| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle GlassFish Server Message Queue 4.5 Administration Guide |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle GlassFish Server Message Queue 4.5 Administration Guide |
Part I Introduction to Message Queue Administration
1. Administrative Tasks and Tools
3. Starting Brokers and Clients
6. Configuring and Managing Connection Services
8. Configuring Persistence Services
9. Configuring and Managing Security Services
10. Configuring and Managing Broker Clusters
11. Managing Administered Objects
12. Configuring and Managing Bridge Services
13. Monitoring Broker Operations
14. Analyzing and Tuning a Message Service
17. Broker Properties Reference
18. Physical Destination Property Reference
19. Administered Object Attribute Reference
20. JMS Resource Adapter Property Reference
21. Metrics Information Reference
22. JES Monitoring Framework Reference
A. Distribution-Specific Locations of Message Queue Data
B. Stability of Message Queue Interfaces
You can specify a broker’s configuration properties in either of two ways:
Edit the broker’s configuration file.
Supply the property values directly from the command line.
The following sections describe these two methods of configuring a broker.
Broker configuration files contain property settings for configuring a broker. Message Queue maintains the following broker configuration files:
A default configuration file (IMQ_HOME/lib/props/broker/default.properties) that is loaded on startup. This file is not editable, but you can read it to determine default settings and find the exact names of properties you want to change.
An installation configuration file (IMQ_HOME/lib/props/broker/install.properties) containing any properties specified when Message Queue was installed. This file cannot be edited after installation.
A separate instance configuration file (IMQ_VARHOME/instances/instanceName/props/config.properties) for each individual broker instance.
In addition, if you connect broker instances in a cluster, you may need to use a cluster configuration file (cluster.properties) to specify configuration information for the cluster; see Cluster Configuration Properties for more information.
Also, Message Queue makes use of en environment configuration file, imqenv.conf, which is used to provide the locations of external files needed by Message Queue, such as the default Java SE location and the locations of database drivers, JAAS login modules, and so forth.
At startup, the broker merges property values from the various configuration files. As shown in Figure 4-1, the files form a hierarchy in which values specified in the instance configuration file override those in the installation configuration file, which in turn override those in the default configuration file. At the top of the hierarchy, you can manually override any property values specified in the configuration files by using command line options to the imqbrokerd command.
Figure 4-1 Broker Configuration Files
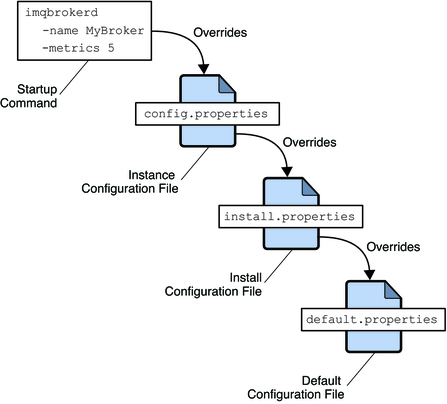
The first time you run a broker, an instance configuration file is created containing configuration properties for that particular broker instance. The instance configuration file is named config.properties and is located in a directory identified by the name of the broker instance to which it belongs:
IMQ_VARHOME/instances/instanceName/props/config.propertiesIf the file does not yet exist, you must use the -name option when starting the broker (see Broker Utility) to specify an instance name that Message Queue can use to create the file.
Note - The instances/instanceName directory and the instance configuration file are owned by the user who initially started the corresponding broker instance by using the imqbrokerd —name brokerName option. The broker instance must always be restarted by that same user.
The instance configuration file is maintained by the broker instance and is modified when you make configuration changes using Message Queue administration utilities. You can also edit an instance configuration file by hand. To do so, you must be the owner of the instances/instanceName directory or log in as the root user to change the directory’s access privileges.
The broker reads its instance configuration file only at startup. To effect any changes to the broker’s configuration, you must shut down the broker and then restart it. Property definitions in the config.properties file (or any configuration file) use the following syntax:
propertyName=value [ [,value1] … ]For example, the following entry specifies that the broker will hold up to 50,000 messages in memory and persistent storage before rejecting additional messages:
imq.system.max_count=50000The following entry specifies that a new log file will be created once a day (every 86,400 seconds):
imq.log.file.rolloversecs=86400See Broker Services and Chapter 17, Broker Properties Reference for information on the available broker configuration properties and their default values.
You can enter broker configuration properties from the command line when you start a broker, or afterward.
At startup time, you use the Broker utility (imqbrokerd) to start a broker instance. Using the command’s -D option, you can specify any broker configuration property and its value; see Starting Brokers and Broker Utility for more information. If you start the broker as a Windows service, using the Service Administrator utility (imqsvcadmin), you use the -args option to specify startup configuration properties; see Service Administrator Utility.
You can also change certain broker configuration properties while a broker is running. To modify the configuration of a running broker, you use the Command utility’s imqcmd update bkr command; see Updating Broker Properties and Broker Management.