Appendix B Defining Security Policies
Once established, SunScreen controls access to the network through a set of rules and interface definitions that you create in the administration GUI. This appendix describes issues to consider before installing SunScreen. Included are directions and worksheets to help you analyze and define your company's security policy requirements. See the SunScreen 3.2 Administrator's Overview manual for more information. See the SunScreen 3.2 Configuration Examples document to better understand what you need to define for your security policy.
Topics covered include
Before installing SunScreen, review the SunScreen 3.2 Release Notes for the latest product information.
Determining Your Security Policy
Before installing the SunScreen software, determine your network security policy. For a more thorough discussion of this topic, read Computer Security Policies and SunScreen Firewalls by Kathryn M. Walker and Linda Croswhite Cavanaugh from Sun Microsystems Press, Prentice Hall, 1998, ISBN 0130960150. This book and additional resources are listed in the Preface.
General considerations when creating a security policy are:
-
What services do employees need to access?
-
What services do customers need to access?
-
Will you allow Internet access and, if so, what services do users need to access?
-
What type of threat are you trying to protect your company from?
-
Do you need to use network address translation (NAT)?
-
Do you need to use proxies?
Mapping Your Network Configuration
Prior to installing the SunScreen software, make a map of your network. This can help you identify any potential security problems inherent in the way the network is currently connected. A diagram of your network can aid installation and should include:
-
Routers to the Internet
-
FTP, WWW or TELNET servers
-
Remote networks
-
Internal subnetworks
-
Your high availability (HA) configuration
-
Proxy services you plan to run
The following figure is an example of various types of addresses that you can use as a reference when completing your own network map.
Figure B-1 Example of a Network Map
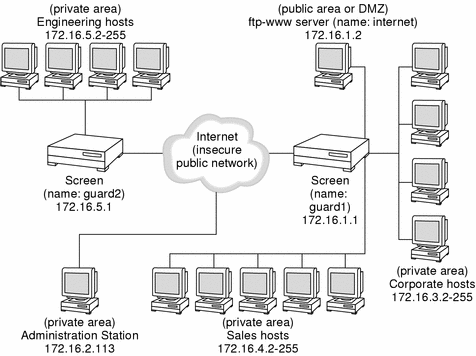
This figure includes the following examples of different types of addresses:
-
The Internet is an example of a group of addresses, in this case defined as all.
-
The ftp-www server is an example of a single host address (172.16.1.2).
-
Corporate, Sales, and the Engineering hosts are examples of ranges of addresses. For example, the range of addresses in the engineering hosts, 172.16.5.2 with the netmask 255.255.255.0, is defined as a range of addresses from 171.16.5.2 to 172.16.5.255.
Deciding on Your Initial Security Level
You must determine your initial level of security. There are three possible security levels when installing SunScreen in routing mode. (Installation in stealth mode automatically uses the Restrictive security level.) Each security level corresponds to a different set of network services permitted to, from, and through the Screen. If you are in doubt about which security level to select for the initial configuration, use a more permissive security mode. You can always use the administration GUI to change the rules to be more secure later.
Security Levels
The security levels are:
-
Restrictive - This level of security denies all traffic to, from, and through the Screen except encrypted administration traffic. This level is best for deploying the Screen in a hostile network environment. Static routing and the naming service must be configured on the host (that is, names must be resolved by means of a local hosts file).
-
Secure - This level of security denies all traffic to and through the Screen except encrypted administration traffic. It allows common services (like NFS) from the Screen, naming service selection (such as DNS and NIS), and routing (RIP). This level is a good starting point to get a Screen up and running on a friendly network, where the Screen may not be a standalone system and may depend on NIS, DNS, or NFS to function properly.
-
Permissive - This level allows the same traffic as the Secure level. It also allows inbound connections to the Screen itself and allows all traffic through the Screen. This security level is appropriate for installing the Screen on a system that has multiple network interfaces and is acting as a router, or on a system that is acting as a server (for example, for NFS, NIS, or HTTP). Permissive is the default level.
Naming Services
You must also choose which naming service to use. You may choose one (NIS or DNS), both (NIS and DNS), or no naming service. Selection of NIS, DNS, or both NIS and DNS allows the name service packets to pass to the Screen. To use a local host file, deselect both services.
Interfaces
In routing mode, SunScreen automatically configures all plumbed interfaces to filter. In stealth mode, only the administrative port is plumbed and after installation, you must configure all filtering interfaces using the SunScreen administration GUI. Stealth interfaces must not be configured in the Solaris operating environment.
Once the following preparation criteria are met, continue to the appropriate chapter for your particular installation.
Worksheets for Defining Your Security Policy
This section contains directions and worksheets to help you analyze and define your security policy requirements.
See the SunScreen 3.2 Administrator's Overview manual for more information. You can also find useful examples in the SunScreen 3.2 Configuration Examples.
To begin the process, create a group of all the IP addresses of which the SunScreen software needs to be aware. SunScreen identifies network elements--network, subnetworks, and individual hosts--by IP address. Before you can define a rule, you must define all the elements or parts that make up the rule.
Addresses
The following types of addresses need to be defined in SunScreen:
-
Host addresses
-
Address ranges
-
Address groups
SunScreen uses IP addresses to define the network elements that make up the configuration. These addresses are then used in defining the Screen's network interfaces and as the source and destination addresses for filtering rules and NAT.
The IP address can be for a single system, or for a whole network or subnetwork. Additionally, addresses (individual and network) can be grouped to form an address group. SunScreen allows you to define address groups that specifically include or exclude other defined addresses (single IP hosts, ranges, or groups).
Use the following worksheets to help you organize your IP addresses. Reproduce them as necessary. Group the IP addresses and names for the following network elements:
-
A single system, or a whole network or subnetwork
-
Addresses (individual and network) grouped to form an address group
Host Addresses
Use the Host Addresses worksheet to list your host addresses. For individual elements, such as the router and individual systems, you need to know the IP address, in standard dotted Internet-address notation (w.x.y.z format), and the name of the host.
|
Name |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Address Ranges
Use the Address Ranges worksheet to list your address ranges. For networks and subnetworks, you need to know the beginning and ending addresses of the network or subnetwork, both in standard dotted Internet-address notation (w.x.y.z format).
|
Name |
Address |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Beginning |
Ending |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Address Group
Use the Address Group worksheet to list your address group. Groups of host addresses, network addresses, and other address groups can be combined to form logical groups of addresses that can then be manipulated as a single element. Groups can be inclusive or exclusive or a combination of both, but cannot be cyclic, as in cases where address group A includes (references) address group B, which in turn includes address group A.
|
Name |
Address |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Include |
Exclude |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NAT
Network address translation (NAT) enables you to map from unregistered addresses to registered addresses allocated by your Internet service provider (ISP). The NAT function in SunScreen uses this translation to replace the IP addresses in a packet with other IP addresses. This allows you to use unregistered addresses to number your internal networks and hosts and yet have full connectivity to the Internet. Using this approach with a small Class C network, which supports only 254 hosts (externally), you can use a private Class B network, which supports as many as 65,000 hosts or 255 networks of 254 hosts (internally).
The following worksheets include:
-
NAT map
-
Screen's interfaces
-
Authorized users
-
Administration Stations
NAT Map
Use the NAT Map worksheet to list type, address, and the translated address.
-
Type, either static or dynamic
-
Address, both source and destination
-
Translated address, both source and destination
|
Type |
Address |
Translated Address |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Static Dynamic |
Source |
Destination |
Source |
Destination |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Screen Interfaces
Use the Screen Interfaces worksheet to list:
-
Type
-
Interface name
-
Group address
-
Logging details, including SNMP alerts, logging, and ICMP rejects
|
Logging Details |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Type |
Interface Name |
Group Address |
SNMP Alert |
Logging |
ICMP Reject |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Authorized Users
Use the Authorized Users worksheet to list:
-
Name
-
Authorized user
-
Details
|
Name |
Authorized User |
Details |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Administration Stations
Use the Administration Station Interface worksheet to list:
-
Name of certificate associated with Administration Station
-
Address of the Administration Station
-
Key algorithm
-
Data algorithm
-
MAC algorithm
-
Admin user name
-
Access level
|
Name of Certificate Associated With Admin Station |
Address of Admin Station |
Key Algorithm |
Data Algorithm |
MAC Algorithm |
Admin User Name |
Access Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rules
You use rules to control access to your computer network and to control encryption for access to your data. In preparing to implement rules, you must determine:
-
The overall services that are available on your network
-
The services available to a particular user or host and user groups over particular IP addresses
-
The correct action for the services and addresses for that user or host
Note -
By default, the Screen drops any packets that do not specifically match a rule. This means you can more easily create rules, since you only have to write a rule for the services you want to pass.
Use the Rules worksheet to organize the individual rules you want to use. Space is provided for you to create your own service groups. Make copies of the worksheet, as necessary.
Following the Rules worksheet is a completed sample of a worksheet that includes the requisite services that you may want for a particular network.
|
Ordered Rule Index |
Service or Service Group |
Source Address |
Destination Address |
Action |
Encryption |
User or Groups of Users (Optional) |
Time of Day (Optional) |
Screen (Optional) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ordered Rule Index |
Service or Service Group |
Source Address |
Destination Address |
Action |
Encryption |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
ftp |
Internal-net |
Internet |
ALLOW |
NONE |
|
2 |
ftp |
* |
ftp Server |
ALLOW |
NONE |
|
3 |
ftp |
Internet |
Internal-net |
DENY |
NONE |
Four Action Types
The following shows the four action types: ALLOW, DENY, ENCRYPT, and SECURE.
-
ALLOW options:
-
LOG_NONE
-
LOG_SUMMARY
-
LOG_DETAIL
-
SNMP_NONE
-
SNMP
-
A proxy type can be chosen if the service can be proxied by one of the SunScreen proxies.
-
-
DENY options:
-
LOG_NONE
-
LOG_SUMMARY
-
LOG_DETAIL
-
SNMP_NONE
-
SNMP
-
ICMP_NONE
-
ICMP_NET_UNREACHABLE
-
ICMP_HOST_UNREACHABLE
-
ICMP_PORT_UNREACHABLE
-
ICMP_NET_FORBIDDEN
-
ICMP_HOST_FORBIDDEN
-
-
ENCRYPT options:
-
NONE
-
SKIP_Version_1 (for connection to a SunScreen SPF-100 system only)
You must decide on:
-
SKIP_Version_2 (for connection to all other SKIP-enabled devices) (Optional: Tunnel addresses are allowed)
You must decide on:
-
Manual IPsec
-
Forward ESP
-
Forward AH
-
Reverse ESP
-
Reverse AH
Note -Forward and Reverse can be set the same or different. This is designated on the administration GUI by the Asymmetric and Symmetric options.
-
Transport or Tunnel Mode
-
Optional:
-
Source Screen (object)
-
Destination Screen (object)
-
Source Tunnel
-
Destination Tunnel
-
-
-
Solaris IKE
-
-
VPN options:
This option is selected only when forming VPN rules using the previously defined VPN gateways.
After you define and map out your network and decide on your security policy, use data objects, such as services and addresses, to configure SunScreen with the policy rules to control access to your network. At installation, the SunScreen software automatically creates a policy named Initial that you can use to build your own security policies.
Additional information on creating security policies can be found at: http://www.sun.com/software/white-papers/wp-security-devsecpolicy/
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
