MySQL Enterprise Firewall is an extension included in MySQL Enterprise Edition, a commercial product. To learn more about commercial products, see https://www.mysql.com/products/.
MySQL Enterprise Firewall is an application-level firewall that enables database administrators to permit or deny SQL statement execution based on matching against lists of accepted statement patterns. This helps harden MySQL Server against attacks such as SQL injection or attempts to exploit applications by using them outside of their legitimate query workload characteristics.
In MySQL 9.4, MySQL Enterprise Firewall is available as a plugin (see Section 8.4.8.1, “The MySQL Enterprise Firewall Plugin”), and as a component (see Section 8.4.8.2, “The MySQL Enterprise Firewall Component”). The firewall plugin is deprecated as of MySQL 9.4.0; the firewall component was introduced in the same release. We recommend that you upgrade from the plugin to the component as soon as possible, since the plugin is subject to removal in a future version of MySQL. See Upgrading to the MySQL Enterprise Firewall Component, for help with migrating to the MySQL Enterprise Firewall component.
The firewall plugin and firewall component supply the same
functionality with the exception of account profiles, which are
deprecated in the firewall plugin and not supported by the
component. If you are using account profiles with the firewall
plugin, you can migrate them to group profiles using the migration
tool, as described in
Migrating Account Profiles to Group Profiles. This
is done automatically when you migrate from the firewall plugin to
the firewall component by running
upgrade_firewall_to_component.sql (see
MySQL Enterprise Firewall Component Scripts) or MySQL Configurator (see
Section 2.3.2.1, “MySQL Server Configuration with MySQL Configurator”).
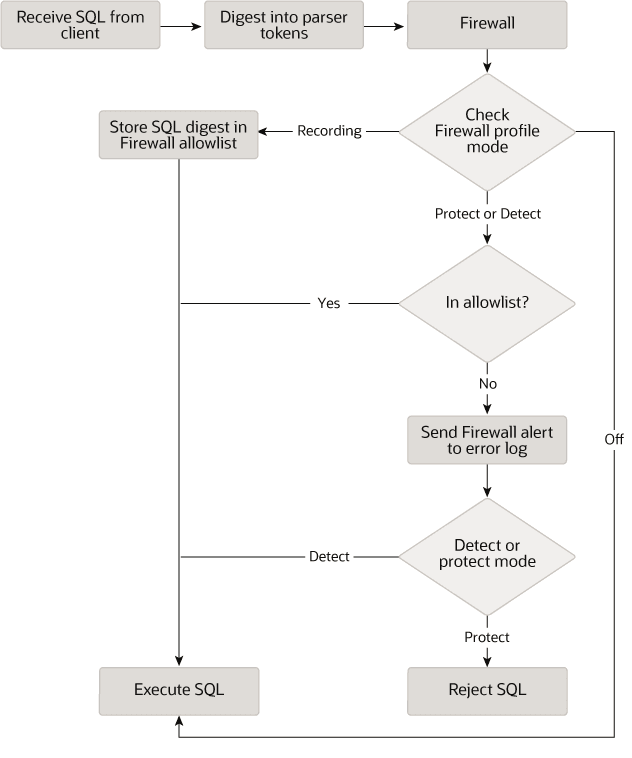
Each MySQL account registered with the firewall has its own statement allowlist, enabling protection to be tailored per account. For a given account, the firewall can operate in recording, protecting, or detecting mode, for training in the accepted statement patterns, active protection against unacceptable statements, or passive detection of unacceptable statements. The diagram illustrates how the firewall processes incoming statements in each mode.
The following two sections describe, respectively, the MySQL Enterprise Firewall plugin and the MySQL Enterprise Firewall component, discussing how to install and use each of these, and providing reference information for the elements of each as well. Upgrading to the MySQL Enterprise Firewall Component, and Downgrading the MySQL Enterprise Firewall Component, provide information about migrating between the plugin and component versions of MySQL Enterprise Firewall.