Oracle TSO Business Processes
This chapter covers the following topics:
- Oracle TSO Business Processes Overview
- Configuring New Item Instances
- Reconfiguring Installed Item Instances
- Disconnecting Installed Item Instances
- Changing Item Instances from Oracle Installed Base
- Pricing a Configuration
- Placing the Order and Verifying Order Fulfillment
- Integration with Oracle Telecommunications Billing Integrator
Oracle TSO Business Processes Overview
The Oracle Telecommunications Service Ordering (TSO) solution consists of the following processes:
-
Create new configuration of equipment and/or services
-
Reconfigure installed equipment and/or services
-
Disconnect installed equipment and/or services
You can initiate these processes from Oracle iStore, Oracle Quoting, Oracle Contact Center (TeleService), or Oracle Order Management.
Configuring New Item Instances
The process of configuring a new item begins when a user selects a configurable item from the Oracle Inventory catalog and launches Oracle Configurator. In Configurator, the user selects options available in the Container Model and then creates a quote or order line.
The following figure shows the process of configuring new items.
Process for Configuring New Item Instances
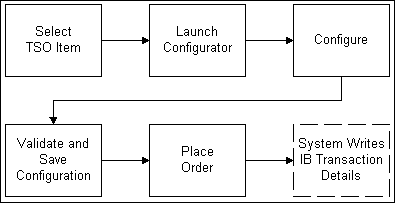
The following paragraphs explain the above figure.
Process for Configuring New Item Instances
-
From the product catalog or Oracle Inventory, the user selects the TSO item. Each selected item instance creates a quote line or order line. This may occur, for example, in Oracle Quoting, where the user is a sales agent creating a quote (and eventually an order) for a customer.
-
In the configuration process, the hosting application launches Oracle Configurator, and the user configures the item. For example, a customer in Oracle iStore may select a telephone to configure; in the Configurator, the user will add options to the phone, such as a service plan or a warranty. When finished configuring the item, the user places the order with the item instance. For example, an agent in Oracle Contact Center may place the order for a customer.
During the Oracle Configurator session, users can configure pick-to-order (PTO) model items by selecting their attributes, locations, connections between items, and by specifying the instance names for the selected items. Oracle Configurator identifies -- for every item in the configuration -- a provisioning action (for example, add or disconnect). Oracle Configurator validates the configuration against defined technical and business configuration rules.
-
When the user is finished with the configuration, he submits the configuration, which results in:
-
The Oracle Configurator window closing and:
-
Passing the changes back to the hosting application
-
Passing information about the transaction lines associated with each item to Oracle Installed Base
-
Multiple lines, selected during the configuration session, appearing in the quote or order
-
-
-
The item instance is then provisioned. In other words, an automatic or manual process writes all of the details of the item instance. For example:
-
The phone number and customer information are recorded into systems and databases
-
A DSL technician comes to the customer's house and installs software and a modem
-
-
Oracle Configurator writes transaction details of the configuration to Oracle Installed Base.
-
After provisioning, install base writing, and fulfillment, the item instance can be reconfigured.
When Oracle Service Fulfillment Manager has fulfilled an order line, Oracle Installed Base is updated with any changes to extended attributes that occurred during fulfillment.
Integration with Oracle Financials applications provides billing/invoicing supporting, and integration with Oracle Telecommunications Billing Integrator provide links to third-party billing systems and two-way communication with Oracle E-Business Suite objects such as product retrieval and orders.
Reconfiguring Installed Item Instances
From within a hosting application (e.g., Oracle Quoting) the user begins the process of reconfiguring an item instance by selecting a configurable item instance from the customer's installed base. Item instances created in a common Container Model appear as separate quote/order lines, as child lines of a single parent container line. Each instance shows up on a separate line, but each line is a child of a single parent line.
If integrating with Oracle iStore, customers reconfigure their own install base items in the Oracle iStore Customer Application. This flow is covered in the chapter, Oracle TSO Functionality.
The following figure shows the process of reconfiguring item instances.
Process for Reconfiguring Installed Item Instances
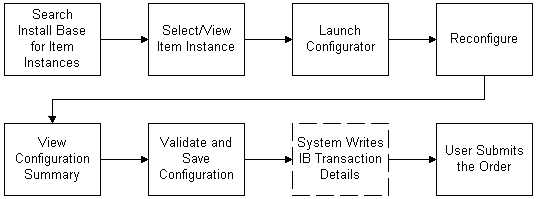
The following paragraphs explain the above figure.
Prerequisites: An order has been placed for an item instance, the item instance has been provisioned, and the details have been written to the customer's install base.
Reconfiguring Installed Item Instances
-
After an order has been placed for a item instance and the details written to the customer's installed base, ordered item can be reconfigured using one of the hosting applications. In this process, the user begins by searching Oracle Installed Base from within the hosting application. The user selects the item. For example, from within Oracle Quoting, a sales agent can search a customer's installed base items and select an item to reconfigure.
-
The user selects the item instance, or a subset of the product instances, to move, add or change -- that is, reconfigure. The selected item instances appear in the quote or order line within their original Container Model.
-
The user launches Oracle Configurator. Oracle Configurator retrieves the baseline configuration status from Oracle Installed Base. The baseline configuration represents the latest revision of a configurable item and reflects the current installation at a customer's site.
-
The user reconfigures item instances. For example, he changes attributes, locations, and connections between item instances, or he moves or disconnects the item instance or adds new item instances. Oracle Configurator validates the changed configuration against defined configuration rules.
-
Optionally, in sales agent-enabled applications, the user can compare the reconfiguration to the previous configuration in the Configurator summary window. The summary window shows the changes since the previously fulfilled, baseline configuration.
The summary window indicates the type of change in the Line Type column. When an Oracle Quoting agent submits a quote, creating a sales order in Oracle Order Management, the provisioning action for each quote and order line appears in the Line Type column in the Oracle Order Management Sales Orders window. Downstream applications, such as Oracle Service Fulfillment Manager, also reference the line type for further processing.
-
After the user is satisfied with and has completed the configuration, the Oracle Configurator session ends, and the quote or order line displays the details of the configuration.
-
The user places the order. The quote/order contains the delta between the baseline configuration and the revised one.
-
The reconfigured item instance is then provisioned. In other words, an automatic or manual process writes all of the details of the item instance. For example:
-
The phone number and customer information are recorded into systems and databases
-
A DSL technician comes to the customer's house and installs software and a modem
-
-
Oracle Configurator writes transaction details of the configuration to the Oracle Installed Base.
-
After provisioning, install base writing, and fulfillment, the item instance can be reconfigured again.
Note: In the telecommunications service industry, it is common to use the term, upgrade, to refer to the reconfiguration of a service by moving, adding, changing, or disconnecting items (MACD). However, in the context of the TSO solution, these changes to installed configurations of Container Models are regarded as updates to those configurations. To avoid confusion, this document uses the term, reconfiguration, to encompass both upgrade and update.
Disconnecting Installed Item Instances
The Oracle TSO solution supports the ability of customers to disconnect installed items instances.
The following figure shows the process of disconnecting item instances.
Process for Disconnecting Installed Item Instances
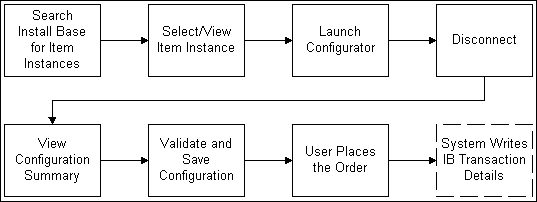
The following paragraphs explain the above figure.
Prerequisites: An order has been placed for an item instance, the item instance has been provisioned, and the details have been written to the customer's install base.
-
After an order has been placed for a item instance and the details written to the customer's installed base, ordered item can be disconnected using one of the hosting applications. In this process, the user begins by searching Oracle Installed Base from within the hosting application. The user selects the item. For example, from within Oracle Order Management, a sales agent can search a customer's installed base items and select an item to disconnect.
-
The user selects the item instance, or a subset of the product instances, to disconnect. The selected item instances appear in the quote or order line within their original Container Model.
-
The user launches Oracle Configurator. Oracle Configurator retrieves the baseline configuration status from Oracle Installed Base. The baseline configuration represents the latest revision of a configurable item and reflects the current installation at a customer's site.
-
The user disconnects the item instance.
-
Optionally, in sales agent-enabled applications, the user can compare the reconfiguration to the previous configuration in the Configurator summary window. The summary window shows the changes since the previously fulfilled, baseline configuration.
-
After the user is satisfied with and has completed the configuration, the Oracle Configurator session ends, and the quote or order line displays the details of the configuration.
-
The user places the order. The quote/order contains the delta between the baseline configuration and the revised one.
-
The disconnected item instance is then provisioned. For example, the telephone company updates its records that a customer's telephone number has been removed from service.
-
Oracle Configurator writes transaction details of the configuration to the Oracle Installed Base.
Changing Item Instances from Oracle Installed Base
In Oracle Installed Base, the user can make changes to an installed item directly, without involving one of the hosting applications.
Use case example: A customer has placed an order for DSL 512KB speed. The DSL was installed as ordered, but the customer receives a bill for a 1MB speed rate. In this case wherein the system records are incorrect, a customer service representative can go directly into the installed base and update the records manually. When users make changes directly in the installed base, provisioning does not take place.
The following figure shows the process of changing an item instance from within Oracle Installed Base.
Process for Changing Item Instances from Installed Base
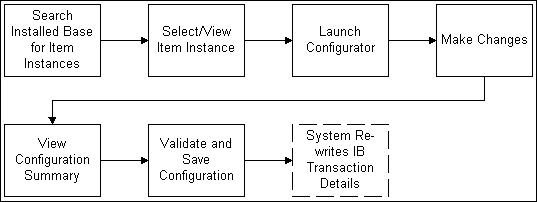
The following paragraphs explain the above figure.
Prerequisites: An order has been placed for an item instance, the item instance has been provisioned, and the details have been written to the customer's install base.
-
In Oracle Installed Base, the user searches for installed item instances.
-
The user selects an item to reconfigure.
-
The user launches Oracle Configurator and reconfigures the item.
-
The user views the configuration summary.
-
The user validates and saves the reconfiguration.
-
The system writes the installed base transaction details into the customer's installed base.
Pricing a Configuration
When a configuration is completed, validated, and saved in Oracle Configurator, the configuration returns to the hosting application. Quote or order lines are created for each item instance in the configuration. The hosting application then calls Oracle Advanced Pricing to price the configuration (using the pricing setup for the hosting application, along with any setups done in Oracle Advanced Pricing). The prices of each item appear on each quote or order line.
In Oracle iStore, the prices appear in the shopping cart with the configuration. In the sales-agent enabled applications, agents can adjust prices and other quote or order information before placing an order.
For more information on placing orders in these applications, refer to the respective product documentation.
Placing the Order and Verifying Order Fulfillment
From the hosting application or Oracle Installed Base, the user places the order with the item instance.
To prevent data corruption, Oracle Configurator locks instances until they are completely fulfilled, to ensure the integrity of their revision data. For details, see the chapter, Set Up Oracle Configurator and Customize the Solution.
Oracle Service Fulfillment Manager (if implemented) receives the order from Oracle Order Management for provisioning. When the system provisions the order, Oracle Installed Base receives the reconfigured item information, and the sales order is complete.
When Oracle Service Fulfillment Manager completes provisioning, the order line status becomes Provisioning Successful, and then it becomes Fulfilled.
Integration with Oracle Telecommunications Billing Integrator
Implementers can use Oracle Telecommunications Billing Integrator (TBI) to integrate with the third-party billing systems. The third-party billing systems rate and generate bills for the services ordered. Oracle TBI provides two-way integration which enables exchange of information between Oracle E-Business Suite and the external billing applications. For more information, see the chapter, Oracle TSO Functionality.