Alarm Severity Levels
The following alarm severities are supported:
- Down Alarms
-
A down alarm
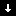 indicates
that a service-affecting condition has occurred that requires immediate corrective
action. An example of this condition is the following: A required resource that is
defined by a managed object has gone out of service. A specific example of this condition
is a module that has gone down.
indicates
that a service-affecting condition has occurred that requires immediate corrective
action. An example of this condition is the following: A required resource that is
defined by a managed object has gone out of service. A specific example of this condition
is a module that has gone down. - Critical Alarms
-
A critical alarm
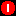 indicates
that a service-affecting condition has developed that requires an urgent corrective
action. An example of this condition occurs when a severe degradation in the capability
of an object has occurred and you need to restore the object to full capability.
indicates
that a service-affecting condition has developed that requires an urgent corrective
action. An example of this condition occurs when a severe degradation in the capability
of an object has occurred and you need to restore the object to full capability. - Alert Alarms
-
An alert alarm
 indicates that a non-service-affecting condition has developed.
Corrective action should be taken to prevent a more serious fault.
indicates that a non-service-affecting condition has developed.
Corrective action should be taken to prevent a more serious fault. - Caution Alarms
-
A caution alarm
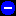 indicates the detection of a potential or impending service-affecting
fault before any significant effects have occurred. You should diagnose further if
necessary and correct the problem before it becomes a serious service-affecting fault.
indicates the detection of a potential or impending service-affecting
fault before any significant effects have occurred. You should diagnose further if
necessary and correct the problem before it becomes a serious service-affecting fault. - Off/Disabled Alarms
-
A disabled alarm
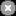 indicates
that a resource for a managed object is disabled. For example, a module is disabled.
indicates
that a resource for a managed object is disabled. For example, a module is disabled.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
