Appendix A Generic Data Services
This appendix provides information on the generic data service (GDS) and shows you how to create a service that uses GDS using either the command line interface or the SunPlexTM Agent Builder.
Generic Data Service Overview
A generic data service (GDS) is a mechanism for making simple applications highly available or scalable by plugging them into the Sun Cluster's Resource Group Management framework. This mechanism does not require the coding of an agent which is the typical approach for making an application highly available or scalable.
The Generic Data Service (GDS) is a single, precompiled data service that you can use to make various applications highly available or scalable. In this approach, the precompiled data service and its components, the callback method implementations and the RTR file, are not subject to change.
The GDS model is especially attractive to people who develop custom HA solutions. With the GDS model, developers are able to separate the user modifiable components from the unchangeable ones and thus are able to better diagnose problems on a customer site.
Precompiled Resource Type
The generic data service resource type, SUNW.gds, is included in the SUNWscgds package. The scinstall utility installs this package on the cluster during cluster installation. The SUNWscgds package includes the following files:
# pkgchk -v SUNWscgds /opt/SUNWscgds /opt/SUNWscgds/bin /opt/SUNWscgds/bin/gds_monitor_check /opt/SUNWscgds/bin/gds_monitor_start /opt/SUNWscgds/bin/gds_monitor_stop /opt/SUNWscgds/bin/gds_probe /opt/SUNWscgds/bin/gds_svc_start /opt/SUNWscgds/bin/gds_svc_stop /opt/SUNWscgds/bin/gds_update /opt/SUNWscgds/bin/gds_validate /opt/SUNWscgds/etc /opt/SUNWscgds/etc/SUNW.gds |
Methods of Creating a Service Using GDS
There are 2 methods of creating a service that uses GDS:
-
GDS using the command line interface
-
GDS using the SunPlex Agent Builder
GDS and the Command Line Interface
This method utilizes the precompiled data service code in SUNWscgds but requires that the developer use the command line interface (scrgadm and scswitch) to enter the parameters required to create and configure the resource.
GDS and the SunPlex Agent Builder
Use the SunPlex Agent Builder and select GDS to generate the driving scripts which rely on the precompiled code being available in SUNWscgds. The user input is used to generate a set of driving scripts that configure resources for the given application.
How to Select Which Method to Use to Create a GDS
As shown in the procedures "Command Line Interface to Create a Highly Available Service Using GDS" and "Command Line Interface to Create a Scalable Service Using GDS", a significant amount of typing is required to issue the appropriate scrgadm commands.
Using GDS with SunPlex Agent Builder simplifies the process since the precompiled binaries are used and there is significant less typing of input information.
Mandatory Inputs
The start command launches the application. It should be a UNIX command complete with its arguments that is acceptable by pmfadm. For network aware (or client-server) applications, the command to launch the application may contain the hostname (or IP address) it's going to listen on. In this case, the user has to configure the LogicalHostname or SharedAddress resources separately. The GDS start method launches the application under the control of Process Monitoring Facility (PMF) using the start command.
Optional Inputs
The optional inputs to GDS include the following:
-
Stop command
-
Probe command
-
Timeout for start method
-
Timeout for stop method
-
Timeout for fault monitor probe
-
Child monitor level (only with GDS using command line interface)
Stop Command
The stop command is supposed to stop the application and not return until the application has been completely stopped. It should be a UNIX command complete with its arguments that is acceptable by hatimerun.
If the stop command is provided, the GDS stop method launches the stop command with 80% of the timeout. Regardless of the outcome of launching the stop command, the GDS stop method still sends SIGKILL with 15% of the stop timeout. The remaining 5% of the time is assumed to have been used by the house keeping overhead.
If the stop command is omitted, the GDS tries to stop the application using signals. GDS first sends SIGTERM with 80% of the stop timeout. If the SIGTERM fails to stop the application, GDS then sends SIGKILL with 15% of the stop timeout. The remaining 5% of the time is assumed to have been used by the house keeping overhead.
Probe Command
The probe command checks the health of the given application. It should be a UNIX command complete with its arguments that is acceptable by hatimerun. The exit status of the probe command is used to determine the severity of the failure of the application. This exit status, called probe status, must be an integer between 0 (for success) and 100 (for complete failure). The probe status is used with in the GDS probing algorithm to take the decision of restarting the application locally, versus failing it over to another node.
If the probe command is omitted and the application uses network, GDS provides its own simple probe. This alternative probe simply connects to the application on the given hostname and port number. If the connect succeeds, it disconnects immediately. If both connect and disconnect succeed, the application is deemed to be running healthily.
Note -
The probe provided with GDS is only intended to be a simple substitute for the fully functioning application specific probe.
Start Method Timeout
The default timeout for the start method is 300 seconds.
Stop Method Timeout
The default timeout for the stop method is 300 seconds.
Fault Monitor Probe Timeout
The default timeout for the fault monitor probe is 30 seconds.
Child Monitor Level
This option provides more control over what level of processes get monitored through PMF. It denotes the level up to which the forked children processes have to be monitored. This is the -C argument to the pmfadm command. See the pfmadm(1M) man page for more details.
Note -
This option can only be specified using the command line interface. This option cannot be specified if you are using the SunPlex Agent Builder.
Using the Command Line to Create a Service Using GDS
In this section we describe how the above mentioned parameters would actually be input to the GDS. The GDS will be used and administered using the existing Sun Cluster administrative commands, such as scrgadm(1M) and scswitch(1M).
Command Line Interface to Create a Highly Available Service Using GDS
-
Register the resource type SUNW.gds.
# scrgadm -a -t gds
-
Create the resource group containing the LogicalHostname resource and the failover service itself.
# scrgadm -a -g haapp_rg
-
Create the resource for the LogicalHostname resource.
# scrgadm -a -L -g haapp_rs -l hhead
-
Create the resource for the failover service itself.
# scrgadm -a -j haapp_rs -g haapp_rg -t SUNW.gds \ -y Scalable=false -y Start_timeout=120 \ -y Stop_timeout=120 -x Probe_timeout=120 \ -x Start_command="/usr/local/ha/appctl start" \ -x Stop_command="/usr/local/ha/appctl stop" \ -x Probe_command="/usr/local/app/bin/probe" \ -x Child_mon_level=0 -y Network_resources_used=hhead
Note -See "Start Command Arguments" for information on issuing the start command.
-
Bring the resource group haapp_rg online.
# scswitch -Z -g haapp_rg
Command Line Interface to Create a Scalable Service Using GDS
-
Register the resource type SUNW.gds.
# scrgadm -a -t gds
-
Create the resource group for the SharedAddress resource
.
# scrgadm -a -g sa_rg
-
Create the SharedAddress resource on sa_rg.
# scrgadm -a -S -g sa_rg -l hhead
-
Create the resource group for the scalable service.
# scrgadm -a -g app_rg -y Maximum_primaries=2 \ -y Desired_primaries=2 -y RG_dependencies=sa_rg
-
Create the resource group for the scalable service itself.
# scrgadm -a -j app_rs -g app_rg -t SUNW.gds \ -y Scalable=true -y Start_timeout=120 \ -y Stop_timeout=120 -x Probe_timeout=120 \ -x Start_command="/usr/local/app/bin/start" \ -x Stop_command="/usr/local/app/bin/stop" \ -x Probe_command="/usr/local/app/bin/probe \ -x Child_mon_level=0 -y Network_resource_used=hhead
Note -See "Start Command Arguments" for information on issuing the start command.
-
Bring the resource group containing the network resources online.
# scswitch -Z -g sa_rg
-
Bringing the resource group app_rg online.
# scswitch -Z -g app_rg
Start Command Arguments
The arguments to the start script will vary according to the type of resource. Check the customized man page or run the start script without any argument to get a usage statement.
# /opt/NETapp/util/startapp The resource name of LogicalHostname or SharedAddress must be specified. For failover services: Usage: startapp -h <logical host name> -p <port and protocol list> [-n <nafogroup/adapter list>] [-v] For scalable services: Usage: startapp -h <shared address name> -p <port and protocol list> [-l <load balancing policy>] [-n <nafogroup/adapter list>] [-w <load balancing weights>] [-v] For stand-alone (non-network aware applications): Usage: startapp [-v] |
Using the SunPlex Agent Builder to Create a Service Using GDS
You can use the SunPlex Agent Builder to create the service that uses GDS. See the Sun Cluster 3.0 12/01 Data Services Developer's Guide for information on the SunPlex Agent Builder as well as a definition of the fields.
Create a Service Using GDS in the SunPlex Agent Builder
Creating a Service Using GDS in the Agent Builder
-
Bring up the SunPlex Agent Builder.
# /usr/cluster/bin/scdsbuilder
-
The SunPlex Agent Builder panel appears.
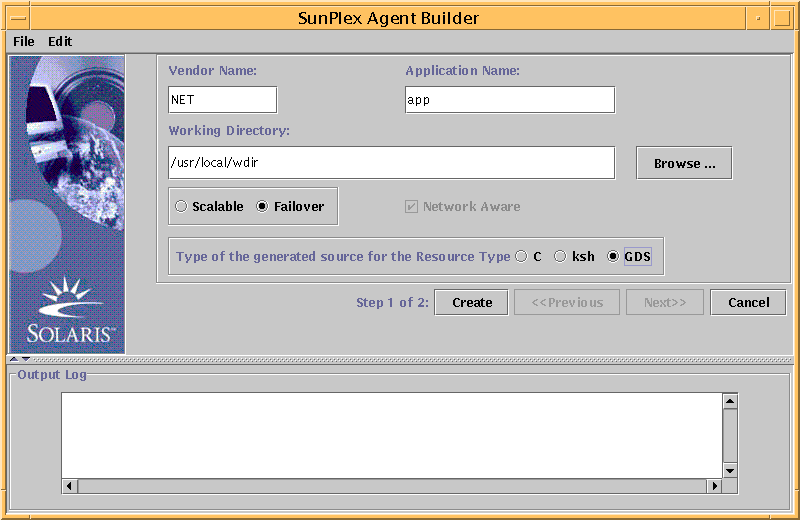
-
Enter the Vendor Name.
-
Enter the Application Name.
Note -The combination of Vendor and Application Name may not contain more than nine characters. It will be used as the name of the package for the driving scripts.
-
Enter the Working Directory. You can use the Browse pull-down to select the directory rather than typing the path.
-
Select whether the data service is scalable or failover.
-
You do not need to select Network Aware since that is the default when creating GDS.
-
Select GDS.
-
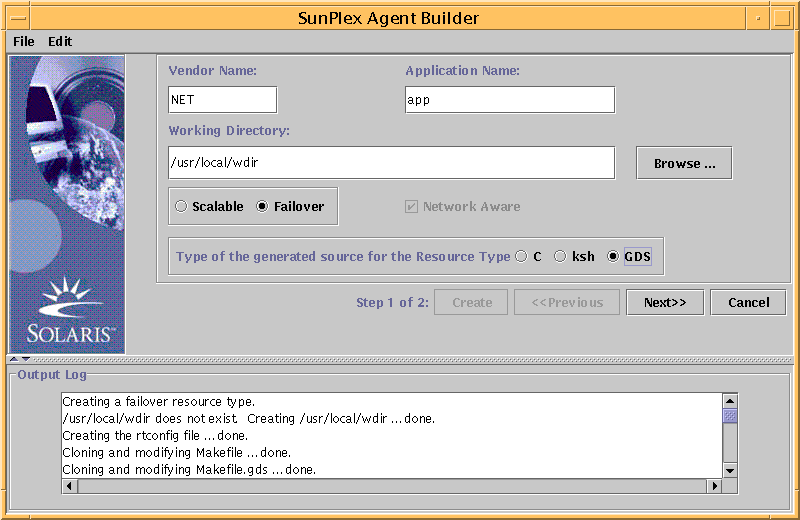
Click the Create button to create the driving scripts.
The SunPlex Agent Builder panel displays the results of the creation of the service. The Create button is grayed out and the Next button is now available.
Configuring the Driving Scripts of the Service
After creating the driving scripts, you need to use the SunPlex Agent Builder to configure the new service.
-
Click the Next button and the configuration panel appears.
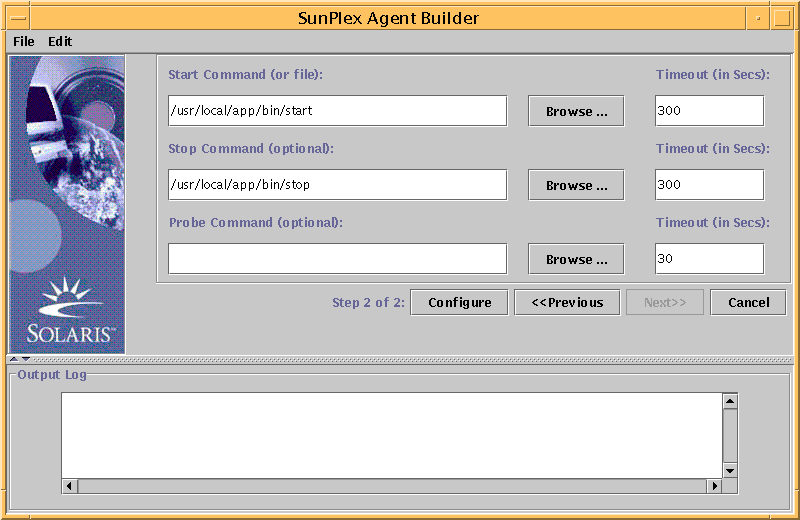
-
Either enter the location of the Start command or use the browse button to locate the Start command.
-
(Optional) Enter the Stop command or use the browse button to locate the Stop command.
-
(Optional) Enter the Probe command or use the browse button to locate the Probe command.
-
(Optional) Specify the timeout values for the Start, Stop, and Probe commands.
-
Click Configure to start the configuration of the driving scripts.
Note -The package name will consist of a concatenation of the Vendor Name and Application Name.
A package for driving scripts will be created and placed in the following file:
<working-dir>/<vendor_name><application>/pkg
For example, /usr/local/wdir/NETapp/pkg.
-
Install the completed package on both nodes of the cluster.
# cd /usr/local/wdir/NETapp/pkg # pkgadd -d . NETapp
-
The following files will be installed during the pkgadd:
/opt/NETapp /opt/NETapp/README.app /opt/NETapp/man /opt/NETapp/man/man1m /opt/NETapp/man/man1m/removeapp.1m /opt/NETapp/man/man1m/startapp.1m /opt/NETapp/man/man1m/stopapp.1m /opt/NETapp/man/man1m/app_config.1m /opt/NETapp/util /opt/NETapp/util/removeapp /opt/NETapp/util/startapp /opt/NETapp/util/stopapp /opt/NETapp/util/app_config
Note -The man pages and script names will correspond to the Application Name you entered above preceded by the script name; for example, startappname.
To view the man pages, you need to specify the path to the man page. For example, to view the startapp man pages, use the following command:
% man -M /opt/NETapp/man startapp
-
On one node of the cluster, configure the resources and start the application.
# /opt/NETapp/util/startapp -h logichostname \ -p port-and-protocol-list
The arguments to the start script will vary according to the type of resource: failover or scalable. Check the customized man page or run the start script without any argument to get a usage statement.
# /opt/NETapp/util/startapp The resource name of LogicalHostname or SharedAddress must be specified. For failover services: Usage: startapp -h <logical host name> -p <port and protocol list> [-n <nafogroup/adapter list>] [-v] For scalable services: Usage: startapp -h <shared address name> -p <port and protocol list> [-l <load balancing policy>] [-n <nafogroup/adapter list>] [-w <load balancing weights>] [-v] For stand-alone (non-network aware applications): Usage: startapp [-v]
Output from SunPlex Agent Builder
The SunPlex Agent Builder generates three driving scripts based on input you provide during package creation as well as a configuration file. The configuration files specify the names of the resource group and resource type.
Customizable Driving Scripts
The following are the driving scripts:
-
Start script: Used to configure the resources and start the application under cluster control
-
Stop script: Used to stop the application and take down resources and resource groups
-
Remove script: Used to remove the resources and resource groups created by the start script
You can customize these scripts to provide your own names for resource groups or other parameters that are normally given as inputs to the scrgadm command. If you do not customize the scripts, the driving scripts will provide reasonable defaults for the scrgadm parameters.
Configuration File for an HA Service
Following is a sample configuration file for a highly available service. The default name for the resource group and resource application are applicationname-hars and applicationname-harg where applicationname is the name of the application that you specified to the SunPlex Agent Builder.
You can modify these names if you want to use an existing resource group. You must make any required changes before you run the start script. Open the configuration file using your favorite editor and make the changes.
# # Parameter file for application generated by SunPlex Data Service # Builder # # This file will be sourced in by startapp, stopapp and removeapp # The parameters listed below will be used in those scripts. # These parameters can be customized in (key=value) form # # RS_NAME: name of the resource for the application # RG_NAME: name of the resource group containing RS_NAME # MAXIMUM_PRIMARIES: Maximum primaries of RG_NAME # DESIRED_PRIMARIES: Desired primaries of RG_NAME # # For example: # # RS_NAME=rs_app # RG_NAME=rg_app # MAXIMUM_PRIMARIES=1 # DESIRED_PRIMARIES=1 # RS_NAME=app-hars RG_NAME=app-harg MAXIMUM_PRIMARIES=1 DESIRED_PRIMARIES=1 |
Configuration File for Scalable Services
Following is a sample configuration file for a scalable service. The default names for the resource application and resource group are applicationname-sars and applicationname-sarg where applicationname is the name of the application that you specified to the SunPlex Agent Builder. The name of the SharedAddress resource is the concatenation of sa-rg- and the name of the SharedAddress.
You can modify these names if you want to use an existing resource group or SharedAddress. You must make any required changes before you run the start script.
Open the configuration file using your favorite editor and make any required changes.
#
# Parameter file for application generated by SunPlex Data Service # Builder
#
# This file will be sourced in by startecho, stopecho and removeecho
# The parameters listed below will be used in those scripts.
# These parameters can be customized in (key=value) form
#
# RS_NAME: name of the resource for the application
# RG_NAME: name of the resource group containing RS_NAME
# SA_RG_NAME: the resource group containing the Shared Address resource
# MAXIMUM_PRIMARIES: Maximum primaries of RG_NAME
# DESIRED_PRIMARIES: Desired primaries of RG_NAME
#
# For example:
#
# RS_NAME=rs_echo
# RG_NAME=rg_echo
# SA_RG_NAME=sa_rg
# MAXIMUM_PRIMARIES=4
# DESIRED_PRIMARIES=4
#
RS_NAME=echo-sars
RG_NAME=echo-sarg
SA_RG_NAME=sa-rg-${HOSTNAME}
MAXIMUM_PRIMARIES=${NO_OF_NODES}
DESIRED_PRIMARIES=${NO_OF_NODES}
|
Command Line Equivalent of the SunPlex Agent Builder
You can use the command line interface to create a service that uses DGS that is the equivalent of using the SunPlex Agent Builder.
Creating A Service that Uses GDS Using the Command Line Equivalent of the SunPlex Agent Builder
-
Create the service.
For a failover service, use the following command:
# scdscreate -g -V NET -T app -d /usr/local/wdir
For a scalable service, use the following command:
# scdscreate -g -s -V NET -T app -d /usr/local/wdir
Note -The -d parameters are optional. If it is not specified, the working directory defaults to the current directory.
-
Configure the service.
# scdsconfig -s "/usr/local/app/bin/start' \ -t "/usr/local/app/bin/stop" \ -m "/usr/local/app/bin/probe" \ -d /usr/local/wdir
Note -Only the start command is required. All other parameters are optional.
-
Install the completed package on both nodes of the cluster.
# cd /usr/local/wdir/NETapp/pkg # pkgadd -d . NETapp
-
The following files will be installed during the pkgadd:
/opt/NETapp /opt/NETapp/README.app /opt/NETapp/man /opt/NETapp/man/man1m /opt/NETapp/man/man1m/removeapp.1m /opt/NETapp/man/man1m/startapp.1m /opt/NETapp/man/man1m/stopapp.1m /opt/NETapp/man/man1m/app_config.1m /opt/NETapp/util /opt/NETapp/util/removeapp /opt/NETapp/util/startapp /opt/NETapp/util/stopapp /opt/NETapp/util/app_config
Note -The man pages and script names will correspond to the Application Name you entered above preceded by the script name; for example, startappname.
To view the man pages, you need to specify the path to the man page. For example, to view the startapp man pages, use the following command:
% man -M /opt/NETapp/man startapp
-
On one node of the cluster, configure the resources and start the application.
# /opt/NETapp/util/startapp -h logichostname \ -p port-and-protocol-list
The arguments to the start script will vary according to the type of resource: failover or scalable. Check the customized man page or run the start script without any argument to get a usage statement.
# /opt/NETapp/util/startapp The resource name of LogicalHostname or SharedAddress must be specified. For failover services: Usage: startapp -h <logical host name> -p <port and protocol list> [-n <nafogroup/adapter list>] [-v] For scalable services: Usage: startapp -h <shared address name> -p <port and protocol list> [-l <load balancing policy>] [-n <nafogroup/adapter list>] [-w <load balancing weights>] [-v] For stand-alone (non-network aware applications): Usage: startapp [-v]
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
