The following SQL CRUD functions are available in X DevAPI.
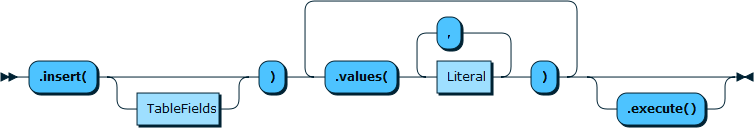
The Table.insert() method works like an
INSERT statement in SQL. It is used to store
data in a relational table in the database. It is executed by
the execute() function.
The following example shows how to use the
Table.insert() function. The example assumes
that the test schema exists and is assigned
to the variable db, and that an empty table
called my_table exists.
MySQL Shell JavaScript Code
// Accessing an existing table
var myTable = db.getTable('my_table');
// Insert a row of data.
myTable.insert(['id', 'name']).
values(1, 'Imani').
values(2, 'Adam').
execute();
MySQL Shell Python Code
# Accessing an existing table
myTable = db.get_table('my_table')
# Insert a row of data.
myTable.insert(['id', 'name']).values(1, 'Imani').values(2, 'Adam').execute()
Node.js JavaScript Code
// Accessing an existing table
var myTable = db.getTable('my_table');
// Insert a row of data.
myTable.insert(['id', 'name']).
values(1, 'Imani').
values(2, 'Adam').
execute();
C# Code
// Assumptions: test schema assigned to db, empty my_table table exists
// Accessing an existing table
var myTable = db.GetTable("my_table");
// Insert a row of data.
myTable.Insert("id", "name")
.Values(1, "Imani")
.Values(2, "Adam")
.Execute();
Python Code
# Accessing an existing table
my_table = db.get_table('my_table')
# Insert a row of data.
my_table.insert(['id', 'name']).values(1, 'Imani').values(2, 'Adam').execute()
Java Code
// Accessing an existing table
Table myTable = db.getTable("my_table");
// Insert a row of data.
myTable.insert("id", "name")
.values(1, "Imani")
.values(2, "Adam")
.execute();
C++ Code
// Accessing an existing table
var myTable = db.getTable("my_table");
// Insert a row of data.
myTable.insert("id", "name")
.values(1, "Imani")
.values(2, "Adam")
.execute();
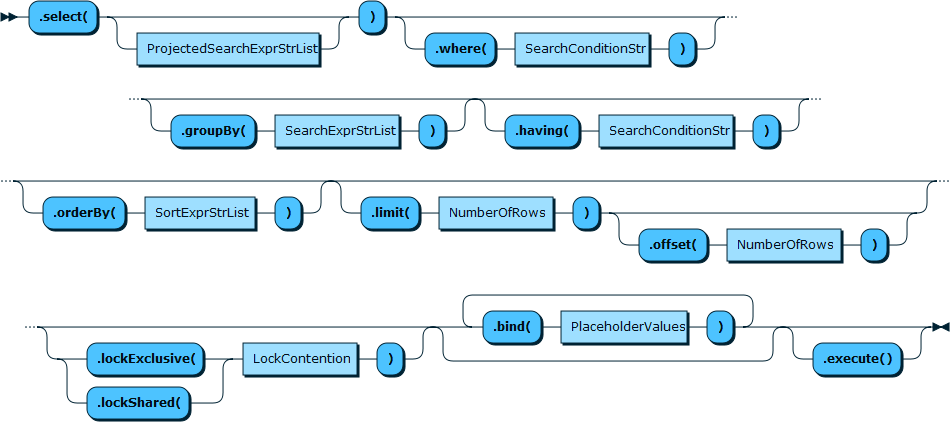
The Table.select() method works like a
SELECT statement in SQL. Notice that
Table.select() and
collection.find() use different methods for
sorting results: Table.select() uses the
method orderBy(), reminiscent of the
ORDER BY keyword in SQL, while the
sort() method is used to sort the results
returned by Collection.find().
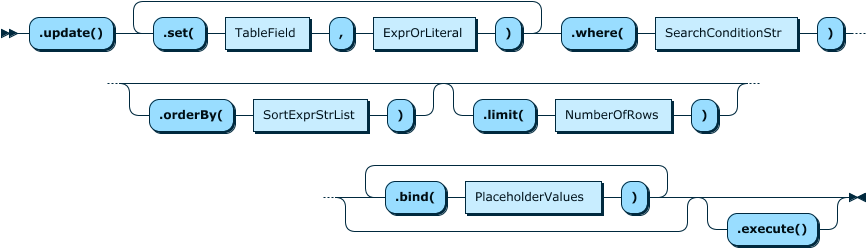
The Table.update() method works like an
UPDATE statement in SQL.