18 Configuring and Managing the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog
This chapter describes how to configure and manage the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog and provides information about basic maintenance procedures and configuring for full-text searching.
This chapter contains the following sections:
-
Section 18.3, "Maintaining the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog"
-
Section 18.4, "Starting Catalog Manager and Opening Catalogs"
-
Section 18.8, "Searching for and Replacing Catalog Text Using Catalog Manager"
-
Section 18.9, "Creating Reports to Display Catalog Data Using Catalog Manager"
-
Section 18.10, "Archiving and Unarchiving a Catalog Using Catalog Manager"
-
Section 18.12, "Replicating Oracle BI Presentation Catalogs"
18.1 About the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog
The Oracle BI Presentation Catalog stores the content that users create in a directory structure of individual files. This content includes folders, shortcuts, Oracle BI EE objects (such as analyses, filters, prompts, and dashboards), and Oracle BI Publisher objects (such as reports and templates).
Each object is stored in its own file. For example, an analysis called Analysis 1 would be stored in a file named Analysis1. Each object has a corresponding attributes file. For example, the analysis called Analysis1 would have a corresponding attributes file named Analysis1.atr. The attributes file contains the object's full name, access control list (ACL), description, and so on. To access an object in the catalog, users must have appropriate ACL entries for that object. All objects in the catalog use ACL entries.
Note:
To guarantee that only one user can write to a file at one time, a lock file is created when an object is being written to. On rare occasions (for example, after a power outage), temporary lock files in the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog might not get cleaned up completely. If Presentation Services reports of such a lock file, then you must delete it manually.The following locations are the default locations for the catalog directory:
-
On Windows
ORACLE_INSTANCE\bifoundation\OracleBIPresentationServicesComponent\coreapplication_obipsn\catalog
-
On UNIX
ORACLE_INSTANCE/bifoundation/OracleBIPresentationServicesComponent/coreapplication_obipsn/catalog
18.2 About Catalog Manager
Catalog Manager is a tool that lets you perform online and offline management of Oracle BI Presentation Catalogs. It should be installed on a secure computer that is accessible only to Oracle BI Administrators.
18.2.1 Uses for Catalog Manager
You can use Catalog Manager to:
-
Manage folders, shortcuts, and objects (analyses, filters, prompts, dashboards, and so on). For example, you can rename and delete objects, and you can move and copy objects within and between catalogs.
-
View and edit catalog objects in Extensible Markup Language (XML).
-
Preview objects, such as analyses and prompts.
-
Search for and replace catalog text.
-
Search for catalog objects.
-
Create analyses to display catalog data.
-
Localize captions. See Section 16.2.2, "Localizing Oracle BI Presentation Catalog Captions."
Many of the operations that you can perform in Catalog Manager, can also be performed through the Catalog page in Oracle BI Presentation Services. For information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
18.2.2 Guidelines for Working with Catalog Manager
Follow these guidelines when working with Catalog Manager:
-
Always make backup copies of the Oracle BI Presentation Catalogs that you are working with.
-
Be sure of changes that you plan to make. Catalog Manager commits changes immediately. There is no undo function nor are there any error messages to tell you that a particular change does not display well to users. However, if you do make any unwanted changes, then you can revert to your latest saved backup.
-
Do not copy and paste into e-mail, as this is not supported.
18.2.3 Tips for Working with Catalog Manager
As you work with Catalog Manager, keep the following tips in mind:
-
While working in online mode, you can paste catalog contents into or out of a read-only folder by turning off the read-only property of the folder tree before copying, then re-apply the read-only attribute after pasting.
-
You cannot copy, archive, or drag files from the /system/security directory in the Catalog Manager.
-
Some keyboard shortcuts might not work properly.
-
Even if a resize indicator is not shown, Catalog Manager panes might still be resizable.
18.3 Maintaining the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog
This section contains the following topics on maintaining a catalog:
-
Section 18.3.1, "Manually Changing Additional Configuration Settings for the Catalog"
-
Section 18.3.2, "Manually Creating a New Oracle BI Presentation Catalog"
18.3.1 Manually Changing Additional Configuration Settings for the Catalog
In addition to the presentation settings that you can change in Fusion Middleware Control, you can modify other settings manually. Use various elements in the instanceconfig.xml file to change these settings.
Before you begin this procedure, ensure that you are familiar with the information in Section 3.4, "Using a Text Editor to Update Oracle Business Intelligence Configuration Settings".
To manually change additional configuration settings for the catalog:
-
Open the instanceconfig.xml file for editing as described in Section 3.6, "Where are Configuration Files Located?"
-
Locate the section in which you must add the following element:
-
HashUserHomeDirectories: Specifies the hashing of directories. If you have more than 4000 catalog users or if you intend to have more than 4000 catalog users in the future, then you must turn on the hashing of users' home directories to address a file system limitation. To do so, set the HashUserHomeDirectories element to 2 from its default value of 0. When this element is turned on, for example, the default name for user Steve's home directory would become /users/st/steve.
Caution:
The HashUserHomeDirectories element must be set immediately after installing Oracle BI EE to be effective. -
-
Include the element and its ancestor elements as appropriate, as shown in the following example:
<ServerInstance> <Catalog> <HashUserHomeDirectories>2</HashUserHomeDirectories> </Catalog> </ServerInstance> -
Save your changes and close the file.
-
Restart Presentation Services.
18.3.2 Manually Creating a New Oracle BI Presentation Catalog
You can manually create a new catalog.
To manually create a new catalog:
-
Stop the service for Presentation Services.
The Oracle BI Server and WebLogic Server must be running.
-
Specify a new location (one that does not exist) for the catalog on the Repository tab of the Deployment page in Fusion Middleware Control.
-
Ensure that the new location for the catalog is empty.
-
Save your changes and close the file.
-
Restart Presentation Services.
18.3.3 Deploying a Catalog Object to Production
You can deploy a simple object (for example, a dashboard with privileges) to your production environment using the archive and unarchive functionality.
Deploying a complex object (for example, an object that includes references to external filters) is a more advanced process. Oracle offers advanced training courses to guide you through this process. It is recommended that you attend one of these courses before you attempt to deploy a complex object to production.
To deploy a catalog object to a production environment:
-
(Optional) If you are deploying a catalog object to a new production environment.
Archive the catalog object in the test environment and unarchive it in the production environment as follows:
-
Archive the catalog object in the test environment using one of the following:
-
Oracle BI Presentation Services.
-
Catalog Manager.
For information, see Section 18.10, "Archiving and Unarchiving a Catalog Using Catalog Manager."
-
-
Copy the archived file to the production computer.
-
On the production computer, unarchive the object.
For information on how to unarchive an object, see Section 18.10, "Archiving and Unarchiving a Catalog Using Catalog Manager."
-
Set the permissions on the object as appropriate.
-
-
(Optional) If you are deploying the catalog to an existing production environment.
Copy and paste new or updated objects from the test catalog into the production catalog as follows:
-
Open two Catalog Manager windows: one with the test catalog, and another with the production Catalog.
-
Selectively copy and paste the folders from the test catalog into the production catalog.
If you copy and paste folders where the same content has been changed in the test or production environments, then test content overwrites the production content.
-
-
(Optional) If you are deploying the catalog from test to a new production environment, use Fusion Middleware Control to specify the location of the new catalog in the production environment.
For more information, see Section 10.1, "Using Fusion Middleware Control to Upload a Repository and Set the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog Location."
18.4 Starting Catalog Manager and Opening Catalogs
This section describes the following topics:
18.4.1 Starting Catalog Manager
Use the following procedure to start Catalog Manager.
To start Catalog Manager:
-
On Windows, double-click the runcat.cmd script in the following directory:
ORACLE_HOME\bifoundation\web\catalogmanager
or
Using the command line, provide the full path to the script:
runcat.cmd (on Windows)
runcat.sh (on UNIX)
18.4.2 Understanding the Two Catalog Modes
You can open a catalog in one of two modes:
-
Online mode — Connects to a catalog on a running Web server. In this mode your permissions are applied. You can see only those objects for which you have the appropriate permissions. Both Presentation Services and the Web Server must be running for you to open catalogs in online mode.
Use online mode when you want to make minor incremental changes or additions to the catalog, such as changes to permissions, updates to a single object, or migration of new objects to a production environment
-
Offline mode — Connects to a local file system. In this mode, you are logged in as a super user or system user, and no permissions are applied. You can see all objects in the catalog.
Use offline mode when you want to make catalog-wide changes, such as globally renaming objects or moving multiple objects for reorganization.
Note:
Generally, working in offline mode is faster than working in online mode. This is because you are accessing, creating, and updating the individual files directly, and the catalog does not have to communicate with Presentation Services as it does when you are working in online mode.18.4.3 Operations Available in Online Mode and Offline Mode
Many of the operations that you can perform using Catalog Manager are available in both online mode and offline mode. A few operations are available in only one mode or the other. Generally, the operations available in:
-
Online mode are read-only operations and write operations that do not affect the entire catalog, such as setting permissions for an object.
-
Offline mode include most of the operations available in online mode and write functions that affect the entire catalog, such as searching for and replacing catalog text.
You can perform the following operations in online and offline modes (or as stated), as follows:
-
Cutting objects
-
Copying objects
-
Pasting objects
-
Copying objects for another catalog
-
Pasting objects from another catalog
-
Creating shortcuts of objects
-
Deleting objects
-
Renaming objects without reference updates
-
Refreshing the Catalog Manager workspace
-
Creating folders
-
Setting permissions for objects
-
Working with properties of objects
-
Managing the view of the workspace
-
Searching for objects
-
Creating reports to display Catalog Manager data
-
Setting browser preference
-
Either:
-
Previewing objects (available in online mode only)
-
Renaming objects with reference updates (known as Smart Rename and available in offline mode only)
-
-
Exporting captions for localization purposes
-
Searching for and replacing catalog text (available in offline mode only
18.4.4 Opening an Oracle BI Presentation Catalog
To open an Oracle BI Presentation Catalog:
-
In Catalog Manager, from the File menu, select Open Catalog.
-
Complete the necessary fields.
Some fields are described in the following list.
-
Type — Select the mode (online or offline) in which to open the catalog
-
Path — If you are opening the catalog in offline mode, then enter the path to the catalog folder on the local file system, for example:
Click Browse to display a dialog for locating the catalog.
C:\ORACLE_INSTANCE\bifoundation\OracleBIPresentationServicesComponent\coreapplication_obipsn\catalog\default
-
URL — If you are opening the catalog in online mode, then enter the URL to Oracle BI Presentation Services, for example:
http://<hostname>/analytics/saw.dll
-
User — If you are opening the catalog in online mode, then enter the user name for the host URL (disabled in offline mode).
-
Password — If you are opening the catalog in online mode, then enter the password for the host URL (disabled in offline mode).
-
Read-Only — Select this field to open the catalog in read-only mode (disabled in offline mode).
-
-
Click OK.
18.5 Using the Catalog Manager Workspace
This section provides the following topics on the workspace for Catalog Manager:
-
Section 18.5.1, "What Does the Catalog Manager Workspace Do?"
-
Section 18.5.2, "What Does the Catalog Manager Workspace Look Like?"
-
Section 18.5.3, "Managing the View of the Catalog Manager Workspace"
18.5.1 What Does the Catalog Manager Workspace Do?
The Catalog Manager workspace enables you to view and work with catalog objects. It displays the following folders for an open catalog:
-
The shared folder— Contains content that is shared among catalog users. This includes the preconfigured dashboards and analyses that are distributed with prebuilt applications, and other objects such as shared filters.
-
The system folder — Contains administrative elements of Presentation Services. Some of these elements are distributed with the product, and others are set up by you as the administrator, such as privileges.
-
The users folder — Contains content that catalog users with the appropriate permissions have saved to their personal folders, such as individual analyses.
18.5.2 What Does the Catalog Manager Workspace Look Like?
Catalog Manager consists of the following main components:
-
Menu bar — Lets you access the following menus:
-
File — Provides options that let you open and close catalogs, exit Catalog Manager, and so on.
-
Edit — Provides options that let you manage catalog objects, such as Cut, Copy, Permissions, and so on. (Many of these options are also available on the right-mouse pop-up menu.)
-
View — Provides options to manage the view of the Catalog Manager workspace, such as Show Tree, Show Job Status, and so on.
-
Tools — Provides options that let you manage catalogs, such as XML Search and Replace, Create Report, and so on.
-
Help — Provides options to access the Oracle BI Enterprise Edition Web site and to display information about Catalog Manager.
-
-
Toolbar — Provides quick access to commonly used options, such as Cut, Copy, Paste, and so on.
-
Tree pane — Displays catalog folders. The pane also displays objects but only if the Show Objects in Tree option on the View menu is selected.
-
Table pane — Displays catalog folders and objects. It consists of:
-
The navigation bar, where you can move to the catalog object to work with by typing its path name.
-
These columns: Name, Type, Owner, My Permissions, Attributes, Date Created, and Last Modified. Click the column name to sort by that value, such as by type.
The Type column identifies the type of object. Objects that are identified as "unknown file" are generally internally-used objects, and their type is not exposed in Catalog Manager.
-
-
Right-mouse pop-up menu — Provides options that let you manage catalog objects, such as Rename, Properties, Permissions, and so on. (Many of these options are also available on the Edit menu.)
18.5.3 Managing the View of the Catalog Manager Workspace
You can manage what you view in the Catalog Manager. For example, you can show objects in the Tree pane or show job statuses.
To manage the view of the Catalog Manager workspace:
-
In Catalog Manager, choose View and then one of these options:
-
Show Tree — Displays the Tree pane, if you previously had closed it.
-
Show Table — Displays the Table pane, if you previously had closed it.
-
Show Job Status — Displays the Background Job Status pane, where you can view the progress of processes that you have run, such as Search and Replace, Smart Rename, and so on. You can also remove all finished jobs and set progress preferences using the icons in the upper-right corner of the pane.
-
Show Objects in Tree — Displays objects (that is, analyses, filters, and so on) in addition to folders in the Tree pane.
-
Refresh — Refreshes the objects that are displayed in the Tree and Table panes. (You might want to refresh the data, for example, if someone else makes changes to the catalog while you are working with it and you want to see the changes.)
-
18.6 Working with Objects in Catalog Manager
This section provides the following information on working with objects:
-
Section 18.6.1, "Searching for Catalog Objects Using Catalog Manager"
-
Section 18.6.4, "Working with the Properties of Catalog Objects"
In the Catalog page of Presentation Services, you can view folders and contents including hidden objects. You can create, rename, copy, move, and delete folders and contents. For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
Note:
Changes made in the Presentation layer of the Oracle BI Administration Tool can affect analyses and dashboards based on those tables and columns. You can use Catalog Manager to keep the catalog synchronized with these changes in the Presentation layer.18.6.1 Searching for Catalog Objects Using Catalog Manager
You can search for objects in the catalog using the Search function. For example, you might want to search for all objects that have a property with the value of "administrator."
When you search, you can limit the search by:
-
Case Sensitive — Select this check box to apply case sensitivity to the search criteria. The default value is unchecked.
-
Name — Limits the search to the names of objects.
-
Description — Limits the search to the Description property.
-
Property values — Limits the search to the values of properties.
-
Owner — Limits the search to the owners of objects.
-
Object type — Searches for all types of objects or limits the search to a specific type of object that you specify (for example, analyses, filters, agents, dashboard prompts, dashboard pages).
-
Date — Limits the search to objects that were created on the dates that you specify or to objects that were last modified on the dates that you specify.
To search for an object:
-
In Catalog Manager, open the catalog and navigate to the location in the tree where you want to begin the search.
-
Click Search on the toolbar.
-
In the Search for any or all criteria below field, enter the word or phrase to search for.
-
To make the search case sensitive, select the Case Sensitive box.
-
To limit the search, then click Advanced Search.
-
In the Advanced Search area, specify the constraints for the search.
-
Click Search.
Tip:
When you have finished searching, click Explore the entire catalog tree on the toolbar to return to the Tree and Table panes.
18.6.2 Copying and Pasting Objects
You can copy and paste objects within a single catalog. You can also copy objects from one catalog and paste them into another catalog.
18.6.2.1 Tips for Copying and Pasting
Use the following tips as you copy and paste objects:
-
You can copy and paste objects using menu options, and you can use drag and drop functionality to copy objects between two catalogs and within the same catalog. Drag and drop always makes a copy of the dragged objects, even when performing a drag and drop within a single catalog.
-
Catalogs are structured in hierarchical folders. When copying or merging objects, remember to also copy any objects that are associated with them, such as dashboard folders, shortcuts, and analyses. URL paths in external applications can be reestablished after a copy or merge operation if the entire folder path is not copied, for example, if added to the dashboard as a shortcut or text.
-
Most often, you can simply copy and paste objects as needed. If required, you can set advanced options that affect the objects that you are pasting. For complete information, see Section 18.6.2.4, "Advanced Options for Pasting Objects."
18.6.2.2 Online and Offline Mode for Copying and Pasting
When you are copying between catalogs, the mode in which the catalogs are opened makes no difference. You can copy and paste objects from an:
-
Online catalog to an offline catalog (or an offline catalog to an online catalog)
-
Online catalog to another online catalog
-
Offline catalog to another offline catalog
This is especially useful, for example, to develop new objects in a catalog offline and migrate them to a production environment without having to shut down Presentation Services.
18.6.2.3 Copying and Pasting Objects Between Catalogs
The following procedure describes how to copy and paste objects between two catalogs using menu options. If the two catalogs have the same name, then you might want to rename one of the catalogs before opening it to help distinguish between the two catalogs as you work. Both catalogs must be the same version 11.1.1 (or later).
To copy and paste objects between catalogs using menus:
-
In Catalog Manager, open the catalog to change, that is the target catalog.
-
Using another instance of the Catalog Manager, open the catalog that contains the objects to copy, that is the source catalog.
-
If necessary, reposition both instances of Catalog Manager on your screen so you can display the title bars of both Catalog Manager instances.
-
In the source catalog, right-click the source object and select Copy.
-
In the target catalog, right-click at the point where you want to paste the source object and select Paste.
18.6.2.4 Advanced Options for Pasting Objects
You can set advanced options for pasting objects that you have copied. These options are available in the Preferences dialog and must be set before the copy and paste operation begins.
18.6.2.4.1 Paste Overwrite
The Preferences dialog contains the following options in the Paste Overwrite area:
-
Force — Pastes all files, even those that have the read-only attribute set.
-
All — Pastes all files, whether they exist or not. (Default)
-
Old — Pastes all files, but does not paste any existing files unless they are older than the source.
-
None — Pastes all files, but does not paste any existing files.
Consider the following example of pasting with overwrite options set. Suppose that the /users/joe folder contains the following analyses:
Analysis A (created 01-Jan-2010)
Analysis B (created 31-May-2010)
Analysis C (created 01-Jan-2010)
Suppose that the /users/sue folder contains the following analyses, but no Analysis C
Analysis A (created 28-Feb-2010)
Analysis B (created 01-Jan-2010)
Suppose that Sue copies the A, B, and C Analyses from the /users/joe folder and pastes them to the /users/sue folder. If the Paste Overwrite option is set to:
-
None, then Sue keeps her A and B Analyses, and Joe's analyses are ignored. Sue gets a copy of Analysis C.
-
All, then Sue's A and B Analyses are overwritten with Joe's, and Sue gets a copy of Analysis C.
-
Old, then Sue keeps her A Analysis (Sue's A Analyses is not "old"), Sue's B Analysis gets overwritten by Joe's analysis (Sue's B Analysis was "old"), and Sue gets a copy of Analysis C.
18.6.2.4.2 Paste ACL
The Preferences dialog contains the following options in the Paste ACL area:
-
Inherit — Inherits the object's permissions (ACL) from its new parent folder. (Default)
-
Preserve — Preserves the object's permissions (ACL) as it was in the original, mapping accounts as necessary.
-
Preserve Only Groups — Same as Preserve, but applies to group accounts and Application Roles, not to user accounts. This is for a development to production environment in which a customer might use the same groups (such as Sales and Marketing) in both development and production. However, the users in each group might be very different, such as TestUserA and TestAdminB in development and Steve and Sue in production.
-
Create — Preserves the object's permissions (ACL) as it was in the original, creating and mapping accounts as necessary.
-
Create Only Groups — Same as Create, but applies only to group accounts and Application Roles, not to user accounts. Works in a development to production environment similarly to Preserve Only Groups.
Consider the following example of pasting with ACL options set. Suppose that Steve owns the /users/steve/MyFavReport folder and has permissions (ACL) "all users can read/execute, steve has full control". Joe (who has some administration privileges) logs in and copies MyFavReport, pasting it to /users/sue (which is owned by "administrator", with permissions "admins have full control, sue has full control").
If Joe sets the Paste ACL option is set to:
-
Inherit, then the /users/sue/MyFavReport folder is owned by Joe with whatever permissions are set on the /users/sue folder (that is, "admins have full control, sue has full control").
-
Preserve, then the /users/sue/MyFavReport folder is owned by Joe with whatever permissions were set on the /users/steve/MyFavReport folder (that is, "all users can read/execute, steve has full control"). If Joe pastes in a second Catalog Manager and if "steve" does not exist in this Catalog, then the permissions for Steve are discarded. If "steve" exists but has a different user ID, then Steve's user ID is mapped to the new one.
-
Create, then the /users/sue/MyFavReport folder is owned by Joe with whatever permissions were set on the /users/steve/MyFavReport folder (that is, "all users can read/execute, Steve has full control"). If Joe pastes in a second Catalog Manager and if "steve" does not exist in this Catalog, then the user "steve" is created.
This feature is used in applications whose administrators create accounts in a staging area before moving the users to the production environment.
After the paste, the object is owned by the person who performed the paste. If you have the appropriate permissions, then you can select the newly pasted object and set ownership recursively to the appropriate user.
18.6.3 Renaming Catalog Objects
You can rename objects in the catalog. This can be useful when you are migrating from a test environment to a production environment.
There are two ways to rename an object:
-
Rename without reference updates — Renames the object and preserves the references to the original name that other catalog objects might have.
-
Rename with reference updates — Renames the object and changes references that other objects might have to the new name (that is, original name references are not preserved). You must open the catalog in offline mode.
Caution:
Do not rename the "My Dashboard" dashboards in the Users folder (displayed as _portal in Catalog Manager).To rename an object without reference updates:
-
In Catalog Manager, open the catalog.
-
Navigate to the object to be renamed.
-
Right-click the object in the Name column and select Rename.
-
Type a new name for the object.
To rename an object with reference updates:
-
In Catalog Manager, open the catalog in offline mode.
-
Navigate to the object to be renamed.
-
Right-click the object in the Name column and select Smart Rename.
-
Type a new name for the object.
A progress bar in the lower right-hand corner of the window shows the progress of the reference updates.
18.6.4 Working with the Properties of Catalog Objects
Using the Properties option of Catalog Manager, you can:
-
Create, view, edit, and delete the properties of catalog objects.
-
Change attributes of catalog objects to hide them from display in Oracle Business Intelligence.
To work with the properties of a catalog object:
-
In Catalog Manager, open the catalog.
-
Navigate to the object.
-
Right-click the object in the Name column and select Properties.
-
Perform the necessary tasks:
-
If you have the appropriate permissions, then select the appropriate owner for the object in the Owner list.
-
To change the attribute of an object, select either Read-Only or Hidden, if appropriate. A hidden object is not visible in Oracle Business Intelligence.
Note:
The System option indicates that the object is maintained internally and should not be altered. -
To create, edit, or delete a property, use the New, Edit, or Delete button as appropriate.
Note:
The New button is used to create a property. You should use it only if instructed to do so by Oracle Support.
-
-
Click OK.
You can select multiple objects and update their properties or permissions simultaneously. If any of the selected objects are a folder, then you can also apply those changes recursively to all the objects in that folder's tree structure.
For example, you can set all files in the /shared/DontTouch directory to be Read-Only. Right-click the DontTouch directory and select Properties. In the Properties dialog, select the Read-Only option, select the Apply Recursively option, and click OK.
18.6.5 Setting Permissions of Catalog Objects
Permissions are used to control access to catalog objects.
To set permissions of a catalog object:
-
In Catalog Manager, open the catalog.
-
Navigate to the object.
-
Right-click the object in the Name column and select Permissions.
The Permissions dialog displays these two lists:
-
Users and groups (Explicit Permissions) — Shows the users, groups, and application roles that have explicit permissions granted to this object.
-
Additional users and groups — Shows the users, groups, and application roles that have access granted through group inheritance, and users, groups, and application roles that have no access to the request.
For details on how permissions and privileges are assigned in Presentation Services, see Section C.1.3, "How Are Permissions and Privileges Assigned to Users?"
-
-
If the user, group, or application role whose permissions you want to set is in the Additional users and groups list, then move it into the Users and groups (Explicit Permissions) list by selecting it and clicking the left arrow button (<).
-
(Optional) To filter the users, groups, and application roles displayed in the Additional users and groups list, use the List button with the drop-down list, and the adjacent field, as follows:
-
Enter filter criteria in the field next to the List button (case insensitive).
To enter partial filter criteria, use the asterix (*) symbol. For example, enter bi* to display users or groups beginning with bi, BI, bI, and Bi.
-
Select a value from the drop-down list.
Available values are: All, User, Group, or Application Role.
-
-
Select the user or group in the Users and groups (Explicit Permissions) list.
-
Select a new permission from the list in the Permissions column, or click Custom from the list to display the Custom Permissions dialog, where you can select a combination of permissions.
For details on what each permission means, see Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
-
Select the Apply Recursively option to apply the changes to all the objects that the object contains.
-
Select a value from the Replace Option list as follows:
-
Replace All — Replaces the existing ACL with what is currently in the dialog.
-
Replace Listed — Changes only the accounts currently displayed in the dialog and leaves others unchanged.
-
Remove Listed — Removes only the accounts currently displayed and leaves others unchanged.
-
-
Click OK.
Note:
If you move a user or group from the Users and groups (Explicit Permissions) list to the Additional users and groups list, then the user or group privileges are reset to No Access. To move a user or group from one list to another, highlight it and click the right or left arrow button, as appropriate.See Appendix C, "Managing Security for Dashboards and Analyses" for additional information on permissions and groups and users.
18.6.6 Previewing Objects from Catalog Manager
You can preview objects, such as analyses or prompts, from Catalog Manager in online mode. If you are going to preview objects from Catalog Manager, then you must identify the default browser in which to display these objects.
To set the browser preference:
-
In Catalog Manager, from the Tools menu, select Preferences.
-
In the Select Web Browser to use for report previews field, select the browser that is the same one that you have set to be the default browser for your operating system. You can click the Browse button in which you can select the executable file for the appropriate browser.
-
Click OK.
To preview an object:
-
In Catalog Manager, open the catalog in online mode.
-
Navigate to the object.
-
Right-click the object in the Name list and select Preview.
18.7 Viewing and Editing Catalog Objects in XML
You can view and edit the XML description of catalog objects such as analyses, dashboards, filters, and so on.
Caution:
If you change the XML code, then you change the representation of the object in the catalog. Do not edit the XML code for system catalog objects, for example in the /system/metadata directory. These objects are maintained by the system and should not be updated by users.To view the XML description of an object:
-
In Catalog Manager, open the catalog.
-
Navigate to the object.
-
Right-click the object in the Name column and select Properties.
-
Click Edit XML.
-
When you have finished viewing the XML definition, click Cancel.
-
Click OK in the Properties dialog.
To edit the XML description of an object:
-
In Catalog Manager, open the catalog.
-
Navigate to the object.
-
Right-click the object in the Name column and select Properties.
-
Click Edit XML, then Edit.
-
Make the changes in the Object XML area.
Note:
When you edit the XML description of an object, the catalog checks only that the XML is well-formed; it does not check for any other errors. -
Click OK in the Edit XML dialog.
-
Click OK in the Properties dialog.
18.8 Searching for and Replacing Catalog Text Using Catalog Manager
You can search for specific text in the catalog and replace it with other text using Catalog Manager. You can open the catalog in either online or offline mode.
Specifically, you can search for and replace:
-
A single text string
-
Multiple text strings all at once
18.8.1 Searching for and Replacing a Single Catalog Text String
Use the following procedure to search for a single text string in the catalog and replace it with other text.
To search for and replace a single text string:
-
In Catalog Manager, open the catalog in either online or offline mode.
-
From the Tools menu, select XML Search and Replace.
-
In the Old text field, enter the text string to search for.
-
In the Replace with field, enter the replacement text.
-
To make the search case insensitive, clear the Case Sensitive box.
-
Click OK.
18.8.2 About Searching for and Replacing Multiple Catalog Text Strings
You can search for and replace multiple catalog text strings all at once by importing a XML file that identifies each text string to search for and replace.
18.8.2.1 XML File Format for Searching for and Replacing Text Strings
In the search and replace XML file, you use an action element to identify each text string to search for and replace. The action elements are contained in a commands element.
The action element has the following attributes:
-
command — Specifies whether you want to replace text, a column name, a subject area name, a table formula, or an entire formula. Valid values are:
-
textReplace — Replaces text other than the name of a table, column, formula, or subject area.
The textReplace action occurs first, before other node-specific actions (for example, before renameSubjectArea).
-
renameTable — Renames the Table part of a formula alone.
-
renameColumn — Replaces the name of a column.
-
renameFormula — Renames the entire formula.
-
renameSubjectArea — Replaces the name of a subject area.
-
subjectArea — Apply this optional attribute to renameTable, renameColumn, or renameFormula.
-
-
oldValue — Specifies the text string to search for.
When specifying this attribute for the textReplace command, you must use the regex syntax that is described in
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.5.0/docs/api/java/util/regex/Pattern.html.Table 18-1 illustrates using regex syntax in search criteria.
Table 18-1 Using regex syntax in search criteria
Search String Entered Result a
Adds wildcards before and after your search string (for example, *a*), enabling the search to return results that contain the letter "a".
^a
Adds a wildcard after your search string (for example, a* ), enabling the search to return results that begin with the letter "a".
a$
Adds a wildcard before your search string (for example, *a ), enabling the search to return results that end with the character "a".
a\*
Searches explicitly for strings containing a character followed by an asterix (*) for example, "a*".
?
Use a question mark (?) with a character and an asterix (*) to return zero (0) or more occurrences of a character. For example ?a* returns zero or more occurrences of the character "a".
[] or {}
Not recognized by search.
-
newValue — Specifies the replacement text.
-
ignoreCase — Ignores case when set to true, but becomes case sensitive when set to false. The default value is false.
18.8.2.2 Example XML File for Searching for and Replacing Text Strings
The following is an example of an XML file for searching for and replacing multiple text strings all at once:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <actions> <action command="textReplace" oldValue="paint" newValue="HoleyShoes" ignoreCase="true"/> <action command="renameSubjectArea" oldValue="SnowflakeSales" newValue="GG SALES" ignoreCase="false"/> <action command="renameTable" subjectArea="Paint Exec" oldValue="forecast measures" newValue="GGFCMEASURES" ignoreCase="true"/> <action command="renameColumn" oldValue="CategoryID" newValue="GG CATID" ignoreCase="false"/> <action command="renameFormula" oldValue=""Paint Exec".Measures."Year Ago Dollars"" newValue=""Paint Exec".Measures."GG YAGODOLLARS"" ignoreCase="false"/> <action command="renameFormula" subjectArea=""Paint Exec"" oldValue=""Products".Brand" newValue="GGPRODUCTS."GG BRAND"" ignoreCase="false"/> </actions>
18.8.3 Searching for and Replacing Multiple Catalog Text Strings
Use the following procedure to search for and replace multiple catalog text strings all at once.
To search for and replace multiple text strings:
-
Create the XML file for searching for and replacing multiple text strings.
For information, see Section 18.8.2, "About Searching for and Replacing Multiple Catalog Text Strings."
-
In Catalog Manager, open the catalog in offline mode.
-
From the Tools menu, select XML Search and Replace.
-
In the Import from File field, enter the path or click Browse to specify the XML file that you created in Step 1.
-
To make the search case-sensitive, select the Case Sensitive box.
-
Click OK.
18.9 Creating Reports to Display Catalog Data Using Catalog Manager
You can create reports to display catalog data for all catalog object types. You can either display the report on the screen or save it to a file.
For example, to find out which dashboards are using an analysis, you could run a Dashboard report including analyses, and search that report for the analysis. Or, to find analyses that are affected by a changed column in an RPD table, you could run an Analysis report including all columns and formulas, and then search the report for the items that must then be replaced in Catalog Manager.
When you create a report, a blank or empty field is exported as a tab character. If you are creating a report with the default of a tab as the field separator, then two tab characters in the report file indicate a blank field.
To create a report that displays catalog data:
-
In Catalog Manager, open the catalog. To create a report that shows the SQL statement that is sent to the Oracle BI Server for the object, open the catalog in online mode.
-
Select the top folder for the catalog.
-
From the Tools menu, select Create Report.
-
Select the catalog object type to create a report on.
-
To eliminate any rows that are exactly the same from the report, select the Distinct box.
-
Specify the columns to appear in the report in the Columns in Report list. Use the left and right arrow buttons (< and >) to move the columns between the Available Columns list and the Columns in Report list, and the plus and minus buttons (+ and -) to set the order in which columns are displayed in the report.
-
Click OK.
-
To save the report to a file, in the Save report to field, specify the path name of the file. Click the Browse button to display the Save As dialog for selecting the path name (if the file does not exist, then it is created).
-
Click OK to overwrite an existing file or click Cancel and enter a new name to save to a new file.
-
Select Excel Format to specify to create a file with a .tab extension that can be imported into Microsoft Excel 2003 or higher.
-
Click OK.
18.10 Archiving and Unarchiving a Catalog Using Catalog Manager
You can archive and unarchive an entire catalog or an individual catalog folder in a catalog. When you:
-
Archive a catalog (that is, the catalog root folder) or an individual catalog folder, all objects in the folder and the folder's subfolders are saved in single compressed file. Properties and attributes of objects are included in the archive file.
-
Unarchive a catalog or an individual catalog folder, the archive file is uncompressed and all objects in the folder and the folder's subfolders are then stored in the current offline catalog. Existing folders that have the same names as folders being unarchived are overwritten.
It is recommended for a complete catalog to archive and unarchive using 7Zip.
You also can use Oracle BI Presentation Services to archive and unarchive a catalog. For information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
To archive an entire catalog or an individual catalog folder in the catalog to a file that you specify:
-
In Catalog Manager, open the catalog in offline mode.
-
To archive:
-
The entire catalog, highlight the top-level catalog folder and from the File menu, select Archive.
-
An individual catalog folder, highlight the catalog folder and from the File menu, select Archive.
-
-
In the Archive File Path field, specify the path name of the file in which to archive the catalog or individual catalog folder. Click Browse to display a dialog for selecting the path name.
-
To archive the:
-
Timestamps that are assigned to the objects and folders that you are archiving, then select the Keep file time stamps option.
If you do not select this option, then the archiving process does not include timestamp information. Upon unarchiving, the system applies a timestamp that indicates the time at which the object or folder is unarchived.
-
Permissions that are assigned to each object or folder, then select the Keep permissions option.
If you do not select this option, then the archiving process does not include any permissions. Upon unarchiving, the system assigns the parent folder's permissions to all of the objects and folders.
-
-
Click OK.
To unarchive an entire catalog or a catalog folder:
-
In Catalog Manager, open the catalog in offline mode.
-
If you are unarchiving a catalog folder, then navigate to the location where you want to unarchive the folder.
-
From the File menu, select Unarchive.
-
In the Archive File Path field, specify the path name of the catalog or catalog folder to unarchive. Click Browse to display a dialog for selecting the path name.
When unarchiving an entire catalog, you must select '\' (the root folder).
-
Click OK.
18.11 Configuring for Full-Text Catalog Search
As the administrator, you can configure a search engine to crawl and index the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog. With this configuration, you provide content designers and users with the ability to perform a full-text catalog search for objects and attachments.
This section contains the following topics:
-
Section 18.11.2, "Deployment of Oracle Full-Text Catalog Search"
-
Section 18.11.3, "How is Security Handled in the Full-Text Catalog Search?"
-
Section 18.11.4, "Process for Configuring the Full-Text Catalog Search"
For information on content designers and users using the full-text catalog search, see Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
18.11.1 What is a Full-Text Catalog Search?
The full-text catalog search provides a mechanism for searching for objects in the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog that is similar to a full-text search engine. Users can search for objects by various attributes, such as name and description. Users obtain search results that correspond to the object that they have access to open. As the administrator, you must configure the use of the full-text catalog search.
The full-text catalog search can index catalogs that contain translated text. For this release the full-text catalog search uses Secure Enterprise Search, which limits each of its registered sources to a single locale. Therefore, a multilingual translated Oracle BI Presentation Catalog can be indexed only in a single language. The user interface for Secure Enterprise Search supports multiple languages.
18.11.2 Deployment of Oracle Full-Text Catalog Search
Figure 18-1 shows a deployment diagram for the full-text catalog search. This search runs as a separate service from Oracle BI Enterprise Edition and has its own port number and URL The WebLogic Server on which Secure Enterprise Search is hosted communicates with the index for SES and with the full-text catalog search. The search uses the Web Services of Oracle BI Enterprise Edition on its WebLogic Server for accessing the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog. The services on that WebLogic Server send the requests to the catalog.
The full-text catalog search is deployed on the same WebLogic Server as Oracle BI EE. The instance for the full-text catalog search can be used with only one Oracle BI EE instance at a time. Multiple instances of Secure Enterprise Search can be connected to the same instance of the full-text catalog search.
Figure 18-1 Deployment of the Full-Text Catalog Search
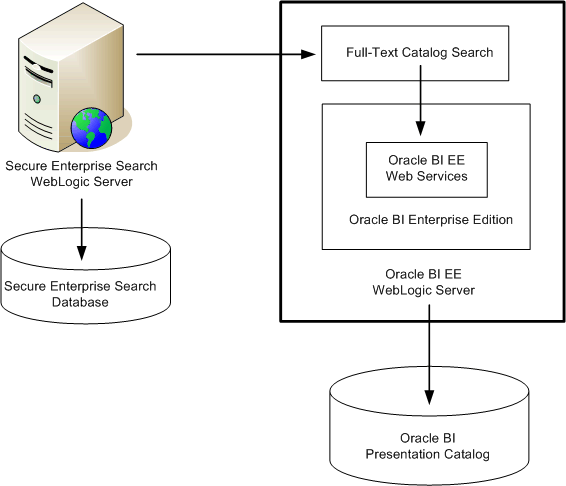
Description of "Figure 18-1 Deployment of the Full-Text Catalog Search"
18.11.3 How is Security Handled in the Full-Text Catalog Search?
The search engine enforces all the security that is defined on the Oracle BI content. Security for Oracle BI content can be defined at the object level, enforced through folder level security on the Oracle BI Server, and at the data level, enforced at run time or query time through user variables that are used to constrain the data.
In addition, the Do Not Index setting in the Properties dialog for an object affects whether the object can be indexed.
See Oracle Fusion Middleware Security Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition for details on security.
18.11.4 Process for Configuring the Full-Text Catalog Search
You must configure the use of the full-text catalog search. For this release, this functionality requires Oracle Secure Enterprise Search, an application that provides crawling and indexing of the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog. The index that Secure Enterprise Search creates is used by the full-text catalog search for locating objects for which users are searching.
The following list describes the steps for configuring the full-text catalog search:
-
"Step 2: Ensuring that Secure Enterprise Search is Available"
-
"Step 3: Configuring Identity Management for Full-Text Catalog Search"
-
"Step 4: Creating the Data Source for Full-Text Catalog Search"
-
"Step 7: Enabling Incremental Crawls for Full-Text Catalog Search"
-
"Step 8: Configuring Properties for Full-Text Catalog Search Manually"
-
"Step 9: Allowing Users to Access the Full-Text Catalog Search"
18.11.4.1 Step 1: Assigning Privileges for Crawling and Indexing
The process of crawling and indexing the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog is initiated from the search engine. However, the catalog cannot be crawled and indexed unless a user with administrator privileges gives the appropriate privileges to the BISystem role.
To assign the appropriate privileges for crawling and indexing the catalog:
-
In Oracle BI Enterprise Edition, log in as an administrator.
-
Click Administration in the global header.
-
On the Administration tab, click Manage Privileges.
-
In the SOAP section, ensure that the BISystem role has the following privileges:
- Access "ReplicationService" Service
- Access "CatalogIndexingService" Service
- Access "SecurityService" Service
- Access "CatalogService" Service
- Access "XmlGenerationService" Service
For information on assigning privileges, see Section C.2.3, "Managing Presentation Services Privileges."
18.11.4.2 Step 2: Ensuring that Secure Enterprise Search is Available
The files that are required to use the full-text catalog search are copied to the appropriate directories during the installation of Oracle BI EE. Users cannot access the full-text catalog search if a supported search engine is not installed and configured for use with the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog.
For this release of Oracle BI EE, Oracle Secure Enterprise Search (SES) is the supported search engine. You can use SES Release 11.1.2. You can install SES either before or after you install Oracle BI EE and on either the same computer or a different one. For information on SES, display the following page from Oracle Technology Network:
http://www.oracle.com/technology/products/oses/index.html
Before proceeding, ensure that Secure Enterprise Search is installed at your site and that you know the URL to the Secure Enterprise Search administration tool. You use the administration tool to configure crawling and indexing of the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog. Use a URL in the following format to access the administration tool:
http://host:port/search/admin/control/login.jsp
where host is the computer on which Secure Enterprise Search is installed and port is the port for the administration tool.
18.11.4.3 Step 3: Configuring Identity Management for Full-Text Catalog Search
Use the Secure Enterprise Search administration tool to configure identity management for the full-text catalog search.
To configure Identity Management for the full-text catalog search:
-
Access the Secure Enterprise Search administration tool.
-
Display the Identity Management Setup page using steps such as the following:
Select Global Settings, then Identity Management Setup in the System section.
-
In the list of available identity plug-ins, select Oracle Fusion.
-
On the Activate Identity Plug-in tab, specify the following:
-
HTTP endpoint for authentication: The URL for the full-text catalog search security service, in the following format:
http://host:port/bisearch/crawler/SecurityService
where host is the computer on which the full-text catalog search service is installed and port is its port number.
-
User ID: The ID of a valid Oracle Business Intelligence user.
-
Password: The password of the user.
-
-
Click Finish.
18.11.4.4 Step 4: Creating the Data Source for Full-Text Catalog Search
Use the Secure Enterprise Search administration tool to configure the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog as a source that can be crawled and indexed.
To configure the data source for the full-text catalog search:
-
Access the Secure Enterprise Search administration tool.
-
Select the Home tab, then the Sources tab.
-
In the Source Type list, select Oracle Fusion, then click Create.
-
On the Source Configuration tab, specify the following:
-
Name: Enter a name for the data source.
-
Configuration URL: The URL for the configuration file for the full-text catalog search, in the following format:
http://host:port/bisearch/crawler/oracle.biee.search.BISearchableTreeObject/ConfigFeed?forceInitialCrawl=true
where host is the computer on which the full-text catalog search service is installed and port is its port number.
-
Authentication Type: The type of authentication for users. Select the default value of Native, which allows the full-text catalog search to handle authentication.
-
User ID: The ID of a valid Oracle Business Intelligence user.
-
Password: The password of the user.
-
Realm: Leave this blank.
-
Scratch Directory: Specify a temporary directory where Secure Enterprise Search can store temporary files.
-
-
On the Authorization tab, specify the following:
-
Authorization: Select ACLs Controlled by the Source.
-
HTTP endpoint for authorization: The URL for the full-text catalog search security service, in the following format:
http://host:port/bisearch/crawler/SecurityService
where host is the computer on which the full-text catalog search service is installed and port is its port number.
-
User ID: The ID of a valid Oracle Business Intelligence user.
-
Password: The password of the user.
-
Business Component: Enter the following value: oracle.biee.search.BISearchableTreeObject
-
Display URL Prefix: The URL for the search functionality in Oracle BI Enterprise Edition, in the following format:
http://host:port/bisearch/urlbuilder
where host is the computer on which Oracle BI Enterprise Edition is installed and port is its port number.
-
-
Click Finish.
18.11.4.5 Step 5: Editing the Schedule for Full-Text Catalog Search
When you create a data source in the Secure Enterprise Search administration tool for the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog, a schedule for crawling and indexing of that source is created automatically. You can use the administration tool to edit the schedule.
There are two types of crawls:
-
Full crawl — Crawls the entire catalog. Use this type of crawl the first time that a catalog is crawled or when a large number of changes have occurred since the previous crawl. You should generally schedule a full crawl when most users are not accessing the system, such as over the weekend or a holiday. You must perform a full crawl with replication enabled on a catalog before you can perform an incremental crawl.
-
Incremental crawl — Crawls or actually indexes only those objects in the catalog that have changed. A changed object is one that has been created, edited, or deleted. An incremental crawl does still crawl and build the entire catalog tree structure, but only the changed files are re-indexed. This provides a quick way to update the search index without re-indexing the entire catalog tree.
Incremental crawls occur only if you enable replication, as described in "Step 7: Enabling Incremental Crawls for Full-Text Catalog Search".
After the catalog is crawled fully or incrementally, the objects are indexed so that users can easily search for them as part of the full-text catalog search.
By default, all objects in the catalog are set to be indexed during a crawl. Content designers can use the Properties dialog for an object to set the Do Not Index property of that object. Setting this property prohibits the object from being crawled and indexed. For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
18.11.4.6 Step 6: Specifying the Look and Feel of Search Results
You can specify the look and feel of the results that are returned by the full-text catalog search by using two files that are named bisearch.xslt and bisearch.css. These files are located in the following directory:
ORACLE_HOME\user_projects\domains\bifoundation_domain\config\fmwconfig\biinstances\coreapplication
Use the Secure Enterprise Search administration tool to configure the look and feel for the full-text catalog search.
To configure the look and feel for the full-text catalog search:
-
Access the Secure Enterprise Search administration tool.
-
Select Global Settings, then Configure Search Result List in the Out-of-Box Query Application section.
-
On the Configure Search Result List tab, specify the following:
-
Select Use Advanced Configuration.
-
Select all the attributes in the Not Included list that start with "BI" and move them to the Included list.
-
In the field that is labeled "Enter an XSLT to convert XML result data into HTML," copy and paste the contents of the bisearch.xslt file.
-
In the field that is labeled "Enter a CSS to style the HTML," copy and paste the contents of the bisearch.css file.
-
18.11.4.7 Step 7: Enabling Incremental Crawls for Full-Text Catalog Search
In order for incremental crawls to occur, you must first do the following:
-
Enable the replication of the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog.
-
Perform a full crawl on the catalog.
To enable replication, set the Replication element to true in the instanceconfig.xml file. The following procedure provides information on configuring to enable replication.
Before you begin this procedure, ensure that you are familiar with the information in Section 3.4, "Using a Text Editor to Update Oracle Business Intelligence Configuration Settings".
To manually edit the setting for replication:
-
Open the instanceconfig.xml file for editing, as described in Section 3.6, "Where are Configuration Files Located?"
-
Locate the section in which you must add the Replication element.
The Replication element is set to false by default. If you do not set it to true, then only full crawls of the catalog occur, no matter how minor the changes to the catalog since the last full crawl.
-
Include the element and its ancestor elements as appropriate, as shown in the following example:
<ps:Catalog> <ps:Replication> <ps:Enabled>true</ps:Enabled> </ps:Replication> </ps:Catalog> -
Save your changes and close the file.
-
Restart Oracle Business Intelligence.
After you have enabled replication, use a URL in the following format to start an incremental crawl. Include false at the end of the URL to perform an incremental crawl, and include true at the end to perform a full crawl.
http://host:port/bisearch/crawler/oracle.biee.search.BISearchableTreeObject/ConfigFeed?forceInitialCrawl=false
18.11.4.8 Step 8: Configuring Properties for Full-Text Catalog Search Manually
You can configure properties for the full-text catalog search by manually editing the BISearchConfig.properties file. Because the properties for the full-text catalog search include specifications for the URLs of Web Services that are used in the full-text catalog search, you can set these properties, if URLs change.
Table 18-2 describes the configuration properties for the full-text catalog search, which reside in the BISearchConfig.properties file. The BISearchConfig.properties file is installed into the ORACLE_HOME\user_projects\domains\bifoundation_domain/config/fmwconfig/biinstances/coreapplication directory on the WebLogic Server for Oracle BI Enterprise Edition.
Table 18-2 Configuration Properties for the Full-Text Catalog Search
| Name | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
|
BIServerURL |
Specifies the URL for the Oracle BI Server. |
NA |
|
BISearchServerURL |
Specifies the URL for the servlet for the full-text catalog search. |
NA |
|
CrawlingUserKey |
Specifies the key for the credentials that are used to crawl the catalog. You should not edit this value. |
NA |
|
ExcludePaths |
Specifies the list of directories from the catalog that should not be crawled. Delimit directories with a semicolon (;). |
"/system/*;/shared/*" |
|
IncludePaths |
Specifies the list of directories from the catalog that should be crawled. Delimit directories with a semicolon (;). |
"*" |
|
RootNode |
Specifies the node from which all crawling originates. |
"/" |
18.11.4.9 Step 9: Allowing Users to Access the Full-Text Catalog Search
When you have configured Secure Enterprise Manager to crawl and index the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog, you can notify content designers and users that the Search page is available for performing the full-text catalog search.
18.11.4.9.1 Providing Designers with the URL
You can provide designers with the URL to display the page for the full-text catalog search. Designers can bookmark this page and use it with actions or as a shortcut on a dashboard page.
The person who installs Secure Enterprise Search sees a page that provides the URL in the following form:
http://host:port/search/query/search
where host is the computer on which Secure Enterprise Search is installed and port is the port for the administration tool. The default port is 7777.
18.11.4.9.2 Making the Shortcut Available from the Oracle BI EE Home Page
You can configure the Oracle BI EE Home page to include a shortcut in the All Content area that allows users to display the page for the full-text catalog search. To do so, edit the instanceconfig.xml file to include the SESSearchURL element, as described in the following procedure.
Before you begin this procedure, ensure that you are familiar with the information in Section 3.4, "Using a Text Editor to Update Oracle Business Intelligence Configuration Settings".
To manually add the shortcut for the full-text catalog search to the Home page:
-
Open the instanceconfig.xml file for editing, as described in Section 3.4, "Using a Text Editor to Update Oracle Business Intelligence Configuration Settings."
-
Locate the section in which you must add the SESSearchURL element.
The value for the SESSearchURL element is the URL for the Secure Enterprise Manager page.
-
Include the element and its ancestor elements as appropriate, as shown in the following example:
<Server> <ps:SESSearchURL xmlns:ps="oracle.bi.presentation.services/config/v1.1">http://myhost:7777/search/query/search</ps:SESSearchURL> </Server>
-
Save your changes and close the file.
-
Restart Oracle Business Intelligence.
18.12 Replicating Oracle BI Presentation Catalogs
You can copy and merge the contents of selected catalog folders between instances of Presentation Services. You can split the replication configuration into individual tasks. The replication task is an instruction to periodically merge catalog contents for specified catalog folders from one server to another. Two-way replications are possible.
A typical scenario where replication is useful is when you use one instance of Presentation Services to prepare and publish shared analyses, and you use two or more production instances to support the users. In this scenario, you share the catalog from Instance 1 to two production instances and share the catalogs on each production instance with the other. To accomplish this, you configure the following replication tasks in the configuration file for the Presentation Services Replication Agent:
-
/shared: Instance1 to Instance2
-
/shared: Instance1 to Instance3
-
/users: Instance2 to Instance3
-
/users: Instance3 to Instance2
When an instance of Presentation Services participates in replication, either as a publisher or as a subscriber, it tracks changes made to catalog objects that are marked to be replicated and keeps them internally in replication log files. Another instance of Presentation Services can make a SOAP call to request to export those changes to a file or to import and replay modifications recorded in a file exported earlier from another instance. The Presentation Services Replication Agent uses SOAP to manage replication-related activities on all instances of Presentation Services and performs import and export operations. For information on these SOAP calls, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Integrator's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
18.12.1 About Replication Log Files
Replication log files record modifications made to catalog objects that are subject to replication. There are two types of replication log files:
-
Change log files — Contain records of modifications to catalog objects that were made locally. These files are stored in presentationcatalogpath/replication/changelog folder, where presentationcatalogpath is the full path to the catalog folder.
-
Playback log files — Contain records of modifications to catalog objects that were replayed from other instances of Presentation Services. These files are stored in presentationcatalogpath/replication/playback folder.
Replication log files are stored on disk indefinitely, until you periodically remove them. When performing replication operations, Presentation Services reads only replication log files from the time interval that is specified by the ReadLogRecordsSinceHoursAgo element in the instanceconfig.xml file. For information on this element, see Section 18.12.5, "Editing the instanceconfig.xml File for Replication."
While you might want to review replication log files, for example, for troubleshooting purposes, you should never edit log files manually.
18.12.1.1 Replication Log File Records
A replication log file contains different types of records, with each record consisting of several fields that are separated by commas. The most important types of records in a replication log file are described in Table 18-3.
Table 18-3 Description of Records in Replication Log Files
| Type | Written | Contents |
|---|---|---|
|
File header record |
At the beginning of each log file |
Size, Type, Timestamp, Version, Flags |
|
Startup record |
Each time Presentation Services starts |
Size, Type, Timestamp |
|
Before change record |
When an Oracle BI Presentation Catalog object is about to be changed |
Size, Type, Timestamp, Change sequence number, Change type |
|
After change record |
Immediately after a catalog operation has been completed |
Size, Type, Timestamp, Change sequence number, Operation outcome |
|
File finished record |
As the last record in a replication log file |
Size, Type, Timestamp, Name of next log file |
The following list describes some fields in a replication log file:
-
Size. The size of the record in bytes and encoded as a hexadecimal number.
-
Type. The type of record, such as the following:
-
H. File header record
-
S. Presentation Services startup record
-
B. Before change record
-
A. After change Record
-
F. File finished record
-
-
Timestamp. The timestamp of the record, written as a hexadecimal number that represents the number of seconds from midnight (00:00:00), January 1, 1970 UTC.
-
Change sequence number. A sequence number that should be the same in the corresponding Before change and After change records.
-
Change type. The type of change, written as a hexadecimal number that represents a combination of the following flags:
-
1. Insert
-
2. Delete
-
4. Write
-
8. Change catalog object information
-
16. Change owner
-
32. Change security
-
-
Operation outcome. The operation result, which is one of the following:
-
0. Fail
-
1. Success
-
18.12.2 Configuring to Replicate an Oracle BI Presentation Catalog
To enable replication of an Oracle BI Presentation Catalog, perform the steps that are described in the following sections:
-
Section 18.12.2.1, "Copying Oracle BI Presentation Catalog Files"
-
Section 18.12.3, "Using the Oracle BI Presentation Services Replication Agent"
-
Section 18.12.4, "Creating the config.xml File for Replication"
-
Section 18.12.5, "Editing the instanceconfig.xml File for Replication"
18.12.2.1 Copying Oracle BI Presentation Catalog Files
The Presentation Services Replication Agent copies changes made to an Oracle BI Presentation Catalog. Because it copies only changes and not the entire contents, you must first make a copy of the source catalog on each of the subscribing instances of Presentation Services.
18.12.3 Using the Oracle BI Presentation Services Replication Agent
You can run the Replication Agent on any computer that has network access to both instances of Presentation Services. This agent handles all the replication tasks and provides command line options.
The Replication Agent (whose file name is sawrepaj) is a utility that performs common replication tasks such as copying, exporting, importing, and marking for replication.
The Replication Agent requires information about the instances of Presentation Services and the replication tasks. This information is stored in the config.xml file, and described in Section 18.12.4, "Creating the config.xml File for Replication."
The command line for the Replication Agent uses the following format:
-
In UNIX:
sawrepaj.sh [/C path] command [command parameters]
The sawrepaj.sh file is located in ORACLE_HOME\bifoundation\web\bin\sawrepaj.
-
In Windows
sawrepaj.bat [/C path] command [command parameters]
The sawrepaj.bat file is located in ORACLE_HOME\bifoundation\web\bin\sawrepaj.
The path following the "/C" specifies the path to the config.xml file. The "command" options are described in the following sections:
18.12.3.1 mark
Adds or removes the specified catalog folders from the list of catalog folders that are to be replicated on all or the specified computers that run Presentation Services. The list of catalog folders to be replicated is stored in a configuration item that is located in the presentationcatalogpath/root/system/replication directory, where presentationcatalogpath is the full path to the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog directory.
Adding a catalog folder to the list does not mean that the corresponding catalog object is immediately replicated. Only future modifications are noted in the replication log file and subsequently replicated.
When you replicate and the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog exists on another instance, the list of catalog folders to be replicated might be incorrect. Use the mark command to maintain the list of catalog folders to be replicated.
The syntax for the mark command is:
sawrepaj [/C path] mark {all|servername} [/n] [catalogfolders]
-
all | servername. The name of the computer that is running Presentation Services or "all," on which to run the mark command. If you use a specific server, then the name that you specify must match the name attribute of the corresponding server element in the config.xml file.
-
/n. If present, indicates that the catalog folder should be removed from the list of catalog folders to be replicated. Otherwise, the folder is added.
-
catalogfolders. A list of catalog folders to add or remove from the list of catalog folders to be replicated. Separate each folder name in the list with a space. To add or remove the entire Oracle BI Presentation Catalog (including all folders and such information as system privileges, Catalog Group membership, and so on), use /.
If you do not specify any folders, then the mark command is executed on every folder for the servers that are specified in the config.xml file.
The following line shows a sample command for mark:
sawrepaj /C MyOracleHome\bifoundation\web\bin\sawrepaj mark all /
18.12.3.2 remotecopy
Exports the contents of the specified catalog folders from the source computer and imports them into the folders on the destination computer.
The syntax for the remotecopy command is:
sawrepaj [/C path] remotecopy sourceServer destinationServer catalogfolders
-
sourceServer. The name of the source computer as specified in the config.xml file.
-
destinationServer. The name of the destination computer as specified in the config.xml file.
-
catalogfolders. A list of catalog folders to copy remotely. Separate each folder name in the list with a space. If you do not specify any folders, then the remotecopy command is executed on every folder for the servers that are specified in the config.xml file.
The following line shows a sample command for remotecopy:
sawrepaj /C MyOracleHome\bifoundation\web\bin\sawrepaj remotecopy Server1 Server2 users shared
18.12.3.3 run
Executes all replication tasks that are specified in config.xml file and that have not expired. This command has no run-time parameters.
The syntax for the run command is:
sawrepaj [/C path] run
The following line shows a sample command for run:
sawrepaj /C MyOracleHome\bifoundation\web\bin\sawrepaj run
18.12.4 Creating the config.xml File for Replication
You must create the Replication Agent's configuration file to specify which folders on which instances of Presentation Services are to be replicated. The config.xml file is located in the ORACLE_HOME\bifoundation\web\bin\sawrepaj directory.
The following sections describe the config.xml file:
For information on manual editing, see Section 3.4, "Using a Text Editor to Update Oracle Business Intelligence Configuration Settings."
18.12.4.1 Structure of the Configuration File
The structure of the Replication Agent's config.xml file is as follows:
<Config>
<General>
<ExportDirectory/>
<LogExpiresHours/>
<RetryAttempts/>
</General>
<Server>
<Property/>
</Server>
<Folderset>
<Folder/>
</Folderset>
<ReplicationTask/>
</Config>
18.12.4.2 Elements of the Configuration File
Table 18-4 describes the elements that you can set in the Replication Agent's config.xml file. You must enter the elements manually as they do not exist by default.
Table 18-4 Replication Agent Configuration Elements in config.xml
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
|
Config |
Serves as the root element for the configuration file. |
|
Config/General |
Contains general settings that are applicable to all instances and replication tasks. |
|
General/ExportDirectory |
Contains the UNC path to the shared directory where export files should be placed. Must be accessible by the same name from all instances of Presentation Services. In addition, the user account under which an instance of Presentation Services is running must have read/write permissions to this directory. |
|
General/LogExpiresHours |
Specifies the time in hours (as a double value) that replication logs expire on all instances of Presentation Services. Set this element to the value of the ReadLogRecordsSinceHoursAgo element that is the lowest among all instances of Presentation Services that are participating in replication. For information on the ReadLogRecordsSinceHoursAgo element, see Section 18.12.5, "Editing the instanceconfig.xml File for Replication." |
|
General/RetryAttempts |
Specifies the number of times an attempt to change an object is to be retried. (An attempt to change an object might be retried, for example, if an object was locked.) |
|
Config/Server |
Defines connection information for each computer for Presentation Services. Its attributes are:
|
|
Config/Server/Property |
Defines connection parameters for the Presentation Services (SAWBridge) server, and the transport protocol, its attributes are: Defines server name and value: Note: The settings that you use here are determined by whether the value for the transport protocol below is set to use HTTP (N) or socket based TCP (Y).
Defines the transport protocol name and value: Note: The value that you use here determines the name and value that you use above.
|
|
Config/Folderset |
Defines a list of catalog folders. Its only attribute is name, which you can set to the logical ID of the server or to "all". |
|
Folderset/Folder |
Adds a folder to the folderset. Specifies the full path to the catalog folder. |
|
Config/ReplicationTask |
Defines the replication tasks. Its attributes are:
|
18.12.4.3 Example config.xml File
The following is an example of the config.xml file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!-- Oracle BI Presentation Services Replication Agent Configuration File -->
<!-- replicate entire catalog from host1 to host2 -->
<Config>
<General>
<ExportDirectory>\\host1\shared</ExportDirectory>
<LogExpiresHours>48</LogExpiresHours>
</General>
<Server name="1" user="<admin1user>" pwd="<admin1password>">
<Property name= "oracle.bi.presentation.url"
value ="http://host1.com:<port>/analytics/saw.dll"/>
<Property name="oracle.bi.presentation.usesoaptcptransport" value="N"/>
</Server>
<Server name="2" user="admin2user" pwd="admin2password">
<Property name="oracle.bi.presentation.sawservers"
value ="localhost:10712"/>
<Property name="oracle.bi.presentation.usesoaptcptransport" value="Y"/>
</Server>
<Folderset name="all">
<Folder>/</Folder>
</Folderset>
<ReplicationTask destination="2" source="1" folders="all" />
</Config>
18.12.5 Editing the instanceconfig.xml File for Replication
For each instance of Presentation Services that contains a catalog to replicate, you must edit the instanceconfig.xml file for the following:
-
Enable replication. By default, the replication functionality is disabled for instances of Presentation Services.
-
Configure replication for a clustered environment. In a clustered environment, several instances of Presentation Services can share the same Oracle BI Presentation Catalog. For replication to work properly, you must:
-
Ensure that each instance of Presentation Services writes to its own log file to avoid concurrency issues.
-
Ensure that changes made by all instances are taken into account during import and export operations.
-
-
Specify the number of records to be kept in a replication log file.
-
Specify the time period (in hours) from which replication log files are to be read for replication operations.
The following procedure provides information on configuration changes that you can make for replication. Before you begin this procedure, ensure that you are familiar with the information in Section 3.4, "Using a Text Editor to Update Oracle Business Intelligence Configuration Settings".
To manually edit the settings for the replication of catalogs:
-
Open the instanceconfig.xml file for editing, as described in Section 3.6, "Where are Configuration Files Located?"
-
Locate the section in which you must add the elements that are described in Table 18-5.
-
Include the elements and their ancestor elements as appropriate, as shown in the following example:
<ServerInstance> <CatalogReplication> <Enabled>False</Enabled> <ReadLogRecordsSinceHoursAgo>120</ReadLogRecordsSinceHoursAgo> <RecordsInFileLimit>4000</RecordsInFileLimit> </CatalogReplication> <CatalogReplicationCluster> <IDsinCluster>ID03</IDsinCluster> <MyInstanceID>%INSTANCEID%</MyInstanceID> </CatalogReplicationCluster> </ServerInstance> -
Save your changes and close the file.
-
Restart Presentation Services.
Table 18-5 Elements for Configuring Catalog Replication
| Element | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
|
Enabled |
Specifies whether the instance of Presentation Services is to participate in replication, as either a publisher or subscriber. |
False |
|
ReadLogRecordsSinceHoursAgo |
Specifies the time period (in hours) from which replication log files are to be read for replication operations. |
168 |
|
RecordsInFileLimit |
Specifies the number of records to be kept in a replication log file. |
5000 |
|
IDsInCluster |
Identifies, by ID, all instances of Presentation Services that are in the cluster. Separate each ID by a comma. This element is required in a clustered environment. |
NA |
|
MyInstanceID |
Identifies the suffix (%INSTANCEID%) to be used for the log files generated by this instance of Presentation Services. Log files are named as follows:
This element is required in a clustered environment. |
NA |
18.12.6 Resuming Replication If Replication Log Files Are Unavailable
If, for some reason, replication log files are unavailable in an instance of Presentation Services, then you can resume replication by copying over the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog folders that the instance subscribes to. However, this method loses the catalog contents that were not replicated to other instances. The following method preserves all catalog contents.
Note:
If you must resume replication after Presentation Services has been offline for a time period in excess of that specified in the ReadLogRecordsSinceHoursAgo element in the instanceconfig.xml file, then you can adjust the value of ReadLogRecordsSinceHoursAgo so that log files in the offline period are replicated. Then, reset ReadLogRecordsSinceHoursAgo back to its original setting.To resume replication if replication log files are unavailable:
-
Use Catalog Manager to erase all replication logs in the presentationcatalogpath/replication/changelog and presentationcatalogpath/replication/playback folders, where presentationcatalogpath is the full path to the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog folder.
For information about Catalog Manager, see Chapter 11, "Configuring Connections to External Systems."
-
Set the UseReplication element in the instanceconfig.xml file to false.
For information, see Section 18.12.5, "Editing the instanceconfig.xml File for Replication."
-
Start the instance of Presentation Services.
-
Delete or rename folders that are replicated from other instances and copy them over from other instances using the sawrepaj remotecopy command.
-
Set the UseReplication element in instanceconfig.xml to true.
-
Restart the instance of Presentation Services.
-
Restore the list of folders to be replicated using the sawrepaj mark command on the instance of Presentation Services.
-
Re-enable replication tasks by editing the configuration file to delete the lastPerformed attribute from all ReplicationTask elements that have the instance of Presentation Services as an import or export target.