8 Understanding Fix/Inspect Forms
This chapter contains the following topics:
8.1 Fix/Inspect Forms
A fix/inspect form is used to update and insert single database records. This form type can also be used to display static information to the user, as well as prompt the user for information. Sign-on screens, for example, prompt the user to enter sign-on information.
8.2 Fix/Inspect Events
These events can occur on the fix/inspect form during runtime:
-
Dialog is Initialized
-
Post Dialog is Initialized
-
Clear Screen Before Add
-
Add Record to DB - Before
-
Add Record to DB - After
-
Update Record to DB - Before
-
Update Record to DB - After
-
Post Commit
-
End Dialog
-
XAPI Subscribe Event
8.3 Fix/Inspect Runtime Processing
This section discusses how runtime processes fix/inspect forms.
8.3.1 Dialog Initialization
When a fix/inspect form is called, runtime initializes these items in this order:
-
Thread handling
-
Error handling process
-
Business view columns (BC)
-
Form controls (FC)
-
Static text
-
Helps
-
Event rules structures
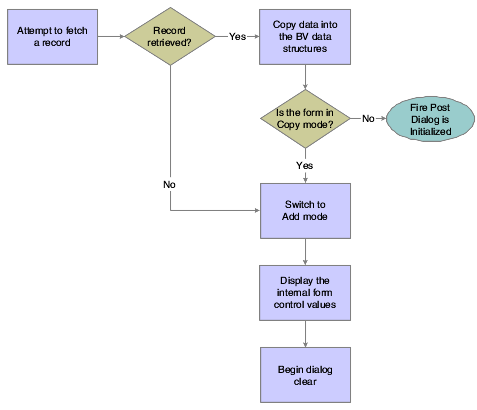
This flowchart illustrates the tasks that runtime performs after initializing these objects to complete dialog initialization:
Figure 8-1 Fix/Inspect dialog initialization
Description of "Figure 8-1 Fix/Inspect dialog initialization"
Note:
FC and BC are sharing internal memory, so copying into the BV is effectively copying into the internal FC memory locations.8.3.2 Dialog Clear
This list discusses how runtime clears the form in preparation to display retrieved data:
-
If the form was called in Copy mode, clear the key (primary index) controls for which the Do not clear after add option was enabled.
-
If the form was not called in Copy mode, clear all FCs for which the Do not clear after add option has been disabled.
-
Fire the Clear Screen Before Add event.
-
Fire the Post Dialog is Initialized event.
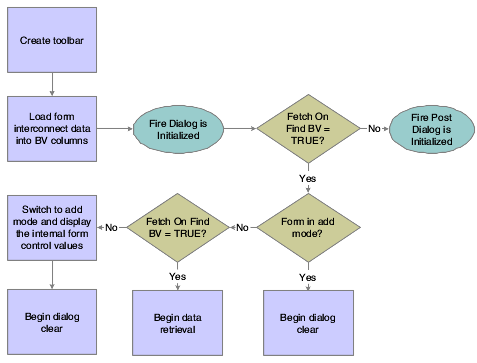
8.3.3 Data Retrieval
A request is issued to the JDEKRNL, which performs the actual fetch from the database. The fetch is based on the information passed to the form through its form data structure.
This flowchart illustrates the tasks that runtime performs to retrieve and display data on the fix/inspect form:
8.3.4 OK Button
The OK button is a standard button on fix/inspect forms that appears by default. It causes runtime to validate the information on the form and update or add it to the database through JDEKRNL function calls.
This flowchart illustrates the initial tasks that constitute runtime processing for the OK button:
Figure 8-3 Fix/inspect OK button processing, part 1 of 4
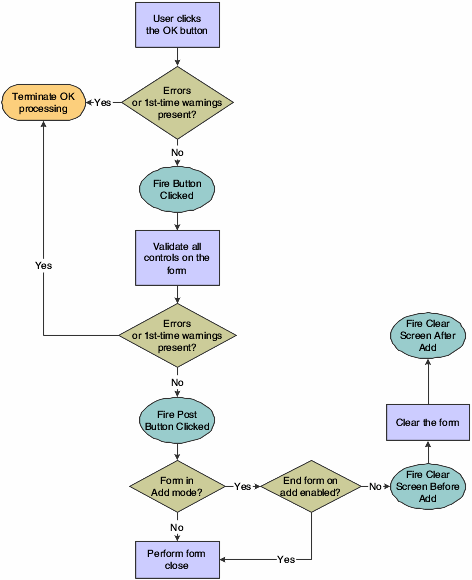
Description of "Figure 8-3 Fix/inspect OK button processing, part 1 of 4"
This flowchart expands on how runtime populates the grid during OK button processing:
Figure 8-4 Fix/inspect OK button processing, part 2 of 4
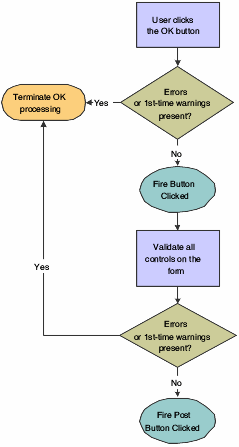
Description of "Figure 8-4 Fix/inspect OK button processing, part 2 of 4"
This flowchart illustrates how runtime processes any mode changes during OK button processing:
Figure 8-5 Fix/inspect OK button processing, part 3 of 4
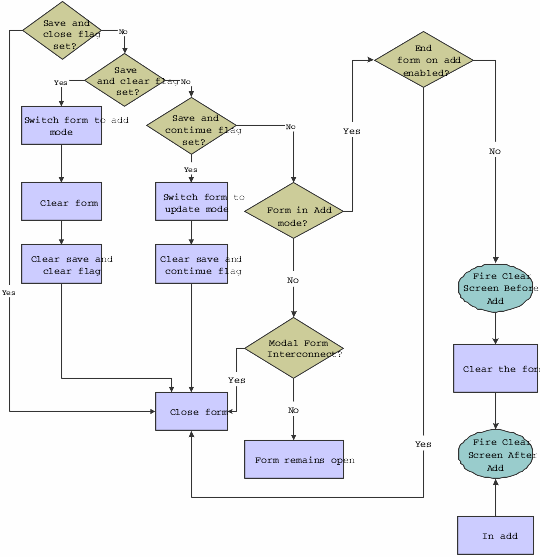
Description of "Figure 8-5 Fix/inspect OK button processing, part 3 of 4"
This flowchart illustrates how runtime completes the form close process during OK button processing:
Figure 8-6 Fix/inspect OK button processing, part 4 of 4
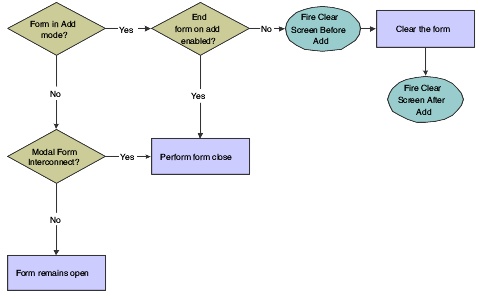
Description of "Figure 8-6 Fix/inspect OK button processing, part 4 of 4"
8.3.5 Cancel Button
The Cancel button is a standard button on fix/inspect forms that appears by default. When the user clicks it, runtime fires the Button Clicked and Post Button Clicked events in immediate succession. If no errors occur, runtime attempts to close all of the modeless child forms, if any exist. If any of these child forms cannot be closed, the Cancel button process is terminated. Otherwise, runtime fires the End Dialog event and initiates the dialog close process.
8.3.6 Dialog Close
Fix/Inspect can be closed either by the user (typically by clicking the OK or Cancel buttons) or by the system. After performing any control-level close processing that might need to occur, runtime closes the form. If the event has not already occurred, runtime fires the End Dialog event. Then it performs these tasks in this order:
-
Load form interconnect data from BC for database commit.
-
Terminate error and thread handling.
-
Terminate helps.
-
Free all form structures.
-
Destroy the window.