Introduction to Oracle HRMS
Introduction to Oracle HRMS
Oracle Human Resources Management System (HRMS) is a major component of the Oracle E-Business Suite of applications. Oracle HRMS is an integrated suite of applications that supports all aspects of the HR function. It includes:
-
Oracle Human Resources (HR)
-
Oracle Payroll
-
Oracle Self-Service Human Resources (SSHR)
-
Oracle Performance Management
-
Oracle iRecruitment
-
Oracle Time & Labor (OTL)
-
Oracle Learning Management
-
Oracle Advanced Benefits (OAB)
-
Oracle HRMS Intelligence (HRMSi)
All Oracle HRMS applications share tables in the Oracle database, which eliminates data redundancy, reduces the possibility of error, and creates a consistent record of every worker. Within this framework, however, you can define a human resources model that supports your enterprise's structures and policies.
The Oracle HRMS applications meet the requirements of a global workforce. For example, HRMS enables you to manage information in a variety of national languages and supports multiple address styles, legislation-specific date formats, and national identifiers (such as social security numbers), which can be validated according to the rules in each country.
Oracle Human Resources (HR) and Oracle Payroll
Oracle Human Resources (HR) enables the efficient management of workforce data and supports all standard HR activities, including workforce organization, development, and measurement. Payroll processing is a fundamental business requirement that demands accuracy, timeliness, and good financial controls. Oracle Payroll can help you ensure that all employees are paid on time and according to your compensation rules.
Oracle HR and Oracle Payroll constitute a closely integrated HR system. Oracle HR and Oracle Payroll windows are available under a single menu structure, sharing windows and underlying tables wherever possible to eliminate redundant data entry, maintenance, and storage.
Oracle Human Resources and Oracle Payroll are separately licensed products.
Oracle Self-Service Human Resources (SSHR)
Oracle Self-Service Human Resources (SSHR) enables your workforce to use a web browser to access HR information and perform personnel actions. The information an individual can access is tailored to the individual's roles and information needs. You can: authorize employees to maintain their own information, including personal profiles, benefits, and expenses; enable managers to conduct performance reviews, transfers, and time and expense approval; and deliver workforce intelligence to managers, HR professionals, and executives. Oracle SSHR is designed for the needs of the casual or untrained user, with simple, intuitive navigation and configurable user assistance integrated with the user interface.
Oracle SSHR is a separately licensed product. The self-service functions you can access depend on your licensing arrangements for other HRMS products. For example, you can use the self-service functions in Oracle Advanced Benefits only if you have licensed OAB.
See What is SSHR?, Oracle SSHR Deploy Self-Service Capability Guide
Oracle Performance Management
Oracle Performance Management is a self-service product that enables enterprises to implement an effective performance management system. It enables managers and employees to manage performance management functions including objectives setting and appraisals process. Enterprises can create and administer questionnaires for the various potential participants in the appraisal process.
Oracle Performance Management is a separately licensed product.
See: Oracle Performance Management Overview, Oracle Performance Management Implementation and User Guide
Oracle iRecruitment
Oracle iRecruitment is a self-service module that offers a fully automated recruitment process. It enables managers, recruiters, and candidates to manage all phases of recruitment, from vacancy definition through recruiting and hiring new employees. Oracle iRecruitment supports both internal and external users (such as visitors to recruitment sites) and is highly configurable to reflect the enterprise image. It can provide reports of your recruitment process, allowing you to monitor its effectiveness.
Oracle iRecruitment is a separately licensed product.
See iRecruitment Overview, Oracle iRecruitment Implementation and User Guide
Oracle Time & Labor (OTL)
Oracle Time & Labor (OTL) is a web-enabled time-recording application that enables you to reduce the costs associated with time and attendance record keeping. OTL ensures all employees are paid correctly and on time, it reduces administration costs by providing self-service time reporting for workers, and it shares worker time-related information with other Oracle applications, such as Oracle Projects and Oracle Payroll.
Oracle Time & Labor is a separately licensed product.
See Oracle Time & Labor Overview, Oracle Time & Labor Implementation and User Guide
Oracle Learning Management
Oracle Learning Management is an enterprise learning management system (LMS) that enables you to train your workforce effectively and at lower cost. Oracle Learning Management enables you to manage, deliver, and monitor your online and classroom-based training: you can efficiently assemble and deliver learning content; you can provide the most appropriate combination of classroom and online training; and you can measure the effectiveness of your training initiatives.
In Oracle Learning Management, self-service access is available not only to the learner but also to those responsible for administration and content management, offering improved efficiency and a lower cost of implementation for managing the learning environment.
Oracle Learning Management is a separately licensed product.
See Introduction to Oracle Learning Management, Oracle Learning Management User Guide
Oracle Advanced Benefits (OAB)
Oracle Advanced Benefits (OAB) is a benefits application that enables you to define and manage benefits programs in support of your enterprise's missions and objectives, while addressing the diverse and complex requirements of evolving benefits practices and governmental regulations. OAB's web-based self-service functionality enables you to both improve service and reduce enrollment costs. You can easily create and modify eligibility rules and other criteria without customizing the application, and you can use advanced analytical tools to evaluate the effectiveness of your benefits programs.
Oracle Advanced Benefits is a separately licensed product. Your Oracle Human Resources license includes Standard Benefits, a more limited set of benefits administration features.
See Standard and Advanced Benefits Administration, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Oracle HRMS Intelligence (HRMSi)
The Oracle HRMS products together hold vast amounts of HR data that, intelligently organized and presented, can facilitate enterprise management and decision making. Oracle HRMS Intelligence (HRMSi) is a configurable analysis tool that provides structured and comprehensive access to your HR data. For example, HRMSi provides predefined reports that enable you to analyze budgets, view employee development and performance data, analyze salary trends, and monitor vacancies and recruitment. You can configure the predefined reports, and you can also define your own reports.
Using HRMSi's web-based interface, you can perform ad hoc queries of HR data, and you can reduce administrative costs by distributing reports using the same web-based interface. HRMSi also provides a performance management framework: you can define targets and receive alerts when workforce changes become critical.
Oracle HRMSi is a separately licensed product.
See Reports and Processes in Oracle HRMS, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Introduction to Oracle HRMS
Oracle Human Resources Management Systems (HRMS) enables you to achieve a well managed human resource system, turning HR management into a strategic advantage.
What is Human Resource Management?
Today, the most successful enterprises continuously review and improve their business functions, searching for new ways to streamline processes to make them more effective and to use them to gain competitive advantage. Human Resource Management is responsible for addressing the workforce aspect of this continuous improvement.
How has the role of Human Resource Management changed?
Human resource management was originally an administrative and welfare role within an enterprise. This often included recruitment and record-keeping functions.
This role was primarily reactive in nature. Human Resources responded to the needs of both managers and workers, but did not anticipate them.
In the last few decades, human resource management has evolved and assumed a more proactive role, from automated processing, to the provision of a new level of strategic value.
Why is Human Resource Management important?
The people within your enterprise produce the goods and provide the services that fuel your enterprise. At the same time, the human cost is often the biggest cost a company incurs. Well managed human resources directly improve your enterprise and contribute to a competitive advantage.
If your enterprise has strategic, value added human resource management you will hire, motivate and retain the most capable workforce. You will have the ability to engage employees and line managers directly in managing their skills and careers to your enterprise's advantage. Furthermore, you will have accurate, up-to-date workforce information for managers and executives.
What applications make up the Oracle HRMS family suite?
Oracle HRMS consists of the following applications. These are all separate products, powerfully integrated into one application family.
-
Oracle Human Resources (HR)
-
Oracle Payroll
-
Oracle Advanced Benefits (OAB)
-
Oracle Self-Service Human Resources (SSHR)
-
Oracle iRecruitment
-
Oracle HRMS Intelligence (HRMSi)
-
Oracle Learning Management
-
Oracle Time & Labor (OTL)
When the term HRMS is used, it refers to this integrated set of applications.
What is Oracle Human Resources?
Oracle Human Resources (HR) is a proactive management solution that helps control costs while developing and supporting an effective workforce. Among the many features of Oracle HR is the ability to:
-
Manage the entire recruitment cycle.
-
Design organizational models that match current and future business strategies and objectives.
-
Perform position management by defining and recording required skills, competencies, experience and qualifications for positions, jobs and organizations.
-
Perform career management functions relating to the definition of competencies, assessments, suitability matching, graphical ranking, and succession planning.
-
Administer and maintain benefits plans, coverage levels, and contribution allocations.
-
Manage salary proposals, and approve these by component.
-
Use spreadsheets to export compensation and benefit details for comparison with external survey figures.
Oracle Human Resources provides the shortest route to fast, smart human resource management.
What is Oracle Payroll?
Oracle Payroll is a high-performance, rule based payroll management system designed to keep pace with changing enterprises and workforce needs.
Payroll managers require a solution to address unique requirements, and offer complex calculations without losing the benefits of a standard supported package. Oracle Payroll offers that capability via a unique, data driven approach that enables the definition and management of diverse payroll requirements.
Among its many capabilities, Oracle Payroll delivers the power to:
-
Process many payrolls quickly and easily in a single day.
-
Define comprehensive personal payment methods.
-
Quickly create complex calculation rules, such as union overtime, without programming.
-
Efficiently check, double check, and reconcile payrolls.
-
Make retroactive adjustments to past earnings and deductions.
-
Examine employee payment histories at any time.
-
Track and monitor employee costs via online access to payroll data.
-
Disburse in multiple currencies.
-
Transfer payroll information to the general ledger and to other accounting systems, including project costing systems.
-
Report on payroll results to the tax office and company executives.
-
Maintain full security and integrity of payroll information, including historical information.
-
Enable access to information when required for inquiries and responses to pay queries.
Oracle Payroll enables fast, flexible, and accurate payroll processing from time capture to ledger costing.
What is meant by separate vs. integrated Oracle HRMS systems?
Traditionally, human resources and payroll departments have often held and managed human resource information in separate, duplicate systems.
Over time there has been a greater demand for more unified information management derived from both human resource and payroll sources.
One solution to this has been to develop interface products, which enable technical specialists to transfer data between the two systems. Oracle HRMS, however, provides an integrated system that both functions can genuinely share with full security and control of access by responsibility.
This system is flexible enough to be implemented for use in a human resources only or a payroll only environment. In each case you have access to the full range of functionality associated with human resources or payroll.
What is Oracle Advanced Benefits?
In addition to the powerful compensation and benefit functionality included in Oracle Human Resources, Oracle also offers Oracle Advanced Benefits. Oracle Advanced Benefits enables the setup and administration of a complete benefits offering for enterprises managing their own benefits administration.
Oracle Advanced Benefits delivers the following key functions:
-
Pre and post-enrollment communications
-
Web and interactive voice response (IVR) enrollment for cafeteria and exceptions
-
Default and mass enrollments
-
Enrollment process monitoring
-
Life event management (for example, new hires, transfers, relocations or age changes)
-
Web-based what-if eligibility analysis
-
Flexibility spending account claims processing and reporting
Oracle Advanced Benefits provides a total compensation framework, setting the stage for exciting and new compensation solutions.
What is Oracle Self-Service Human Resources (SSHR)
SSHR provides self-service human resource management for managers and employees. Using an intranet and a web browser, employees and their managers now have easy to use and intuitive access to personal data and career management functionality.
Oracle Workflow is used extensively in SSHR. SSHR uses Workflow to manage the flow of information between employees and management. The workflow engine is used for business process transactions and can route decision making through approval chains. For example, an employee may apply for a job using the Apply for a Job function, and through a management approvals process be informed and accepted into a job.
The workflow engine is also used to modify and configure much of SSHR.
Using SSHR you can:
-
View employee or contingent worker information.
Managers can review information about employment, salary, performance, training, absence, and job applications for each person within their security access. Employees and contingent workers can view only their own records.
-
Manage careers.
This includes appraising employee's competencies, matching a person to a job or position by competence, and planning succession.
-
Perform web based recruitment using 'Candidate Offers'.
Candidate offers enables you to perform web based recruitment. Managers can seek approval for an appointment, then advise job applicants, by letter, that they have been successful. This function is offered with its own responsibilities.
Is Oracle HRMS a Multilingual, Global Application?
Yes. Oracle HRMS offers the best of both worlds in the same installation. Oracle provides non-legislative information common across all countries, plus localized information specific to each country.
Oracle also enables you to run HRMS in more than one language on a single database. This enables you to enter and report on information using more than one language. For example, your base, or source language, could be French, but you could also install German and English. You would then be able to enter and produce reports in French, German and English.
Introduction to Oracle HR
Human Resource Model
The human resource model is both flexible and adaptable. It is flexible, so that you can reflect the needs of different companies, or different groups within the same company. It is adaptable, so that you can easily change the basic model as your enterprise changes.
Modeling Human Resource Information
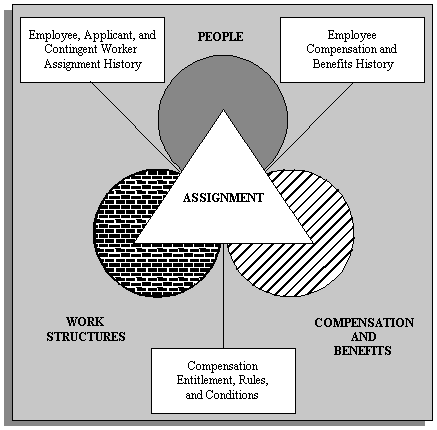
People
In Oracle HRMS, you can hold information about current and former employees, applicants, contingent workers, and contacts such as relatives and dependents.
In addition to standard information such as addresses, nationality, interview records, qualifications, and absence information, you can define any other special information you need to hold for people. For example, you can define what information to hold on medical history, previous employment, or outside interests.
You can also record employment information, such as hours of work and work choices.
Oracle HRMS holds one integrated set of employee-related information. Payroll users access the parts of this information they require, while enterprise business rules determine who is responsible for entering and maintaining it.
Work Structures
Work structures represent the different ways in which your workforce can work within your enterprise. They provide the framework for defining the work assignments of your workforce. They enable you to manage the information about your enterprise that is independent of your workforce. You can also think of work structures as representing the organizational units of your enterprise. The Business Group is the largest unit and represents your enterprise as a whole.
The work structures include your internal organizations (such as departments or divisions), payrolls, jobs or positions, grading structures, and any special workforce groupings that you use in your enterprise.
There is one integrated set of work structures for human resource and payroll users.
Compensation and Benefits
In Oracle HRMS you can define your own types of compensation and benefits, and the business rules you want to apply to them. As you change policies, move people within your enterprise, and adjust their individual remuneration packages, the system maintains their compensation and benefit history.
For example, suppose you want to define a special type of payment and make this available only to employees who work at a particular location. In Oracle HRMS you use a compensation element to represent the payment. You define the business rule as a link between the element and the specific location. Then when you assign employees to the location, they automatically become eligible for the payment.
Assignments
In Oracle HRMS, the assignment describes employees'and contingent workers' places within the enterprise: the organization for which they work, their role, grade, location, and so on. As you change the assignment information for an employee or contingent worker, you automatically build up their work history.
Your compensation eligibility rules link compensation and benefits to work structures, such as jobs or grades. The assignment places employees and contingent workers within the work structures of the enterprise. In this way, an employee's assignment determines their eligibility for compensation and benefits.
You can use assignments to identify major groups of people within the enterprise for management, for reporting and costing, and for compensation and benefit planning and administration.
Shared Information in Oracle HRMS
For all Oracle HRMS applications, you enter and maintain the same fundamental information about your structure and operations, your workforce and their assignments and employee compensation and benefits. You then add the specialized information you need specifically for human resources, or payroll management or benefits administration.
Common Information
The common core of fundamental information used for human resources, payroll and benefits administration includes:
-
Your operational basics:
-
Payrolls with their calendars and pay periods
-
Currencies and methods of payment you use
-
-
Your organizational structure:
-
Internal organizations, such as companies, divisions, departments, work groups, or production team
-
External organizations of key importance to you, such as employment agencies, tax authorities, or union headquarters
-
Organization location information, including addresses and telephone numbers
-
Hierarchies showing the relationships between your organizations
-
Any grade and grade scale structures you use
-
-
Your workforce essential personal information, such as:
-
Name and address
-
Marital status
-
Birth date
-
Nationality
-
Ethnic origin
-
-
Your workforce current work statuses, such as:
-
Active assignment
-
On maternity leave
-
Terminated
-
-
Your employees' assignments to:
-
Internal organizations
-
Grades, or grades and grade steps
-
Jobs, or jobs and positions
-
Salary bases for quoting pay, such as hourly or annual
-
Payrolls
-
-
Your contingent workers' assignments to:
-
Supervisory details
-
Assignment rate types and assignment rates
-
Supplier details
-
-
Elements of your employees' pay and benefits:
-
Earnings such as salary, wages, commissions, bonuses, allowances
-
Employer charges such as employer contributions to legislatively-mandated or private insurance or pension plans
-
Deductions such as contributions for union dues or employee stock purchase plans
-
Nonpayment benefits such as vacation time or a company car
-
Shared Windows in Oracle HRMS
While many of the windows in your system relate exclusively to the human resources, payroll or benefits functions, some include information relevant to more than one function. These latter windows are shared windows.
Shared windows can include some information fields relevant to both human resources and payroll users, and other fields for information specific to either human resources or payroll users but not both.
Using Shared Windows
You can control the use of fields on shared windows by the value your system administrator gives to each user or responsibility for the HR:User Type profile option. The three valid values are:
-
HR with Payroll User
-
HR User
-
Payroll User
Users with an HR User profile
These are restricted in their use of fields on certain windows. In particular they:
-
Do not see certain fields on the Element window, which are only required if you are processing elements
-
Cannot assign employees to a payroll if both Oracle Payroll and Oracle Human Resources are installed
Also, in all legislations, apart from the US, they:
-
Do not see the Statutory Information field in the Payroll window
-
Cannot adjust element entry Pay Values
How to Use Your Documentation and Online Help
The Oracle HRMS online help is organized in the navigation tree by functional groups, such as enterprise and workforce management, payroll, and talent management. The Oracle HRMS guides mirror this organization. A summary of the contents of each Oracle HRMS guide appears below.
Oracle HRMS Implementation Guide
The Oracle HRMS Implementation Guide identifies tasks you need to perform after installing the HRMS applications and before making them generally available to your users. It includes:
-
Descriptions of post-installation utilities
-
A general implementation checklist to help you identify the Oracle HRMS functions you want to implement
-
Implementation flowcharts to guide you through the implementation of all major functional areas
-
Technical essays that explain some fundamental aspects of Oracle HRMS
Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
The Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide describes how to configure the application to meet your requirements. Tasks it addresses include:
-
Controlling user access to data and functions
-
Auditing changes to Oracle HR data
-
Downloading Oracle HR data to generated Microsoft Excel or Word documents on the desktop using Web ADI
-
Generating letters
-
Adding fields to windows and defining additional information for existing fields
-
Setting up user tables and lookups
-
Extending user types and statuses
-
Using and configuring predefined alerts
-
Customizing form processing using custom code
-
Enabling context-sensitive links to web pages and information provider web sites
-
Defining task flows by linking windows in an appropriate order
-
Using the People Management Configurator to design windows
-
Defining different versions of windows using CustomForm
Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
The Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide describes how to define and manage the infrastructure of your enterprise in Oracle HR. Tasks it addresses include:
-
Defining and classifying organizations
-
Defining locations
-
Enabling the automatic creation of HR organizations
-
Defining and managing jobs and positions
-
Defining and managing hierarchies of organizations and positions
-
Posting and routing transactions
-
Reorganizing the workforce
-
Estimating and managing HR budgets
-
Defining and managing people types and employment groups
-
Setting up employment agreements and complying with legal requirements
Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
The Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide describes all aspects of workforce management and development in Oracle HR. Tasks it addresses include:
-
Recording and maintaining personal information about employees, applicants, contingent workers, and contacts
-
Creating and maintaining contracts
-
Recording and maintaining information about an individual's assignment to an organization, job, or position
-
Setting up self-service information for individuals
-
Terminating employment and placements
-
Reporting on the workforce
-
Defining and measuring workforce competencies and qualifications
-
Planning careers and succession
-
Matching workers to opportunities
-
Evaluating and appraising the workforce
Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
The Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing and Management Guide describes all aspects of payroll definition and implementation in Oracle HR. Tasks it addresses include:
-
Setting up and managing payrolls
-
Defining payment methods and payslip contents
-
Defining and processing statutory deductions, and reporting on those deductions
-
Running the payroll, performing post processing on a successful payroll, and correcting an unsuccessful payroll
-
Running a payroll for an individual employee using the QuickPay process
-
Applying retrospective changes to the payroll using the RetroPay process
-
Making payments in advance
-
Identifying underpayments and overpayments
-
Correcting payrolls using retries, reversals, and rollbacks
Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
The Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide describes all aspects of compensation management in a modern enterprise. It supports both Standard Benefits (included in Oracle HR) and Oracle Advanced Benefits (OAB). Tasks it addresses include:
-
Defining and processing the components of a compensation and benefits package
-
Defining and managing the policies and business rules that govern allocation of compensation and benefits to employees
-
Reporting on compensation and benefits in the enterprise
-
Designing and managing your benefits plan, and defining eligibility requirements
-
Implementing grade-related compensation packages
-
Setting up compensation and awards programs
-
Managing leave and other types of absence
-
Managing life events, setting up flexible benefits programs, and managing participation
Oracle HRMS FastFormula User Guide
Oracle FastFormula is a simple way to write formulas using English words and basic mathematical functions. Oracle FastFormula performs calculations or comparisons on data taken from a window, a database, or a process, and returns values or messages. The Oracle HRMS Fast Formula User Guide describes:
-
Techniques for writing formulas
-
The supplied sample formulas
-
How to write formulas for specific purposes
Oracle HRMS Deploy Self-Service Capability Guide
Oracle Self-Service Human Resources (Oracle SSHR) enables workers and managers to participate in HR activities using a web browser. Oracle SSHR has simple, intuitive navigation and configurable user assistance integrated with the user interface. The Oracle HRMS Deploy Self-Service Capability Guide describes how to implement, extend, and manage Oracle SSHR. Tasks it addresses include:
-
Setting up SSHR
-
Using generic and function-specific configuration options
-
Controlling user access to data and functions
-
Using the supplied workflows and configuring them using Workflow Builder
-
Personalizing the SSHR page layouts
-
Implementing approval mechanisms for transactions carried out by SSHR users
-
Using SSHR for all HR tasks
Oracle HRMS iRecruitment Implementation Guide
Oracle iRecruitment is an online recruitment system that enables you to manage all recruitment activities using a single self-service interface. The Oracle HRMS iRecruitment Implementation Guide describes how to implement and manage Oracle iRecruitment. Tasks it addresses include:
-
Setting up Oracle iRecruitment
-
Using configuration options
-
Controlling user access to data and functions
-
Personalizing page layouts
-
iRecruitment functions
-
Extending iRecruitment
-
Reporting on the recruitment process
Oracle HRMS Deploy Strategic Reporting (HRMSi) and Strategic Reporting (HRMSi) User Guide
Oracle HRMSi provides a web-enabled suite of strategic reports that provide summaries and details of HRMS application data. It also provides the tools to enable you to create your own reports.
Oracle HRMS Deploy Strategic Reporting (HRMSi) provides instructions and checklists for implementing the HRMSi modules:
-
Discoverer Workbooks and End User Layer (EUL)
-
Discoverer Analytics Reports (for business analysts)
-
Performance Management Framework (for assessing enterprise performance using Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
-
Data Warehouse
-
HTML Reports
-
Daily Business Intelligence for HRMS
The Strategic Reporting (HRMSi) User Guide explains how the information in each type of report is derived, identifies the types of business questions the reports can address, and describes report parameters. It is organized by functional area, such as Leave and Absence Management, Recruiting and Hiring, and Learning Management.
Getting the Most out of HRMS Online Help
This topic explains how to use HRMS online help, and how to get the most out of it.
Accessing the Online Help
There are two ways of accessing the online help:
-
While you are using a window in the Professional User Interface, click on the Help button - this displays the context-sensitive help for that topic.
-
While you are browsing through the online help, selecting topics from the left hand navigator, rather than from the Help button in a context-sensitive window.
Obtaining Online Help for Your Localization
When you click on the Help button in a window, you should see the help topics that are specific to your localization. If you do not see your local topics, ask your system administrator to check that the Help Localization Code user profile is set to the correct code for your HRMS responsibility. For example, US is the correct code for the United States localized help.
For a list of all help localization codes, see: Help Localization Code, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Consistent Arrangement of Information
We arrange our information by functional area rather than strictly by product, and you can see this organization of material applied consistently in all our documentation and curriculum.
Our functional areas are:
-
Enterprise and Workforce Management - which includes details about work structures for organizations, locations, jobs and positions, as well as details about budgeting and costing. This area also includes details about person types and assignment statuses, as well as information about managing your employees and contingent workers.
-
Workforce Sourcing and Deployment - which includes details about iRecruitment and recruiting using HRMS.
-
Talent Management - which includes details about Training Administration and iLearning, as well as competence management, and career and succession planning.
-
Compensation and Benefits Management - which includes details about defining earnings, deductions, grades, compensation and awards, and benefits programs for savings, pensions, health and welfare. This area also includes leave and absence management.
-
Payroll Management - which includes details about defining payroll groups and types of payment, setting up taxation rules, running the payroll processes for each stage of the payroll cycle, and analyzing the results of the payroll process.
-
Time Management - which includes details about defining work schedules and applicable rules, and managing time entry for your workforce.
-
Human Resources Information Systems - which includes details about security and audit, as well as desktop integration for your HR management system. This area also includes the common information on configuring SSHR and HR Intelligence for all functional areas, and information about common interface configurations such as System Extract, BEE, Data Pump, and Payroll Backfeed.
Because we use this same arrangement of information in all documentation and curriculum, you should find it easier to locate the information or training you need. For example, if you want to find out about budget management, you would start by looking at the Enterprise Management section in the online help, or in the Enterprise Management curriculum for training.
Information Types are Common to All Functional Areas
Whichever functional area you use, you can expand the left hand navigation by clicking on a topic that interests you, such as Enterprise Modeling. You'll see the following arrangement of information for every topic, enabling you to access the type of information you require quickly and easily.
-
Enterprise Modeling (Contains the Overview information type)
-
Requirements (The Requirements information type)
-
Sub grouping of related Enterprise Modeling topics (Detailed information, key concepts).
-
How To's (Procedural information types)
Overviews in HRMS Online Help
The Overview information type identifies the key terms and concepts that you and other users need to know about, and explains why you need to know them. This explanation also includes any Oracle-specific terms such as 'elements', 'date track' or 'events'.
Presenting these terms in the overview helps explain what you can do, why you'd want to set up some features, and so on. It helps you to get the most out of the product functionality. The overview also helps set the scene so you can see what you need to read (or ignore), how the subsequent topics fit together, and what you can expect to get from the feature.
Your Business Needs in HRMS Online Help
The Requirements information type uses a question and answer format to explain how the feature meets your business needs. For example, "Can you associate salary changes with performance reviews?" , "Can you create any type of training event?" and so on. This explanation of the feature helps you to identify whether the feature or functionality meets the needs of your enterprise.
The Requirements information type does not explain how the feature works, but instead explains what the feature does, what business problems it solves, and showcases why you might want to use it.
Detailed Information in HRMS Online Help
We then break down any key terms, concepts or Oracle terms identified in the overview to provide you with further information before you go ahead and use the application. Typically, we include explanations of structures you need to set up, or options you might want to adapt the feature to the needs of your particular enterprise.
Procedural Information in HRMS Online Help
We also provide procedural information to enable you to perform a specific task. This grouping of information is referred to as a "How To". For example, "How to create an organization", or "How to schedule an event". You might also need to refer to a process topic to identify where a procedural task fits into the broader picture.
If you access the online help from a window, context-sensitive help displays a page that lists all the tasks you can perform in the active window, including which reports or processes you can run. You select the item that is of the most interest to you, and the online help then displays details about the task that you selected.
Searching for Information in HRMS Online Help
Finding Topics Easily
If you are searching for an exact sequence of words as described in a topic title, include them within parentheses when you launch the search. For example, if you are looking for a topic called Payroll Runs and Processes, enter your search query as "Payroll Runs and Processes" rather than Payroll Runs and Processes.
Using Advanced Search
A search normally operates across all Applications products. However, to provide a more precise set of search results, you can restrict your search to Human Resources only. To do this, select Advanced Search and then select Human Resources from the drop-down list of products, Note that the Human Resources product selection enables you to retrieve help topics for HR, Payroll and Benefits.
Multilingual Oracle HRMS
Oracle HRMS enables you to manage information in a wide variety of languages. To help you enter and retrieve information in the language of your choice, HRMS provides you with the following features.
Multiple Addresses Styles
Every country has its own address style, for example in Italy you can enter the province and in Malaysia you can enter the region. Oracle HRMS enables you to select the correct country address style.
See: Changing Default National Address Styles, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
National Identifiers
Each country has its own method of identifying its citizens. For example, in the UK it is the National Insurance number, in the US it is the Social Security number, and in Canada it is the Social Insurance number.
For supported localizations you can select the correct national identifier for your site and then check on entry that identifiers have the correct national format. For example, in the UK the format is 'AADDDDDDA', where A is a letter and D is a digit, while in Canada it is DDD DDD DDD.
If your localization is not supported, you can define your own validation.
Dates and Numbers
Oracle HRMS enables you to enter dates and numbers in any format and then translates this into the national format supported by your legislation. For example, you do not have to enter a date in a prescribed format such as DD/MM/YYYY. You can enter the date how you want, and HRMS automatically configures it in the national format defined for your site.
Similarly, you do not have to enter numerical information in a prescribed format. For example, US usage has previously required the format 1,000.0 whereas German usage has required the format 1.000,00. You can now enter the number without explicit formatting, as the correct format for your site will be automatically configured.
Translating Information
Oracle HRMS enables you to install additional languages on top of your base or source language. You can then enter information in key fields in your additional languages using the Translations window. This is accessed by choosing the Translation icon on the toolbar, or by choosing the View > Translations menu option. The translated information you enter is then used if you print reports or log on to Oracle HRMS in this language.
HRMS windows where the Translation icon is available are:
-
Organization
-
Location
-
Person Types
-
Assignment Statuses
-
Element
-
Input Values
-
Balance
-
Organizational Payment Method
-
Element Classifications
-
Absence Attendance Type
See: Creating Translations for a Record, Oracle E-Business Suite User's Guide
The following fields are also translatable, and the Translation icon appears in windows where you can update these fields:
-
Competence aliases, descriptions and behavioral indicators
-
Rating scale names and descriptions
-
Rating level names and behavioral indicators
-
Qualification details
-
Position posting descriptions, security requirements, and amendment information
The following fields are partially translatable:
-
Job names
-
Grade names
-
Competence names
-
Position names
Only those parts of the key flexfield name that are derived from value sets appear in translation, using the translated values for the value sets. Value sets can be translated using the Translations window.
Note: The translation of the value set must be available before the flexfield is created, otherwise the translation does not appear in the field name.
Multilingual Reports
Oracle HRMS enables you to print HRMS reports in the languages of your choice. Depending on the type of report, Oracle HRMS either:
-
Enables you to select the language in which to print the report
-
Prints the report in the language, or set of languages, depending on the report parameters you select
See: Multilingual Reporting, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Managing Change Over Time
A key requirement for any enterprise is the ability to manage change confidently and effectively. Typical enterprise changes include corporate restructuring, departmental reorganization, mergers and de-mergers of companies, centralization or decentralization of control and decision making, employee development and turnover.
In Oracle HRMS, you can change each of the major parts of your enterprise model without having to redefine the other parts.
To manage the changes to your enterprise, information within your enterprise is either dated or datetracked.
Dated Information
Work structures are an example of information that is dated. You can attach dates to your work structures to manage different versions over time. You retain previous versions for historical information and you can create future-dated versions to prepare for reorganization in advance.
You can also set up in advance the business rules, including compensation and benefits, associated with the new structures. These become effective on the date you specify, avoiding a workload peak.
The information in Oracle HRMS about your locations, organizations, jobs, positions, grades, payrolls and other work structures is also dated information. All dated information has From and To dates, that is, dates from and to which it is in effect in your enterprise. For example, when defining a position, you enter a date from which it starts. To close it down, you give it a date to which it remains valid.
Oracle HRMS does not permit you to assign your workers to structures on dates earlier than their Date From, or later than their Date To. Similarly, the system protects you from building eligibility rules for compensation and benefits based on work structures that have not yet gone into effect, or are out of date.
Consider using a fixed date, such as 01-JAN-1901 as the start date for all your initial work structures. By choosing a date like this you can immediately identify all of your implementation definitions. You should use accurate dates for all subsequent definitions.
Dated Versions of Hierarchies
You can structure the organizations and positions you enter in Oracle HRMS into organization or position hierarchies that serve various purposes. Reporting hierarchies, for example, reflect reporting lines within your enterprise.
You maintain both dates and version numbers for these hierarchies, to keep a history of your hierarchies as they change over time.
To build a new version of a hierarchy, you can copy an existing one and make the necessary changes to it. When you save the new version the system automatically gives the previous version an end date.
DateTrack
In contrast to work structures, which are simply dated, other key dynamic information in Oracle HRMS is datetracked. This includes information on workers, assignments, and compensation and benefits. DateTrack allows you to maintain a continuous history of the information over time.
You can enter datetracked information or make changes to it at any time. When you set an effective date for your work, DateTrack ensures that only information effective on that day is used for any processing, validation, and reporting you carry out. When you make a change, you can choose whether it is a correction to the last update or a new update to be recorded in the history of the record. You can use DateTrack History to view a report of every update ever made to a record.
You can identify windows containing datetracked, rather than dated, information by the presence of a region labelled Effective Dates.
Effective Date Reminder
When you are new to DateTrack, you may find it useful to be reminded of your effective date whenever you open a window where you can enter or change datetracked information. The reminder appears in a Decision window and asks whether you want to change your effective date. If you choose Yes, the Alter Effective Date window displays.
There is a user profile option called DateTrack:Reminder that determines when the Decision window appears. There are three possible values for this profile option:
-
Always
-
Never
-
Not Today
The Not Today value causes the reminder to appear when you navigate to a window where you can change datetracked information and your effective date is not today's date.
You can set the value of this profile option in the Personal Profile Values window.
Datetracked Information and History
Oracle HRMS maintains a continuous record of changes made to datetracked information. When you view a record in a datetracked window, it shows you a snapshot of the information on your effective date. The Effective Dates region on the datetracked window shows you the dates between which the snapshot is valid.
Suppose you are viewing an assignment with an effective start date of 01-JAN-1999 and no effective end date. This means that the assignment was created or last changed on 1 January 1999, and the snapshot information you are viewing is still valid. There have been no changes to the assignment since 1 January 1999, and there are no future dated changes.
To find out whether the assignment existed before 1 January 1999, you should use DateTrack History.
If there is an effective end date, you know that the record was either deleted or changed on the next day. To find out whether the record continues to exist, you can set your effective date to the day after this end date, or use DateTrack History.
When you update datetracked information, you are prompted to choose between Update and Correction.
If you choose Update, Oracle HRMS changes the record as from your effective date, but preserves the previous information. If you choose Correction, Oracle HRMS overrides the previous information with your new changes. The start and end dates of the snapshot you have corrected remain the same.
Example of Correction Versus Update
Suppose you hire two new employees, Jack Lee and Julie Summers. A few weeks later Julie gets married. At the same time you discover an error in Jack's record relating to his nationality.
You update Julie's information by setting your effective date to the date of her wedding and entering her new married status, her change of name, and new next of kin information. Her previous personal information, which was valid until her wedding, remains in her record.
You correct Jack's wrong nationality by setting your effective date to his hire date and entering the correct nationality. By choosing Correction, you put the record right, from the beginning. You should check whether there is an end date in the Effective Dates region of Jack's record. If there is, you have only corrected the first snapshot of the record. Set your effective date to the day after the end date, and make the correction again. Continue in this way until the To field is blank, indicating that you have reached the last snapshot of this record.
New Records
You cannot create a record and then update it on the same day. If you try to do this, Oracle HRMS warns you that the old record will be overridden, and then changes Update to Correction. This is because DateTrack maintains records for a minimum of a day at a time.
Future Updates
Using DateTrack, you can make future updates. For example, suppose you are relocating an employee, with six months notice. You decide to enter the relocation on the system straight away. So you set your effective date to the first day when the employee will be at the new location, and change the location on the assignment.
Later that month you promote the employee to a new grade. So you set your effective date to today's date and change the grade on the assignment. Oracle HRMS checks to see whether the record has a future update scheduled. It finds that the location changes in the future and prompts you for the type of update you now want to make. You have two choices:
Insert: This simply inserts the change before the next scheduled change. This is the correct choice for the example. The employee would be promoted from today. The future-dated relocation still takes place in six months time.
Replace: This change replaces all future-dated changes. In the example, the employee would be promoted from today. However, the record of the relocation would be completely removed from the system.
DateTrack Date Security
There is a DateTrack:Date Security user profile option, which determines whether you can change your effective date. Your system administrator sets this profile option. You can check its value on the Personal Profile Values window. There are four possible values:
-
All: You can change to any other effective date.
-
Future: You can change between today's date and any future dates.
-
Past: You can change between today's date and any past dates.
-
Present: You cannot change to a date other than today.
DateTrack Deleting Options
When you delete datetracked information, Oracle HRMS prompts you with the following options:
End Date: This ends the record on your effective date. When you re-query the record, this end date displays in the To field.
Purge: This totally removes the record from your database.
If there are any future updates to the record after your effective date, Oracle HRMS may prompt you with another two options:
All: This removes all future updates to the record. The current snapshot is valid until you make another change.
Next: This removes the next future update to the record. It then resets the current snapshot's end date to the end date of the deleted update.
You do not always see all of these options when you choose to delete. Some windows do not allow all four operations.
Setting Your Effective Date
When you log on to Oracle HRMS, your effective date is always the current date.
Additional Information: If you set the profile option DateTrack:Login Date with a value the effective date will default to this date instead of the current date.
To view information current at another date, or to make retrospective or future-dated changes, you need to change your effective date.
To set your effective date
-
Save any outstanding information you have entered or changed, then choose Alter Effective Date from the Tools menu.
-
Enter a new effective date and choose OK.
If your current window is a "top-level" window (one called directly from the Navigator), your new effective date remains in place until you reset it or exit Oracle HRMS. If your current window is not a top-level window, your new effective date only applies while you are working in the current window and any windows subsidiary to it. When you return to a top-level window, your effective date is reset to its previous value.
Note: In certain special cases, when you change your effective date on a subsidiary window, Oracle HRMS returns you to the previous window, and you may have to re-query the records you want to view or update. This protects the integrity of these records.
So long as your effective date remains different from the server date, it is displayed in the title bar of every window.
Removing an End Date
If you have mistakenly set an end date on a datetracked record, you can remove it.
To remove an end date
-
Set your effective date to the day the record ends.
-
Choose Delete Record from the Edit menu.
-
Choose the DateTrack delete option Next. This removes the next change to the record, which is the end date. Save your work.
Viewing the History of Datetracked Information
To see all the changes made to a datetracked record over time, use DateTrack History.
Note: In the second window of the DateTrack History window the From Date and To Date values are not queried directly from the Effective date fields. They are derived values, based on the other displayed columns in the Full History window. Where the other displayed columns values are the same between adjacent database rows then they are merged together into one displayed row. This feature enables you to see the data values for the fields you are interested in and when they have actually changed. The displayed rows are recalculated when the list of fields to be displayed is changed.
To view DateTrack History
-
Choose the DateTrack History icon from the Toolbar.
The DateTrack History Change Field Summary window opens. Each row shows which fields were changed on the From date.
-
Choose the Full History button if you want to open a DateTrack History folder showing the value of each field between the effective dates. The row for the current snapshot (corresponding to your effective date) is highlighted.
You can use the Folder menu to select the fields to view in the folder.
Note: It is possible to customize the information displayed in the Folder by modifying the DateTrack History view for the underlying table.
See: Customizing the Presentation of Data in a Folder, Oracle E-Business Suite User's Guide