11 Integrating with Other Oracle Components
Oracle offers several technologies that compliment and extend the functionality available in Oracle Identity Manager, some of which are described in this chapter. Refer to the "Oracle Fusion Middleware Integration Overview" for complete information about the technologies you can integrate with Oracle Identity Manager. Figure 11-1 shows the integration of Oracle Identity Manager with other Oracle components.
Figure 11-1 Integration with Other Components
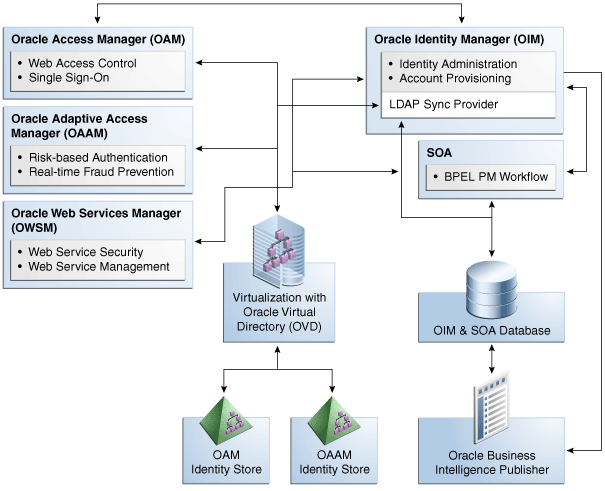
Description of "Figure 11-1 Integration with Other Components"
This chapter discusses the integration of Oracle Identity Manager with the following Oracle components:
11.1 Oracle Access Manager
Oracle Access Manager (OAM) protects applications, data, and cloud-based services through a combination of flexible authentication and single sign-on (SSO), identity federation, risk-based authentication, proactive enterprise fraud prevention, and fine-grained authorization.
Web-based SSO provides secure access to multiple applications with one authentication step. When OAM is combined with Oracle Identity Manager, OAM can SSO-enable the Oracle Identity Administration, along with the other Oracle Identity Management components.
Oracle Identity Manager, OAM, and Oracle Adaptive Access Manager (OAAM) share a common set of LDAP attributes, improving efficiency by making it easier to manage workflows and other processes. Integrated password management makes it easy for users to log in to OAM, OAAM, and Oracle Identity Manager, and to manage expired and forgotten passwords.
For integration details, see "Integration Between OIM and OAM" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Guide for Oracle Identity Management.
11.2 Oracle Adaptive Access Manager
OAAM provides sophisticated multifactor authentication and proactive, real-time fraud prevention functionality for Web-based connections. Risk-based authentication is one such capability OAAM provides. The OAAM risk-scoring engine combats identity fraud in real-time by evaluating whether a user should be allowed to authenticate based on the type of transaction being attempted and the probability of fraud occurring. Next, the OAAM risk-scoring engine evaluates how a user answers a series of dynamically generated questions that are created based on a combination of public and private data sources. OAAM then generates a fraud score and the user is either allowed to continue with the transaction or is denied access.When integrated with Oracle Identity Manager, the robust challenge question feature set found in OAAM replaces the more limited set found in Oracle Identity Manager, which handles password validation, storage, and propagation duties.
For information about how password management is achieved when Oracle Identity Manager is integrated with OAM and OAAM, see "Deployment Options for Password Management" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Integration Guide for Oracle Access Manager.
For integration details, see "Integrating Oracle Access Manager, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager, and Oracle Identity Manager" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Integration Guide for Oracle Access Manager.
11.3 Oracle Identity Analytics
Oracle Identity Analytics (OIA), formerly Sun Role Manager, provides rich identity analytics and dashboards that allow you to monitor, analyze, review, and govern user access in order to mitigate risk, build transparency, and satisfy compliance mandates.
When integrated with Oracle Identity Manager, Oracle Identity Analytics defines the Role-based Access Control (RBAC) framework, the attestation process, and the approach to Segregation of Duties (SoD) policy enforcement, while Oracle Identity Manager serves as the automated provisioning and identity synchronization solution. Rather than assigning individual access entitlements, the RBAC framework allows organizations to assign and unassign roles as a means of controlling user access on various applications.
For integration details, see "Integrating With Oracle Identity Manager" in the Oracle Identity Analytics 11gR1 System Integrator's Guide. You can access the Oracle Identity Analytics 11gR1 System Integrator's Guide at the following URL:
11.4 Oracle Identity Navigator
Oracle Identity Navigator (OIN) is a browser-based administrative portal designed to act as a launch pad for Oracle Identity Management components. It does not replace the individual component consoles. Rather, it allows you to access the Oracle Identity Management consoles from one site.
When integrated with Oracle Identity Manager, OIN replaces the Oracle Identity Administration as the primary Oracle Identity Manager user interface.
OIN has a product discovery feature that can be used to discover all active J2EE components in a domain, including the Oracle Identity Administration.
For integration details, see "Adding a Component Link to the Product Launcher by Using Product Discovery" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle Identity Navigator.
11.5 Oracle Virtual Directory
If you install Oracle Identity Manager with LDAP, you must install Oracle Virtual Directory (OVD). OVD connects to multiple enterprise directories and consolidates the contents of those directories into a unified view. For example, if your enterprise uses Oracle Internet Directory (OID), iPlanet, and Active Directory, OVD can interface with all three directories and create a consolidated view. Oracle Identity Manager can then use a single connector to access the consolidated LDAP data on OVD. The LDAP Sync Provider (also called the LDAP Provider) connects Oracle Identity Manager and OVD.
When integrated with Oracle Identity Manager, OVD provides the following benefits:
-
Oracle Identity Manager connector management is simplified - Only a single LDAP connector is needed for multiple directory providers (although, multiple instances may be needed)
-
LDAP connector reliability is improved - The same connector is used regardless of the underlying LDAP server. OVD handles the data translation that, in the past, required multiple LDAP connectors for multiple LDAP providers
-
The same identity virtualization capability is provided to all Fusion Middleware applications, reducing the overall footprint of components in the Enterprise
For integration details, see the "Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Guide for Oracle Identity Management", which contains multiple procedures for integrating Oracle Identity Manager and Oracle Virtual Directory in various environments.
11.6 Oracle Service-Oriented Architecture
The Oracle Identity Manager workflow feature utilizes Oracle Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) back-end services and management capabilities to provide an interactive environment to request, approve, and manage user access. In order to install Oracle Identity Manager, you also must install Oracle SOA.
Oracle Identity Manager makes use of the following SOA Suite components:
-
BPEL Process Manager, which provides the end-to-end solution for creating and managing business processes
-
Human Workflow, which manages the lifecycle of human tasks, including creation, assignment, deadlines, expiration, and notifications
-
Oracle Business Rules, which allows you to define complex business rules to support request assignment, process selection, and approver resolution
-
Oracle Web Services Manager, which secures the web service and BPEL processes consumed and invoked by Oracle Identity Manager
For integration details, see "Integration with Oracle SOA Suite" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle Identity Manager.
11.7 Oracle Business Intelligence Publisher
The Oracle Identity Manager reporting feature utilizes Oracle Business Intelligence Publisher (BI Publisher) to provide high-fidelity reporting capabilities, allowing you to create, deploy, and use complex reports in a multi-channel environment.
For BI Publisher details, see "Using Reporting Features" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle Identity Manager.