Overview of Oracle Mobile Field Service - Wireless and Voice Implementation
This chapter provides a high level overview of the Oracle Mobile Field Service - Wireless and Voice implementation, provides an architectural overview, and discusses terminology used throughout the implementation process.
This chapter covers the following topics:
- Oracle Mobile Field Service - Wireless and Voice Implementation Overview
- Architectural Overview
- Terminology
Oracle Mobile Field Service - Wireless and Voice Implementation Overview
The Oracle Mobile Field Service - Wireless and Voice applications enable field technicians access to mission-critical data by accessing the enterprise database through a wireless device. The field technician can also perform certain tasks using the voice interface when they are out of wireless coverage.
The Oracle Mobile Field Service - Wireless and Voice applications are a solution for field service technicians on tethered mobile devices. This means that the device has a continuous connection to the Oracle Enterprise applications. Field service technicians connect to this application by choosing a URL on their wireless device's web browser. After completing the required login, they can access real-time information from the enterprise database.
With this solution, the field service technician can carry on his daily tasks using any mobile device with internet capabilities (with a web browser). For the voice interface only a phone is required, which does not have to be a wireless phone.
Oracle Mobile Field Service Wireless and Voice can be deployed over any protocols, including WML, HDML, Tiny HTML, or Voice XML. This solution works over any wireless standard such as, CDMA, CDPD, GSM, GPRS, HSCSD, and TDMA.
Technology Requirements
Oracle Mobile Field Service - Wireless and Voice enables read and write functions to the enterprise database through a wireless connection between a mobile device and the Internet Service Provider (ISP). Voice also requires the AS Wireless Edition server.
The following components are involved:
-
Enterprise Database: This is the enterprise data that field service technicians will access through a wireless device.
-
Enterprise Applications Web Server: This is the http server used to connect to the enterprise applications.
-
Oracle AS Wireless Edition (ASwe): This server is used to transform XML to any markup language (WML, HDML, or Voice XML).
-
WEB-enabled wireless device: This device is capable of displaying Web pages in a web-enabled browser.
Architectural Overview
This section provides an overview of the architectural structure that underpins the functionality of Oracle Mobile Field Service - Wireless and Voice.
Oracle Mobile Field Service Wireless
The following diagram, Architecture of the Wireless Application, is described in the following text.
Architecture of the Wireless Application
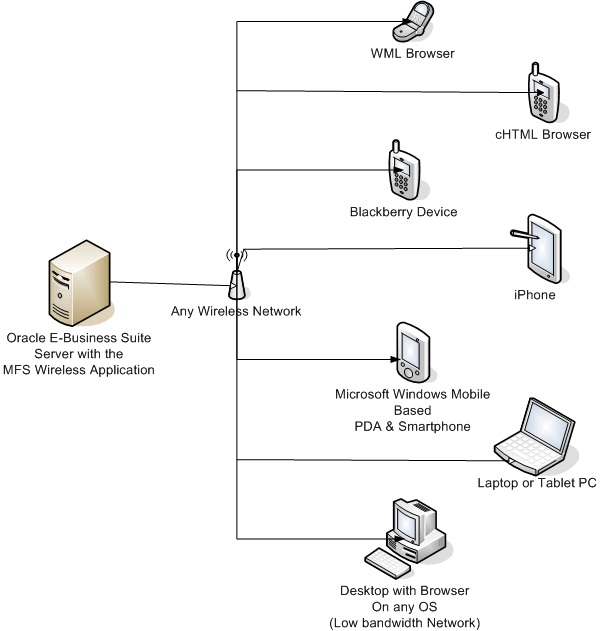
Oracle Mobile Field Service (MFS) Wireless is similar to any other Web-based application, but it is intelligent enough to cater to various kinds of devices like a WAP based device, cHTML (iMode) device, Blackberry, iPhone, PDA, Smartphone, laptop, tablet PC, and a normal PC with a browser using the Multi Channel Service (MCS) capability of Oracle iAS Wireless Server. Because Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) itself now includes MCS, no separate installation or setup for it is required.
Application Logic for Oracle Mobile Field Service Wireless
The application logic for Oracle Mobile Field Service Wireless is as follows:
-
Device browser sends a page request.
-
Request comes to EBS MFS application over a wireless network.
-
MFS Wireless application detects the end device and requests the core EBS server for the data.
-
Core MFS Wireless application generates a Mobile XML (MXML) page with response.
-
MFS Wireless Server application has an built-in MCS server that translates the response MXML page into a mark-up language such as HTML, cHTML, or WAP, that is specific to the end device.
-
Device-specific markup page travels to the device browser over the wireless network.
-
Device browser renders the response page.
Oracle Mobile Field Service Voice
The following diagram, Architecture of the Voice Application, is described in the following paragraph.
Architecture of the Voice Application
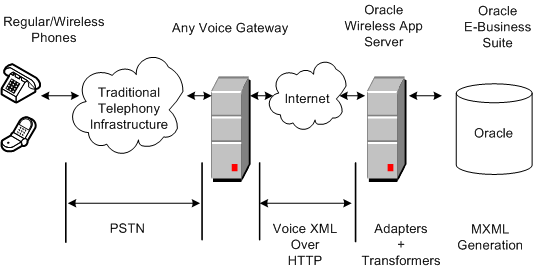
Mobile Field Service Voice has an architecture similar to that of the Mobile Field Service Wireless server. The only difference is the Oracle iAS Wireless server. It is still required for Voice.
Application Logic for Mobile Field Service Voice
The application logic for Oracle Mobile Field Service Voice is as follows:
-
Phone or cell phone sends a request for information over a wireless network or a PSTN network.
-
Request comes to a wireless network service provider or a PSTN network provider.
-
Request is converted into Voice XML (VXML) and forwarded to a voice gateway.
-
Voice gateway understands the request and generates a similar request for Oracle iAS Wireless server using Mobile XML (MXML).
-
Oracle iAS Wireless server then sends the same request to the MFS Voice application.
-
MFS Voice application generates MXML for the response and passes it to the Wireless server.
-
Wireless server converts the response into VXML and passes it to a voice gateway.
-
Voice gateway passes the response to the PSTN/Wireless network.
-
Response is passed back to the land-line phone or the cell phone.
Terminology
The following terms are used throughout this document:
-
WIRELESS_SERVER: This is the Web-Server for the AS Wireless Edition (for example, http://<Wireless_Server_name>:<port number>).
-
ENTERPRISE SERVER: This is the web server for the Oracle Enterprise applications (e-Business applications). Typically, since there are a lot of URLs that access the Enterprise applications, depending on which applications you are using (jtflogin.jsp, csfwlgnm.jsp, and so on), this would indicate the common HTML directory.
For example, if http://<Enterprise Host>:<Port Number>/OA_ HTML/jtflogin.jsp is the JTF URL for the Enterprise application, and http://<Enterprise Host>:<Port Number>1/OA_HTML/csfwlgnm.jsp is the Oracle Mobile Field Service - Wireless and Voice application, then ENTERPRISE_SERVER is http://<Enterprise Host>:<Port Number>/OA_HTML, where <Port Number> is the non-ssl http port for the web server.
-
MIDDLE_TIER: This is the wireless option of the ASwe. The middle tier is divided into two installations: infrastructure and server. In this situation, this would refer to the Server Installation where Wireless Option is selected.
-
ORACLE_HOME: This is where the wireless option of the Oracle ASwe is installed. Please note there might be two ORACLE_HOMEs (Infrastructure Home and the middle-tier home). In this case, ORACLE_HOME is used only for the middle-tier home.
-
PANAMA_HOME: This would be ORACLE_HOME/wireless.
-
OA_HTML is the common html directory for all the products in the Oracle Enterprise application.
-
OA_HTML_URL is the URL for the Enterprise applications (Example: ENTERPRISE_SERVER).