Installing and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server
This chapter explains how to install and configure Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server.
This chapter contains the following procedures:
-
How to Modify the Installation for a Scalable SAP Web Application Server Component
-
How to Enable the SAP Web Application Server to Run in a Cluster
-
How to Verify That the Configuration for the SAP Message Server Is Correct for the Data Service
-
How to Verify the Installation and Configuration of the SAP J2EE Engine
-
How to Register and Configure HAStoragePlus Resources for the SAP Central Services Components
-
How to Register and Configure an SAP Enqueue Server Resource
-
How to Register and Configure an SAP Replica Server Resource
-
How to Register and Configure an SAP Message Server Resource
-
How to Register and Configure an SAP Web Application Server Component
-
How to Verify the Operation of the Fault Monitor for the SAP Enqueue Server
-
How to Verify the Operation of the Fault Monitor for the SAP Replica Server
-
How to Verify the Operation of the Fault Monitor for the SAP Message Server
-
How to Verify the Operation of the Fault Monitor for the SAP Web Application Server Component
-
How to Verify the Installation and Configuration of Sun Cluster HA for SAP J2EE Engine
-
How to Activate Debugging for Sun Cluster HA for SAP J2EE Engine
Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server Overview
The SAP Web Application Server platform consists of the following components:
-
Relational database management system (RDBMS)
-
SAP central services, which include these servers:
-
SAP web application server component
-
One of the following:
If the configuration includes both the ABAP engine and the SAP J2EE engine, two SAP central services components exist.
See the SAP document SAP Web Application Server in Switchover Environments, UNIX Platforms for a detailed description of the SAP Web Application Server platform.
To eliminate potential single points of failure in an SAP Web Application Server platform, Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server provides fault monitoring, automatic restart, and automatic failover for the components of the SAP Web Application Server platform.
The SAP web application server component of the platform can be configured either as a failover or as a scalable data service. The other components must be configured as failover data services.
For conceptual information about failover services and scalable services, see the Sun Cluster Concepts Guide for Solaris OS.
Each component of the SAP Web Application Server platform has a data service that protects the component in a Sun Cluster configuration. See the following table.
Table 1–1 Protection of SAP Web Application Server Components by Sun Cluster Data Services|
SAP Web Application Server Component |
Data Service |
|---|---|
|
SAP enqueue server |
Resource type for SAP enqueue server in Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server. The resource type is SUNW.sapenq. |
|
SAP replica server |
Resource type for SAP replica server in Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server. The resource type is SUNW.saprepl. |
|
SAP message server |
Resource type for SAP message server in Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server. The resource type is SUNW.sapscs. |
|
SAP web application server |
Resource type for SAP web application server component in Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server. The resource type is SUNW.sapwebas. |
|
SAP J2EE engine |
The resource for the SAP Web Application Server stack that is designated for JavaTM software only. |
|
Database |
The data service for the database that you are using, for example:
|
|
NFS file system |
Sun Cluster HA for NFS. The resource type is SUNW.nfs. For more information about this data service, see Sun Cluster Data Service for Network File System (NFS) Guide for Solaris OS. |
Overview of the Installation and Configuration Process for Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server
The following table summarizes the tasks for installing and configuring Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server and provides cross-references to detailed instructions for performing these tasks. Perform the tasks in the order that they are listed in the table.
Table 1–2 Tasks for Installing and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server|
Task |
For Instructions, Go To … |
|---|---|
|
Plan the SAP Web Application Server installation |
Your SAP documentation Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS Planning the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server Installation and Configuration |
|
Install SAP Web Application Server and configure the application to run in a cluster | |
|
Verify the SAP Web Application Server installation and configuration |
Verifying the SAP Web Application Server Installation and Configuration |
|
Install the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server packages |
Installing the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server Packages |
|
Register and configure the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server data service |
Registering and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server |
|
(Optional) Use alternate project identifier (ID) | |
|
(Optional) Tune the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server fault monitors |
Tuning the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server Fault Monitors |
|
Verify the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server installation and configuration |
Verifying the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server Installation and Configuration |
|
(Optional) Activate debugging for the SAP J2EE engine |
Planning the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server Installation and Configuration
This section contains the information that you need to plan your Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server installation and configuration.
Note –
Before you begin, consult your SAP documentation for configuration restrictions and requirements that are not stated in Sun Cluster documentation or imposed by Sun Cluster software.
Configuration Restrictions
Configuration restrictions are planned and are related to design decisions. Your data service configuration might not be supported if you do not observe these restrictions.
For restrictions that apply to all data services, see the release notes for your release of Sun Cluster at http://docs.sun.com. The following configuration restriction applies only to Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server.
The following configuration restrictions apply only to Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server.
-
The maximum length of the node names depends on the SAP release. Refer to the SAP installation guide for your release of SAP. This limitation is an SAP software restriction.
-
Configure the database resource (for example, Oracle) to be in a different resource group from the SAP enqueue server resource.
However, if you are using Oracle as the database, and if you must configure Oracle in the same resource group as the SAP enqueue server resource, you must set the value of the restart_type extension property for Sun Cluster HA for Oracle to RESOURCE_RESTART. By default, the value of the restart_type extension property for a Sun Cluster HA for Oracle resource is set to RESOURCE_GROUP_RESTART. This property setting means that if the response to a fault in the Oracle database is to restart the Oracle resource, all the resources in the resource group are restarted. However, this type of restart is not permitted for the SAP enqueue server. Therefore, you must specify the RESOURCE_RESTART setting, which ensures that only the Oracle database is restarted in response to a fault.
Configuration Requirements
Configuration requirements represent actions that you must perform. If your data service configuration does not satisfy these requirements, the data service configuration might not be supported.
For requirements that apply to all data services, see “Configuration Guidelines for Sun Cluster Data Services” in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS.
The following configuration requirements apply only to Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server.
-
The fault monitor probe for the resource type of the SAP message server requires the msprot program. You must download this binary from service.sap.com. Refer to SAP note 636938 for information about obtaining and using the msprot program.
-
If you are using the SAP Web Application Server stack that is designated for Java only, the following requirement applies.
The Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server data service provides a configuration file and registration script that ensure that the SAP J2EE engine is configured correctly within Sun Cluster. The configuration file is located in /opt/SUNWscswa/util/ha_sap_j2ee_config. The registration script is located in /opt/SUNWscswa/util/ha_sap_j2ee_register. This file and this script are used during the registration and configuration of Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server.
Supported Data Service Configurations
Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server supports configurations that conform to the requirements that are specified in the previous section.
All configurations of Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server have the following requirements:
-
The SAP enqueue server is configured as a failover resource.
-
The SAP replica server is configured as a failover resource.
-
The SAP message server is configured as a failover resource.
-
The SAP web application server component can be configured either as a failover or as a scalable data service resource.
-
The SAP J2EE engine is configured as a failover resource.
-
The SAP enqueue server and the SAP message server are resources in the SAP central services resource group. The SAP replica server is a resource in the SAP replica server resource group.
-
The SAP replica server resource is configured to depend on the SAP enqueue server resource. This dependency ensures that the SAP replica server does not attempt to start until the SAP enqueue server is online.
-
The SAP central services resource group is configured to have weak positive affinity with the SAP replica server resource group. This affinity ensures that, if a hardware or software failure occurs on the node that is mastering the SAP central services resource group, the SAP central services resource group fails over to the node where the SAP replica server resource group is currently running.
-
The SAP replica server resource group is configured to have strong negative affinity with the SAP central services resource group. This affinity ensures that, if the SAP central services resource group fails over, the SAP replica server resource group is off-loaded from the node where it is currently running before the SAP central services resource group is brought online on that same node. The SAP replica server resource group is started on another node, if one is available.
The following examples show the following supported configurations of Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server.
-
The SAP web application server component is configured as a failover resource.
-
The SAP web application server component is configured as a scalable resource.
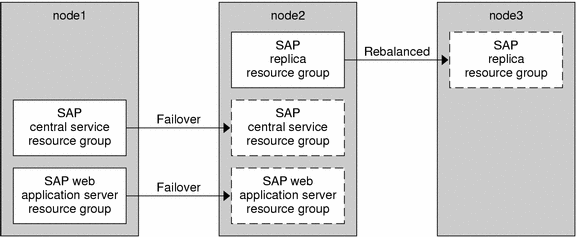
Example 1–1 SAP Web Application Server Component Configured as a Failover Resource
This example shows a standard configuration of Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server with the SAP web application server component that is configured as a failover resource.
The boxes that have a solid border represent the location of the resource groups before failover.
The boxes that have a dashed border represent the location of the resource groups after a failover because of a problem on the first node. The SAP central services resource group fails over, and the SAP replica server resource group consequently moves to another node. The SAP web application server component resource group also fails over.
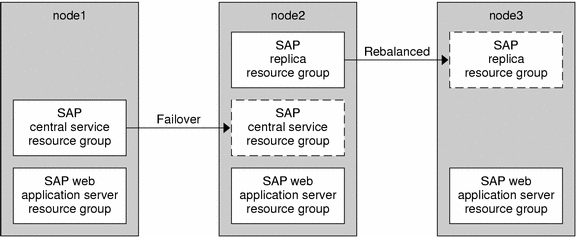
Example 1–2 SAP Web Application Server Component Configured as a Scalable Resource
This example shows a standard configuration of Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server with the SAP web application server component that is configured as a scalable resource.
The boxes that have a solid border represent the location of the resource groups before failover.
The boxes that have a dashed border represent the location of the resource groups after a failover because of a problem on the first node. As in the previous example, the SAP central services resource group fails over, and the SAP replica server resource group consequently moves to another node. Because the SAP web application server component resource group is scalable, it does not fail over, but the corresponding resource groups on the other node continue running.
Configuration Considerations
The following configuration considerations affect the installation and configuration of Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server.
-
The SAP enqueue server and SAP replica server run on different cluster nodes. Therefore, the SAP application files (binary files, configuration files, and parameter files) can be installed either on the global file system or on the local file system. However, the application files for each of these applications must be accessible at all times from the nodes on which these applications are running.
See “Configuration Guidelines for Sun Cluster Data Services” in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS. This section details the advantages and disadvantages of placing the SAP binaries on the local file system or on the cluster file system.
-
The default value of the Retry_count system property for the SAP enqueue server is 0. This value ensures that the SAP enqueue server fails over after the first failure. If replication is running, do not modify this default value because enqueue locks would be lost. When replication is in operation and the Enqueue server is restarted, even on the same node, the locks are no longer valid.
-
The resource group for the SAP web application server component can be configured to be a failover resource group or a scalable resource group. If the SAP web application server component is configured to be a scalable resource group, the directory /usr/sap/SAPSID/INSTANCE_NAME must be local on each node where the SAP web application server component is installed, as explained in How to Modify the Installation for a Scalable SAP Web Application Server Component. Note that SAPSID represents the SAP system identification and INSTANCE_NAME represents the name of the SAP web application server instance.
-
During the installation and configuration process, track any system files that you change, because you need to copy those files to all the nodes that are to run the application.
Configuration Planning Questions
Use the questions in this section to plan the installation and configuration of Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server. Write the answers to these questions in the space that is provided on the data service worksheets in “Configuration Worksheets” in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS.
-
Will you run the SAP web application server component of the application as a failover resource or as a scalable resource?
-
What resource groups will you use for network addresses and application resources and the dependencies between them?
-
What is the logical host name for clients that will access the data service?
-
Where will the system configuration files reside?
See “Configuration Guidelines for Sun Cluster Data Services” in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS for the advantages and disadvantages of placing the SAP binaries on the local file system or on the cluster file system.
Installing and Configuring SAP Web Application Server
To enable Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server to make SAP Web Application Server highly available, additional installation and configuration operations are required. These operations supplement the standard installation and standard configuration of the SAP Web Application Server.
The procedures in this section describe the installation and configuration of the following components of the SAP Web Application Server.
-
SAP central services, which include these services:
-
SAP enqueue server
-
SAP replica server
-
SAP message server
-
-
SAP web application server component
-
SAP J2EE engine
Configuring Your Highly Available Database
SAP supports various databases. You must configure the resource type, the resource group, and the resource for the database that you plan to use so that the database will be highly available. See details in the appropriate Sun Cluster Data Services document for the database that you plan to use.
-
If you plan to use SAP DB as the database, configure the Sun Cluster HA for SAP DB data service. See Sun Cluster Data Service for SAP DB Guide for Solaris OS.
-
If you plan to use Oracle as the database, configure the Sun Cluster HA for Oracle data service. See Sun Cluster Data Service for Oracle Guide for Solaris OS.
How to Install and Configure the SAP Web Application Server
-
On one node of the cluster, install the SAP Web Application Server software.
Refer to the SAP installation documentation.
-
Create profiles for the SAP enqueue server and the SAP replica server.
Refer to the SAP document SAP Web Application Server in Switchover Environments, UNIX Platforms.
Note –The SAPSYSTEM parameter in the SAP enqueue server profile and in the SAP replica server profile must have the same value.
-
Remove the startup of the SAP enqueue server from the SAP start profile.
In the Sun Cluster environment, the SAP enqueue server resource starts the SAP enqueue server application. Therefore, if the SAP start profile contains the startup of the SAP enqueue server, remove it. Otherwise, the SAP enqueue server will be started more than once.
-
If the Process Monitor Facility (PMF) is used with the SAP Web Application Server, the saposcol program must be started outside of the cluster environment so that PMF does not stop the saposcol program when it stops the resource for the SAP web application server.
The saposcol program must be available to all the nodes that are running the SAP Web Application Server. Therefore, the program must be either in a global file system or in the local file system of each node.
-
If the saposcol program is on the global file system and you want it to be on the local file systems, copy the program to the local file systems by performing the following actions on each node:
-
On the installation node, if the saposcol program was started separately, stop the saposcol program.
-
If the SAP system is running, stop the SAP system.
-
If the file system is not mounted, mount it to the installation node.
-
Copy the saposcol executable file from the installation node to a local directory on the target node.
# cp /usr/sap/SAPSID/SYS/exe/saposcol destination-directory
where SAPSID is the SAP system identification.
-
-
Remove the startup of the saposcol program from the SAP start script of the SAP web application server resource that is configured to use PMF. This action is also mentioned in Step 7, together with other modifications to the SAP start and stop scripts.
-
Start the saposcol program from the local directory on each node.
-
-
Create a script to return logical host names for the SAP message server and the SAP web application server components.
Create a script named loghost, which returns the logical host names for each instance of both the SAP message server and the SAP web application server components. The script must be located in the directory $HOME, where $HOME specifies the home directory of the SAP user.
Note –If the SAP web application server component is configured as a scalable resource, you will modify this script in a later section, How to Modify the Installation for a Scalable SAP Web Application Server Component.
Example 1–3 Creating a Script to Return Logical Host Names
if [ "$1" = "DVEBMGS00" ]; then echo loghost-1; fi if [ "$1" = "SCS01" ]; then echo loghost-2; fi if [ "$1" = "D02" ]; then echo loghost-3; fi
-
Set the file permissions for the script so that it is executable.
# chmod 755 $HOME/loghost
-
Modify the SAP start and stop scripts as follows:
-
Ensure the uniqueness of the instance names.
Add a sort -u command to the end of the line that begins with INSTANCE= in the SAP start and stop scripts. This command sorts all the instance names that are found and retains only the unique names.
The original line is the following, where arg is the argument number, for example, 1 or 2.
INSTANCE=`echo $arg | awk '/SCS[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /ASCS[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /DVEBMGS[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /JC[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /D[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /J[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /G[0-9][0-9]/{print $1}'`After you add a pipe to a sort -u command at the end, the line is the following, where arg is the argument number, for example, 1 or 2.
INSTANCE=`echo $arg | awk '/SCS[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /ASCS[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /DVEBMGS[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /JC[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /D[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /J[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /G[0-9][0-9]/{print $1}' | sort -u` -
Update the SAP start and stop scripts to call the script that returns logical host names.
In the section for setting HOSTNAME, insert the name of the script $HOME/loghost, which you created in Step 5. This action is accomplished by replacing the line HOSTNAME='hostname' with the lines in the following example.
Example 1–4 Changing the SAP Start and Stop Scripts to Call the Script to Return Logical Host Names
< remove > add # Set HOSTNAME case `uname` in OS/390* | z/OS* | AIX* | BOS*) HOSTNAME=`hostname -s` ;; *) < HOSTNAME=`hostname` > if [ $# -eq 2 ]; then > HOSTNAME=`$HOME/loghost $2` > else > HOSTNAME=`hostname` > fi ;; esac
-
In order to source the user's profile and thus also source the SAP-specific environment files, add the following line as the second line of the SAP start and stop scripts.
. $HOME/.profile
-
Remove the DB check for the SAP central services components from the SAP start script. The SAP central services components are the SAP enqueue server, the SAP replica server, and the SAP message server.
-
If PMF is used with the SAP web application server, remove the startup of the saposcol program from the SAP start script that is used by this SAP web application server. See also Step 4.
-
-
Modify the file names and contents to use logical host names instead of physical host names.
The standard SAP Web Application Server installation uses the physical host name of the node on which the SAP system is installed. You must modify SAP Web Application Server to use a logical host name so that SAP Web Application Server works in a Sun Cluster environment.
Note –If the SAP web application server component is configured as a scalable resource, you will make additional modifications in a later section, How to Modify the Installation for a Scalable SAP Web Application Server Component.
-
Remove the physical host name from the names of the “.” files in the home directory of the SAP user.
In the following example, physical-hostname represents the physical host name.
Example 1–5 Removing the Physical Host Name From File Names
# for i in .*physical-hostname.* > do > mv $i `echo $i | sed "s/_physical-hostname//"` > done
-
Change the database “.” files to refer to logical host names instead of physical host names.
-
Change the file names and contents of the profile files to use logical host names instead of physical host names.
These files are located in /usr/sap/SAPSID/SYS/profile, where SAPSID is the SAP system identification.
-
Add the following logical-host-name entries to the logical-host-name file SAPSID_INSTANCE_NAMESYSTEM_NUMBER_logical-hostname that is located in the SAP profile directory. Note that SAPSID is the SAP system identification, INSTANCE_NAME is the SAP instance name, and SYSTEM_NUMBER is the SAP system number.
SAPLOCALHOST=logical-hostname
SAPLOCALHOSTFULL=logical-hostname.domain
-
Replace the physical host name with the logical host name in the file /usr/sap/SAPSID/INSTANCE_NAME/igs/conf/igs.xml. Note that SAPSID is the SAP system identification and INSTANCE_NAME is the SAP instance name.
-
How to Modify the Installation for a Scalable SAP Web Application Server Component
The SAP web application server component of the SAP Web Application Server platform can be configured either as a failover resource or as a scalable resource.
-
If you configure the SAP web application server component as a failover resource, skip this section.
-
If you configure the SAP web application server component as a scalable resource, you must perform the following steps.
-
Install the software as described in How to Install and Configure the SAP Web Application Server.
The SAP Web Application Server software is installed on a global file system under /usr/sap/SAPSID/INSTANCE_NAME. Note that SAPSID represents the SAP system identification and INSTANCE_NAME represents the name of the SAP web application server instance.
-
Become the SAP administration user sapsidadm on each node on which you plan to run the scalable SAP web application server component resource group.
-
Update the profile file names and contents to match a string instead of a logical host name.
A scalable resource group does not contain a logical host. Therefore, if a resource group for the SAP web application server component is configured to be scalable, the script $HOME/loghost does not return a logical host name. The script returns a string, for example, “scalable” to identify the instance. Therefore, you must update the profile file names and contents to match a string, for example, “scalable”, instead of a logical host name.
-
Update the profile files for this instance in the directory /usr/sap/SAPSID/SYS/profile. Update the file names and their contents to match the string that you want to use, for example, “scalable”.
-
Update the script $HOME/loghost, as in the following example.
if [ "$1" = "D04" ]; then echo scalable; fi
-
-
On each node, including the original one, create a local file system.
# mkdir /usr/sap/local/SAPSID/INSTANCE_NAME
-
On each node, including the original one, copy the software from the global file system to the local file system that you created in Step 4.
# su - sapsidadm # cp -r /usr/sap/SAPSID/INSTANCE_NAME/* \ /usr/sap/local/SAPSID/INSTANCE_NAME
-
On the original node, remove the original installation directory.
# rm -r /usr/sap/SAPSID/INSTANCE_NAME
-
On each node, including the original one, create a symbolic link from the global file system to the local file system.
# ln -s /usr/sap/local/SAPSID/INSTANCE_NAME \ /usr/sap/SAPSID/INSTANCE_NAME
-
Update the SAP start and stop scripts with unique names for the log files.
When the SAP web application server component resource group is configured to be scalable, multiple instances of the application can be running simultaneously on different nodes. If all instances write to the same log file, they overwrite previously written information. Therefore, change the names of the log files that are specified in the SAP start and stop scripts so that they have unique names. Renaming the log files ensures that each node writes to a unique file. In the following example, the node name is appended to the log file name.
Example of entry in script before updating:
LOGFILE=$R3S_LOGDIR/`basename ${0}_${INSTANCE}.log`
Example of entry in script after updating:
LOGFILE=$R3S_LOGDIR/`basename ${0}_${INSTANCE}`_`uname -n`.log
How to Install and Configure the SAP J2EE Engine
-
On one node of the cluster, install the SAP J2EE engine software.
Refer to the SAP installation documentation.
-
Create profiles for the SAP enqueue server and the SAP replica server.
Refer to the SAP document SAP Web Application Server in Switchover Environments, UNIX Platforms.
Note –The SAPSYSTEM parameter in the SAP enqueue server profile and in the SAP replica server profile must have the same value.
-
Modify the script that returns logical host names for the SAP message server and the SAP J2EE engine.
Modify the script named loghost, which returns the logical host names for each instance of both the SAP message server and the SAP J2EE engine. The script must be located in the directory $HOME, where $HOME specifies the home directory of the SAP user.
Example 1–6 Modifying the Script to Return Logical Host Names
if [ "$1" = "DVEBMGS00" ]; then echo loghost-1; fi if [ "$1" = "SCS01" ]; then echo loghost-2; fi if [ "$1" = "D02" ]; then echo loghost-3; fi
-
Set the file permissions for the script so that it is executable.
# chmod 755 $HOME/loghost
-
Modify the SAP start and stop scripts as follows:
-
Ensure the uniqueness of the instance names.
Add a sort -u command to the end of the line that begins with INSTANCE= in the SAP start and stop scripts. This command sorts all the instance names that are found and retains only the unique names.
The original line is the following, where arg is the argument number, for example, 1 or 2.
INSTANCE=`echo $arg | awk '/SCS[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /ASCS[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /DVEBMGS[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /JC[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /D[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /J[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /G[0-9][0-9]/{print $1}'`After you add a pipe to a sort -u command at the end, the line is the following, where arg is the argument number, for example, 1 or 2.
INSTANCE=`echo $arg | awk '/SCS[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /ASCS[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /DVEBMGS[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /JC[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /D[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /J[0-9][0-9]/{print $1} /G[0-9][0-9]/{print $1}' | sort -u` -
Update the SAP start and stop scripts to call the script that returns logical host names.
In the section for setting HOSTNAME, insert the name of the script $HOME/loghost, which you created in Step 3. This action is accomplished by replacing the line HOSTNAME='hostname' with the lines in the following example.
Example 1–7 Changing the SAP Start and Stop Scripts to Call the Script to Return Logical Host Names
< remove > add # Set HOSTNAME case `uname` in OS/390* | z/OS* | AIX* | BOS*) HOSTNAME=`hostname -s` ;; *) < HOSTNAME=`hostname` > if [ $# -eq 2 ]; then > HOSTNAME=`$HOME/loghost $2` > else > HOSTNAME=`hostname` > fi ;; esac
-
In order to source the user's profile and thus also source the SAP-specific environment files, add the following line as the second line of the SAP start and stop scripts.
. $HOME/.profile
-
Remove the DB check for the SAP central services components from the SAP start script. The SAP central services components are the SAP enqueue server, the SAP replica server, and the SAP message server.
-
If PMF is used with the SAP web application server, remove the startup of the saposcol program from the SAP start script that is used by this SAP web application server.
-
-
Modify the file names and contents to use logical host names instead of physical host names.
The standard SAP J2EE engine installation uses the physical host name of the node on which the SAP system is installed. You must modify the SAP J2EE engine to use a logical host name so that the SAP J2EE engine works in a Sun Cluster environment.
-
Remove the physical host name from the names of the “.” files in the home directory of the SAP user.
In the following example, physical-hostname represents the physical host name.
Example 1–8 Removing the Physical Host Name From File Names
# for i in .*physical-hostname.* > do > mv $i `echo $i | sed "s/_physical-hostname//"` > done
-
Change the database “.” files to refer to logical host names instead of physical host names.
-
Change the file names and contents of the profile files to use logical host names instead of physical host names.
These files are located in /usr/sap/SAPSID/SYS/profile, where SAPSID is the SAP system identification.
-
Add the following logical-host-name entries to the logical-host-name file SAPSID_INSTANCE_NAMESYSTEM_NUMBER_logical-hostname that is located in the SAP profile directory. Note that SAPSID is the SAP system identification, INSTANCE_NAME is the SAP instance name, and SYSTEM_NUMBER is the SAP system number.
SAPLOCALHOST=logical-hostname
SAPLOCALHOSTFULL=logical-hostname.domain
-
Replace the physical host name with the logical host name in the file /usr/sap/SAPSID/INSTANCE_NAME/igs/conf/igs.xml. Note that SAPSID is the SAP system identification and INSTANCE_NAME is the SAP instance name.
-
-
Use the SAP configuration tool to modify the SAP J2EE engine settings to reference the logical host name.
To start the SAP configuration tool, you can use the script offlinecfgeditor.sh, which is located in the directory /usr/sap/SAPSID/JCINSTANCE_NUMBER/j2ee/configtool.
-
In the LockingManager section, modify enqu.host to refer to the logical host name for the SAP enqueue server. Check this entry under all the settings (the general and the instance-specific).
-
In the LockingManager section, modify all occurrences of enq.profile.filename to use the logical host name. For example, change SAPSID_JCINSTANCE_NUMBER_physicalhost to SAPSID_JCINSTANCE_NUMBER_logicalhost. The new file name should be the same as the file name in the file /sapmnt/SAPSID/profile.
-
In the ClusterManager section, change ms.host to refer to the logical host name for the SAP message server.
-
Ensure that the enqu.port parameter and the URL in the dbpool parameter have the correct settings.
-
How to Enable the SAP Web Application Server to Run in a Cluster
The following resource groups are created in this procedure:
-
SAP central services resource group, to contain the following resources:
-
SAP enqueue server resource
-
SAP message server resource
-
Logical host name for these resources
-
-
SAP replica server resource group, to contain the following resources:
-
SAP replica server resource
-
Logical host name for this resource
-
-
SAP web application server resource group, to contain the following resources:
-
SAP web application server component resource
-
Logical host name for this resource, if the resource is configured as a failover resource
-
Note that the procedure to enable the SAP J2EE engine to run in a cluster is located in a separate section. See How to Enable the SAP J2EE Engine to Run in a Cluster.
-
Become superuser on a cluster node.
-
Create a resource group for the SAP central services.
The SAP central services resource group is a failover resource group to contain the SAP enqueue server resource, the SAP message server resource, and the logical host name for these resources.
# scrgadm -a -g central-rg
- -a
-
Specifies that a new resource group is to be added.
- -g central-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be added. This name can be your choice but must be unique for the resource groups within the cluster.
-
Add a logical-host-name resource to the resource group that you created in Step 2.
# scrgadm -a -L -g central-rg -l central-logical-hostname [ -n netiflist]
- -a
-
Specifies that a new configuration is to be added.
- -L
-
Specifies that a logical-host-name resource is to be added.
- -g central-rg
-
Specifies the logical-host-name resource to be added to the resource group that you created in Step 2.
- -l central-logical-hostname
-
Specifies the logical-host name of the SAP central services resource.
- -n netiflist
-
Specifies a comma-separated list of network interfaces. All nodes in the node list of the resource group must be represented in the list of network interfaces. Specifying a list of network interfaces is optional. If you omit the list, an attempt is made for each node to discover a network interface on the subnet that the host-name list identifies.
-
Bring online the SAP central services resource group.
# scswitch -Z -g central-rg
- -Z
-
Specifies that a resource group is to be brought online.
- -g central-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be brought online. This name is the name of the resource group that was created in Step 2.
-
Create a resource group for the SAP replica server.
The SAP replica server resource group is a failover resource group to contain the SAP replica server resource and the logical host name for this resource.
# scrgadm -a -g repl-rg
- -a
-
Specifies that a new resource group is to be added.
- -g repl-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be added. This name can be your choice but must be unique for the resource groups within the cluster.
-
Add a logical-host-name resource to the resource group that you created in Step 5.
# scrgadm -a -L -g repl-rg -l saprepl-logical-hostname [ -n netiflist]
- -a
-
Specifies that a new configuration is to be added.
- -L
-
Specifies that a logical-host-name resource is to be added.
- -g repl-rg
-
Specifies the logical-host-name resource to be added to the resource group that you created in Step 5.
- -l saprepl-logical-hostname
-
Specifies the logical-host name of the SAP replica server resource.
- -n netiflist
-
Specifies a comma-separated list of network interfaces. All nodes in the node list of the resource group must be represented in the list of network interfaces. Specifying a list of network interfaces is optional. If you omit the list, an attempt is made for each node to discover a network interface on the subnet that the host-name list identifies.
-
Bring online the SAP replica server resource group.
# scswitch -Z -g repl-rg
- -Z
-
Specifies that a resource group is to be brought online.
- -g repl-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be brought online. This name is the name of the resource group that was created in Step 5.
-
Set weak positive affinity between the SAP central services resource group and the SAP replica server resource group.
The weak positive affinity setting ensures that, in case of failover, the SAP central services resource group fails over to the node where the SAP replica server resource group has been running.
# scrgadm -c -g central-rg -y RG_affinities=+repl-rg
- -c
-
Specifies that a resource group is to be modified
- -g central-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be modified
- -y RG_affinities=+repl-rg
-
Specifies that the central-rg resource group has weak positive affinity with the repl-rg resource group
-
If the SAP central services resource group and the SAP replica server resource group are online on the same node, switch one of them to another node.
The two resource groups must be mastered on different nodes before the strong negative affinity can be set between the resource groups.
# scswitch -z -g rg -h node
- -z
-
Specifies that a resource group is to be switched to another node.
- -g rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be switched. This resource group can be either the SAP central services resource group or the SAP replica server resource group.
- -h node
-
Specifies the node to which the resource group is to be switched.
-
Set strong negative affinity between the SAP replica server resource group and the SAP central services resource group.
The strong negative affinity setting ensures that node failover behavior is appropriate. The SAP central services resource group fails over to the node where the SAP replica server resource group has been running. The SAP replica server resource group then fails over to another available node.
The SAP replica server resource group is never brought online nor allowed to remain online on a node on which the SAP central services resource group is online.
# scrgadm -c -g repl-rg -y RG_affinities=--central-rg
- -c
-
Specifies that a resource group is to be modified
- -g repl-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be modified
- -y RG_affinities=--central-rg
-
Specifies that the repl-rg resource group has strong negative affinity with the central-rg resource group
-
Create a resource group for the SAP web application server component.
The SAP web application server resource group can be configured as a failover or scalable resource group to contain the resource for the SAP web application server component. If the SAP web application server is configured as a failover resource, the logical host name for this resource is also contained in the SAP web application server resource group.
-
To create a failover resource group, run the following command.
# scrgadm -a -g webas-rg
-
To create a scalable resource group, run the following command.
# scrgadm -a -g scalwebas-rg \ -y Maximum_primaries=value -y Desired_primaries=value
- -a
-
Specifies that a new resource group is to be added.
- -g webas-rg
-
Specifies the name of the failover resource group to be added. This name can be your choice but must be unique for the resource groups within the cluster.
- -g scalwebas-rg
-
Specifies the name of the scalable resource group to be added. This name can be your choice but must be unique for the resource groups within the cluster.
- -y Maximum_primaries=value
-
Specifies the maximum number of primary nodes for this scalable resource group.
- -y Desired_primaries=value
-
Specifies the desired number of primary nodes for this scalable resource group.
-
-
If the resource group that you created in Step 11 is configured as a failover resource group, add a logical-host-name resource to the resource group.
If the resource group that you created in Step 11 is configured as a scalable resource group, skip this step.
# scrgadm -a -L -g webas-rg -l webas-logical-hostname [ -n netiflist]
- -a
-
Specifies that a new configuration is to be added.
- -L
-
Specifies that a logical-host-name resource is to be added.
- -g webas-rg
-
Specifies the logical-host-name resource to be added to the resource group that you created in Step 11.
- -l webas-logical-hostname
-
Specifies the logical-host name of the SAP web application server component resource.
- -n netiflist
-
Specifies a comma-separated list of network interfaces. All nodes in the node list of the resource group must be represented in the list of network interfaces. Specifying a list of network interfaces is optional. If you omit the list, an attempt is made for each node to discover a network interface on the subnet that the host-name list identifies.
-
Bring online the SAP web application server resource group.
# scswitch -Z -g webas-rg
- -Z
-
Specifies that a resource group is to be brought online.
- -g webas-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be brought online. This name is the name of the resource group that was created in Step 11.
-
(Optional) Consider configuring your cluster to off-load noncritical resource groups.
You might plan to run a noncritical, lower-priority SAP web application server component resource on a node to which a critical, higher-priority SAP central services resource can fail over. In this situation, consider setting strong negative affinity between the resource groups. This setting ensures that, if a higher-priority SAP central services resource fails over to the node where a lower-priority SAP web application server component resource is running, the lower-priority resource is off-loaded, thereby automatically freeing the node's resources to be used for the critical SAP central services resource.
# scrgadm -c -g webas-rg -y RG_affinities=--central-rg
- -c
-
Specifies that a resource group is to be modified.
- -g webas-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be modified.
- -y RG_affinities=--central-rg
-
Specifies that the webas-rg resource group has strong negative affinity with the central-rg resource group. If the central-rg resource group fails over to the node where the webas-rg resource group is running, the webas-rg resource group is off-loaded.
-
Copy all system files that were changed during the SAP Web Application Server installation and configuration process to all the nodes that are to run the SAP Web Application Server resources. These files might include the following:
-
/etc/passwd
-
/etc/group
-
/etc/system
-
/etc/services
-
How to Enable the SAP J2EE Engine to Run in a Cluster
-
Create a resource group for the SAP J2EE engine.
The SAP J2EE engine resource group is a failover resource group to contain the resource for the SAP J2EE engine and the logical host name for this resource.
# scrgadm -a -g j2ee-rg
- -a
-
Specifies that a new resource group is to be added.
- -g j2ee-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be added. This name can be your choice but must be unique for the resource groups within the cluster. Use this name when configuring the SAP J2EE engine resource in Step 4 in How to Register and Configure an SAP J2EE Engine Resource.
-
Add a logical-host-name resource to the resource group that you created in Step 1.
# scrgadm -a -L -g j2ee-rg -l j2ee-logical-hostname [ -n netiflist]
- -a
-
Specifies that a new configuration is to be added.
- -L
-
Specifies that a logical-host-name resource is to be added.
- -g j2ee-rg
-
Specifies the logical-host-name resource to be added to the resource group that you created in Step 1.
- -l j2ee-logical-hostname
-
Specifies the logical-host name of the SAP J2EE engine resource. Use this name when configuring the SAP J2EE engine resource in Step 4 in How to Register and Configure an SAP J2EE Engine Resource.
- -n netiflist
-
Specifies a comma-separated list of network interfaces. All nodes in the node list of the resource group must be represented in the list of network interfaces. Specifying a list of network interfaces is optional. If you omit the list, an attempt is made for each node to discover a network interface on the subnet that the host-name list identifies.
-
Bring online the SAP J2EE engine resource group.
# scswitch -Z -g j2ee-rg
- -Z
-
Specifies that a resource group is to be brought online.
- -g j2ee-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be brought online. This name is the name of the resource group that was created in Step 1.
Verifying the SAP Web Application Server Installation and Configuration
Before you install the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server packages, verify that the SAP Web Application Server software is correctly installed and configured to run in a cluster. These procedures do not verify that the SAP Web Application Server application is highly available because you have not yet installed your data service.
Note –
See Appendix B, “SAP Web AS Compliance Tests,” of SAP Web Application Server in Switchover Environments, UNIX Platforms, This appendix describes in detail the recommended tests to verify the functionality of the SAP Web Application Server software.
The procedures in this section verify the installation and configuration of the following SAP Web Application Server components.
-
SAP central services, which includes these servers:
-
SAP enqueue server
-
SAP replica server
-
SAP message server
-
-
SAP web application server component
-
SAP J2EE engine
How to Verify the Installation and Configuration of the SAP Enqueue Server and the SAP Replica Server
Perform this procedure on each set of two nodes that can master the SAP central services resource group and the SAP replica server resource group.
For a description of the extension properties for the SAP enqueue server resource type, SUNW.sapenq, see SUNW.sapenq Extension Properties. For a description of the extension properties for the SAP replica server resource type, SUNW.saprepl, see SUNW.saprepl Extension Properties.
-
Become the superuser on one node, Node1.
-
Bring the SAP central services resource group online on Node1.
# scswitch -z -g central-rg -h node1
- -z
-
Specifies that a resource group is to be brought online
- -g central-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be brought online
- -h node1
-
Specifies the name of the node on which the resource group is to be brought online
-
Become the administration user for the SAP enqueue server on Node1.
The extension property SAP_User for the SUNW.sapenq resource type specifies the name of the administration user.
-
Start the SAP enqueue server manually on Node1.
# enq_server_cmd pf=enq_profile
- enq_server_cmd
-
Specifies the full path to the SAP enqueue server executable. The extension property Enqueue_Server for the SUNW.sapenq resource type contains this value. The name of the SAP enqueue server executable file is enserver.
- pf=enq_profile
-
Specifies the full path to the profile for the SAP enqueue server. The extension property Enqueue_Profile for SUNW.sapenq resource type contains this value.
-
Confirm that the SAP enqueue server is up on Node1.
The name of the SAP enqueue server executable file is enserver.
# ps -ef | grep enserver
-
Verify that the SAP enqueue server has started correctly.
You can verify that the SAP enqueue server has started correctly in two ways.
-
Run the SAP utility ensmon.
# ensmon -H localhost -S port 1
- -H localhost
-
Specifies that the name of the host is localhost.
- -S port
-
Specifies the enqueue port.
- 1
-
Specifies that the probe should check the SAP enqueue server only.
If this command is run on the command line, a return code is returned on the command line.
-
Check the log files that are written to the directory that was current when the SAP enqueue server command was run.
-
-
On a different node, Node2, log in as superuser.
-
Bring the SAP replica server resource group online on Node2.
# scswitch -z -g repl-rg -h node2
- -z
-
Specifies that a resource group is to be brought online
- -g repl-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be brought online
- -h node2
-
Specifies the name of the node on which the resource group is to be brought online
-
Become the administration user for the SAP replica server on Node2.
The extension property SAP_User for SUNW.saprepl resource type specifies the name of the administration user.
-
Start the SAP replica server manually on Node2.
# repl_server_cmd pf=repl_profile
- repl_server_cmd
-
Specifies the full path to the SAP replica server executable. The extension property Replica_Server for the SUNW.saprepl resource type contains this value. The name of the SAP replica server executable file is enrepserver.
- pf=repl_profile
-
Specifies the full path to the profile for the SAP replica server. The extension property Replica_Profile for the SUNW.saprepl resource type contains this value.
-
Confirm that the SAP replica server is active on Node2.
The name of the SAP replica server executable file is enrepserver.
# ps -ef | grep enrepserver
-
Verify that the SAP replica server has started correctly.
You can verify that the SAP replica server has started correctly in two ways.
-
Run the SAP utility ensmon.
# ensmon -H localhost -S port 2
- -H localhost
-
Specifies that the name of the host is localhost.
- -S port
-
Specifies the enqueue port.
- 2
-
Specifies that the probe should check both the SAP enqueue server and the SAP replica server.
If this command is run on the command line, a return code is returned on the command line.
-
Check the log files that are written to the directory that was current when the SAP replica server command was run.
-
-
Set up a test profile to be used with the enqt utility.
In order to create and check enqueue lock entries in Step 14, you must prepare entries in a test SAP profile, including SAPSYSTEM, SAPSYSTEMNAME, and INSTANCE_NAME.
See the SAP document The SAP Lock Concept (BC-CST-EQ) for details about all profile parameters. See also SAP Web Application Server in Switchover Environments, UNIX Platforms.
-
Confirm that enqueue replication is working by performing the following steps.
-
Create some enqueue lock entries.
# /usr/sap/SAPSID/SYS/exe/run/enqt pf=app_server_profile 11
- SAPSID
-
SAP system ID
- app_server_profile
-
Specifies the full path to the test SAP profile that you set up in Step 13
-
Stop the SAP enqueue server on Node1.
# ps -ef | grep enserver # kill -9 pid
-
Stop the SAP replica server on Node2.
# ps -ef | grep enrepserver # kill -9 pid
-
Bring the SAP central services resource group online on Node2.
# scswitch -z -g central-rg -h node2
-
Become the administration user for the SAP enqueue server on Node2.
-
Start the SAP enqueue server manually on Node2.
# enq_server_cmd pf=enq_profile
-
Confirm that no enqueue entries are lost.
# /usr/sap/SAPSID/SYS/exe/run/enqt pf=app_server_profile 20
- SAPSID
-
SAP system ID.
- app_server_profile
-
Specifies the full path to the test SAP profile that you set up in Step 13.
-
How to Verify That the Configuration for the SAP Message Server Is Correct for the Data Service
Perform this procedure on each node that can master the SAP central services resource group.
For a description of the extension properties for the SAP message server resource type, SUNW.sapscs, see SUNW.sapscs Extension Properties.
-
Bring the SAP central services resource group online on a node.
# scswitch -z -g central-rg -h node
- -z
-
Specifies that a resource group is to be brought online
- -g central-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be brought online
- -h node
-
Specifies the name of the node on which the resource group is to be brought online
-
Become superuser with superuser environment. Then become the sapsidadm user, while retaining the superuser environment.
Note that, in the first su command, the “dash” (-) argument causes the environment to be changed to the environment of superuser. The second su command, which is used without the “dash” argument, causes the environment to be retained.
# su - root # su sapsidadm
-
Set the following environment variables:
-
Set the LD_LIBRARY_PATH variable to /sapmnt/SAPSID/exe.
-
Set the SAPSYSTEMNAME variable to the appropriate SAP system identification.
-
Add the following paths to the PATH variable: /usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/cluster/bin.
-
Set the SAPSYSTEM variable to the system number configured for the specific instance of SAP which should be handled by the resource.
-
Set the HOME environment variable to the home directory of the SAP administration user.
-
Set the LOGNAME variable to root.
-
-
Run the SAP start script for the SAP message server using the absolute path and the appropriate arguments.
The following command is an example that runs the SAP start script for the SAP message server. You must run the equivalent command for your installation.
# /usr/sap/SC3/SYS/exe/run/startsap r3 SCS01
-
After the SAP system starts successfully, run the fault monitor probe for the SAP message server.
The full path to the probe is specified by the extension property Msg_Server_Monitor for the SUNW.sapscs resource type. For example, type the following command or the equivalent command.
# /usr/sap/SC3/SYS/exe/run/msprot -mshost host -msport port
-
Verify that the probe was successful.
The probe is successful when the return code equals zero.
-
Run the SAP stop script for the SAP message server to verify that the SAP message server can be stopped.
Verify that the SAP message server can be stopped correctly. Run the SAP stop script for the SAP message server with the full path and the appropriate arguments. The following command is an example that runs the SAP stop script. Run the equivalent command for your installation.
# /usr/sap/SC3/SYS/exe/run/stopsap r3 SCS01
How to Verify That the Configuration for the SAP Web Application Server Component Is Correct for the Data Service
Perform this following procedure on each node that can master the resource group for the SAP web application server component.
If the SAP web application server component is configured as a scalable resource, the resource runs on all these nodes simultaneously.
-
Become superuser, then the sapsidadm user with superuser environment.
# su - root # su sapsidadm
-
Set the following environment variables:
-
Set the LD_LIBRARY_PATH variable to /sapmnt/SAPSID/exe.
-
Set the SAPSYSTEMNAME variable to the appropriate SAP system identification.
-
Add the following paths to the PATH variable: /usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/cluster/bin.
-
Set the SAPSYSTEM variable to the system number configured for the specific instance of SAP which should be handled by the resource.
-
Set the HOME environment variable to the home directory of the SAP administration user.
-
Set the LOGNAME variable to root.
-
-
If you have configured the resource group for the SAP web application server component as a failover resource group, enable the logical-host-name resource for the resource group.
-
Start the database.
Before running the SAP start script in the next step, you must start the database.
-
Run the SAP start script for the SAP web application server component using the absolute path and the appropriate arguments.
The following command is an example that runs the SAP start script for the SAP web application server component. You must run the equivalent command for your installation.
# /usr/sap/SC3/SYS/exe/run/startsap r3 D01
-
Change to the home directory of the SAP administration user.
The dpmon utility writes files to the current directory, and this directory must be writable by the SAP administration user. In Step 2 you set the HOME environment variable to the home directory of the SAP administration user.
# cd $HOME
-
After the SAP system starts successfully, run the probe command for the dispatcher of the SAP instance. The following command is an example:
# /usr/sap/SC3/SYS/exe/run/dpmon -info
-
Verify that the probe was successful.
The probe is successful when the return code equals zero.
-
Run the SAP stop script for the SAP web application server component to verify that the SAP Web Application Server can be stopped.
Verify that the SAP Web Application Server can be stopped correctly. Run the SAP stop script for the SAP web application server component with the full path and the appropriate arguments. The following command is an example that runs the SAP stop script. Run the equivalent command for your installation.
# /usr/sap/SC3/SYS/exe/run/stopsap r3 D01
How to Verify the Installation and Configuration of the SAP J2EE Engine
-
Become superuser, then the sapsidadm user with superuser environment.
# su - root # su sapsidadm
-
Set the following environment variables:
-
Set the LD_LIBRARY_PATH variable to /sapmnt/SAPSID/exe.
-
Set the SAPSYSTEMNAME variable to the appropriate SAP system identification.
-
Add the following paths to the PATH variable: /usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/cluster/bin.
-
Set the SAPSYSTEM variable to the system number configured for the specific instance of SAP which should be handled by the resource.
-
Set the HOME environment variable to the home directory of the SAP administration user.
-
Set the LOGNAME variable to root.
-
-
Enable the logical-host-name resource for the resource group.
-
Start the database.
Before running the SAP start script in the next step, you must start the database.
-
Run the SAP start script for the SAP J2EE engine using the absolute path and the appropriate arguments.
The following command is an example that runs the SAP start script for the SAP J2EE engine. You must run the equivalent command for your installation.
# /usr/sap/SC3/SYS/exe/run/startsap j2ee D01
-
Change to the home directory of the SAP administration user.
The probe utility writes files to the current directory, and this directory must be writable by the SAP administration user. In Step 2 you set the HOME environment variable to the home directory of the SAP administration user.
# cd $HOME
-
After the SAP J2EE engine starts successfully, verify it by deploying and running some examples. See the SAP Web Application Server Installation Guide for instructions.
-
Run the SAP stop script for the SAP J2EE engine to verify that the SAP J2EE engine can be stopped.
Verify that the SAP J2EE engine can be stopped correctly. Run the SAP stop script for the SAP J2EE engine with the full path and the appropriate arguments. The following command is an example that runs the SAP stop script. Run the equivalent command for your installation.
# /usr/sap/SC3/SYS/exe/run/stopsap j2ee D01
Installing the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server Packages
The Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server data service includes resource types for the following components of SAP Web Application Server:
-
SAP enqueue server
-
SAP replica server
-
SAP message server
-
SAP web application server component
-
SAP J2EE engine
If you did not install the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server packages during your initial Sun Cluster installation, perform this procedure to install the packages. Perform this procedure on each cluster node where you are installing the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server packages. To complete this procedure, you need the Sun Java Enterprise System Accessory CD Volume 3.
If you are installing more than one data service simultaneously, perform the procedure in “Installing the Software” in Sun Cluster Software Installation Guide for Solaris OS.
Install the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server packages by using one of the following installation tools:
-
The Web Start program
-
The scinstall utility
Note –
The Web Start program is not available in releases earlier than Sun Cluster 3.1 Data Services 10/03.
How to Install the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server Packages by Using the Web Start Program
You can run the Web Start program with a command-line interface (CLI) or with a graphical user interface (GUI). The content and sequence of instructions in the CLI and the GUI are similar. For more information about the Web Start program, see the installer(1M) man page.
-
On the cluster node where you are installing the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server packages, become superuser.
-
(Optional) If you intend to run the Web Start program with a GUI, ensure that your
DISPLAYenvironment variable is set. -
Load the Sun Java Enterprise System Accessory CD Volume 3 into the CD-ROM drive.
If the Volume Management daemon vold(1M) is running and configured to manage CD-ROM devices, it automatically mounts the CD-ROM on the /cdrom/cdrom0 directory.
-
Change to the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server component directory of the CD-ROM.
The Web Start program for the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server data service resides in this directory.
# cd /cdrom/cdrom0/\ components/SunCluster_HA_SAPWebAS_1.0
-
Start the Web Start program.
# ./installer
-
When you are prompted, select the type of installation.
-
Follow instructions on the screen to install the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server packages on the node.
After the installation is finished, the Web Start program provides an installation summary. This summary enables you to view logs that the Web Start program created during the installation. These logs are located in the /var/sadm/install/logs directory.
-
Exit the Web Start program.
-
Unload the Sun Java Enterprise System Accessory CD Volume 3 from the CD-ROM drive.
Where to Go From Here
Go to Registering and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server.
How to Install the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server Packages by Using the scinstall Utility
-
Load the Sun Java Enterprise System Accessory CD Volume 3 into the CD-ROM drive.
-
Run the scinstall utility with no options.
This step starts the scinstall utility in interactive mode.
-
Select the menu option, Add Support for New Data Service to This Cluster Node.
The scinstall utility prompts you for additional information.
-
Provide the path to the Sun Java Enterprise System Accessory CD Volume 3.
The utility refers to the CD as the “data services cd.”
-
Specify the data service to install.
The scinstall utility lists the data service that you selected and asks you to confirm your choice.
-
Exit the scinstall utility.
-
Unload the CD from the drive.
Where to Go From Here
Go to Registering and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server.
Registering and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server
To enable the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server data service to make SAP Web Application Server applications highly available, configure the data service as described in the procedures in this section. These procedures perform the following tasks.
-
Register and configure the HAStoragePlus resources.
-
Register and configure the SAP central services resources. The SAP central services consist of the following components:
-
SAP enqueue server
-
SAP replica server
-
SAP message server
-
-
Register and configure resources for the SAP web application server component.
-
Register and configure the SAP J2EE engine.
Before You Begin
Before performing these procedures, ensure that the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server data service packages are installed.
The procedures in this section assume that the database resources have been previously created and that these resources are online.
-
If you are using SAP DB as the database, configure the Sun Cluster HA for SAP DB data service before continuing. See Sun Cluster Data Service for SAP DB Guide for Solaris OS.
-
If you are using Oracle as the database, configure the Sun Cluster HA for Oracle data service before continuing. See Sun Cluster Data Service for Oracle Guide for Solaris OS.
Perform each task as superuser on a cluster node.
Setting Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server Extension Properties
The sections that follow contain instructions for registering and configuring resources. These instructions explain how to set only extension properties that Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server requires you to set. For information about all Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server extension properties, see Appendix A, Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server Extension Properties. You can update some extension properties dynamically. You can update other properties, however, only when you create or disable a resource. The Tunable entry indicates when you can update a property.
To set an extension property of a resource, include the following option in the scrgadm(1M) command that creates or modifies the resource:
-x property=value |
- -x property
-
Identifies the extension property that you are setting
- value
-
Specifies the value to which you are setting the extension property
You can also use the procedures in “Administering Data Service Resources” in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS to configure resources after the resources are created.
How to Register and Configure HAStoragePlus Resources for the SAP Central Services Components
An HAStoragePlus resource is created to ensure the high availability of the global device groups where the components are installed.
-
Register the SUNW.HAStoragePlus resource type.
# scrgadm -a -t SUNW.HAStoragePlus
-
Create an HAStoragePlus resource for the global device group on which the SAP enqueue server and the SAP message server are installed.
Create this resource in the SAP central services resource group, which is the resource group to which the SAP enqueue server and the SAP message server resources belong.
# scrgadm -a -j hsp-central-rs -g central-rg -t SUNW.HAStoragePlus \ -x filesystemmountpoints="mountpoint-list" \ -x globaldevicepaths=sapenq-device-group
- -a
-
Specifies that a new configuration is to be added.
- -j hsp-central-rs
-
Specifies the name of the resource that you are creating.
- -g central-rg
-
Specifies that the resource is to be added to the SAP central services resource group.
- -t SUNW.HAStoragePlus
-
Specifies that the resource is an instance of the SUNW.HAStoragePlus resource type.
- -x filesystemmountpoints="mountpoint-list"
-
Specifies a list of valid mount points for the file system. For more information, see the SUNW.HAStoragePlus(5) man page.
- -x globaldevicepaths=sapenq-device-group
-
Specifies the name of the global device group on which the SAP enqueue server software and the SAP message server software are installed.
-
Enable the HAStoragePlus resource that you created in Step 2.
# scswitch -ej hsp-central-rs
- -ej hsp-central-rs
-
Specifies that the HAStoragePlus resource that you created in Step 2 is to be enabled
-
Create an HAStoragePlus resource for the global device group on which SAP replica server is installed.
Create this resource in the SAP replica server resource group.
# scrgadm -a -j hsp-repl-rs -g repl-rg -t SUNW.HAStoragePlus \ -x filesystemmountpoints="mountpoint-list" \ -x globaldevicepaths=saprepl-device-group
- -a
-
Specifies that a new configuration is to be added.
- -j hsp-repl-rs
-
Specifies the name of the resource that you are creating.
- -g repl-rg
-
Specifies that the resource is to be added to the SAP replica server resource group.
- -t SUNW.HAStoragePlus
-
Specifies that the resource is an instance of the SUNW.HAStoragePlus resource type.
- -x filesystemmountpoints="mountpoint-list"
-
Specifies a list of valid mount points for the file system. For more information, see the SUNW.HAStoragePlus(5) man page.
- -x globaldevicepaths=saprepl-device-group
-
Specifies the name of the global device group on which the SAP replica server software is installed.
-
Enable the HAStoragePlus resource that you created in Step 4.
# scswitch -ej hsp-repl-rs
- -ej hsp-repl-rs
-
Specifies that the HAStoragePlus resource that you created in Step 4 is to be enabled
How to Register and Configure an SAP Enqueue Server Resource
The SAP enqueue server resource and the SAP message server resource must be in the same failover resource group because they fail over together.
The SAP enqueue server resource is configured to depend on its associated HAStoragePlus resource. This dependency ensures that the SAP enqueue server does not attempt to start until its associated HAStoragePlus resource is online.
-
Register SUNW.sapenq, the resource type for the SAP enqueue server.
# scrgadm -a -t SUNW.sapenq
- -a
-
Specifies that a new resource type is to be added.
- -t SUNW.sapenq
-
Specifies the name of the resource type to be added. This name is predefined for the SAP enqueue server.
-
Create an SAP enqueue server resource in the SAP central services resource group.
# scrgadm -a -j enq-rs -g central-rg -t SUNW.sapenq \ -x Enqueue_Profile=path-to-enq-profile \ -x Enqueue_Server=path-to-enq-server-binary \ -x SAP_User=enq-user \ -x Enqueue_Instance_Number=enq-instance \ -y Resource_Dependencies=hsp-central-rs
- -a
-
Specifies that a new resource is to be added.
- -j enq-rs
-
Specifies the name of the resource to be added.
- -g central-rg
-
Specifies the resource group to which the resource is to be added. The SAP central services resource group is configured as a failover resource group.
- -t SUNW.sapenq
-
Specifies that the resource is an instance of the SUNW.sapenq resource type.
- -x Enqueue_Profile=path-to-enq-profile
-
Specifies the full path to the SAP enqueue server profile.
- -x Enqueue_Server=path-to-enq-server-binary
-
Specifies the full path to the SAP enqueue server executable.
- -x SAP_User=enq-user
-
Specifies the administration user for the SAP enqueue server.
- -x Enqueue_Instance_Number=enq-instance
-
Specifies the two-digit instance number for the SAP enqueue server. This number is the value of SAPSYSTEM in the SAP profile for SAP enqueue server.
- -y Resource_Dependencies=hsp-central-rs
-
Specifies that the HAStoragePlus resource for the global device group on which SAP enqueue server is installed must be online in order for the SAP enqueue server to be online.
-
Verify that the default values for the SAP enqueue server extension properties are acceptable.
Refer to SUNW.sapenq Extension Properties.
-
Ensure that SAP enqueue server is not already running on the cluster.
If SAP enqueue server is already running on any node of the cluster, you risk the simultaneous running of multiple SAP enqueue server processes.
-
Enable the SAP enqueue server resource.
# scswitch -ej enq-rs
- -ej
-
Specifies that the specified resource is to be enabled.
- enq-rs
-
Specifies the name of the resource to be enabled.
How to Register and Configure an SAP Replica Server Resource
The SAP replica server resource must be in a different failover resource group from the SAP enqueue server resource, because the SAP replica server resource must not fail over with the SAP enqueue server resource.
The SAP replica server resource is configured to depend on its associated HAStoragePlus resource being online. The SAP replica server resource also depends on the SAP enqueue server resource. These dependencies ensure that the SAP replica server does not attempt to start until both its associated HAStoragePlus resource and the SAP enqueue server are online.
-
Register SUNW.saprepl, the resource type for the SAP replica server.
# scrgadm -a -t SUNW.saprepl
- -a
-
Specifies that a new resource type is to be added.
- -t SUNW.saprepl
-
Specifies the name of the resource type to be added. This name is predefined for the SAP replica server.
-
Create an SAP replica server resource in the SAP replica server resource group.
# scrgadm -a -j repl-rs -g repl-rg -t SUNW.saprepl \ -x Replica_Profile=path-to-repl-profile \ -x Replica_Server=path-to-repl-server-binary \ -x SAP_User=repl-user \ -y Resource_Dependencies=enq-rs,hsp-repl-rs
- -a
-
Specifies that a new resource is to be added.
- -j repl-rs
-
Specifies the name of the resource to be added.
- -g repl-rg
-
Specifies the resource group to which the resource is to be added. The SAP replica server resource group is configured as a failover resource group.
- -t SUNW.saprepl
-
Specifies that the resource is an instance of the SUNW.saprepl resource type.
- -x Replica_Profile=path-to-repl-profile
-
Specifies the full path to the SAP replica server profile.
- -x Replica_Server=path-to-repl-server-binary
-
Specifies the full path to the SAP replica server executable.
- -x SAP_User=repl-user
-
Specifies the administration user for the SAP replica server.
- -y Resource_Dependencies=enq-rs,hsp-repl-rs
-
Specifies that the following resources must be online before the SAP replica server resource can be online:
-
SAP enqueue server resource
-
HAStoragePlus resource for the global device group on which the SAP replica server is installed
-
-
Verify that the default values for the SAP replica server extension properties are acceptable.
Refer to SUNW.saprepl Extension Properties.
-
Enable the SAP replica server resource.
# scswitch -ej repl-rs
- -ej
-
Specifies that the specified resource is to be enabled.
- repl-rs
-
Specifies the name of the resource to be enabled.
How to Register and Configure an SAP Message Server Resource
The SAP enqueue server resource and the SAP message server resource must be in the same failover resource group because they fail over together.
The SAP message server resource is configured to depend on its associated HAStoragePlus resource. This dependency ensures that the SAP message server does not attempt to start until its associated HAStoragePlus resource is online.
-
Register SUNW.sapscs, the resource type for the SAP message server.
# scrgadm -a -t SUNW.sapscs
- -a
-
Specifies that a new resource type is to be added.
- -t SUNW.sapscs
-
Specifies the name of the resource type to be added. This name is predefined for the SAP message server.
-
Create an SAP message server resource in the SAP central services resource group.
# scrgadm -a -j msg-rs -g central-rg -t SUNW.sapscs \ -x SAP_SID=scs-system-ID \ -x SAP_Instance_Number=scs-instance-number \ -x SAP_Instance_Name=scs-instance-name \ -x Msg_Server_Port=msg-server-port \ -x Scs_Startup_Script=scs-server-startup-script \ -x Scs_Shutdown_Script=scs-server-shutdown-script \ -y Resource_Dependencies=hsp-central-rs
- -a
-
Specifies that a new resource is to be added.
- -j msg-rs
-
Specifies the name of the resource to be added.
- -g central-rg
-
Specifies the resource group to which the resource is to be added. The SAP central services resource group is configured as a failover resource group.
- -t SUNW.sapscs
-
Specifies that the SAP message server resource is an instance of the resource type that is named SUNW.sapscs.
- -x SAP_SID=scs-system-ID
-
Specifies the SAP system ID for the SAP message server. This ID is SAPSYSTEMNAME in the SAP profile.
- -x SAP_Instance_Number=scs-instance-number
-
Specifies the instance number for the SAP message server. This number is SAPSYSTEM in the SAP profile.
- -x SAP_Instance_Name=scs-instance-name
-
Specifies the instance name for the SAP message server. This name is INSTANCE_NAME in the SAP profile.
- -x Msg_Server_Port=msg-server-port
-
Specifies the listen port for the SAP message server.
- -x Scs_Startup_Script=scs-server-startup-script
-
Specifies the full path to the startup script for the SAP message server instance.
- -x Scs_Shutdown_Script=scs-server-shutdown-script
-
Specifies the full path to the shutdown script for the SAP message server instance.
- -y Resource_Dependencies=hsp-central-rs
-
Specifies that the HAStoragePlus resource for the global device group on which the SAP message server is installed must be online in order for the SAP message server to be online.
-
Verify that the default values for the SAP message server extension properties are acceptable.
Refer to SUNW.sapscs Extension Properties.
-
Enable the SAP message server resource.
# scswitch -ej msg-rs
- -ej
-
Specifies that the specified resource is to be enabled.
- msg-rs
-
Specifies the name of the resource to be enabled.
How to Register and Configure an SAP Web Application Server Component
An HAStoragePlus resource is created to ensure the high availability of the global device groups where the components are installed.
The resource for the SAP web application server component is configured to depend on its associated HAStoragePlus resource. The resource for the SAP web application server component also depends on the database resource, as well as the SAP message server resource. These dependencies ensure that the resource for the SAP web application server component does not attempt to start until its associated HAStoragePlus resource, the database, and the SAP message server resource are all online.
Note –
The SAP web application server component can be configured to run under PMF or not to run under PMF. See the extension property Webas_Use_Pmf in SUNW.sapwebas Extension Properties. If the component is configured to run under PMF control, and if the network is not available, PMF stops the resource in such a way that no data is lost. However, if the component is configured not to run under PMF, and if the network is not available, the resource and the resource group for the SAP web application server component are in the stop_failed state and user intervention is required. Because no SAP utility is available to stop all SAP processes, in order to prevent possible data corruption, the data service does not automatically restart the processes.
-
Create an HAStoragePlus resource for the global device group on which SAP web application server component is installed.
Create this resource in the SAP web application server resource group.
# scrgadm -a -j hsp-webas-rs -g webas-rg -t SUNW.HAStoragePlus \ -x filesystemmountpoints="mountpoint-list" \ -x globaldevicepaths=sapwebas-device-group
- -a
-
Specifies that a new configuration is to be added.
- -j hsp-webas-rs
-
Specifies the name of the resource that you are creating.
- -g webas-rg
-
Specifies that the resource is to be added to the SAP web application server resource group.
- -t SUNW.HAStoragePlus
-
Specifies that the resource is an instance of the SUNW.HAStoragePlus resource type.
- -x filesystemmountpoints="mountpoint-list"
-
Specifies a list of valid mount points for the file system. For more information, see the SUNW.HAStoragePlus(5) man page.
- -x globaldevicepaths=sapwebas-device-group
-
Specifies the name of the global device group on which the SAP web application server component software is installed.
-
Enable the HAStoragePlus resource that you created in Step 1.
# scswitch -ej hsp-webas-rs
- -ej hsp-webas-rs
-
Specifies that the HAStoragePlus resource that you created in Step 1 is to be enabled
-
Register SUNW.sapwebas, the resource type for the SAP web application server component.
# scrgadm -a -t SUNW.sapwebas
- -a
-
Specifies that a new resource type is to be added.
- -t SUNW.sapwebas
-
Specifies the name of the resource type to be added. This name is predefined for the SAP web application server component.
-
Create a resource for the SAP web application server component.
The SAP web application server component can be configured either as a failover resource or as a scalable resource by adding the resource to a resource group that was created as a failover or a scalable resource group.
# scrgadm -a -j webas-rs -g webas-rg -t SUNW.sapwebas \ -x SAP_SID=webas-system-ID \ -x SAP_Instance_Number=webas-instance-number \ -x SAP_Instance_Name=webas-instance-name \ -y Resource_Dependencies=hsp-webas-rs,db-webas-rs,msg-rs
- -a
-
Specifies that a new resource is to be added.
- -j webas-rs
-
Specifies the name of the resource to be added.
- -g webas-rg
-
Specifies the resource group to which the resource is to be added. The SAP web application server resource group can be configured as a failover or a scalable resource group.
- -t SUNW.sapwebas
-
Specifies that the resource is an instance of the SUNW.sapwebas resource type.
- -x SAP_SID=webas-system-ID
-
Specifies the SAP system ID for the SAP web application server component. This ID is SAPSYSTEMNAME in the SAP profile.
- -x SAP_Instance_Number=webas-instance-number
-
Specifies the two-digit SAP system number for the SAP web application server component instance. This number is SAPSYSTEM in the SAP profile.
- -x SAP_Instance_Name=webas-instance-name
-
Specifies the instance name for the SAP web application server component. This name is INSTANCE_NAME in the SAP profile.
- -y Resource_Dependencies=hsp-webas-rs,db-webas-rs,msg-rs
-
Specifies that the following resources must be online before the resource for the SAP web application server component can be online:
-
HAStoragePlus resource for the global device group on which the SAP web application server component is installed.
-
Database resource. The database resource is created by the relevant data service.
-
SAP message server resource.
-
-
Verify that the default values for the SAP web application server component extension properties are acceptable.
Refer to SUNW.sapwebas Extension Properties.
-
Enable the SAP web application server component resource.
# scswitch -ej webas-rs
- -ej
-
Specifies that the specified resource is to be enabled.
- webas-rs
-
Specifies the name of the resource to be enabled.
How to Register and Configure an SAP J2EE Engine Resource
-
Become superuser on one of the nodes in the cluster that is to host the SAP J2EE engine.
-
Register SUNW.gds, the resource type for the SAP J2EE engine.
# scrgadm -a -t SUNW.gds
- -a
-
Specifies that a new resource type is to be added.
- -t SUNW.gds
-
Specifies the name of the resource type to be added. This name is predefined for the SAP J2EE engine.
-
Create an HAStoragePlus resource for the SAP J2EE engine disk storage.
# scrgadm -a -j hsp-j2ee-rs -g j2ee-rg -t SUNW.HAStoragePlus \ -x filesystemmountpoints="mountpoint-list"
- -a
-
Specifies that a new configuration is to be added.
- -j hsp-j2ee-rs
-
Specifies the name of the resource that you are creating.
- -g j2ee-rg
-
Specifies that the resource is to be added to the SAP J2EE engine resource group.
- -t SUNW.HAStoragePlus
-
Specifies that the resource is an instance of the SUNW.HAStoragePlus resource type.
- -x filesystemmountpoints="mountpoint-list"
-
Specifies a list of valid mount points for the file system. For more information, see the SUNW.HAStoragePlus(5) man page.
-
Configure the Sun Cluster SAP J2EE engine resource.
Edit the ha_sap_j2ee_config file and follow the comments with that file, as in the following example.
# cd /opt/SUNWscswa/util # # more ha_sap_j2ee_config # # Copyright 2003 Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved. # Use is subject to license terms. # # This file will be sourced in by ha_sap_j2ee_register and the parameters # listed below will be used. # # These parameters can be customized in (key=value) form # # RS - name of the resource for the application # RG - name of the resource group containing RS # JAVA_HOME - name of the Java home directory # SAPID - The SAP System Name # J2EE_INSTANCE - name of the SAP J2EE Engine instance # LH - name of the LogicalHostname SC resource # HAS_RS - name of the SAP J2EE HAStoragePlus SC resource # # Optional parameters # # SAP_START - Optional, name of a startsap script within # <SAPID>adm home directory that will be used # instead of the default startsap. # # SAP_STOP - Optional, name of a stopsap script within # <SAPID>adm home directory that will be used # instead of the default stopsap. # # SAP_LOGDIR - Optional, where to put the logfiles from # startsap and stopsap. Default is the <SAPID>adm home # directory # # RESOURCE_PROJECT_NAME - Optional, name of a SRM project. # # The following examples illustrate sample parameters # for SAP J2EE Engine Instance # # RS=RES-SAP-J2EE # RG=RG-SAP-J2EE # JAVA_HOME=/usr/java # SAPID=TST # J2EE_INSTANCIES=JC00 # LH=j2eelh # HAS_RS=RES-SAP-J2EE-HAS # # SAP_START= # SAP_STOP= # SAP_LOGDIR= # RESOURCE_PROJECT_NAME= # # RS= RG= JAVA_HOME=/usr/java SAPID= J2EE_INSTANCE= LH= HAS_RS= SAP_START= SAP_STOP= SAP_LOGDIR= RESOURCE_PROJECT_NAME=
-
Register the Sun Cluster SAP J2EE engine resource.
# cd /opt/SUNWscswa/util # ./ha_sap_j2ee_register
-
Set the resource dependencies.
The SAP J2EE engine resource depends on the database resource, the SAP enqueue server, and the SAP message server resource.
# scrgadm -c -j j2ee-rs -y Resource_Dependencies=db-rs,enq-rs,msg-rs
- -c
-
Specifies that an existing configuration is to be changed.
- -j j2ee-rs
-
Specifies the name of the resource to be changed. This resource name must be the same resource name that you specified in the configuration file in Step 4.
- -y Resource_Dependencies=db-rs,enq-rs,msg-rs
-
Specifies that the following resources must be online before the SAP J2EE engine resource for the can be online:
-
Database resource. The database resource is created by the relevant data service.
-
SAP enqueue server resource.
-
SAP message server resource.
-
-
Enable the Sun Cluster SAP J2EE engine resource.
# scswitch -ej j2ee-rs
- -ej
-
Specifies that the specified resource is to be enabled.
- j2ee-rs
-
Specifies the name of the resource to be enabled.
Examples of Configuring the SAP Web Application Server
The following examples show how the SAP Web Application Server can be configured to be highly available in Sun Cluster. The examples assume that the resource groups have been created, the resource groups are online, and the resource types have been registered.
-
Configuring the SAP central services, which consist of the following components:
-
SAP enqueue server
-
SAP replica server
-
SAP message server
-
-
Configuring the SAP web application server component
Example 1–9 Configuring the SAP Central Services Components
In this example the SAP central services resource group is called centralrg, and the SAP replica server resource group is called replrg.
-
To create an HAStoragePlus resource called hspcentralrs for the global device group enqdg in the resource group centralrg, the following command is run. The group centraldg is the global device group on which the SAP enqueue server is installed, and centralrg is the resource group to which the SAP enqueue server resource and the SAP message server resource belong.
# scrgadm -a -j hspcentralrs -g centralrg -t SUNW.HAStoragePlus \ -x filesystemmountpoints="/global/sapdata" \ -x globaldevicepaths=centraldg
-
To enable the hspcentralrs resource, the following command is run.
# scswitch -ej hspcentralrs
-
To create an HAStoragePlus resource called hspreplrs for the global device group repldg in the resource group replrg, the following command is run. The group repldg is the global device group on which SAP replica server is installed, and replrg is the resource group to which the SAP replica server resource belongs.
# scrgadm -a -j hspreplrs -g replrg -t SUNW.HAStoragePlus \ -x filesystemmountpoints="/global/sapdata" \ -x globaldevicepaths=repldg
-
To enable the hspreplrs resource, the following command is run.
# scswitch -ej hspreplrs
-
To create an SAP enqueue server resource called enqrs in the resource group centralrg, the following command is run. This resource is dependent on the hspcentralrs resource.
# scrgadm -a -j enqrs -g centralrg -t SUNW.sapenq \ -x Enqueue_Profile=/usr/sap/SC3/SYS/profile/SC3_ASCS07_central-lh \ -x Enqueue_Server=/sapmnt/SC3/exe/enserver \ -x SAP_User=sc3adm \ -x Enqueue_Instance_Number=07 \ -y Resource_Dependencies=hspcentralrs
-
To enable the enqrs resource, the following command is run.
# scswitch -ej enqrs
-
To create an SAP replica server resource called replrs in the resource group replrg, the following command is run. This resource is dependent on the hspreplrs resource and the enqrs resource.
# scrgadm -a -j replrs -g replrg -t SUNW.saprepl \ -x Replica_Profile=/usr/sap/SC3/SYS/profile/SC3_REP07 \ -x Replica_Server=/sapmnt/SC3/exe/enrepserver \ -x SAP_User=sc3adm \ -y Resource_Dependencies=hspreplrs,enqrs
-
To create an SAP message server resource called msgrs in the resource group centralrg, the following command is run. This resource is dependent on the hspcentralrs resource. The SAP message server resource is an instance of the resource type that is named SUNW.sapscs.
# scrgadm -a -j msgrs -g centralrg -t SUNW.sapscs \ -x SAP_SID=SC3 \ -x SAP_Instance_Number=07 \ -x SAP_Instance_Name=ASCS07 \ -x Msg_Server_Port=3607 \ -x Scs_Startup_Script=/usr/sap/SC3/SYS/exe/run/my_startsap \ -x Scs_Shutdown_Script=/usr/sap/SC3/SYS/exe/run/my_stopsap \ -y Resource_Dependencies=hspcentralrs
-
To enable the replrs resource and the msgrs resource, the following command is run.
# scswitch -ej replrs,msgrs
Example 1–10 Configuring the SAP Web Application Server Component
In this example the resource group for the SAP web application server component is called webasrg.
-
To create an HAStoragePlus resource called hspwebasrs for the global device group webasdg in the resource group webasrg, the following command is run. The group webasdg is the device group on which the SAP web application server component is installed, and webasrg is the resource group to which the SAP web application server resource belongs.
# scrgadm -a -j hspwebasrs -g webasrg -t SUNW.HAStoragePlus \ -x filesystemmountpoints="/global/sapdata" \ -x globaldevicepaths=webasdg
-
To enable the haspwebasrs resource, the following command is run.
# scswitch -ej hspwebasrs
-
To create a resource called webasrs for the SAP web application server component, the following command is run. This resource is created in the failover resource group webasrg. This resource is dependent on the hspwebasrs resource. The webasrs resource is also dependent on the database resource dbwebasrs, which has already been created by the relevant data service. In addition, this resource is dependent on the SAP message server resource, which is called msgrs in the previous example.
# scrgadm -a -j webasrs -g webasrg -t SUNW.sapwebas \ -x SAP_SID=SC3 \ -x SAP_Instance_Number=08 \ -x SAP_Instance_Name=D08 \ -y Resource_Dependencies=hspwebasrs,dbwebasrs,msgrs
-
To enable the webasrs resource, the following command is run.
# scswitch -ej webasrs
Using Alternate Project Identification
You can create a specific project, that is, an alternate project identification (ID), for the application. Set either RG_project_name or Resource_project_name or both, for the resource group and/or the resource, so that the application is started up under the specified project. Refer to the RGM doc for how to set these system properties.
See “Cluster Administration and Application Development” in Sun Cluster Concepts Guide for Solaris OS.
Tuning the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server Fault Monitors
Fault monitoring for the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server data service is provided by the following fault monitors:
-
The fault monitor for the SAP enqueue server
-
The fault monitor for the SAP replica server
-
The fault monitor for the SAP message server
-
The fault monitor for the SAP web application server component
-
The fault monitor for the SAP J2EE engine
Each fault monitor is contained in a resource whose resource type is shown in the following table.
Table 1–3 Resource Types for the Fault Monitors of Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server|
SAP enqueue server |
SUNW.sapenq |
|
SAP replica server |
SUNW.saprepl |
|
SAP message server |
SUNW.sapscs |
|
SAP web application server component |
SUNW.sapwebas |
|
SAP J2EE engine |
SUNW.gds |
System properties and extension properties of the resource types control the behavior of the fault monitors. The default values of these properties determine the preset behavior of the fault monitors. The preset behavior should be suitable for most Sun Cluster installations. Therefore, you should tune the fault monitors only if you need to modify this preset behavior.
Tuning these fault monitors involves the following tasks:
-
Setting the interval between fault monitor probes
-
Setting the timeout for fault monitor probes
-
Defining the criteria for persistent faults
-
Specifying the failover behavior of a resource
Perform these tasks when you register and configure Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server, as described in Registering and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server.
For detailed information about these tasks, see “Tuning Fault Monitors for Sun Cluster Data Services” in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS.
Operation of the Fault Monitor for the SAP Enqueue Server Resource Type
To determine whether the SAP enqueue server and the SAP replica server are operating correctly, the fault monitor for the SAP enqueue server resource type probes these resources periodically.
The probe uses the SAP utility ensmon to check the health of the SAP enqueue server and the SAP replica server.
# ensmon -H localhost -S port option |
- -H localhost
-
Specifies that the name of the host is localhost.
- -S port
-
Specifies the enqueue port.
- option
-
Specifies the resources that the probe should check. The possible values of this option are as follows:
-
1 – Check the SAP enqueue server only.
-
2 – Check both the SAP enqueue server and the SAP replica server.
-
If this command is run on the command line, a return code is returned on the command line.
During a probe, the fault monitor first determines whether both the SAP enqueue server and the SAP replica server are online by running the ensmon command with the option argument set to 2.
# ensmon -H localhost -S port 2 |
The result of this command determines the action of the probe, as follows:
-
If the command times out, the SAP enqueue server fault monitor checks whether only the SAP enqueue server is online by running the ensmon command with the option set to 1.
# ensmon -H localhost -S port 1
-
If this command times out, the SAP enqueue server issues a partial failure. If this timeout occurs one more time within the probe interval period, a failover occurs.
-
If this command succeeds, the SAP enqueue server fault monitor logs a warning message to explain that the SAP enqueue server is online but the status of the SAP replica server is unknown.
-
If this command causes a system error, the SAP enqueue server issues a less serious partial failure. If a system error occurs three more times within the probe interval period, a failover occurs.
-
For all other unsuccessful conditions, the SAP enqueue server triggers a failover.
-
-
If the command does not time out, the probe checks the value of the return code from the ensmon command, as follows:
-
A return code value of 0 indicates that the command is successful, and no further action is taken until the next probe.
-
A return code value of 4 indicates that the enqueue is running, and the replica is configured, but the replica is not running. The probe logs a warning message to indicate that the replica is not running.
-
A return code value of 8 indicates that the enqueue server is not running, and the probe triggers a failover.
-
A return code of 12 indicates an invalid parameter for the command, and the probe triggers a failover.
-
All other return codes are treated as a partial failure. If such a failure occurs three more times within the probe interval period, a failover occurs.
-
Note that the values for the number of timeouts and the probe interval period are assigned by the SAP enqueue server fault monitor. You cannot change these values.
Operation of the Fault Monitor for the SAP Replica Server Resource Type
Fault monitor responsibility for the SAP replica server resource type is currently handled by the Process Monitor Facility (PMF) in Sun Cluster.
Operation of the Fault Monitor for the SAP Message Server Resource Type
The fault monitor probe for the SAP message server resource type requires the msprot program. See Configuration Requirements.
The msprot program is not configurable.
Operation of the Fault Monitor for the SAP Web Application Server Component Resource Type
The fault monitoring for the SAP message server component resource type is performed by the dpmon program.
The dpmon program is not configurable.
Operation of the Fault Monitor for the SAP J2EE Engine Resource Type
The fault monitor probe for the SAP J2EE engine resource type requires the sap_j2ee_probe program.
The sap_j2ee_probe program is not configurable.
Verifying the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server Installation and Configuration
You have installed, registered, and configured the data service for SAP Web Application Server. Now verify that the data service makes the SAP Web Application Server highly available by performing the following tasks.
-
Verify the operation of the fault monitor for the SAP enqueue server
-
Verify the operation of the fault monitor for the SAP replica server
-
Verify the operation of the fault monitor for the SAP message server
-
Verify the operation of the fault monitor for the SAP web application server component
-
Verify the installation and configuration of the SAP J2EE engine
See Tuning the Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server Fault Monitors for a description of the fault monitors.
How to Verify the Operation of the Fault Monitor for the SAP Enqueue Server
Perform this procedure on each set of two nodes where the SAP enqueue server and the SAP replica server can run.
-
Log in to a node as superuser.
-
Ensure that the SAP replica server resource group is offline on all nodes.
At this point in this procedure you are testing the behavior of the SAP enqueue server resource group without the SAP replica server resource group. Therefore, the SAP replica server resource group must be offline on all nodes. Further in this procedure you will test the behavior of the SAP enqueue server with the SAP replica server resource group.
-
Bring online the resource group to which the SAP enqueue server belongs.
# scswitch -z -g central-rg -h node
- -z
-
Specifies that a resource group is to be brought online.
- -g central-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be brought online. This group is the resource group to which the SAP enqueue server belongs.
- -h node
-
Specifies the name of the node on which the resource group is to be brought online. This node is the node that you have just logged in to.
-
Abnormally terminate the SAP enqueue server.
-
Determine the process ID of the SAP enqueue server, where the name of the SAP enqueue server executable file is enserver.
# ps -ef | grep enserver
-
Kill the process for the SAP enqueue server.
# kill -9 pid
- pid
-
Specifies the process ID of the SAP enqueue server. This ID is the process ID that you determined with the ps and grep commands.
-
-
Confirm that the SAP enqueue server fails over to another node.
Run the scstat command to confirm that the SAP enqueue server resource is offline on the first node and online on the second node.
-
Again, bring online the resource group to which the SAP enqueue server belongs.
# scswitch -z -g central-rg -h node
- -z
-
Specifies that a resource group is to be brought online.
- -g central-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be brought online. This group is the resource group to which the SAP enqueue server belongs.
- -h node
-
Specifies the name of the node on which the resource group is to be brought online.
-
Log in to a different node as superuser.
-
On the node where you logged in in Step 7, bring online the resource group to which the SAP replica server belongs.
# scswitch -z -g repl-rg -h node
- -z
-
Specifies that a resource group is to be brought online.
- -g repl-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be brought online. This group is the resource group to which the SAP replica server belongs.
- -h node
-
Specifies the name of the node on which resource group is to be brought online. This node is the node that you have just logged in to.
-
Again, abnormally terminate the SAP enqueue server, as in Step 4.
-
Confirm that the SAP enqueue server resource group fails over to the node on which the SAP replica server resource group is running.
As the SAP enqueue server resource group starts on the node on which the SAP replica server resource group is running, the SAP replica server resource group fails over to another available node. If no node is available, the SAP replica server resource group is offline.
Run the scstat command to confirm that the SAP enqueue server resource group is offline on the first node and online on the second node. Confirm also that the SAP replica server resource group is offline on the second node. The SAP replica server resource group can be either online on another available node or offline.
How to Verify the Operation of the Fault Monitor for the SAP Replica Server
Perform this procedure on each set of two nodes where the SAP replica server and the SAP enqueue server can run.
-
Log in to a node as superuser.
-
Bring online the resource group to which the SAP enqueue server belongs.
The SAP replica server resource is configured to be dependent on the SAP enqueue server resource.
# scswitch -z -g central-rg -h node
- -z
-
Specifies that a resource group is to be brought online.
- -g central-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be brought online. This group is the resource group to which the SAP enqueue server belongs.
- -h node
-
Specifies the name of the node on which the resource group is to be brought online. This node is the node that you have just logged in to.
-
Log in to a different node as superuser.
-
Bring online the resource group to which the SAP replica server belongs.
# scswitch -z -g repl-rg -h node
- -z
-
Specifies that a resource group is to be brought online.
- -g repl-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be brought online. This group is the resource group to which the SAP replica server belongs.
- -h node
-
Specifies the name of the node on which the resource group is to be brought online. This node is the node that you have just logged in to.
-
Abnormally terminate the SAP replica server.
-
Determine the process ID of the SAP replica server, where the name of the SAP replica server executable file is enrepserver.
# ps -ef | grep enrepserver
-
Kill the process for the SAP replica server.
# kill -9 pid
- pid
-
Specifies the process ID of the SAP replica server. This ID is the process ID that you determined with the ps and grep commands.
-
-
Confirm that the SAP replica server either restarts or fails over.
If the abnormal termination action in Step 5 is repeated a specified number of times within a specified time interval, the SAP replica server fails over to an available node that is not running the SAP enqueue server. If no node is available, the SAP replica server is offline.
If the abnormal termination action is not repeated a specified number of times within a specified time interval, the SAP replica server restarts on the same node.
Run the scstat command to determine the status of the SAP replica server.
The maximum number of times that the application can be abnormally terminated before failing over is specified with the standard property Retry_count. The time interval is specified with the standard property Retry_interval. These properties are described in “Resource Properties” in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS.
How to Verify the Operation of the Fault Monitor for the SAP Message Server
Perform this procedure on each node where the SAP message server can run.
-
Log in to a node as superuser.
-
Bring online the resource group to which the SAP message server belongs.
# scswitch -z -g central-rg -h node
- -z
-
Specifies that a resource group is to be brought online.
- -g central-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be brought online. This group is the resource group to which the SAP message server belongs.
- -h node
-
Specifies the name of the node on which the resource group is to be brought online. This node is the node that you have just logged in to.
-
Specify that failover is to be enabled for the resource group.
# scrgadm -c -g central-rg -y Failover_Enabled=True
- -c
-
Specifies that an existing configuration is to be modified
- -g central-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be modified
- -y Failover_Enabled=True
-
Specifies that the resource group is to fail over when Retry_count is exceeded during Retry_interval
-
Terminate the SAP message server.
-
Confirm that the SAP message server either restarts or fails over.
If the abnormal termination action in Step 4 is repeated a specified number of times within a specified time interval, the SAP message server fails over to an available node. If no node is available, the SAP message server is offline.
If the abnormal termination action is not repeated a specified number of times within a specified time interval, the SAP message server restarts on the same node.
Run the scstat command to determine the status of the SAP message server.
Note that the maximum number of times that the application can be abnormally terminated before failing over is specified with the standard property Retry_count, and the time interval is specified with the standard property Retry_interval. These properties are described in “Resource Properties” in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS.
-
Again, bring online the resource group to which the SAP message server belongs, as described in Step 2.
-
Specify that failover is to be disabled for the resource group.
# scrgadm -c -g central-rg -y Failover_Enabled=False
- -c
-
Specifies that an existing configuration is to be modified
- -g central-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be modified
- -y Failover_Enabled=False
-
Specifies that the resource group is not to fail over when Retry_count is exceeded during Retry_interval
-
Terminate the SAP message server.
-
Confirm that the SAP message server restarts.
Because the Failover_Enabled is set to False, the SAP message server always restarts.
How to Verify the Operation of the Fault Monitor for the SAP Web Application Server Component
Perform this procedure on each node where the SAP web application server component can run.
-
Log in to a node as superuser.
-
Bring online the resource group to which the SAP message server belongs.
The SAP web application server component resource is configured to be dependent on the SAP message server resource.
# scswitch -z -g central-rg -h node
- -z
-
Specifies that a resource group is to be brought online.
- -g central-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be brought online. This group is the resource group to which the SAP message server belongs.
- -h node
-
Specifies the name of the node on which resource group is to be brought online. This node is the node that you have just logged in to.
-
Bring online the resource group to which the SAP web application server component belongs.
# scswitch -z -g webas-rg -h node
- -z
-
Specifies that a resource group is to be brought online.
- -g webas-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be brought online. This group is the resource group to which the SAP web application server component belongs.
- -h node
-
Specifies the name of the node on which the resource group is to be brought online. This node is the node that you have just logged in to.
-
Terminate the SAP web application server component.
-
Confirm that the SAP web application server component is restarted locally.
If the abnormal termination action in Step 4 is repeated a specified number of times within a specified time interval, the resulting behavior depends on whether the SAP web application server component resource was configured as a failover or a scalable resource.
-
If the SAP web application server component resource was configured as a failover resource, the resource fails over to an available node. If no node is available, the SAP web application server component is offline.
-
If the SAP web application server component resource was configured as a scalable resource, the resource is offline on this node.
Run the scstat command to determine the status of the SAP web application server component.
Note that the maximum number of times that the application can be abnormally terminated before failing over or becoming offline is specified with the standard property Retry_count, and the time interval is specified with the standard property Retry_interval. These properties are described in “Resource Properties” in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS.
-
How to Verify the Installation and Configuration of Sun Cluster HA for SAP J2EE Engine
-
Become superuser on one of the nodes in the cluster that is to host the SAP J2EE engine.
-
Run the scstat command to ensure all the resources are online.
# scstat
For each SAP J2EE engine resource that is not online, run the scswitch command as follows.
# scswitch -e -j j2ee-rs
- -e
-
Specifies that a resource is to be enabled
- -j j2ee-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource that is to be enabled
-
Run the scswitch command to switch the SAP J2EE engine resource group to another cluster node, such as node2.
# scswitch -z -g j2ee-rg -h node2
- -z
-
Specifies that a resource group is to be brought online
- -g j2ee-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group to be brought online
- -h node2
-
Specifies the name of the node on which the resource group is to be brought online
Debugging Sun Cluster HA for SAP J2EE Engine
Sun Cluster HA for SAP J2EE Engine can be used by multiple Sun Cluster instances. However, it is possible to activate debugging for all Sun Cluster instances or for a particular Sun Cluster instance.
Each Sun Cluster component has a DEBUG file in /opt/SUNWscswa/etc.
This file allows you to activate debugging for all Sun Cluster resources or for a specific Sun Cluster resource on a particular node with Sun Cluster. If you require debugging to be turned on for Sun Cluster HA for SAP J2EE Engine across the entire Sun Cluster, repeat these steps on all nodes within Sun Cluster.
How to Activate Debugging for Sun Cluster HA for SAP J2EE Engine
-
Edit the file /etc/syslog.conf.
In the file /etc/syslog.conf, change daemon.notice to daemon.debug.
# grep daemon /etc/syslog.conf *.err;kern.debug;daemon.notice;mail.crit /var/adm/messages *.alert;kern.err;daemon.err operator
Change daemon.notice to daemon.debug and restart syslogd. The command grep daemon /etc/syslog.conf issues the following output, which shows that daemon.debug has now been set.
# grep daemon /etc/syslog.conf *.err;kern.debug;daemon.debug;mail.crit /var/adm/messages *.alert;kern.err;daemon.err operator # # pkill -1 syslogd
-
Edit the file /opt/SUNWscswa/etc/config.
In the file /opt/SUNWscswa/etc/config, change DEBUG= to DEBUG=ALL or DEBUG=resource.
# cat /opt/SUNWscswa/etc/config # # Copyright 2003 Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved. # Use is subject to license terms. # # Usage: # DEBUG=<RESOURCE_NAME> or ALL # DEBUG=ALL #
Note –
To deactivate debugging, perform the steps in this procedure in the reverse order.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
