C Configuring F5 Load Balancers for MAN/WAN Failover
WebLogic Server provides failover within MAN and WAN networks. This feature provides more reliability by allowing failover to occur across a larger geographic area. It also provides failover across multiple WebLogic Server domains.
To provide failover within a MAN/WAN environment, you must use hardware load balancers. This document outlines the procedures for configuring F5 hardware load balancers to work with WebLogic Server.
For information on configuring WebLogic Server to use MAN/WAN, see Session State Replication Across Clusters in a MAN/WAN. For information on configuring F5 hardware load balancers, see http://www.f5.com.
The following sections describe how to configure F5 hardware load balancers.
Requirements
Before performing the procedures described in this appendix, you must have performed the following:
-
Installed and configured your WebLogic Server environment. This includes creating and configuring clusters and Managed Servers.
-
Installed and configured at least one F5 3-DNS global load balancer and at least two F5 BIG-IP local load balancers. This is the minimum hardware requirement for failover in a MAN/WAN environment
-
Ensured that your network and DNS are configured correctly
Once these requirements are met, perform the following procedures to configure your load balancers to work within a MAN/WAN environment.
Configure Local Load Balancers
This section describes the procedures for configuring F5 local load balancers to work with WebLogic Server in a MAN/WAN environment.
Virtual Server IPs and Pools
On each local load balancer you must configure two virtual server IPs as well as a multi-layer pool and a failover trigger pool. The diagram in Figure C-1 shows how these pools and virtual server IPs work within a MAN/WAN environment.
Figure C-1 Hardware Load Balancers in a MAN/WAN Environment
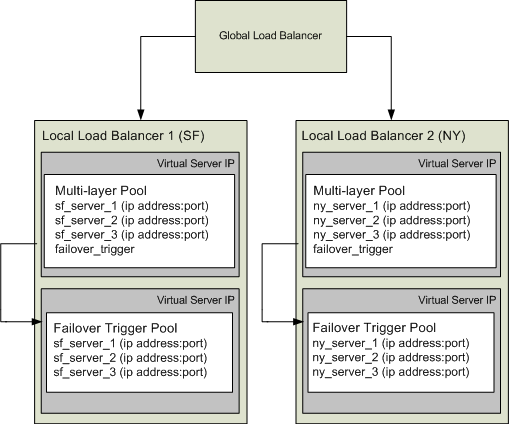
Description of "Figure C-1 Hardware Load Balancers in a MAN/WAN Environment"
In this diagram, multiple Managed Servers are distributed across separate physical locations. This diagram shows individual Managed Servers, but this could also represent a clustered configuration as well.
Each local load balancer contains a virtual server IP that references a multi-layer pool. The multi-layer pool references each of the local WebLogic Server IP addresses and host names and the virtual server of the failover trigger pool. The failover trigger is used to indicate that a site is down. This triggers failover to the other local load balancer.
The following sections describe how to configure multi-layer and failover trigger pools.
Create a Failover Trigger Virtual Server and Pool
Create a new BIG-IP pool on the local load balancer that references each of the local WebLogic Server host names and ports to be load-balanced. Then, create a new virtual server that specifies this pool. This virtual server will be utilized by the 3-DNS global load balancer for health monitoring and will later be embedded inside another local load balancer pool/virtual server.
-
In the BIG-IP navigation panel, click Pools.
-
Add a pool name
-
Add all the WebLogic Server host:port combinations to be load balanced
The default priority may used. Session persistence does not need to be configured.
-
In the BIG-IP navigation panel, click Virtual Servers.
-
Add a virtual server that references your new pool.
-
You should specify a port that by convention would be a failover-trigger port, for example 17001.
-
Specify an IP address for the Virtual Server, for example 10.254.34.151.
-
Create a Multi-layered Virtual Server and IP Pool
Using the F5 administration utility, create a new BIG-IP pool on the local load balancer that references the host and port of each local WebLogic Server instance and also the failover-trigger virtual server. The failover-trigger virtual server must be a lower priority than the WebLogic Servers. By assigning a lower priority, the failover-trigger virtual server will never receive client requests unless all the WebLogic Server instances have failed. Session persistence should be configured also.
-
In the BIG-IP navigation panel, click on Pools.
-
Add a pool name, for example
multilayeredPool-
Add all the WebLogic Server host:port combinations to be load balanced. All host:port combinations should be configured with
priority=10 -
Add the failover-trigger virtual server with priority=1
-
Specify persistence attributes on the pool (active with insert mode)
-
In the BIG-IP navigation panel, click on Virtual Servers
-
-
Create a Virtual Server that references your new pool, for example: 10.254.34.151:7001
Configure the 3-DNS Global Hardware Load Balancer
A global load balancer type of network hardware that acts as an authoritative DNS server and can distribute Web requests across multiple BIG-IP virtual servers based on chosen criteria. Clients send http requests to the global load balancer, which uses built in health monitors to direct the Web requests to the optimal server based on the chosen method of load balancing.
The global load balancer must be an authoritative source of DNS because a regular DNS server is incapable of the monitoring that the global load balancer can perform. A regular DNS server would still send http requests to a server that was down if it were next in the default round-robin load balancing method. In order to compensate for the multiple shortcomings of a regular DNS server, many vendors (including F5) have created specialized hardware and software that is capable of performing not only DNS resolution but also intelligent routing of network traffic.
The primary steps of configuring an F5 3-DNS global load balancer are: defining its DNS name, configuring the BIG-IP hosts, configuring data centers, and configuring the 3-DNS distribution of work to the virtual servers (VIPs). These are covered in the following sections.
Configure DNS Zones
The global server load balancer must be configured to manage its own DNS zone. This is done by creating a new delegation on the local DNS management machine. The following procedures describe how to configure DNS zones.
-
On your DNS management machine, create a new delegation, for example: gslb
-
Specify the fully qualified name of your 3-DNS machine as a name server
-
Specify the IP address of your 3-DNS machine as a name server
Configure BIG-IP Addresses Managed by 3-DNS
The 3-DNS global balancer needs to be configured with the addresses of the BIG-IP local load balancers. The following procedures outline how to configure BIG-IP addresses:
-
In the 3-DNS navigation panel, click Servers, then BIG-IP.
-
Add BIG-IP
-
Specify a name for the BIG-IP box, and its IP address.
-
When you revisit the list of BIG-IP boxes, the 3-DNS device should display a column with a count of virtual servers available on each BIG-IP box. Click on this count of virtual servers.
-
Find your multi-layered virtual server, and click dependencies.
-
Specify the associated failover-trigger virtual server as a dependency.
Configure Data Centers
In most cases, global load balancers spread service requests to virtual servers in multiple physical sites. These sites are called data centers and you must create two of them. Data centers resolve to the two different subnets of BIG-IP local load balancers.
Configure Wide IPs
It is recommended that you configure the 3-DNS device so it will distribute requests evenly to servers in a VIP in one data center. If these servers fail, they should fail requests over to a VIP in the other data center. In order to do this, a wideip address must be created. This wideip address will be the target of client requests, and can be given a fully qualified domain name. The Wide IP defines how connections are distributed to local load balancer virtual servers.
The following procedures describe how to configure wide IPs:
-
In the 3-DNS navigation panel, click Wide IPs, and then Add Wide IP
-
Specify an available network address for the Wide IP, a port (e.g. 7001) for the Wide IP, and an associated fully qualified domain name (e.g. cs.gslb.bea.com).
-
Add a 3-DNS pool that should specify the virtual servers on the local load balancers. The 3-DNS global load balancer automatically identifies the virtual servers available on each local load balancer after the BIG-IP hosts are configured. Specify the multi-layered Virtual Servers.
-
Create two entries in the DNS database on your DNS nameserver that resolve to the
wideip.
Configuring WebLogic Server Components
After you have configured your F5 devices, you must configure WebLogic Server to use MAN/WAN failover. For information on configuring WebLogic Server to use MAN/WAN, see Session State Replication Across Clusters in a MAN/WAN.