reclassify the tax information successfully. If this situation happens, you can view the error in the Work Center.
If a fatal error occurs during VAT reclassification and no journal entries are generated, you must calculate the VAT amount to reclassify and enter the journal entry manually.
When the AAI does not exist or when an invalid account has been set up for the Mexican VAT process, the reclassification journal entry is generated with a blank account number. In this case, you must correct the account number on the journal entry and post the journal entry.