Implementation Considerations
Overview of Implementation Considerations
This chapter contains general implementation considerations for the Audits Quality Solution. Once implemented, you will have the audits solution collection plans to collect all the information you need to initiate, conduct audits across the enterprise as well as log and track corrective actions.
Prerequisites
The following are the prerequisites to implement the audits solution:
-
Oracle Discrete Manufacturing Family Pack 1
-
Knowledge of Oracle Quality's functionality and capabilities, including Parent-Child Collection Plans (See Oracle Quality User's Guide)
Types of Audits
Audits addressed by the quality audits system are compliance based audit that measure processes in your organization according to a set standard and management based audits that focus on results that help auditors review the processes and question how they are accomplished. Following are the types of audits that you can execute:
Internal Audits within an Organization
You can initiate, track and monitor the process of an audit throughout its lifecycle within an organization. You can modify the audits solution to work with different business divisions within the organization. You can define audits for each audit area in the organization, assign auditor/audit teams, log and track corrective action throughout the lifecycle of each audit.
External Audits of Suppliers
You can conduct Audits at supplier’s locations the same way you conduct internal audits. You will have access to the supplier information and can record the findings on the basis of the suppliers to an audit questionnaire.
Audits Solution Implementation Tasks
To implement the Quality Audits solution, you will need different user roles to perform different tasks. You can identify factors that you need to consider for your organization and do the necessary modifications prior to using the audits solution. The tasks are as follows:
To implement the audit solution, the applications system administrator will copy the Audit Solution Template that is a set of parent-child collection plans using the “Copy Collection Plans” program.
After copying the solution template, the administrator modifies it to suit the business and implementation needs. The administrator can add, delete, and updates the collection elements and its values; update parent child relationships, and make certain collection elements mandatory etc. This modified template is the Master audit solution template.
The administrator will copy this Master Audit Solution to organizations where audits will be implemented.
The applications system administrator can also build audit reports using the Quality Results Report Writer or Oracle Discoverer based on the audit reporting needs of the audit system users and publish them on the company’s intranet.
The Lead Auditor will initiate the audits using the Audits menu to create an audit, enter the planned audit dates, and assign the auditors/teams for these for each audit area.
The lead auditor or the assigned auditor for a given audit and audit area, will copy the audit questions that are relevant to the audit from the audit question bank.
Depending on the roles and privileges assigned, the user enters the audit response, observations and findings related to the audit. Different menu options are available for the users to enter the information.
Based on the findings, the lead auditor initiates the necessary corrective actions.
Audit Inquiry/Reporting Tasks
Valid Values
The solution has included commonly used values for validation of some collection elements. These values can be modified to your valid values, according to your business rules. Some of these elements are listed below:
-
Audit Type
-
Audit Standard
-
Audit Status
Audits Identification
When you initiate an audit, you generate a unique ID for tracking the audit during its lifecycle.
Audits Solution Data Privileges
Use the collection plan security feature during implementation to set roles and privileges of the users of the audits solution. This would allow the users access of only the relevant data they need.
The security features use “User Groups” and “Grant Privileges” to grant or restrict the ability to enter, update, delete or view Quality Results and change plan setup.
Implementation Roadmap
The following processes flows illustrate the general flow of an audit lifecycle.
Audits Planning and Scheduling Business Flow
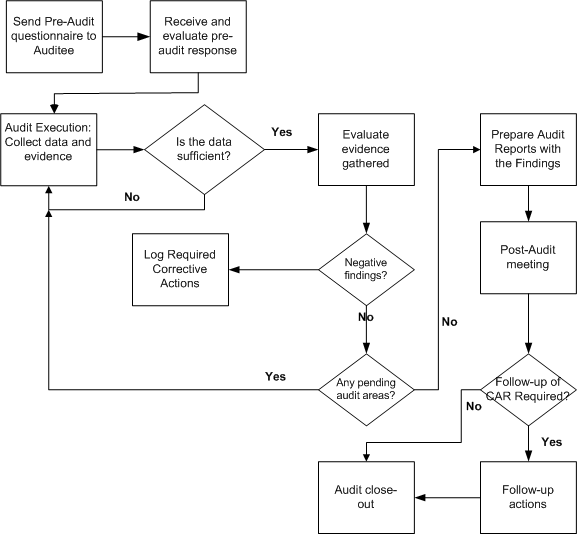
The diagram traces the audits business flow from the initiation of an audit till the audit is scheduled for execution. To implement the initiation of an audit, you will copy the Audit Solution Template provided, modify it to suit your organization's needs, assign the lead auditor, and determine the scope and policies of the audit. The lead auditor will determine the audit areas, and auditors/audit teams, prepare the plan, schedules and distribute it for the audit execution.
Audits Execution, Reporting, and Follow-up
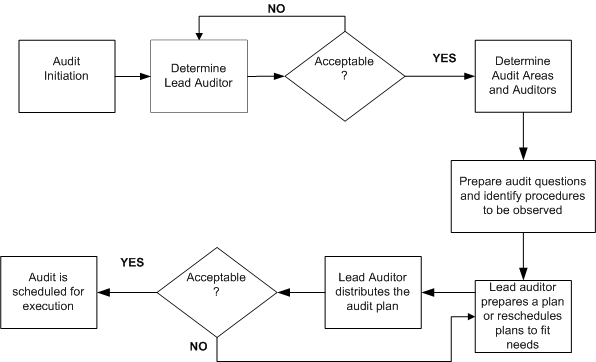
This diagram traces the audits business flow from the beginning of its execution to the close or follow-up of the audit. To execute the audit, you will send out the pre-determined questionnaire to the auditees, evaluate the responses, collect data and determine if the evidence is enough. You will also determine if there are any negative findings for which you will log corrective actions, and plan follow-up actions to see that the corrective action is implemented. If satisfied with the audit, you will close the audit.
Implementation Check List
This check list provides you with a quick reference on the process and the sequence of steps needed to implement the quality audits solution:
Prerequisites
-
Install Oracle Discrete Manufacturing Family Pack 1.
Set Up
-
Copy the Audits Solution Template using the Copy Collection program.
-
Modify the plan to suit your business needs.
-
Determine scope, policies and audit areas.
-
Identify Lead Auditor, auditors, and audit teams.
Refer to chapter 17 Setting Up for more details and the subsequent steps required for execution.
Audits Implementation
-
Initiate an internal audit within your organization.
-
Initiate an external audit of suppliers.
-
Log corrective action if necessary.
Reporting and Tailoring your Solution
-
Generate audit reports on the findings for management review.
-
Tailor your solution which includes workflow configuration and email notifications to suit your business needs.